Group micro-irrigation (GMI) [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Pratik Ramteke
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Joana Eichenberger
approaches_7415 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de l'Approche
Personne(s) ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Bhagat Arun
arun.bhagat@wotr.org.in
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
The Forum, 2nd Floor (3rd if taken lift, Pune - Satara Rd, above Ranka Jewellers, Padmavati Nagar, Corner, Maharashtra 411009
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
D'Souza Marcella
+91 9422226415
marcella.dsouza@gmail.com
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
The Forum, 2nd Floor (3rd if taken lift, Pune - Satara Rd, above Ranka Jewellers, Padmavati Nagar, Corner, Maharashtra 411009
Inde
Social Adviser:
Koli Upasana
upasana.koli@gmail.com
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
The Forum, 2nd Floor (3rd if taken lift, Pune - Satara Rd, above Ranka Jewellers, Padmavati Nagar, Corner, Maharashtra 411009
Inde
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de l'Approche (si pertinent)
Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
22/04/2023
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de l'Approche de GDT
2.1 Courte description de l'Approche
The group micro-irrigation (GMI) approach encourages farmers to share water more sustainably by facilitating cooperative management of irrigation resources. The aim is to improve water security and agricultural productivity by promoting climate-resilient agricultural practices and addressing the behavioural factors that influence water resource sharing.
2.2 Description détaillée de l'Approche
Description détaillée de l'Approche:
The group micro-irrigation (GMI) approach encourages farmers to share water more sustainably by facilitating cooperative management of irrigation resources in semi-arid regions. The aim is to improve water security and agricultural productivity by promoting climate-resilient agricultural (CRA) practices and addressing the behavioural factors that influence water resource sharing. By treating water as a shared community resource rather than private property, GMI promotes equitable distribution and sustainable use of limited water resources among farmers by organizing farmer groups and utilizing shared water management infrastructure.
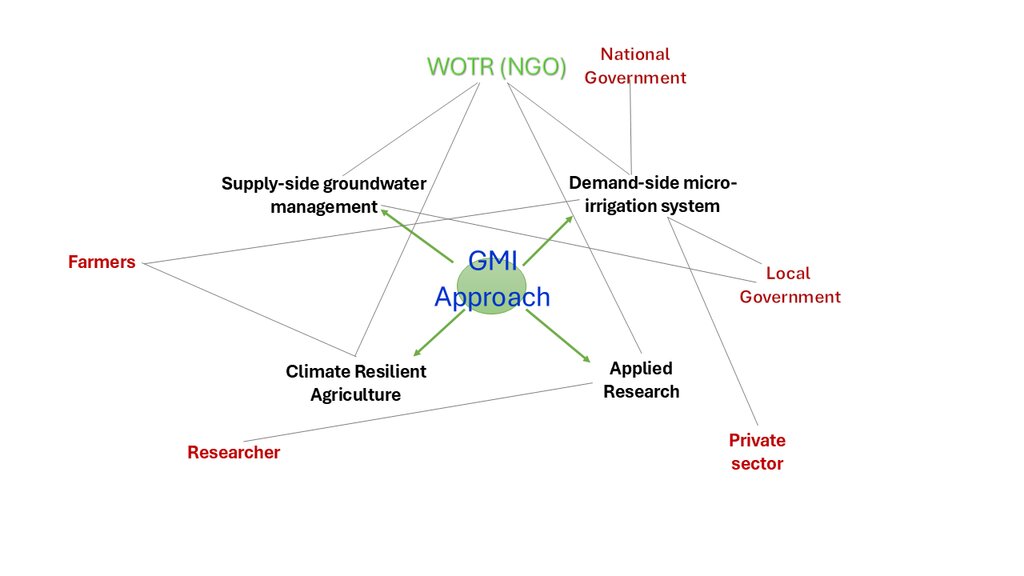
The GMI approach is divided into four major components: (1) supply-side groundwater management to recharge and conserve water sources, (2) demand-side management via efficient micro-irrigation systems, (3) promotion of CRA practices to improve soil health, and (4) integration of applied research to develop tools that allow farmers to assess and improve their agricultural practices. These components aim to optimize water use, reduce crop production costs, and encourage farmer collaboration for shared resources and access to advanced agricultural technologies.
The primary objectives of the GMI approach are to improve water productivity, enhance crop yield, and reduce dependency on groundwater for irrigation, especially in regions facing water scarcity. Through group collaboration, the approach also aims to reduce individual investment costs for farmers, facilitate access to subsidies, and increase resilience to climate fluctuations. Additionally, by integrating CRA practices, GMI supports sustainable agricultural practices that contribute to long-term soil health and ecosystem stability.
The GMI approach involves several methods, including:
•Groundwater Management: rainwater harvesting and construction of soil and water conservation structures to replenish groundwater levels.
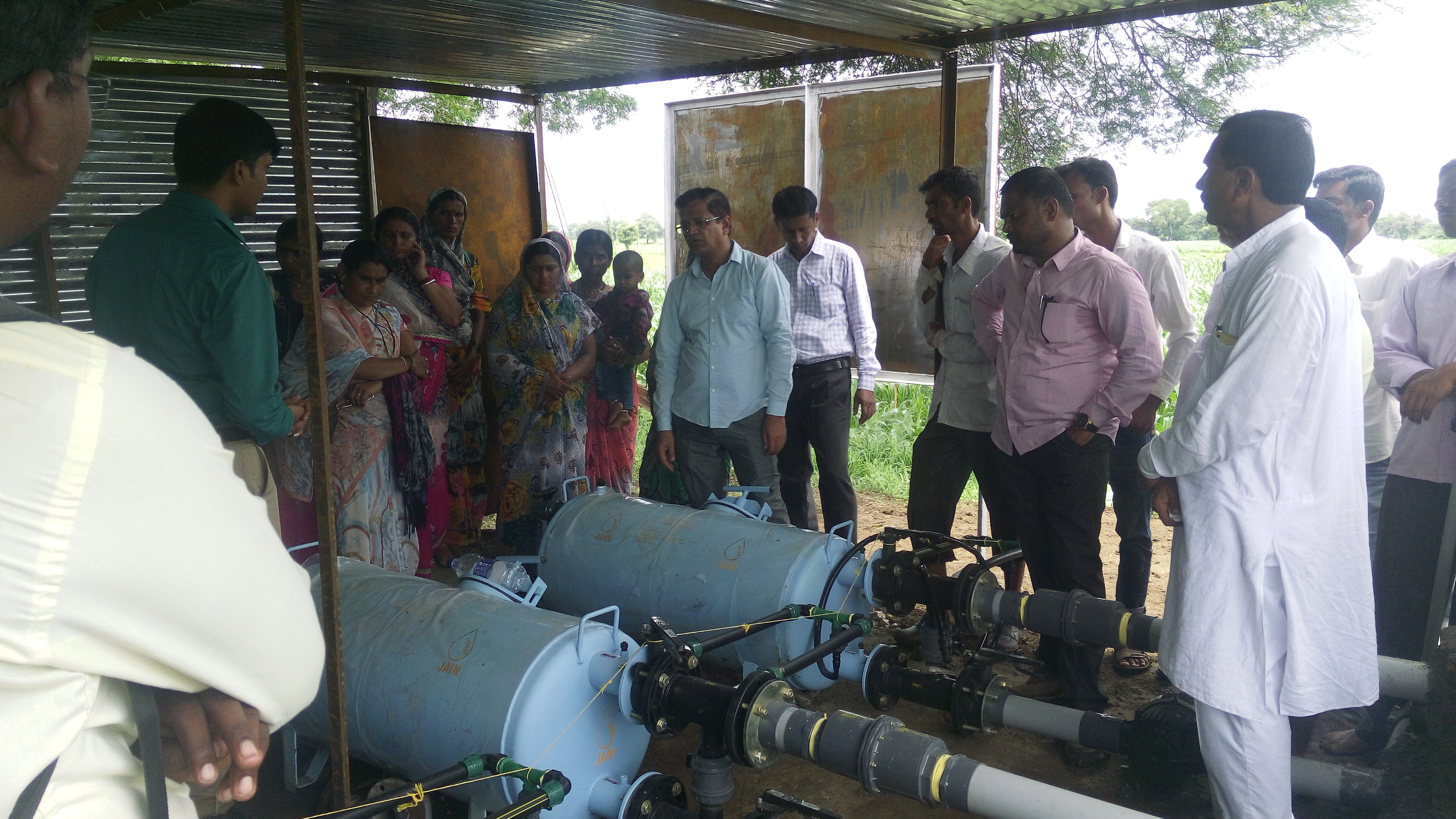
•Micro-Irrigation Systems: installation of shared drip and sprinkler irrigation systems that optimize water use and are accessible to all group members.
•CRA Practices: seed treatment, crop spacing, intercropping & trap cropping, applying farmyard manure (FYM), vermicompost, and organic waste compost, and making use of organic inputs, Bio-pest management practices including the use of pheromone traps, light traps, and bio-pesticides.
•Applied Research: use of tools like crop water budgeting, groundwater testing, and field book record-keeping, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions.
The implementation of GMI involves four stages:
•Planning and Assessment: identifying suitable villages, farmer groups, and available water resources. Farmers with similar irrigation needs are grouped based on geographic proximity and water source access.
•Infrastructure Development: establishing common irrigation systems and water conservation structures, including dug wells, check dams, and pipelines.
•Training and Capacity Building: educating farmers on CRA practices, irrigation management, and using applied research tools for decision-making.
•Monitoring and Evaluation: regular assessment of crop and water productivity, adjustment of practices based on field data, and continuous training to ensure sustainability.
The GMI approach involves a range of stakeholders:
•Farmers: key participants who manage day-to-day operations, share resources, and implement CRA practices.
•Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR): the primary implementing organization, providing technical support, training, and ongoing assessment.
•Local Government: supports funding for infrastructure, provides access to subsidies, and helps promote CRA practices.
•Agricultural Experts and Researchers: developing tools for applied research and supporting data analysis to improve productivity and water efficiency.
Farmers value the GMI approach for a variety of reasons, including lower individual investment, access to reliable water resources, and increased crop productivity. The cooperative aspect has strengthened community bonds and ensured equal access to resources. However, some farmers were initially hesitant to share water resources and bear the upfront costs of micro-irrigation systems. These concerns faded as the benefits of increased productivity and resource efficiency became clear.
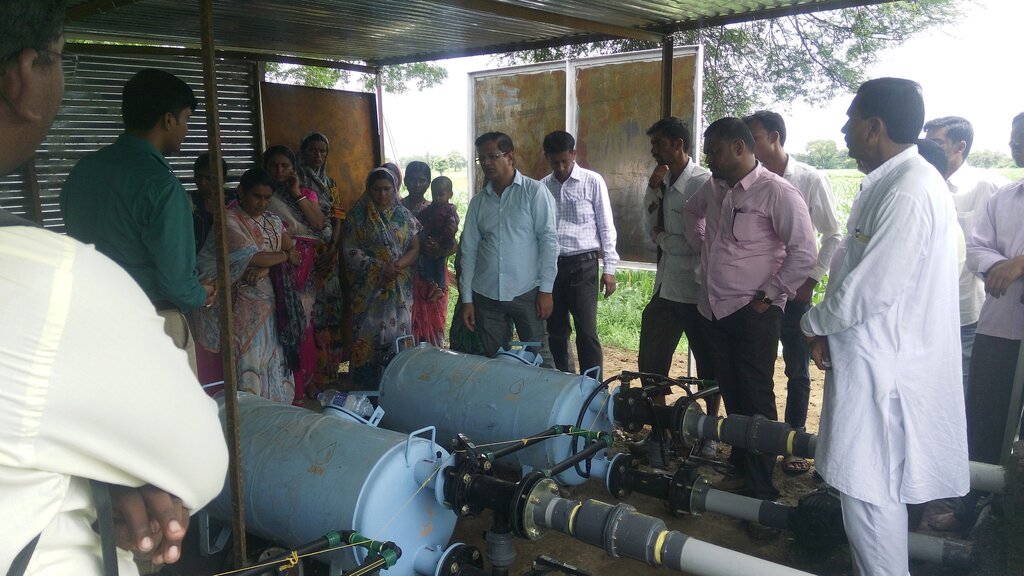
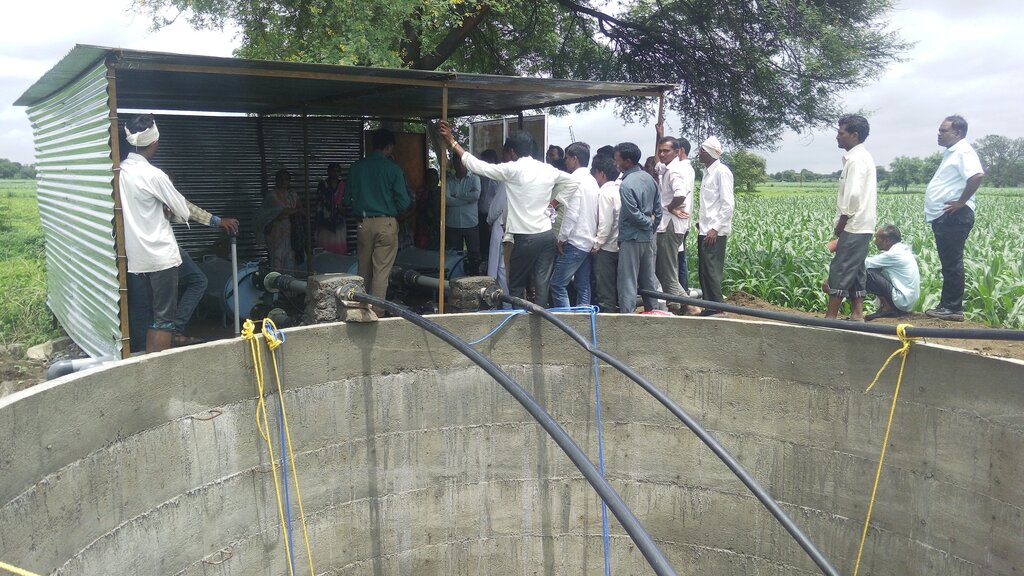
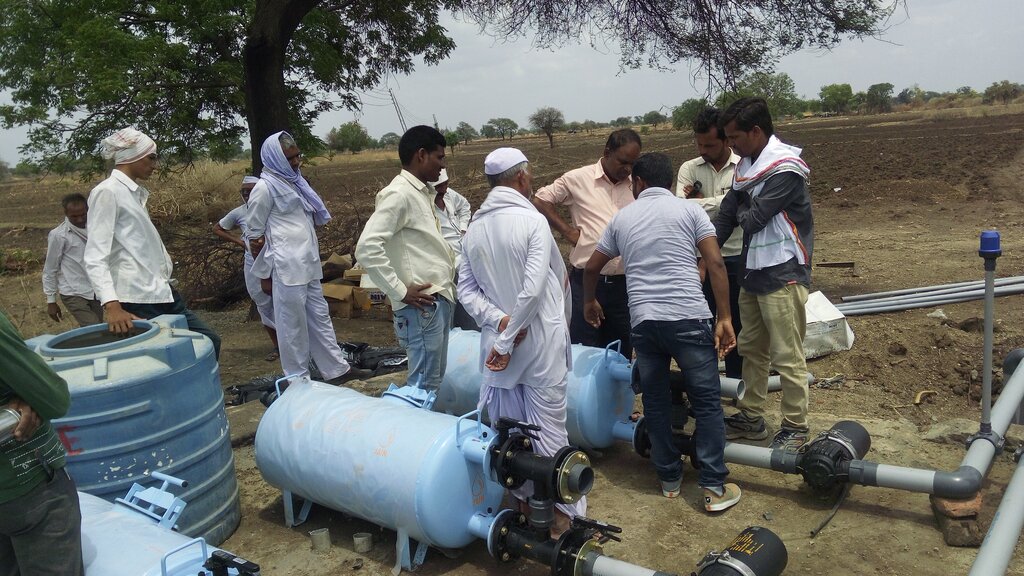
2.3 Photos de l'approche
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où l'Approche a été appliquée
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tigalkheda, Bhokardan Block, state: Maharashtra
Commentaires:
Tigalkheda, a village in the Bhokardan block of Jalna district, Maharashtra, is part of India's semi-arid Marathwada region, prone to droughts and severe water scarcity. Tigalkheda, located on a dissected plateau, relies heavily on groundwater for irrigation due to a scarcity of surface water. The soils in this region are predominantly clayey, and the climate is characterized by annual rainfall ranging from 400 to 600 mm, with the majority occurring during the monsoon season. Farmers cultivate cotton, cereals, and pulses that rely heavily on consistent water access, therefore efficient irrigation is critical for sustaining agriculture in this challenging environment.
Map
×2.6 Dates de début et de fin de l'Approche
Indiquez l'année de démarrage:
2017
Commentaires:
Still ongoing
2.7 Type d'Approche
- fondé sur un projet/ programme
2.8 Principaux objectifs de l'Approche
The primary goal of the GMI approach is to boost agricultural productivity by ensuring consistent irrigation access, particularly in water-scarce areas. It focuses on improving water use through shared micro-irrigation systems, ensuring efficient and equitable resource distribution among farmers. Furthermore, the approach encourages climate-resilient practices that improve soil health and crop resilience, allowing farmers to adapt to climate variability. By encouraging collaboration within farming communities, GMI creates a cooperative framework for sharing resources and lowering individual costs. Finally, it seeks to improve rural sustainability by reducing production costs, increasing income stability, and promoting food security.
2.9 Conditions favorisant ou entravant la mise en œuvre de la(des) Technologie(s) appliquée(s) sous l'Approche
normes et valeurs sociales/ culturelles/ religieuses
- favorise
Community cooperation and shared values regarding resource management help in collaboration among farmers.
disponibilité/ accès aux ressources et services financiers
- favorise
Access to microfinance or government subsidies supported the initial investment.
cadre institutionnel
- favorise
Support from NGO and agricultural institutions provides technical assistance and training.
collaboration/ coordination des acteurs
- favorise
Strong collaboration among farmers, NGOs, and local authorities enhances resource sharing and knowledge transfer.
cadre juridique (régime foncier, droits d'utilisation des terres et de l'eau)
- favorise
Water use rights were verbally stated
cadre politique
- favorise
Supportive government policies facilitate the implementation
gouvernance foncière (prise de décisions, mise en œuvre et application des décisions)
- favorise
Local governance structures enhance the decision-making processes related to resource management.
connaissances sur la GDT, accès aux supports techniques
- favorise
Availability of training programs and technical support helps farmers adopt best practices in micro-irrigation.
marchés (pour acheter les intrants, vendre les produits) et prix
- favorise
Access to markets for selling produce encourages investment in improved irrigation methods
charge de travail, disponibilité de la main-d'œuvre
- favorise
Availability of community labor facilitates the implementation of irrigation systems
3. Participation et rôles des parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche
3.1 Parties prenantes impliquées dans l'Approche et rôles
- exploitants locaux des terres / communautés locales
The primary stakeholders of the
GMI model. They contribute to
decision-making and
implementation processes related
to the irrigation system
- Spécialistes de la GDT/ conseillers agricoles
Offer guidance on
sustainable land management (SLM)
practices and assist farmers in
adopting climate-resilient agricultural
techniques, ensuring effective use of
the micro-irrigation system.
- chercheurs
Researchers conduct studies to
evaluate the effectiveness of the GMI
model, focusing on behavioral aspects
and mental models of farmers
regarding water sharing. Their findings
contribute to improving practices and
informing policy decisions related to
water management.
- ONG
Watershed Organisation Trust, (WOTR) Pune
WOTR is the implementing NGO that provides technical support, training, and capacity-building initiatives for farmers. WOTR facilitate community engagement and help establish the GMI model as a sustainable water-sharing approach. WOTR also carried out impact analysis and research components of GMI approach
- secteur privé
Providing materials, micro-irrigation system
- gouvernement national (planificateurs, décideurs)
Promoted policies that support sustainable irrigation practices, such as the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY), which encourages micro-irrigation technologies across India. Provide subsidies for micro-irrigations
- organisation internationale
GIZ
Funding of the project
Si plusieurs parties prenantes sont impliquées, indiquez l'organisme chef de file ou l'institution responsable:
Watershed Organisation Trust, (WOTR) Pune
3.2 Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales aux différentes phases de l'Approche
| Participation des exploitants locaux des terres/ communautés locales | Spécifiez qui était impliqué et décrivez les activités | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | Local farmers were actively engaged during the initiation phase, participating in discussions facilitated by the Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR) to understand the benefits of the GMI model. They expressed their interest in sustainable water management practices |
| planification | interactive | Farmers contributed to planning sessions where they identified their needs and preferences for irrigation practices. They collaborated with WOTR to outline the logistics of water sharing and resource management |
| mise en œuvre | interactive | Local farmers played a crucial role in implementing the GMI model by assisting in the installation of irrigation infrastructure, such as drip systems and automation technologies. They also participated in de-silting the selected well to enhance its capacity for water storage |
| suivi/ évaluation | interactive | Farmers were involved in monitoring the effectiveness of the irrigation system and evaluating its impact on crop yields. They provided feedback on water usage, crop performance, and any challenges faced, allowing for adjustments to be made collaboratively with WOTR. |
| research | interactive | Farmers participated in research activities aimed at better understanding their mental models of water sharing. They collaborated with researchers to provide insights into their experiences, beliefs, and attitudes towards cooperative water management practices under the GMI model. |
3.3 Diagramme/ organigramme (si disponible)
3.4 Prises de décision pour la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies
Indiquez qui a décidé de la sélection de la Technologie/ des Technologies à mettre en œuvre:
- tous les acteurs concernés dans le cadre d'une approche participative
Spécifiez sur quelle base ont été prises les décisions:
- l'évaluation de connaissances bien documentées en matière de GDT (prises de décision fondées sur des preuves tangibles)?
- les résultats de recherches?
- expériences et opinions personnelles (non documentées)
4. Soutien technique, renforcement des capacités et gestion des connaissances
4.1 Renforcement des capacités/ formation
Une formation a-t-elle été dispensée aux exploitants des terres/ autres parties prenantes?
Oui
Spécifiez qui a été formé:
- exploitants des terres
- personnels/ conseillers de terrain
Si pertinent, spécifiez le genre, l'âge, le statut, l'ethnie, etc.
The training primarily involved local farmers from Tigalkheda, including small, medium, and large landholders. Participants were predominantly male, but women also participated in some training sessions. The age range varied from young adults to older farmers
Formats de la formation:
- sur le tas
- entre agriculteurs (d'exploitants à exploitants)
- zones de démonstration
- réunions publiques
Thèmes abordés:
Water management practices, micro-irrigation systems installation, maintenance of drip irrigation, fertigation technologies, sustainable agricultural practices, climate-resilient farming techniques, cooperative management, collective decision-making and resource sharing among farmers.
4.2 Service de conseils
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils accès à un service de conseils?
Oui
Spécifiez si le service de conseils est fourni:
- dans les champs des exploitants?
- dans des centres permanents
4.3 Renforcement des institutions (développement organisationnel)
Des institutions ont elles été mises en place ou renforcées par le biais de l'Approche?
- oui, beaucoup
Spécifiez à quel(s) niveau(x), ces institutions ont été renforcées ou mises en place:
- local
- régional
Précisez le type de soutien:
- financier
- renforcement des capacités/ formation
- équipement
4.4 Suivi et évaluation
Le suivi et l'évaluation font ils partie de l'Approche? :
Oui
Commentaires:
Monitoring and evaluation are integral components of the GMI approach, for the assessment of its effectiveness in promoting sustainable water-sharing practices and improving agricultural productivity among local farmers.
Si oui, ce document est-il destiné à être utilisé pour le suivi et l'évaluation?
Oui
Commentaires:
The documentation serves as a valuable resource for monitoring and evaluating the implementation and impact of the GMI model, providing insights into farmer behaviors, water management practices, and overall project outcomes
4.5 Recherche
La recherche a-t-elle fait partie intégrante de l’Approche?
Oui
Spécifiez les thèmes:
- sociologie
- économie/ marketing
- écologie
- technologie
- Agriculture
Donnez plus de détails et indiquez qui a mené ces recherches:
Research was conducted by Miss. Upasana Koli, Dr. Arun Bhagat, and Dr. Marcella D’Souza from the Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR). The focus of the research included understanding the mental models that promote water sharing for agriculture through the GMI approach. It examined behavioural aspects related to water resource management, cooperative practices among farmers, and the socio-economic impacts of adopting sustainable irrigation technologies. The findings aim to inform policymakers and practitioners about effective water-sharing policies and sustainable agricultural interventions.
Arun Bhagat: Contributed to the conceptualization, methodology design, investigation, data curation, formal analysis, original draft writing, and reviewing and editing of the manuscript.
Upasana Koli: Contributed to the conceptualization, methodology design, investigation, and data curation for the study.
Marcella D'Souza: Provided supervision and contributed to conceptualizing the research project.
5. Financement et soutien matériel externe
5.1 Budget annuel de la composante GDT de l'Approche
Si le budget annuel précis n'est pas connu, indiquez une fourchette:
- 2 000-10 000
Commentez (par ex. principales sources de financement/ principaux bailleurs de fonds):
The annual budget varies between 2000-10000 US$. GIZ acts as a core funder, primarily supporting project design, monitoring, and capacity-building activities. However, co-funding comes from various sources:
1.State Government: Provides subsidies for micro-irrigation systems and infrastructure, such as those under the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
2.WOTR: Contributes technical expertise, facilitates training, and monitors implementation, often covering operational costs.
3.Farmers: Contribute funds for system maintenance and may also pool resources for initial installations.
Regarding training, WOTR plays a pivotal role, offering on-field demonstrations and workshops on water management, climate-resilient agriculture, and system maintenance. Farmers benefit from continuous knowledge sharing and capacity-building initiatives.
•Tigalkheda is a semi-arid village in Maharashtra's Bhokardan block, spanning approximately 32.34 acres, as mentioned in the documentation.
•The GMI approach involves 14 farmers, all managing plots within this shared irrigation system.
•Further, within a single village several GMI models can be created based on the farmer groups.
5.2 Soutiens financiers/ matériels fournis aux exploitants des terres
Les exploitants des terres ont-ils reçu un soutien financier/ matériel pour la mise en œuvre de la Technologie/ des Technologies?
Oui
Si oui, spécifiez le(s) type(s) de soutien, les conditions et les fournisseurs:
Support: Farmers received subsidies for the installation of micro-irrigation systems and installation of the pumping system and pipe distribution network.
Condition: The farmer should be a member of the GMI group and ready to contribute financially to maintaining the GMI model.
Providers: Government Bodies: Local and national government (Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY); Partial funding from GIZ; Knowledge & implementation support by WOTR.
5.3 Subventions pour des intrants spécifiques (incluant la main d'œuvre)
- main d'œuvre
| Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|
| en partie financé | labor costs related to the installation of irrigation systems. |
- équipement
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| outils | en partie financé | Drip irrigation system |
- intrants agricoles
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| semences | en partie financé | National government subsidies |
| fertilisants | en partie financé | National government subsidies |
- matériaux de construction
| Spécifiez les intrants subventionnés | Dans quelle mesure | Spécifiez les subventions |
|---|---|---|
| pierres | en partie financé | |
| Cement, steel | en partie financé | Dug-well development |
Si la main d'œuvre fournie par les exploitants des terres était un intrant substantiel, elle était:
- volontaire
5.4 Crédits
Des crédits ont-ils été alloués à travers l'Approche pour les activités de GDT?
Oui
Spécifiez les conditions (taux d'intérêts, remboursements, etc.):
Interest rate: 8.3 to 10.1%, payback period: NA
Spécifiez les fournisseurs du crédit:
Banks, Private lenders,
Spécifiez les destinataires du crédit:
Farmers
5.5 Autres incitations ou instruments
D'autres incitations ou instruments ont-ils été utilisés pour promouvoir la mise en œuvre des Technologies de GDT?
Oui
Si oui, spécifiez:
Supporting Policies: Government policies such as the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY) provide financial assistance for micro-irrigation technologies
6. Analyses d'impact et conclusions
6.1 Impacts de l'Approche
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les exploitants locaux des terres, amélioré la participation des parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
GMI developed a sense of ownership among farmers, leading to increased involvement in decision-making processes related to water management
Est-ce que l'Approche a permis la prise de décisions fondées sur des données probantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Training sessions and workshops provided farmers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about irrigation practices
Est-ce que l'Approche a aidé les exploitants des terres à mettre en œuvre et entretenir les Technologies de GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Farmers received hands-on training and technical support, enabling them to effectively implement micro-irrigation systems.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré la coordination et la mise en œuvre de la GDT selon un bon rapport coût-efficacité?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The cooperative model promoted collaboration among farmers, leading to more efficient resource use
Est-ce que l'Approche a mobilisé/ amélioré l'accès aux ressources financières pour la mise en œuvre de la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Subsidies and credit options facilitated financial access for farmers adopting new technologies
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Continuous training enhanced farmers' skills in sustainable agricultural practices
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les connaissances et les capacités des autres parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
NGOs and local government bodies benefited from increased understanding of sustainable practices through their engagement in the project
Est-ce que l'Approche a construit/ renforcé les institutions, la collaboration entre parties prenantes?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The GMI model strengthened local farmer groups and enhanced collaboration with NGOs.
Est-ce que l'Approche a atténué les conflits?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The shared water management approach reduced competition for resources among farmers.
Est-ce que l'Approche a autonomisé les groupes socialement et économiquement défavorisés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The project specifically targeted small and marginal farmers, providing them with resources and support
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré l'égalité entre hommes et femmes et autonomisé les femmes et les filles?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Women participated in training sessions, enhancing their roles in agricultural decision-making.
Est-ce que l'Approche a encouragé les jeunes/ la prochaine génération d'exploitants des terres à s'engager dans la GDT?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Training and awareness campaigns have sparked interest among younger generations in sustainable farming practices.
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré les questions foncières et des droits d'utilisation qui entravent la mise en œuvre des Technologies?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
The project addressed rights issues by promoting Community driver visual indicator (CDVI) tool
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à améliorer la sécurité alimentaire et/ou la nutrition?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Enhanced irrigation practices have resulted in better crop yields, contributing to food security
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré l'accès aux marchés?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
By connecting the farmers with the local Farmers Produce Organisation (FPO) and market
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à améliorer l'accès à l'eau et l'assainissement?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Efficient water management has improved overall access to water resources for agricultural and domestic use.
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à l'utilisation/ sources d'énergie plus durables?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Adoption of efficient irrigation systems has encouraged sustainable energy practices among farmers
Est-ce que l'Approche a amélioré la capacité des exploitants des terres à s'adapter aux changements/ extrêmes climatiques et a atténué les catastrophes liées au climat?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
By efficient water management practices and promoting climate resilient agricultural practices
Est-ce que l'Approche a conduit à des emplois, des opportunités de revenus?
- Non
- Oui, un peu
- Oui, modérément
- Oui, beaucoup
Increased agricultural productivity has created additional income sources for farmers.
6.2 Principale motivation des exploitants des terres pour mettre en œuvre la GDT
- augmenter la production
Water availability increased with GMI therefore providing option for crop diversification
- augmenter la rentabilité/ bénéfice, rapport coûts-bénéfices
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- réduire la charge de travail
- améliorer les connaissances et compétences en GDT
6.3 Durabilité des activités de l'Approche
Les exploitants des terres peuvent-ils poursuivre ce qui a été mis en œuvre par le biais de l'Approche (sans soutien extérieur)?
- oui
Si oui, décrivez de quelle manière:
Farmers in Tigalkheda have developed a strong sense of ownership over the GMI approach. They have gained valuable knowledge and skills through training sessions provided by WOTR, enabling them to manage irrigation systems effectively. The cooperative structure established among local farmers facilitates resource sharing and collective decision-making, ensuring that they can maintain the technologies implemented. Additionally, the financial support received through subsidies has alleviated initial investment burdens, allowing farmers to sustain operations independently over time. This sustainability is further supported by the ongoing commitment of farmers to engage in sustainable agricultural practices, as they recognize the long-term benefits of improved water management and crop productivity for their livelihoods and the environment.
6.4 Points forts/ avantages de l'Approche
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
1) Improved Water Management Farmers appreciate the effective management of water resources through the GMI which allows for better distribution and utilization of water, leading to enhanced crop yields. |
|
2) Increased Crop Productivity The implementation of micro-irrigation technologies has resulted in higher agricultural output, which is crucial for the livelihoods of local farmers. |
|
3) Community Collaboration The approach promotes cooperation and shared responsibility in managing irrigation resources. |
|
4) Access to Financial Support Availability of subsidies and financial assistance has made it easier for farmers to adopt new technologies, reducing the economic burden of transitioning to sustainable practices. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
1) Sustainability of Practices The GMI approach emphasizes sustainable agricultural practices that enhance long-term resilience against climate variability and water scarcity. |
|
2) Capacity Building Training programs have significantly improved the skills and knowledge of farmers, enabling them to implement and maintain sustainable land management technologies effectively. |
|
3) Access to Market Information Farmers were connected with the Farmer Producing Organisation (FPO) for accessing timely market information. |
|
4) Reduction in Conflicts Over Water Resources By establishing clear water-sharing agreements among users, the GMI model has reduced competition and conflicts over water resources in the community |
6.5 Faiblesses/ inconvénients de l'Approche et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
|
1) Initial Costs of Technology Implementation While subsidies help, some farmers still find the initial costs of installing micro-irrigation systems prohibitive |
Increased awareness about available financial assistance and community pooling of resources could help mitigate these costs. |
|
2)Maintenance Challenges Some farmers lack the technical skills needed for ongoing maintenance of irrigation systems. |
Regular training sessions focused on maintenance skills can empower farmers to manage their systems effectively. |
|
3) Dependence on Weather Conditions The success of irrigation practices is still heavily reliant on overall weather patterns, which can be unpredictable. |
Implementing rainwater harvesting techniques alongside micro-irrigation could provide additional water security during dry spells. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
|
1) Scalability Issues The GMI model may face challenges in scaling up due to varying local conditions across different regions. |
Tailoring approaches to specific local contexts while maintaining core principles could enhance scalability. |
|
2) Sustainability of Financial Support There is uncertainty regarding the long-term availability of subsidies and financial support from government programs. |
Advocating for policy changes that ensure sustained funding for sustainable agriculture initiatives could address this issue. |
|
3) Cultural Resistance to Change Some farmers may resist adopting new technologies due to traditional practices. |
Engaging community leaders and demonstrating successful case studies can help shift perspectives towards embracing innovation. |
|
4) Limited Research on Long-Term Impacts There is a need for more comprehensive research on the long-term impacts of the GMI approach on both agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability. |
Collaborating with academic institutions for ongoing research projects can provide valuable insights into effectiveness and areas for improvement |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
25 informants
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
14 Land users
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
3 SLM specialist
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
02, (attached in the reference)
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Book chapter: Understanding the Mental Models that Promote Water Sharing for Agriculture Through Group Micro-Irrigation Models in Maharashtra, India. Authors: Upasana Koli, Arun Bhagat & Marcella D’Souza Year: 2023 Print ISBN978-981-99-2205-5 Online ISBN978-981-99-2206-2
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-99-2206-2_15
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Report Bhagat A, and Koli U. (2022). Effectiveness of Group Micro Irrigation Model and Package of Agricultural Practices in Enhancing Climate Resilience in Semi-Arid Region of Maharashtra, Watershed Organisation Trust (WOTR), Pune
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://wotr-website-publications.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/Effectiveness_GMI_Climate_Resilient_Semi_Arid_Maharashtra.pdf
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Climate-resilient strategies for sustainable management of water resources and agriculture
URL:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11356-021-14332-4
Titre/ description:
Economics, adoption determinants, and impacts of micro-irrigation technologies: empirical results from India
URL:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00271-007-0065-0
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé