Vermiculture [Nicaragua]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Mathias Gurtner
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Deborah Niggli
Lombricultura
technologies_1022 - Nicaragua
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Gómez Martínez Julio César
De ENITEL
3c al Norte y 75 varas al Este. Calle Santa Ana
Nicaragua
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
01/02/2004
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Continuous breeding of earthworms in boxes for production of high quality organic compost.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
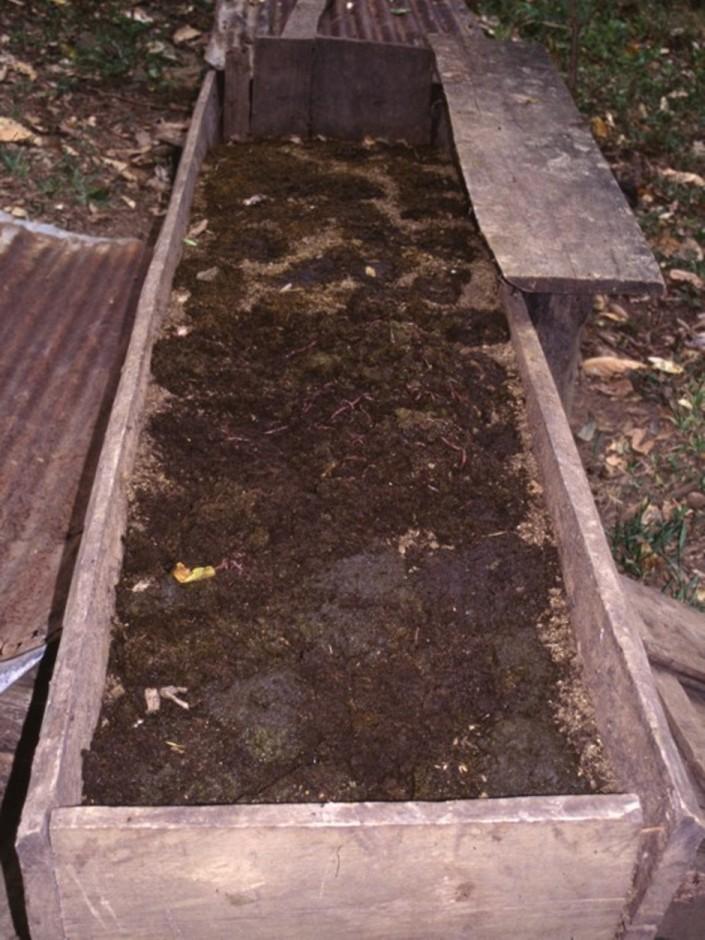
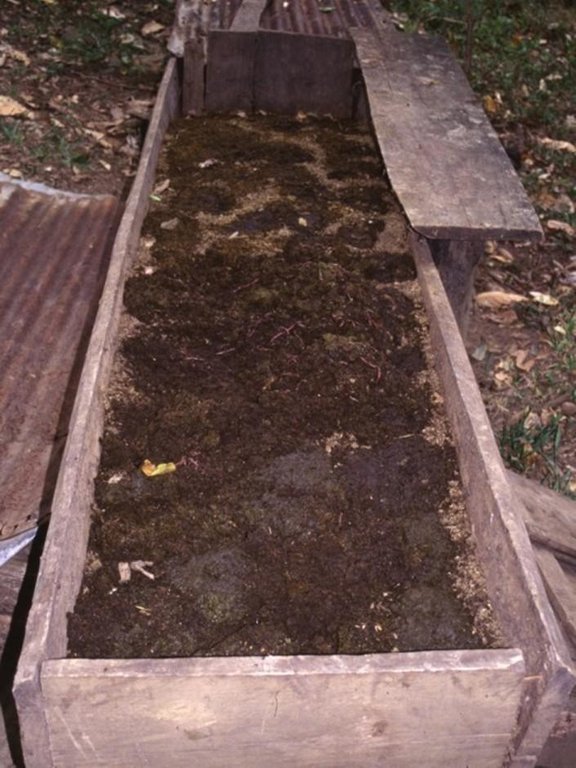
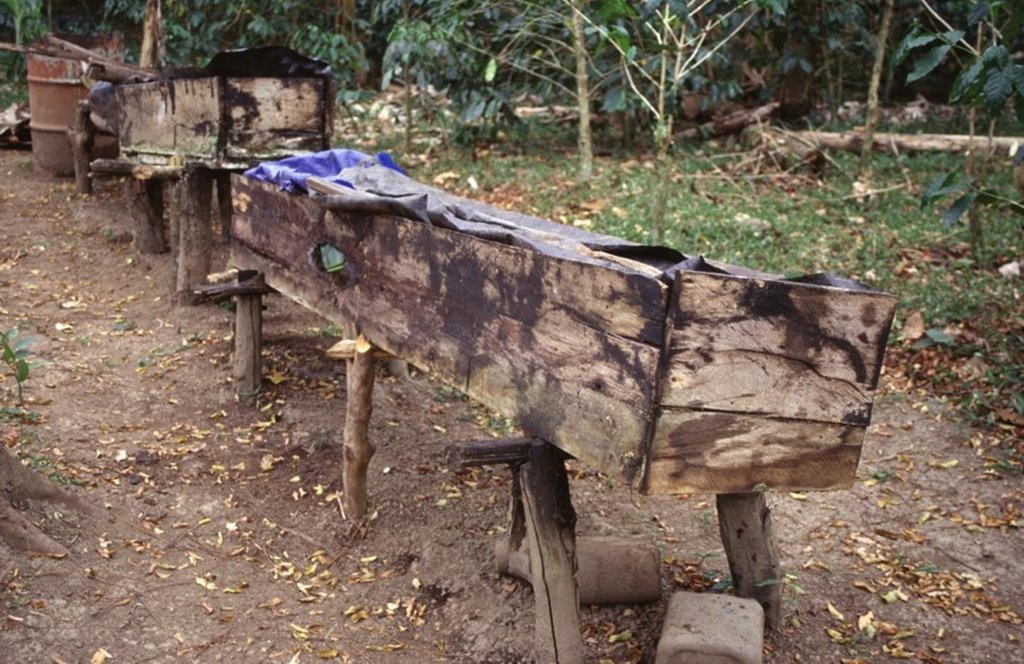
Vermiculture is a simple and cheap way to produce a continuous supply of organic compost of high quality. Eisenia foetida, the Red Californian earthworm (also called ‘the red wiggler’) is ideal for vermiculture since it is adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions. Under culture, the worms are kept under shade, in long wooden boxes filled with earth, cattle manure and an absorbent material (eg straw). The box is covered by sheet metal (or wood, thick plastic sheeting, or banana leaves) to protect the worms against UV radiation and birds/chickens, and also to maintain a favourably humid microclimate. Fresh cattle manure is a perfect food for the worms, but rotten coffee pulp can also be fed. Chopped crop residues (eg cowpeas, leucaena leaves or other legumes) may be added.
The compost produced by the earthworms has a dark colour, no smell and a loose and spongy structure. It is a high value, high quality product which is very rich in nutrients, and in a form that makes them readily available to vegetation. The content of a full box can be harvested every 3-4 months, and is used for crops -mainly coffee and vegetables, but also maize and beans. It is very effective in increasing soil fertility and thus crop production. It also improves soil structure, infiltration and water storage capacity.
The compost can either be applied directly to coffee, mixing it with an equal amount of earth and applying 1 kg to each plant. Alternatively it can be sprayed: for preparation of liquid fertilizer 50 kg compost are mixed with 50 litres of water and left to soak for 5 days. The concentrated solution produced is mixed with water at a ratio of 1 to10 and applied to the crop using a knapsack sprayer. The earthworms reach their reproductive age after three months and live for many years. In perfect conditions an earthworm produces up to 1,500 offspring per year. Thanks to their rapid reproduction, new cultures can easily be established, or earthworm stocks can be sold according to the farmer’s needs. A certain amount
of earthworm compost is kept back and being used instead of fresh earth to reinitiate the whole process, or to start new cultures.
The area is characterised by humid climate, steep slopes and low soil fertility. Farmers are mainly smallholders with individual properties. Earthworm culture does not depend closely on the external environment, but it is essential to maintain favourable conditions inside the box - namely continuous feeding and wetting. That’s why it is usually recommended to keep cultures near the house and the home-garden. Ants, the main enemy of earthworms, can be controlled standing the boxes on poles in cans filled with water.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Nicaragua
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Matagalpa
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Matiguas, Pancasán
Map
×2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion):
- low crop yields due to soil fertility decline
- water and wind erosion
- small landholdings
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 300, Longest growing period from month to month: May untill February
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
- apiculture, aquaculture, élevage de volailles, de lapins, du ver à soie, etc.
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 m2.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A4: Traitement de la couche profonde du sol
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing (on a single cattle farm), poverty / wealth (lack of capital)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (impacts of hurricane Mitch), governance / institutional (lack of strenght of law and authorities), inter-generational subdivision of land
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
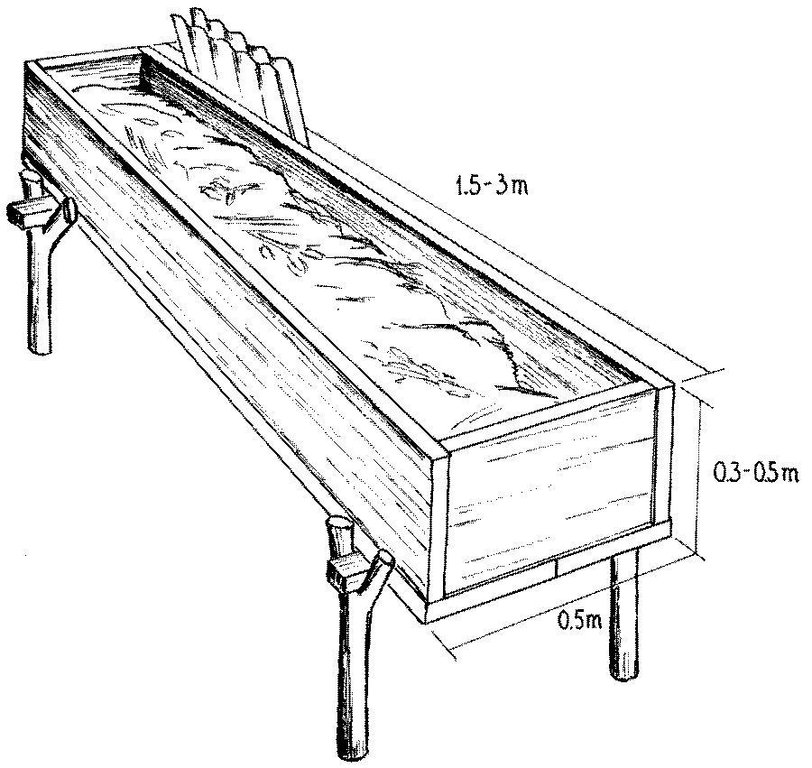
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Detailed view of wooden box for compost production by earthworms. Cover (corrugated iron or alternative) is important to protect worms from light, from birds and other natural enemies, and to maintain moisture in the box.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: compost
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | wood | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Sheet metal, plastic | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | earthworms (kg) | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 122,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.07 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. Feeding: add another layer of cattle manure(1 kg earthworms eat 1 kg manure per day). | Agronomique | no specific timing for maintenance / every 3–5 days |
| 2. | 2. Maintain humidity at 80%, water frequently in dry season, maintaintemperature between 15–30°C: do not exceed 42°C. | Agronomique | no specific timing for maintenance / frequently in dry season |
| 3. | 3.The worms migrate into the fresh manure. After 2–3 days take out thesieve and gather the ready, worm free compost. | Agronomique | no specific timing for maintenance / every 3–4 months |
| 4. | 4. Apply compost to the crops (1 kg/coffee plant, see description). | Agronomique | no specific timing for maintenance / every 3–4 months |
| 5. | 6. Possible improvement: add lime to raise pH to a optimum level of 7.0. | Agronomique | no specific timing for maintenance / |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 60,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: hammer, nails, buckets/wheelbarrow, shovel, possibly water hose, hammer, nails, buckets/wheelbarrow, shovel, possibly water hose
60% of the land users have their own cattle, others get manure free from their neighbours. The cattle manure has no commercial price in the region - there is no market for it. The inputs and costs are estimated for the production of approx. 4,000 kg of worm compost, which is enough for one hectare of coffee per year (note figures from India for vermiculture suggest higher input-output ratios: in other words less output for the same amount of input).
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Off-farm income specification: nearly all land users are fully occupied with agricultural activities, very few are involved in commerce or are employed
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
through improvement of soil water storage capacity
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
the compost attracts pests like ants, chickens, moles
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
lower inputs of chemical fertilizers
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
88 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. As ADDAC (the Association for Agricultural Community Development and Diversification) has a permanent and longterm presence in the approach area, most interested farmers are directly involved in the programme activities: this explains the fact that only 5% of the technology users (6 people) took up earthworm culture without incentives (see approach).
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Additional economic income through commercialization of earthworm stocks |
| Health: clean products without chemical treatment. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Continuous and increasing production of organic and very effective compost with high nutrient content (replacing chemical fertilizers) |
|
Appropriate for different crops (though in different forms – direct application or spraying). |
| Simple and cheap technology; low labour input |
| Increased crop yields |
| Earthworm culture is becoming an integrated part of the production system, especially for land users who have cows. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Requires permanent access to water | A close fitting and secure box cover, as well as placement of the box in the shade reduces loss of humidity. Roof-top rainwater collection helps to get over dry periods. |
| Requires continuous availability of manure to feed worms. | Improve the construction of the boxes (close holes and cover the box tightly). |
| Attracts natural enemies like ants, chickens, moles, flies; needs protection |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
PASOLAC. Guía Técnica de Conservación de Suelos y Agua.. 2000.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
PASOLAC, Managua
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Ferruzzi C. Manual de Lombricultura. Ediciones Mundi-Prensa. Madrid, Spain. 1986.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Castillo H . La lombricultura. in Altertec. Alternativas de Mejoramiento de Suelos.Proceso de Capacitación para Profesionales. Modulo II. Altertec, Ciudad de Guatemala. 1994.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé