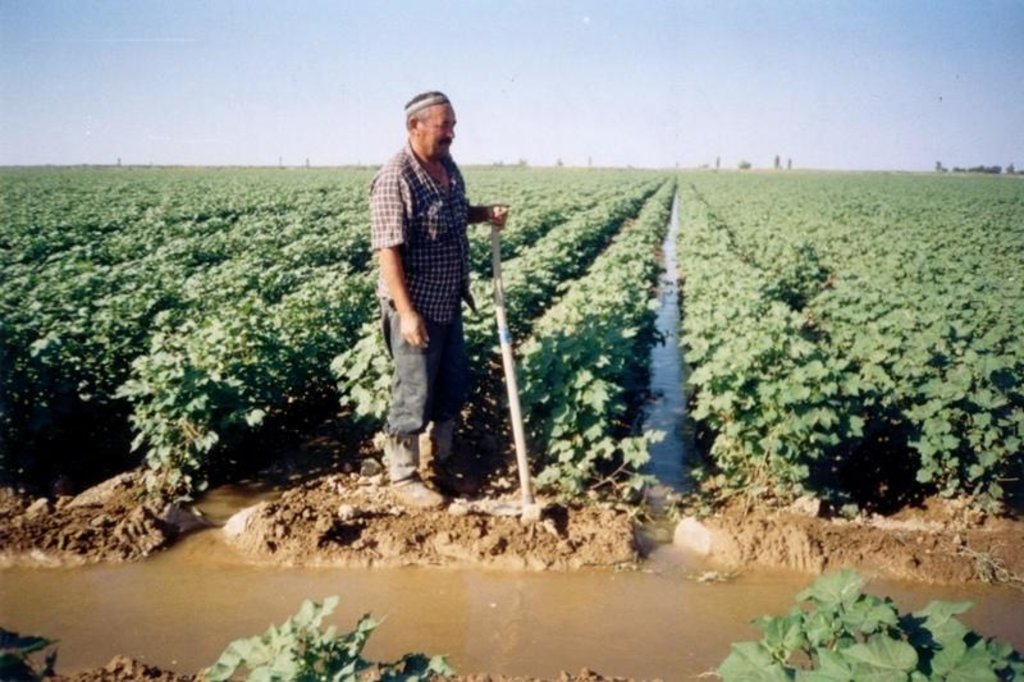
Water-conservation technology at cultivation of the cotton in south. K [Kazakhstan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Watering through furrow
technologies_1091 - Kazakhstan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Vyshepolsky Frank
Kazakhstan
Spécialiste GDT:
Khe Tatyana
kniv@nursat.kz
Taraz city
Kazakhstan
Spécialiste GDT:
Mukhamedzhanov Khamit
Scientific Production Center for Water management
12 Koigeldy str
Kazakhstan
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan (MoA) - Erythrée1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
30/09/2003
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
The technology of watering through furrow reduces the settlement (recommended) sizes of irrigating norms up to 30% keeps soil fertility
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
It is applied for watering on furrow at ploughed cultures.
It is intended for decrease in irrigating norms and preservation of fertility of soils.
The technology of watering through furrow
-Does not result in change of zone system of agriculture
-Provides pass of soil-cultivating technique on dry furrow therefore are reduced the rates of soil condensation
-Reduces technological losses of irrigating water to filtration shed from the irrigated grounds evaporation
-Reduces the sizes of irrigating norms (recommended) up to 30%
-Reduces loading to drainage system up to 30%
-Slows down the rates of development of erosive processes and keeps soil fertility
-Raises productivity of cultivated cultures at deficiency of water
-Improves ecological conditions due to reduction of drainage shed of water for limits of irrigated files
-Does not demand additional expenses for its introduction
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kazakhstan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Southern Kazakhstan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Basin of Syrdarya
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Caused (provocative) waterings for reception of shoots at drying up of soil in a zone of an arrangement of seeds.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- Reduce amount of irrigation water
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
major cash crop: Cotton

Pâturages
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water resources management. Reduction of technological losses of irrigating water at its transportation from water-fence up to fields of an irrigation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Technologies of the water-conservation, reduction of norms of entering of mineral fertilizers, increase in soil fertility. Normalization of water-submission on cultures and soil-meliorative conditions.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 10-100 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 40 km2.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A4: Traitement de la couche profonde du sol

structures physiques
- S3: Fossés étagés, canaux, voies d'eau
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), breaking compacted topsoil, pits, deep tillage / double digging
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: phospho-gypsum
Remarks: 4t/hec
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: tillage through grooves
Pits
Remarks: breaking compacted soil
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: by cultivator
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.50
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 650,0 | 650,0 | |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Polyethylene film | ha | 1,0 | 55,0 | 55,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 745,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage | Agronomique | between / weekly |
| 2. | entering of phospho-gypsum | Agronomique | watering / once a year in the autumn |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Si possible, ventilez le coût de l'entretien selon le tableau suivant: spécifiez les intrants et le coût par intrant. Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de ventiler le coût, donnez une estimation du coût total de l'entretien de la Technologie:
3,0
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Tillage and appliyng phospho-gypsum | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Polyethylene film | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 125,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
For arrangement of 1 ha width of furrow makes 100 meters, quantity of furrow makes 50
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Arrangement of furrows its cutting and reinforcing of the bottom of furrow
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
235,00
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Growing pirriod 4-5 months
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Valley of the Syrdarya river . Foothill plains of a ridge of the Karatau
Slopes on average: Flat for valley landforms for foothill plains
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is medium (Alluvial gray soils) - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium for alluvial meadow soils and poor for light gray soils
Soil water storage capacity is low for alluvial meadow soils and very low for light gray soils
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are rich and own 50% of the land.
19% of the land users are average wealthy and own 39% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 1% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Due to pasturable live stock and cultivation of gourds
Market orientation of production system:Mixed for grain-crops, grasses and commercial orientation for cotton
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for ploughing, chasing and harvesting and mechanised for tillage interrow cultivation
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- loué
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Autres impacts socio-économiques
expenses on water
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
perte en sol
Autres impacts écologiques
soil fertility
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The area of flooding at the end of a field is reduced 3-4 times
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Dump of drainage waters is reduced up to 2 times
norms of entering of mineral fertilizers
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to decrease of washing out nutrients
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 10-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
850 households in an area of 40km2 (10-50 persons per km2)
Commentaires:
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
850 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The existing system of water-subdivision does not provide for water consume on demand of farmers within the limits of allocated limit but establishes sequence of watering. At present water-subdivision the farmers who watering on furrows an create, additional stocks of a moisture and so the watering technology through furrows has not received universal application
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Improves working conditions of labours and work of soil-cultivating technics |
| Reduces the sizes of irrigating norms |
| Raises productivity of agriculture at deficiency of wate |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Reduces technological losses of irrigating water to filtration, evaporations, shed from fields of on irrigation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Till progressive method od an irrigation drop, rain |
| Reduces intensity of soil condensation and development of denitrify processes |
| Reduces loading to drainage system and rates of pollution of water sources |
| Prevents degradation of the irrigated soils |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Increase in expenses for interrow processing | Application of soil cultivating technics |
| Increase in quantity of watering | Reinforcing furrows by pipes |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Reduction of the interwatering period | By increase in volume of use of subsoil waters to subirrigation |
| Increase in interrow processing | Regime of subsoil water management |
| Increase in cost the current expenses at watering and interrow processing | Increase in productivity of cultivated cultures |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Reports: Technology of an irrigation on the farm site in zone of Arys-Turkestan channal. 2000-2002 year.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
SPC for Water management
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Recommendations on stabilization of agriculture in a zone of Arys-Turkestan channal
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé