Soil-protective minimal technology of the tillage and sowing [Kazakhstan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Ervin Gossen
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Soil-protective system of agriculture
technologies_1092 - Kazakhstan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Budnikova Taisia
taiss3@rambler.ru
National Ecological Society
480036 Almaty U/G 5
Kazakhstan
Spécialiste GDT:
Kaskarbaev Jaksenbay Aitanovich
8(316) 31-2-10-80
SPC for Crain Husbandry
Kazakhstan
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan (MoA) - Erythrée1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
29/03/2004
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
The minimal tillage for cultivation of grain crops (the second and third culture after fallow).
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
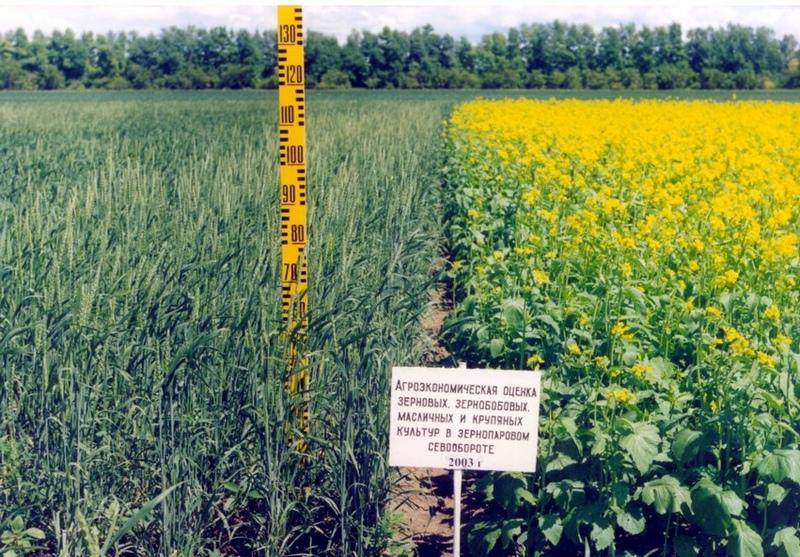
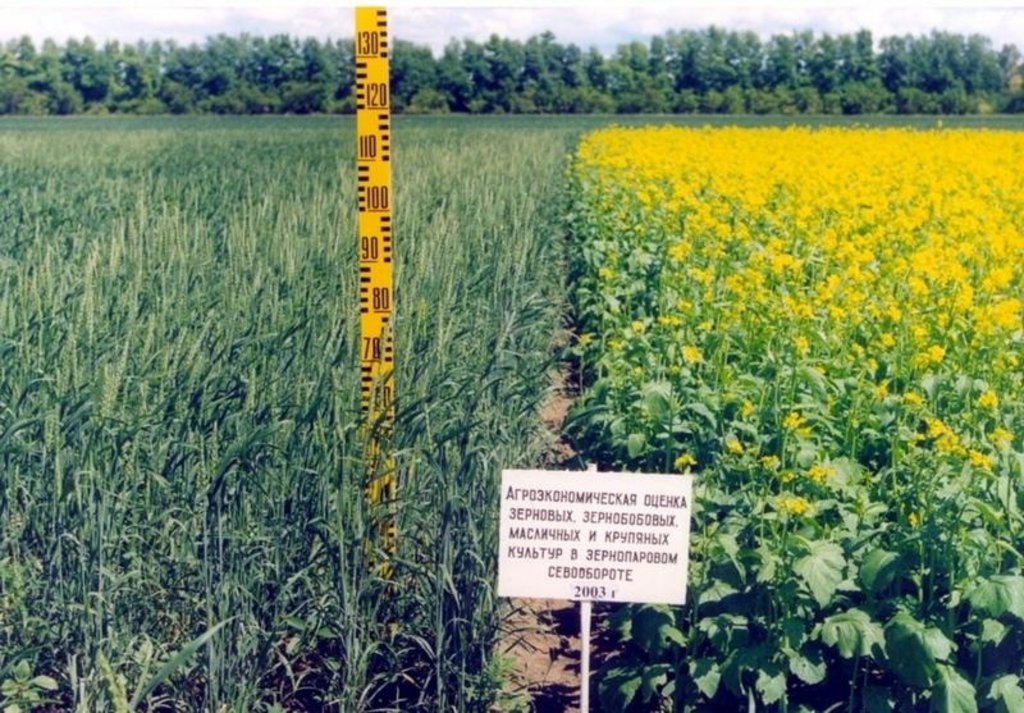
The technology is directed on struggle against wind and water erosion.
After harvesting of grain crops on a field it is left stubble background which carries out some functions:
1)Accumulation of moisture.
2)Prevention of water and wind erosion
3)Accumulation of organic in humus layer.
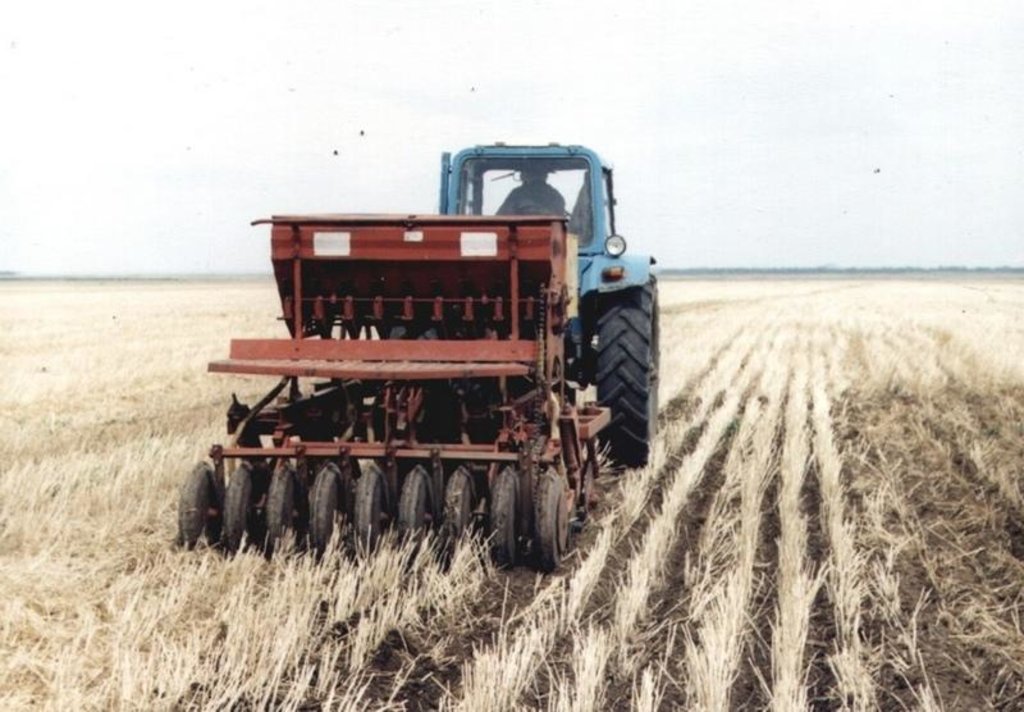
During the spring period on the stubble background there is a sowing of grain crops by the direct or combined seeder there (cultivation, sowing, application of fertilizers, compacting) with covering of seeds on depth of 3,8 centimeters.
After shoots at presence of weeds it is carried out a local tilling of the littered sites of a field.
In the autumn harvesting of the grain is carried out with crushing of strow and formation of the stubble layer.
Productivity of the grain makes 8,6-12,5 c/ha depending on humidity of year.
-fertilized fallow with minimum and chemical tillage;
-sowing of spring rapes on the fallow by seeding-machine “Flexy-Coil” +sowing of winter rye to spring rapes stubble in the second summer half – “direct sowing”
-winter rye of early ripening sorts (August)+ semifallow soil tillage+ fertilizers under sowing of steadfast spring wheat;
-steadfast spring wheat;
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kazakhstan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Northern Kazakhstan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kustanay, Northern Kazakhstan, Akmola
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
from Canada
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
major cash crop: Spring, wheat
major food crop: Wheat
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil-fertility is reduced on 10-25% (humus loss for 50 years).
Deterioration of technique Fertilizers are not brought in full.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Dissociation of farms with the average size of an arable land – 60 ha.
Struggle against wind and water erosion is directed on increase of soil fertility and receptions of steady cultures at full protection.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 166; Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- système de rotation (rotation des cultures, jachères, agriculture itinérante)
- perturbation minimale du sol
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 10-100 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 28 km2.
Before disintegration of the USSR the tillage and sowing on the stubble background in 1990 has made the area in 61,4 mill.ha on a steppe droughty zone (chernozem and dark chestnut zone of the USSR).
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, mulching, temporary trashlines, legume inter-planting, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, zero tillage / no-till, minimum tillage
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wm: mouvements de masse/ glissements de terrain

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cp: pollution des sols
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cp: soil pollution
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Development vergin and lay lands.)
Secondary causes of degradation: land tenure (land subdivision), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Also rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: straw 100%
Temporary trashlines
Material/ species: stubble 100%
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: herbicides
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: fallows-rape-wheat 100% 2,5 mln seeds for hectar
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: Sowing on a stubble
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: on depth of 3,8 centm
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
10.00
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | persons/day/ha | 5,0 | 10,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 90,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fallows creating | Agronomique | autumn / in 3 years |
| 2. | Rape sowing + winter rye | Agronomique | early spring, august / in 3 years |
| 3. | Winter rye + semi-fallow + fertilizing | Agronomique | early spring, august / in 3 years |
| 4. | Wheat sowing | Agronomique | early spring / in 3 years |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | persons/day/ha | 5,0 | 10,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 90,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: SZS-2,1, K-700, Kamaz-with tractor carriages PTS-9,3 PTS-12, combine Enisey
Calculation of expenses is made on 1 ha an arable land.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Rent of the mechanized means for creation the fallow crop and harvesting of cultures of a crop rotation make the most part of article of expenses on SWS technologies (tractor K-700, combine “Enisey”, automobile – Kamaz seeders – 2,1 carriages to tractors PTC-9,3 PTC-12).
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Steppe
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Wavy plain
Altitudinal zone: 150-340 m a.s.l.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Humus horizon up to 80 cm
Soil texture (topsoil): Heavy and average
Soil fertility is medium with a humus content of 4-5%
Topsoil organic matter: 1-5%
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium at bottom part of the slopes and otherwise low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
6% of the land users are very rich and own 3% of the land (5).
5% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (3).
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land (2).
4% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (1).
4% of the land users are poor and own 2% of the land (4).
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By means of struggle against erosion and deflation
Autres impacts socio-économiques
input contstraints
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
High cost
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Promotes stubble creation
perte en sol
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Promotes stubble creation
Autres impacts écologiques
soil fertility
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to introduction of fertilizers reduces erosion
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduces adjournment of melkozem
erosion processes
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduces intensity of erosive processes
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 10-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
100 households covering 40 percent of stated area
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: At low cost of petroleum products fertilizers small and average farm with pleasure apply SWC technology . Cost of petroleum products and fertilizers sharply changes from year to year
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
It is accessible in application How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
|
Improves agromeliorative conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
|
Allows to receive guaranteed profit How can they be sustained / enhanced? At presence of means for SWC introduction |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
It is traditional for region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
|
It is effective as a measure of struggle against wind erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? At threat of processes of wind erosion |
|
It is effective at struggle against water erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? At threat of processes of water erosion |
|
Promotes accumulation of a moisture in ground How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constantly |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Opportunity of application SWC to the limited circles of farmers. | Additional grants investments are necessary for small farms or the sponsor’s help. |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Soil protective agriculture Baraev A.I., Moscow, "Floc". Without rotation of the Almaty layer , 2000y, Gossen E.F.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
SPC for Crain Husbandry Shartandy city
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé