FISH POND MANURING USING CRIB METHOD [Tanzanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Philip Ileta
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
UFUGAJI WA SAMAKI KWENYE BWAWA
technologies_1154 - Tanzanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Zawadi Waziri
Enviroment Ngara
Tanzanie
Spécialiste GDT:
Mugishagwe Wilson
Forestry Ngara
Tanzanie
Spécialiste GDT:
Josephat Sangatati
Livestock Ngara
Tanzanie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - Tanzanie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
This is a practice of fish farming whereby farmers excavate ponds ,fill in fresh water,stock-in fish fingerings and manage them to mature or marketable size
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
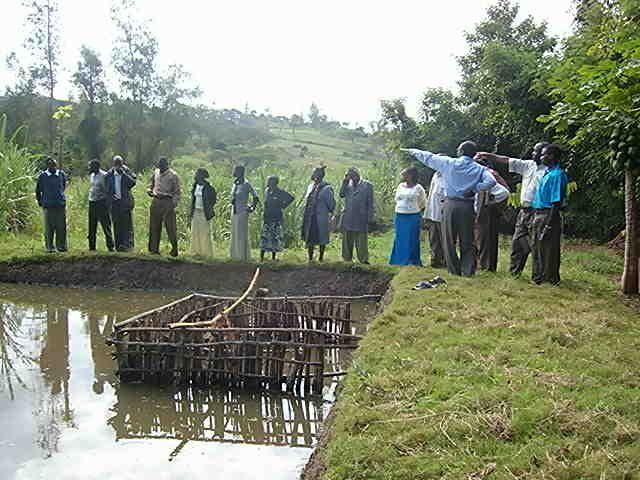
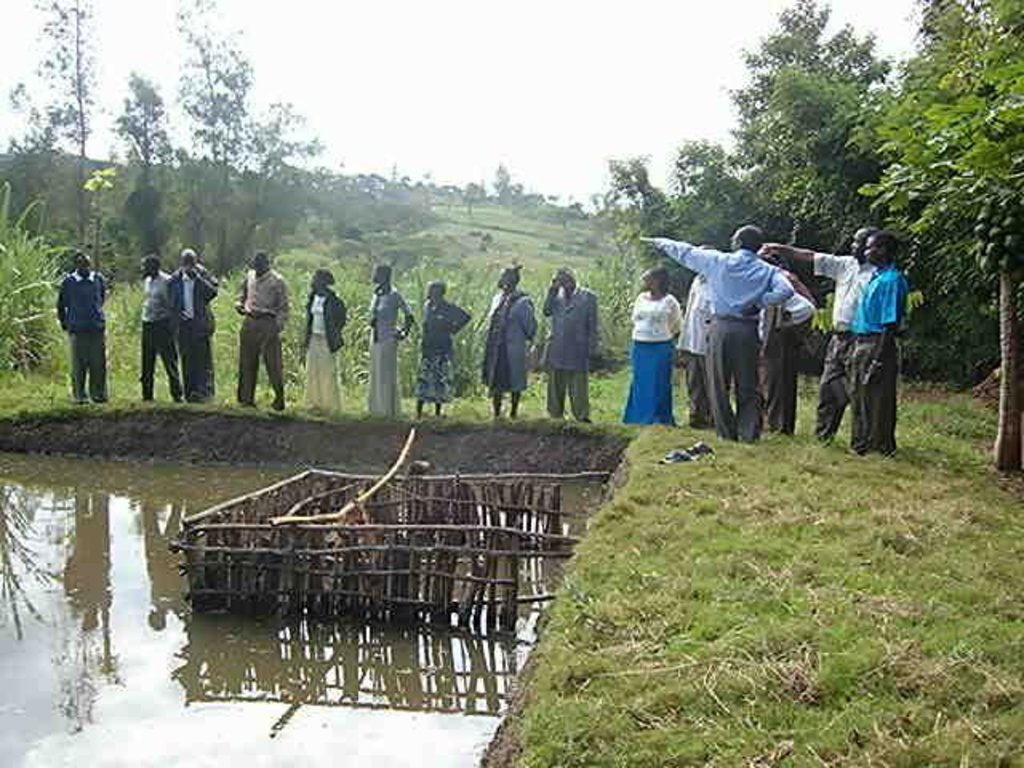
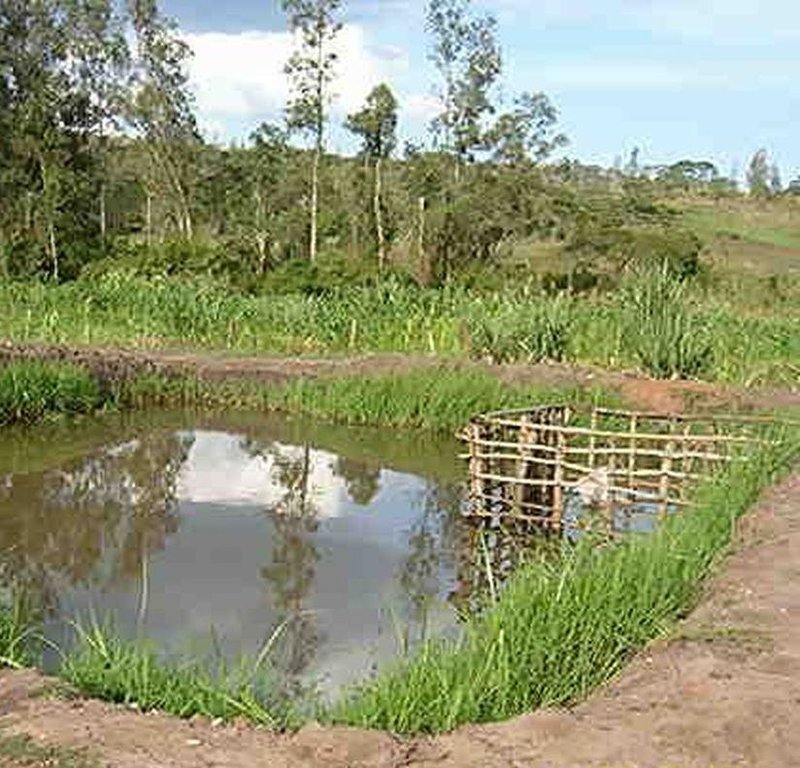
Select a suitable area/site with permanent water source or alongside the flowing river/stream preferably with a clay soil and excavate a suitable sized pond(30mx20m)and a depth of 1,5-2m at the upper and lower side respectively. A crib of 4 m2 for application of manure is constructed using short tree poles at the shallow portion of the pond before filling in water and introducing fish fingerings
Purpose of the Technology: The crib provides an area where Farm yard manure or compost is put to decompose and thereby stimulate the growth of fish foods (phytoplanktons).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: ESTABLISHMENT
-Selection of suitable area and pegging to required size/area
-Excavations to suitable depth
-Dig inlet canal from the water source through the shallow side and outlet canal from the deeper portion of the pond back to the main stream (Alternatively use small metal pipes,bamboo or plastic pipes for inlets and outlets)
-Compact the embankment and stabilize soil by planting suitable grass species such as vetiva spp etc
-Cut 2.5m long strong poles and construct a crib for manure application
-Spread manure at the bottom of the pond and wait for weeds growth (normally 2 weeks)
-Fill in water and stock in fingerings( 1 fingering per sq meter)
-Protect the pond by fencing preferably planting around live fence trees such as Dovyalis caffra,Pthecelobium dulce etc
MAINTANANCE
-Regular cleaning of the pond,and weeding the sorounding environment
-Feeeding with extra foods such as rice/maize brun,rice husks,chopped vegetables,pumpkins and potatoes etc
-Weekly application of farm yard manure or compost(1 tin 15-20 kg) by putting and tying by hanging a sac full in a crib.
-Shaking once daily the hanging sac while in water to release nutrients
Natural / human environment: The pond site should be easily accesible and where possible near homesteads for security purpose
-Harvesting may done by draining the water from the pond, using a seine net,and catch the desired size of fish while returning the young fish to continue growing
In good pond management/feeding farmers are able to harvest every after six months
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tanzanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tanzania
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Ngara District Council
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
fish farming in Ngara has been supported since the 1980s by UNICEF,DRDPS and recently by DANIDA through NGOs(REDESO and TCRS)
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Etangs, barrages, retenues d'eau
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): -less utilisation of wetlands resources to contribute in improving (livelihood) nutrition and groups/huosehold income
-some fish species (larvifish)may be stocked in ponds to feed on diseases vectors such as mosquitoe larva and reduce malaria incidences
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): To obtain fish for food and surplus harvest for income
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers cultivate small plots of vegetables,sweet potatoes in valleys near fish ponds and chop them to supplement fish meals
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: October to January; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- apiculture, aquaculture, élevage de volailles, de lapins, du ver à soie, etc.
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.06 ha.
The group owns a fish pond of size 30mx20m in a wetland located in Kasulo village and is stocked with Tilapia spp fingerings
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A6: Autres

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs

modes de gestion
- M5: Contrôle/ changement de la composition des espèces
Commentaires:
Secondary measures: management measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: water storage for fish culture
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bh: perte d’habitats
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (over exploitation of fish in natural water bodies)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Causing siltation,flooding of already constructed fish ponds), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (blocking of water channels, ponds due to mud)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
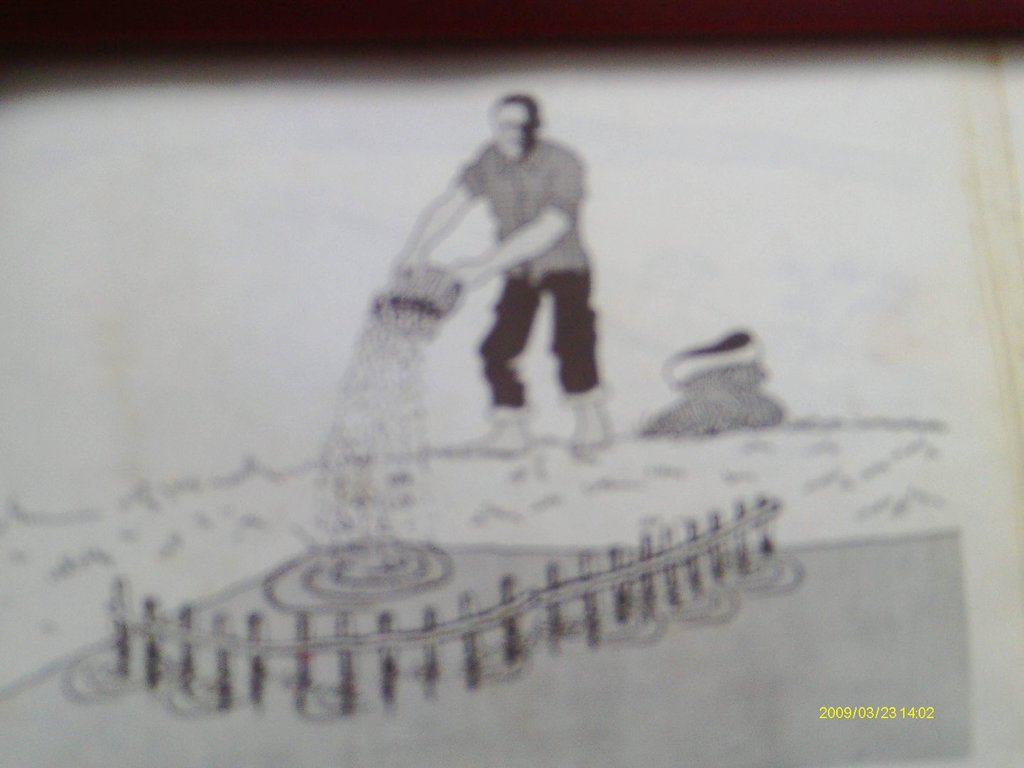
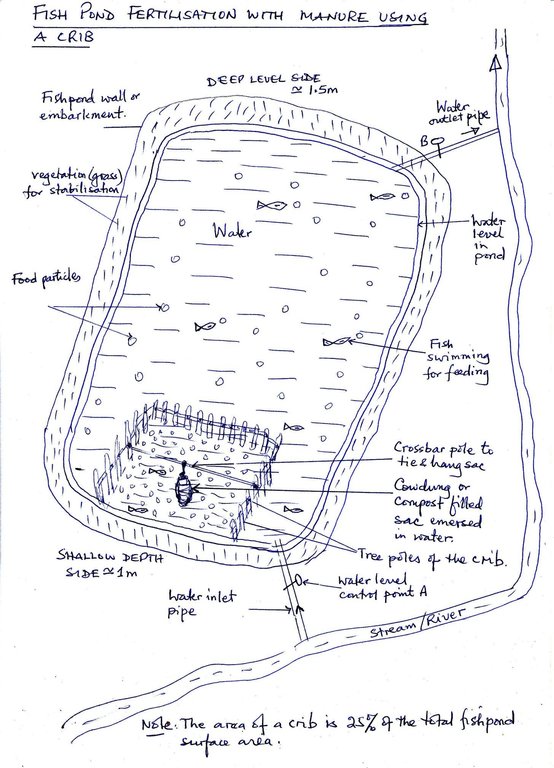
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Fish pond fertilization with manure using a crib
Location: yyy village. Ngara District Council/Tanzania
Date: 15 May 2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Once the fishpond is established,the extension kit requires regular monitoring for improvement of fish feeds and outbreak of diseases which are relatively few compared to other livestocks such as pok)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Following the fish pond manual developed by the district is simple with regard to pond management and feeding regimes)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: cowdung
Quantity/ density: 50 kgs
Remarks: applied in crib once weekly per pond
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 300
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): seedlings
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Grass species: vetiva planted to stablise pond embarkments
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 20
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 30
Reshaping surface
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Construction material (earth): The pond has the deeper side 1.5m and shallower side 1.0m,with the top earth compacted 2m wide
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Wetlands were marginally used only for dry season agriculture and some vegatable growing-now aquaculture intergration adding productive value to it
Control / change of species composition: Most farmers preferered Tilapia nilotica for stocking in fishponds,phytoplanktons growth promoted
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Fishpond
Spécifiez le volume, la longueur, etc. (si pertinent):
30m x 20m
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tanzania shilling
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
1600,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.25
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying of vetiva | Végétale | during the rains |
| 2. | Planting of vetiva on embarkments | Végétale | during rains |
| 3. | Allignment and layout of pond | Structurel | before rains |
| 4. | Excavation of the pond | Structurel | before rains |
| 5. | Raising embarkments,compaction construction inlets and outlets | Structurel | before rains |
| 6. | Collect cow dung | Agronomique | |
| 7. | Purchase fish fingerings | Agronomique | |
| 8. | Purchase tools | Agronomique |
Commentaires:
Lifespan of dung, fish fingerings and tools: 3 years
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Planting of vetiva on embarkments | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Allignment and layout of pond | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 50,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Excavation of the pond | persons/day | 120,0 | 1,88 | 225,6 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Raising embarkments,compaction construction inlets and outlets | persons/day | 3,0 | 1,25 | 3,75 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Fish fingerings | pieces | 1000,0 | 0,06 | 60,0 | 20,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | pieces | 4,0 | 12,5 | 50,0 | 20,0 |
| Equipements | Vetiva | pieces | 300,0 | 0,16666 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Cowdung | kg | 50,0 | 1,25 | 62,5 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 456,85 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Application of cowdung | Agronomique | weekly |
| 2. | Application of extra feeds | Agronomique | fortnight |
| 3. | Clean weeding | Agronomique | monthly |
| 4. | Trimming the live fence,weeding and monitoring | Végétale | dry seson |
| 5. | Repairing of walls | Structurel | after heavy storms |
| 6. | Management of fingerings -monitoring of growth,control of overpopulation | Modes de gestion | monthly |
| 7. | Cowdung application and manipulation for nutrients release | Modes de gestion | weekly |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Clean weeding | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Trimming the live fence,weeding and monitoring | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Repairing of walls | persons/day | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Management of fingerings | persons/day | 4,0 | 1,6 | 6,4 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Extra feeds (maize and ricebran) | kg | 10,0 | 1,88 | 18,8 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Cowdung | kg | 50,0 | 1,25 | 62,5 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Labour: Cowdung application and manipulation for nutrients release | persons/day | 1,0 | 1,25 | 1,25 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 96,45 | |||||
Commentaires:
the costs are calculated per fish pond of size 20m width,30m length and depth 1.5m
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
labour especially during excavations(establishment phase)
cowdung when the land user buys instead of obtaining from the homestead/kraal
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
950,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Length of dry periods 4 months
Main rain season Oct to Dec/January, Second season March to Mid May
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics. Hot during the days slighly cold nights,avarage temp range18-30C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, loamy to heavy clayey basement) and moderately deep (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter is medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor and retains water in pond permanently, but medium in severe dry spell and water level decrease to half pond depth.
Soil water storage capacity is high near wetlands and permanent streams. Sometimes also very high
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
en surface
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: Good (ranked 1) and excess (ranked 2, the site of the pond is located such that at maximum flooding it shoul d not be reached by flood water to prevent fish escape/overflow)
Water quality (untreated): For agricultural use only: Wetlands used for dry season farming and small horticultural gardens. Farmers fetch water in the streams due to unavailability of safe water points
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Decreasing rapidly due to pollution of water sources, deforeatstion and overexploiation of natural fish stocks
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Excavations usually by men labour but for maintanance activitiies women play increasing roles
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
60% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Most of the farmers with ponds have livestock and apply cow dung instaed of compost
Market orientation of production system: Mixed (farmers sell some surplus fish although productivity still below avarage)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- groupe
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Commentaires:
water use is free for use by all community members especially for agricultural activities
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Phytoplanktons feeds
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
0.06
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
This is the surface area of the pond
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
100
Quantité après la GDT:
375
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Market for fish is available when good size
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From increased income
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Animal protein source menu, but malaria and bilhazia vectors when ponds are not well kept/managed
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
When the suitable species of fish is stocked and proper fish pond management procedures adhered to -the harvest are high-at least once to twice per year-but this requires high initial and maintanance capital -routine extension from aquaculture experts is highly needed to enable farmers realise profits
Impacts écologiques
Sols
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From decomposition of cow dung
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Phytoplanktons and water weeds
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Other water fauna and flora which are not predators may be allowed to flourish
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Water retained in ponds when adopted farmers increase
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Commentaires:
The productivity of the fish pond is determined by many factors including the selected species of fish,the feeding levels and the temperature of water. Most tropical fish species grows well when the temperature of the pond water remains warm
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
Initial establishment capital high
Cow dung may be obtained free from kraal or altenative use compost
manure
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
3 households
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
3 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The fish ponds project attracted many families to engage in the activities,the constraints were high capital investments and poor pond managent
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: especially for well off farmers with land holdings near wetlands and streams
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Availability of permanent water sources especially streams How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation bylaws enforced on bufferzones |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Availability of permanent water sources especially streams How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation bylaws enforced on bufferzones |
|
Farmers owns cattle/shorts How can they be sustained / enhanced? Enhance crop and livestock intergration |
|
Wetlands are owned comunally and by village governments How can they be sustained / enhanced? Bylaws enforcement to prevent encroachment and pollution |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High capital investments | Family oriented groups have some success ,to think of some subsidies throgh government or simple credit schemes |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High capital investments | Group approach used -although many groups fail to sustain the ponds |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé