Agroforestry homegarden [Sénégal]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Julie Zähringer
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1166 - Sénégal
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CSE (CSE) - Sénégal1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
07/08/2009
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
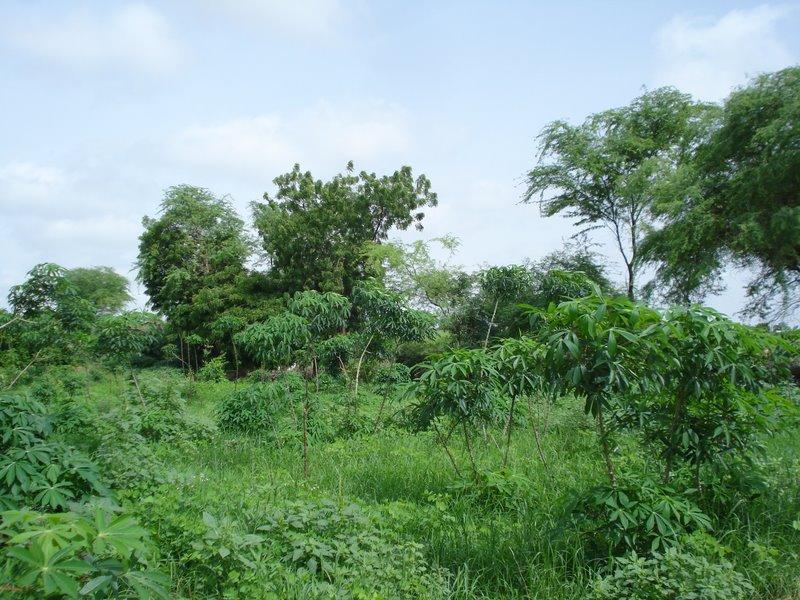
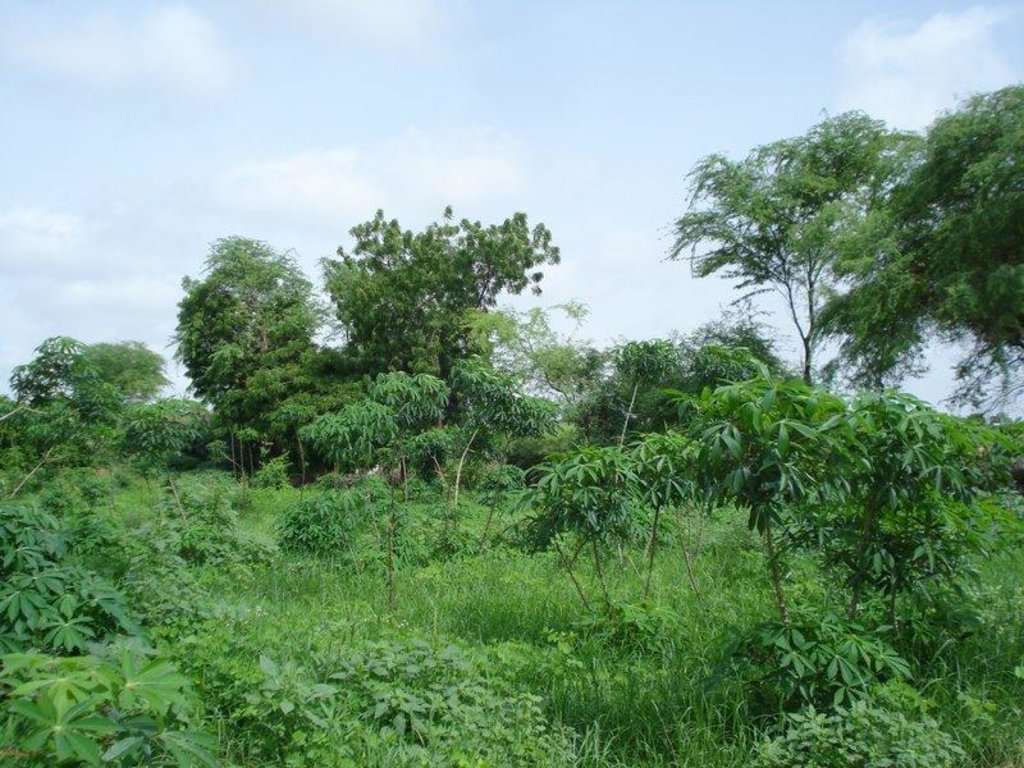
A tropical homegarden of about 0.5 ha with a variety of exotic and indigenous tree species, planted or raised for fruit production, medicinal value and / or other services, intercropped with vegetables in the herbaceous layer.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
During the dry season, tomato, eggplant, chili, beans, cabbage, okra and bissap are cultivated, in the rainy season replaced with maïz. One part of the garden is cultivated with cassava, planted in the rainy season and harvested all year round. Main tree species are Prosopis juliflora, Citrus sp. and Eucalyptus camaldulensis. A hedge of mainly dead wood, alive Euphorbia balsamifera shrubs and few Eucalyptus camaldulensis trees is protecting the homegarden from roaming animals. It has the positive off-site effect of preventing the temporary pond beneath the plot from being filled up with sediments, as a consequence of wind erosion. Organic manure obtained from cattle faeces is used as a natural fertilizer.
Purpose of the Technology: The garden was established and is managed by a single land user and his family. Main objectives are to provide food security for his family, to make a wide range of fruits and vegetables available in a zone far from the next market and to improve income through diversification. As the plot is situated on a slope (7 %) and prone to water erosion during heavy rains, a further objective is to prevent the formation of gullies and ravines through better soil stabilization.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Trees planted in this plot were chosen upon seed or seedling availability in other peoples land as the land user planted whatever he could obtain. He constructed a fence of dead wood with the aim to turn it into a life fence of Eucalyptus camaldulensis trees later. A small retention basin was built to assure the storage of water tapped from the village borehole. However, because of breakdowns of the pump and the generally low outflow of the borehole, lack of water caused high mortality in the tree nursery of Eucalyptus camaldulensis seedlings. The fence therefore remains a mainly dead fence and is very weak in certain places. The main cost of the technology is the access to the borehole which costs the landuser 20'000 CFA (US-Dollar 45) per month. For the purchase of seeds for horticulture about 15'000 CFA (US-Dollar 33.50) are spent per year. The use of organic manure does not involve any costs as cattle is abundant in the area.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. The main land use type in the area is extensive pastoralism followed by rainfed agriculture. Pastoralism is primarily practiced by transhumant Fula (Peulh) herders and further by Mauritanian Moor herders with herds of dromedaries. Vegetation cover in the area has largely been degraded due to cutting for domestic uses and cattle feeding, bushfires and overgrazing. The soil is exposed to wind erosion which carries away nutrients in the topsoil and therefore declines soil fertility. During intense rains in the rainy season, surface runoff is accelerated and leads to the formation of gullies and ravines.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Sénégal
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Louga / Linguère
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Barkédji / Diagali
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Agroforesterie
Principaux produits/ services:
Maïz, manioc
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): degradation of vegetation cover, wind erosion, increased surface runoff, formation of gullies and ravines, management of natural water sources (people using temporary ponds for laundry and body hygiene and at the same time as sources of drinking water)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): surface runoff, formation of gullies and ravines, decrease of soil fertility, wind erosion, limited water access, presence of insect pests
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jul-Oct
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- brise-vent/ plantations abris
- système de rotation (rotation des cultures, jachères, agriculture itinérante)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
The surface of this homegarden is about 0.5 ha
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: retaining more vegetation cover, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)
- Eo: effets hors site de la dégradation

dégradation biologique
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Eo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (for domestic uses), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (by oversized cattle and dromadaires herds), poverty / wealth (poverty), education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (absence (or insufficient use) of inorganic and organic fertilizers)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: (the landuser concerned does not have this level of knowledge)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: trees
Quantity/ density: 118 / ha
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: organic manure
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 118
Trees/ shrubs species: Citrus sp. (planted), Eucalyptus camaldulensis (planted), Azadirachta indica (planted), Tamarindus i
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
CFA
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
455,0
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | access to irrigation water for tree nursery | Végétale | per month |
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | seeds or seedlings for horticulture | Végétale | once a year |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 33,0 | 33,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Irrigation water | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 78,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Costs indicated apply to an agroforestry plot of 0.5 ha surface. No costs were involved with the initial planting of trees in the plot, as seedlings were either given by the extensive agent for "Water and Forest" or obtained from other landusers. Organic manure can be obtained for free due to the strong presence of cattle in the area. For the construction of the fence, dead wood was collected in the area.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
rainfall regime: water for irrigation needed during dry season
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
300-400 mm during one rainy season / length of dry season: 9 months
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Valley floors (depression)
Slopes on average: Moderate (7%)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Very low
Topsoil organic matter: Low (carbon in the labile fraction: 0.09 g / kg soil)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, ranked 1, groundwater during dry season) and for agricultural use only (irrigation, ranked 2, surface water from temporary ponds during rainy season)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Compared to other regions of the country
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: women can not aquire land to cultivate unless it is attributed to them by their husbands
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
22% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Apart from the plot the landuser is cultivating some village fields
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
diversité des produits
surface de production
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased food security, improved diversification of alimentation
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
évaporation
Sols
couverture du sol
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
envasement en aval
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: many inhabitants of this village try to establish similar plots
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| increase of product diversification, availability of vegetables in village |
|
increase of revenues How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase production and fight against soil fertility decline |
| increased food security |
| increased availability of plants used in traditional medicine |
|
mitigation of gully formation How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve strenght of fence |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
increased woody plant diversity and density How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain trees in plot |
|
the fence reduces siltation of the village's most important temporary pond beneath the plot How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve the fence with live trees |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| outflow of village borehole too weak to maintain irrigation of seedlings in tree nursery and vegetables | better maintenance of borehole |
| high mortality in tree nursery because insufficience of water | improve access to water from borehole |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| use of chemical pesticides against soil insects which are believed to be a cause for decline in soil fertility | research to know more about cause of fertility decline or use of biological pesticides |
| degradation of soil properties because of inappropriate soil management in parts of the plot | training in soil management for landuser |
| removal of herbaceous cover to gain space for cultivation | training |
| no system applied to distribution of trees in the field | apply structural soil conservation measures, such as terraces etc. |
| gully formation because of slope and weak fence threatens future maintenance of plot |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé