Oyster Mushroom [Népal]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Sabita Aryal
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Parale Chyau
technologies_1194 - Népal
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Dahal Dikshya
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Karki Nabina
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Budhathoki Karuna
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Ghimire Kishor
9844148065
Agricultural Office, Sindhuli
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Singh Yubraj
9841673072
Agricultural Office, Sindhuli
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Neupane Shankar
01-5010090
Management Post Institution Lalitpur, Hattiban
Népal
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Kathmandu University (KU) - NépalNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
District Agriculture Development Office, Sindhuli (DADO) - Népal1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
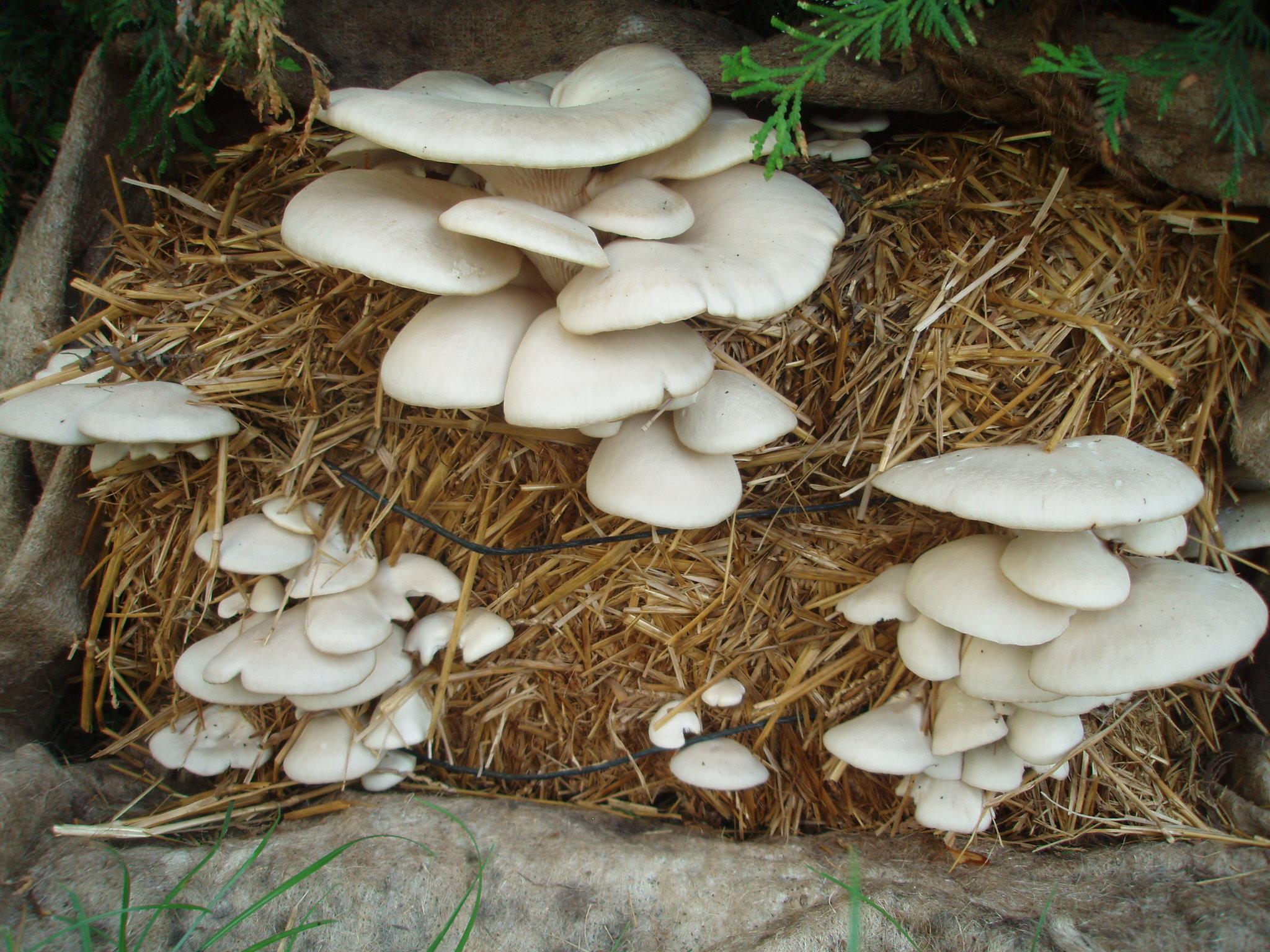
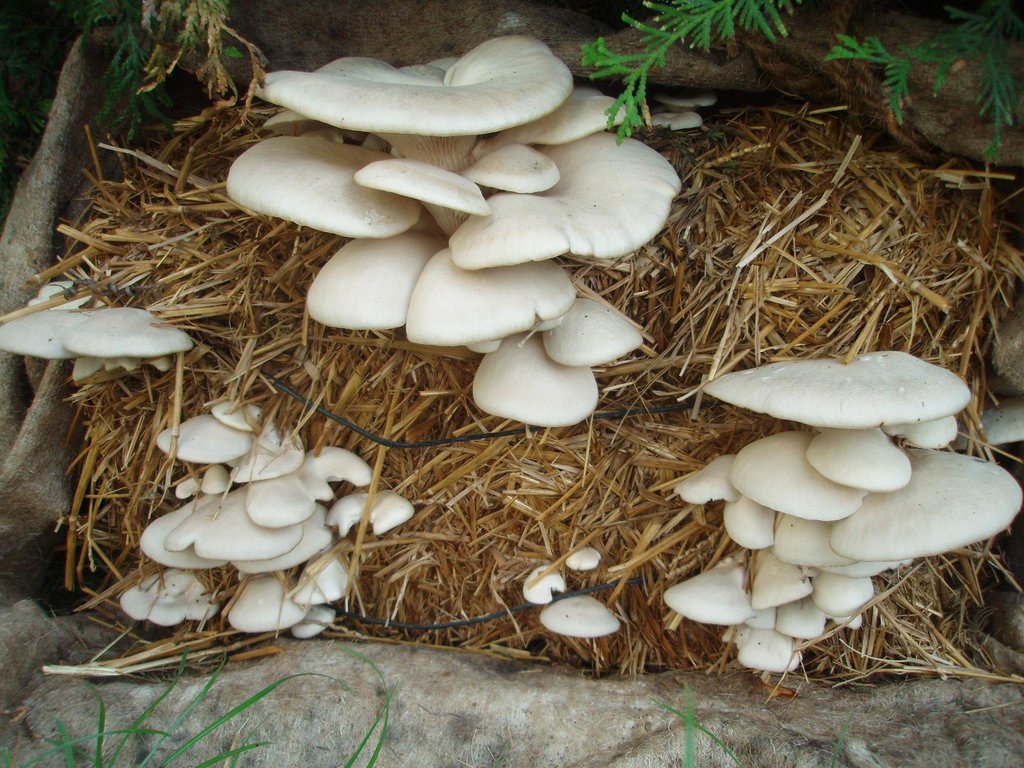
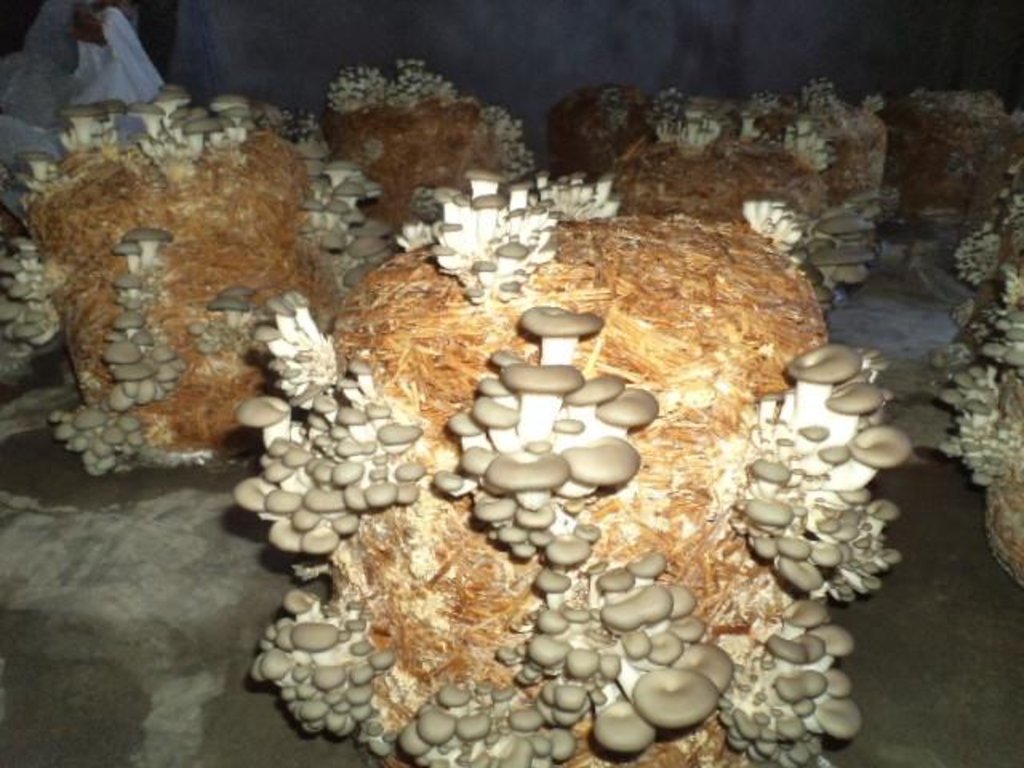
Oyster Mushroom Farming Technology is the cultivation of oyster mushrooms as a food source, economic source, and as primary compost, to increase the quality of soil and help upgrade living standards of local farmers.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The technology is carried out in Kamalamai Municipality, Sindhuli District, Janakpur, Nepal. The Pennsylvania Department Of Environmental Protection (DEP), other regulator agencies and the community are at charge. Oyster were identified as being both economically viable and suited for local cultivation. Nepal Agriculture Research Council (NARC) and a few private organizations are the major resources centers for supplying the quality spawn to the farmer/growers.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of this document is to provide uniform instructions and operating procedures for the use or disposal of mushroom compost (as soil amendment or conditioner). Another basic purpose is use of mushroom as food and income source for local farmers.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Best Practices for Environmental Protection in the Mushroom Farm
Community (1997) was developed as a result of realization among authorities of Pennsylvania DEP, to help people to understand that farms are operating according to the highest environmental standards, and will help improve coexistence with nearby residents, through environmental regulation. This implemented a mushroom farm development for specific operations with the natural resource conservation. The member co-ordination, knowledge, and experiences are critical in establishing the practices as workable and rational means to meet the goal of environmental protection and agricultural operation.
Natural / human environment: Mushroom Farm Environmental Management Plan (MFEMP) is designed to prevent pollution or danger of ground or surface water on common health, by helping in maintaining/improving the condition of soil, and prevent the pollution of surface water, groundwater and air, as well, at little or no cost. This technology helps local farmers to increase soil fertility and act as a good income source in small scale.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Népal
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Janakpur
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Sindhuli
Map
×2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
This practice was performed by American mushroom institutions in 1997 and earlier 1984.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Autre
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low productivity of land, soil erosion, water scarcity, cultivation of land slopes, tillage resulting in soil loss.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Infertility of land, having to use fertilizers and pesticides, scarcity of water for irrigation, having to plow farm seasonally and repeatedly.
Constraints of recreation: Dark and moist environment is necessary.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 75; Longest growing period from month to month: January-March
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12*18 inch.
The straw and spawn (mushroom) should be packed in plastic bags. Two or three inches of straw are packed into the plastic bag and the spawn is lightly sprinkled on top. This should be repeated until the bag is almost filled, the top of the plastic should be closed and holes should be poked in the bag.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, mulching, manure / compost / residues, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (soil erosion, low productivity of land, tillage), overgrazing (Fodder for domestic animals such as cow, buffalo, goat etc.), change in temperature (Uneven rainfall, long dry or cold seasons)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (terrace farming problems), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Use of timber for burning), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Only required vegetation was used), poverty / wealth (Medium to large scale production costly for local farmers)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
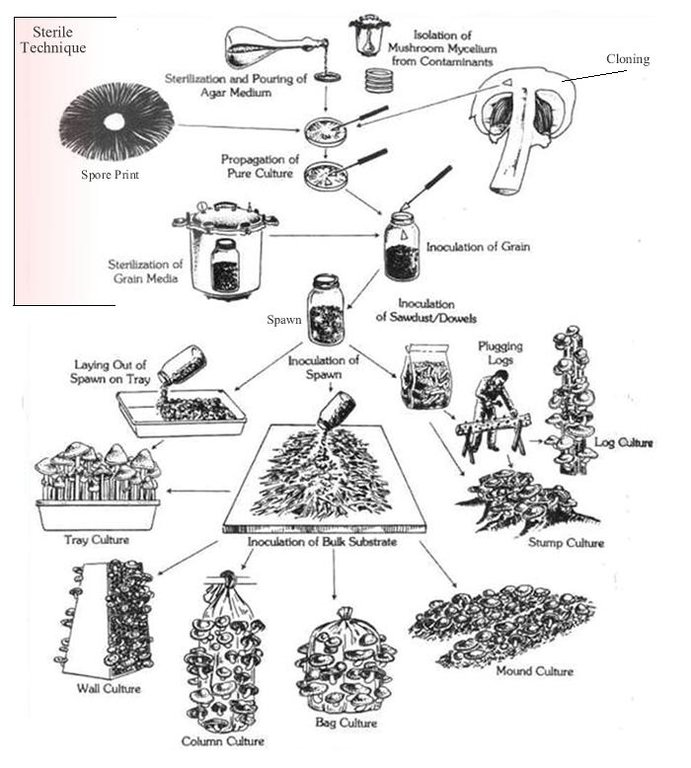
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
It is kept in a room with temperature 22-28 degree.
Location: Room. Sindhuli
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Knowledge on preparing substrate, incubation period and harvesting of mushroom and proper use of mushroom compost.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Since land usage is very less.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mulching
Material/ species: straw and spawn
Quantity/ density: 2:1
Construction material (earth): mud in cement
Construction material (stone): stone
Construction material (wood): wood plants
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rupees
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
90,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.00
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matériaux de construction | Straw | unit | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Container | unit | 1,0 | 990,0 | 990,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Fuel | unit | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stove | unit | 1,0 | 770,0 | 770,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Plastic | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Cutting Machine | unit | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2210,0 | |||||
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Method of cutting straw | Agronomique | dry season |
| 2. | Warming the straw | Agronomique | dry season |
| 3. | Harvesting the mushroom | Agronomique | dry season |
| 4. | Maintainance of mushroom | Agronomique | dry season |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Method of cutting straw | persons/day | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 150,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: plastic bag,water storage tank.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour should be managed properly.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
DADO Sindhuli, 2010
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Mostly mushroom grow in about 24 degree Celsius.
Mostly mushroom grow in about 24 degree Celsius.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Flat surface is needed.
5.3 Sols
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil water storage capacity is medium: Mushroom need water daily two times.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: May face scarcity of drinking water in dry seasons.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Found mostly in eastern region, and almost in the western parts as well.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There is no difference in involvement of men and women in this technology, both can be involved.
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- individuel
Commentaires:
It is found that this technique is used even by people with little amount of land.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mushroom Compost usage
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Leftover straw
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Richer in nutrients than dry hay
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Little to no cost required
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mushrooms sold widely as food source
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Recreational method, provides options for farmers
disparités économiques
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
1 or 2 individuals are enough.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cheap and easy way for earning money
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mushroom compost used instead of chemical fertilizers
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Good way to utilize time, gain profits
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It has helped to increase knowledge
Impacts écologiques
Sols
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Provide nutrients to plants
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Composting
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Composting
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mushroom: edible fungi
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Alternative mushroom composts
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas connu |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
The technology could be made more tolerant by keeping the room dark and warm (22-28 degrees), and carry out cultivation in almost all seasons (except winter).
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
Yes,this technology can give both short-term returns and long-term returns.Positive result because it is the best type of production for the environment and economic resources.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
3 households covering 32 percent of stated area
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 10-50%
Commentaires:
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: By government point of view almost all members of a village and city, both can cultivate this technology.
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Without external support also this technology can be carried out.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Best Practices for Environmental Protection in the Mushroom Farm
Community
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
It is used as vegetable. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It gives nutrients. |
|
Waste water management How can they be sustained / enhanced? Waste water can be used as part of this farming. |
|
It is used as manure How can they be sustained / enhanced? High productivity |
|
Good income source How can they be sustained / enhanced? Requires less space and materials. Easily cultivated in favorable season. Can be sold commercially because of its food value. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Erosion and sedimentation control How can they be sustained / enhanced? This section looks at the soil, geology, ground cover and other natural feature site, by providing nutrients to the soil as a conditioner. |
|
Surface water and stormwater management How can they be sustained / enhanced? At most mushroom farm operation stormwater run off can be divide into uncontaminated and contaminated water. |
|
Economic purpose How can they be sustained / enhanced? Constructed to increase income source with little initiation cost. Substrate can be used as compost, so no need for chemical fertilizers. |
|
Nutrient management for substrate utilization How can they be sustained / enhanced? The season methods and amount of nutrient used to maintain the technology. |
|
Integrated pest management How can they be sustained / enhanced? Pest control may be accompained by using non-chemical or alternative controls. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Place for growing | All locals do not have spare rooms or sheds for mushroom cultivation. This proves to be a huge disadvantage as they require dark room and moist conditions. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Less theoritical knowledge | Locals should be made aware about growing technologies that can help increase their quality of life. |
| Place for growing | Rooms or shed may not always be available. Providing darkness during can be a problem. |
| Seasonal problem | Room temperature required is 20-30 degree Celsius. |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé