Soil faced deep trench bunds [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Eyasu Yazew
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Nay Hamed Amik Metrebwi Zala
technologies_1197 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Sibhatleab Mulugeta
+251 910 170415
Mekelle University
P.O.Box 231, Mekelle, Ethiopia
Ethiopie
Spécialiste GDT:
Weldearegay Kifle
+251 910 170415
Mekelle University
P.O.Box 231, Mekelle, Ethiopia
Ethiopie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Mekelle University (Mekelle University) - Ethiopie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/11/2012
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
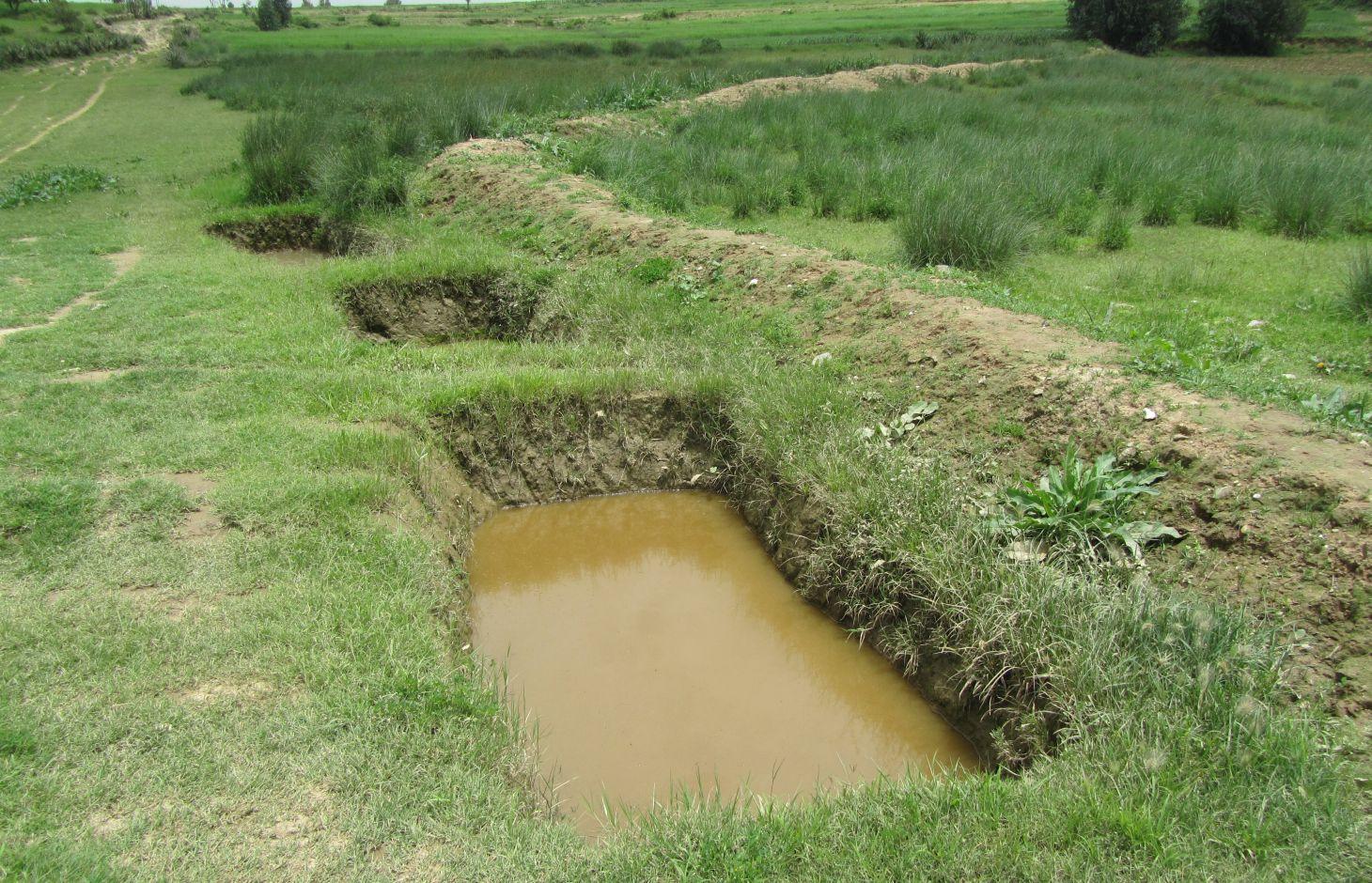
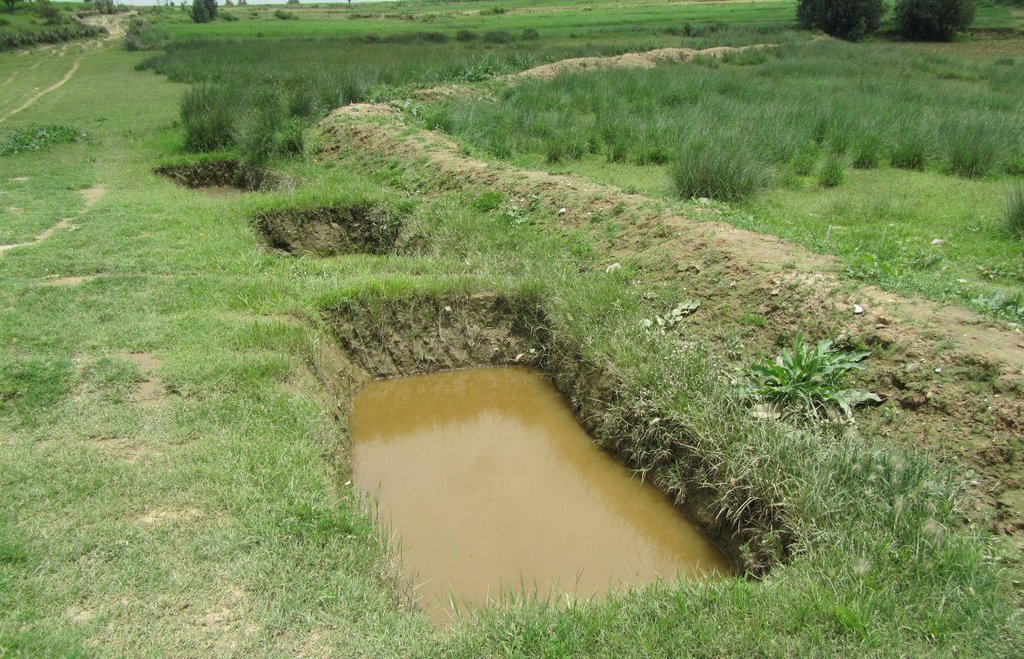
Compacted soil bund constructed following a contour using a soil excavated from deep trenches on the up-slope side.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
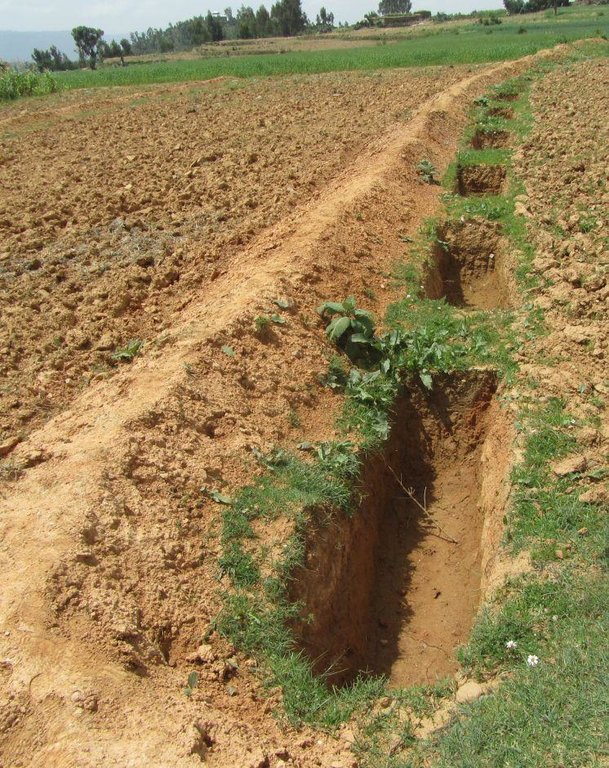
Soil faced deep trench bund is constructed by excavating trenches of 1 m deep, 0.5 - 1 m wide and 2 - 3.5 m long with spacing between trenches of 0.3 - 0.5 m along the contour and using the excavated soil to construct a compacted bund downslope. The smaller dimensions are usually used in cultivated lands while the larger are implemented in grazing lands.
Purpose of the Technology: Soil faced deep trench bund decreases slope length, runoff velocity and soil loss; and increases runoff harvesting, soil moisture and groundwater recharge.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Construction of soil faced deep trench bund involves alignment of a contour, excavation of trenches, construction and compaction of bund and planting grass, while the maintenance involves dredging of sediment from the trenches and use it for reinforcing the embankment.
Line level, tape meter, digging hoe, shovel and grass are needed for the establishment and maintenance.
Natural / human environment: The technology is implemented in moderate (5 - 8%) and hill (8 - 16%) slopes and in medium and heavy soil types of at least 1 m depth. It reduces runoff amount and velocity thereby decreasing soil loss and desertification/land degradation. It also improves soil moisture availability and groundwater recharge by encouraging lateral and vertical movement of water respectively.
It is mostly constructed using communal labour and there is an encouraging trend of spontaneous adoption. The technology is witnessed to be increasing crop and fodder production thereby improving the livelihood of the land users. It, however, is labour intensive and slightly reduces farm size.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tigray
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kilte Awlaelo
Map
×2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major food crop: Wheat, barley, teff, maize, sorghum
Major other crops: Oil seeds

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
- Prairies améliorées
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, overgrazing, decline of soil fertility and productivity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion, reduced soil depth, fertility and productivity.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: June - November
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
50-100 LU /km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- gestion des eaux souterraines
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 10-100 km2
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

structures physiques
- S2: Diguettes, digues
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management, overgrazing, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Crop residues are removed during harvesting), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, change of seasonal rainfall, droughts, land tenure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
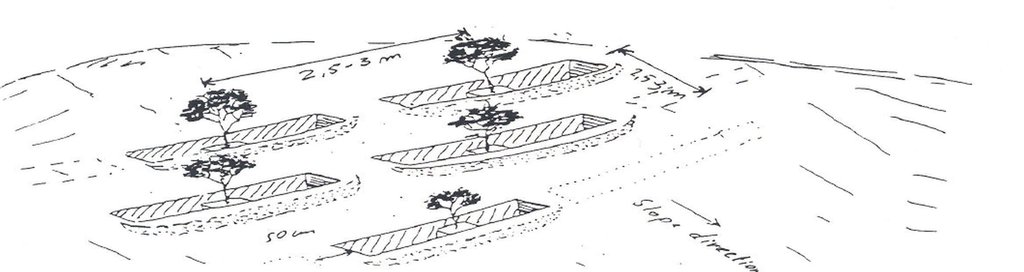
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Soil faced deep trench bunds are structures constructed by excavating trenches following the contour and using the excavated soil to establish compacted bund on the lower side.
Location: Tigray. Kilte Awlaelo
Date: 10/10/2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 1600
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 - 1.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10 - 15
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Grass species: Elephant grass is mostly planted on the bunds in a single row at spacing of 0.5 m.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6.5 and 12%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1 - 1.2
Spacing between structures (m): 10 - 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5 - 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2 - 3.5
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75 - 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3 - 1.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60 - 100
Construction material (earth): Soil excavated from the trenches is used to construct bunds
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6.5 and 12%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Birr
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
18,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.50
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of elephant grass | Végétale | June/July |
| 2. | Grass plantation | Végétale | July |
| 3. | Contour alignment, marking trench dimensions, trench excavation and construction and compaction of bund | Structurel | January - May |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 2119,0 | 2119,0 | 60,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 36,0 | 36,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2199,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dredging of deposited sediment from trenches and compacting it on the bund | Structurel | January - May |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 833,0 | 833,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 833,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Digging hoe, shovel (Costs are included in the structural measures), Line level, tape meter, digging hoe, shovel
The cost was calculated for an average bund length and spacing of 80 m and 12.5 m respectively, which would result in a construction of 10 bunds per ha. In addition, an average trench length and spacing between trenches along the contour of 2.75 m and 0.4 m was considered respectively resulting in 25 trenches per bund and 250 trenches per ha.
The excavation of one deep trench and construction of the corresponding bund requires 3 person days during establishment while maintaining it needs 1.5 person days per year. A single row of grass is planted on the bunds at 0.5 m interval and a person is assumed to plant about 100 seedlings per day. The cost calculation rates apply to 2012. Accordingly, the price of single elephant grass is 0.4 Birr and the daily labour wage is 40 Birr for light work such as grass planting and 50 Birr for medium work such as trench excavation.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour, slope, landuse, soil depth.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average rainfall of 450-550 mm, Main rainy season from Mid-June to August
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: An average slope of 6.5% is taken for moderate slope and 12% for hill slope.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: The deep trench should usually be 1 m deep.
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, Appropriate in case of grazing lands.)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and medium (Clay soils in rehabilitated grazing lands, ranked 2.)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (more in cultivate lands, ranked 1) and Medium (more in grazing lands, ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (ranked 1) and poor (in clay soils, ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 55% of the land (35 birr/person/day).
30% of the land users are poor and own 35% of the land.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average land holding is 0.6 ha per household.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Mobile communication:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production animale
surface de production
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
charge de travail
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased investment in health as a result of increased income.
institutions communautaires
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
8735
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 50-90%
Commentaires:
27% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2541 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
73% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6194 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Reduce soil erosion and increase soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance and excavation of sediment |
|
Increase soil moisture and yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting grass, sunflower and other fodder plants on the bund to increase conservation as well as economic benefits |
|
Reduce surface runoff, increase water storage in trenches and recharging downstream springs How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance and excavation of sediment |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Decreased slope length, reduced runoff amount and velocity and soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance of the structures and controlled grazing of the grass |
|
Increase in rainwater harvesting, soil moisture and groundwater recharge How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance of the structures |
|
Increase in crop and fodder production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting improved and high yielding crop and fodder varieties |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Reduced farm land | Increase the productivity of the bunds. |
| Increased labour requirement | Mass mobilization and/or increased incentives to households. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive | Mass mobilization and improving the design. |
| Reduced farm land | Increasing the spacing and reduce dimension of bunds without compromising their effectiveness. |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Staff members of the Kilte Awlaelo Wereda Office of Agriculture and Rural Development
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Carucci, V. (2000). Guidelines on Water Harvesting and Soil Conservation for Moisture Deficit Areas in Ethiopia:the productive use of water and soil. First draft manual for trainers, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Lakew, D., Carucci, V., Asrat, W. and Yitayew, A. (2005). Community Based Participatory Watershed Development: A guideline. Part I, first edition, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé