Multiplier fertilization of banana using small ruminants in Kibanja farming system [Tanzanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : ALLAN BUBELWA
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Matumizi ya mifugo katika shamba la kibanja.
technologies_1207 - Tanzanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Pancras Egidius
Missenyi District
Tanzanie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - TanzanieNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - Tanzanie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
04/06/2014
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Enhancement of sustainable land management by capitalizing on the rapid growth, short gestation nature and multiple benefits of small ruminants kept under zero grazing in a banana based farming system.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
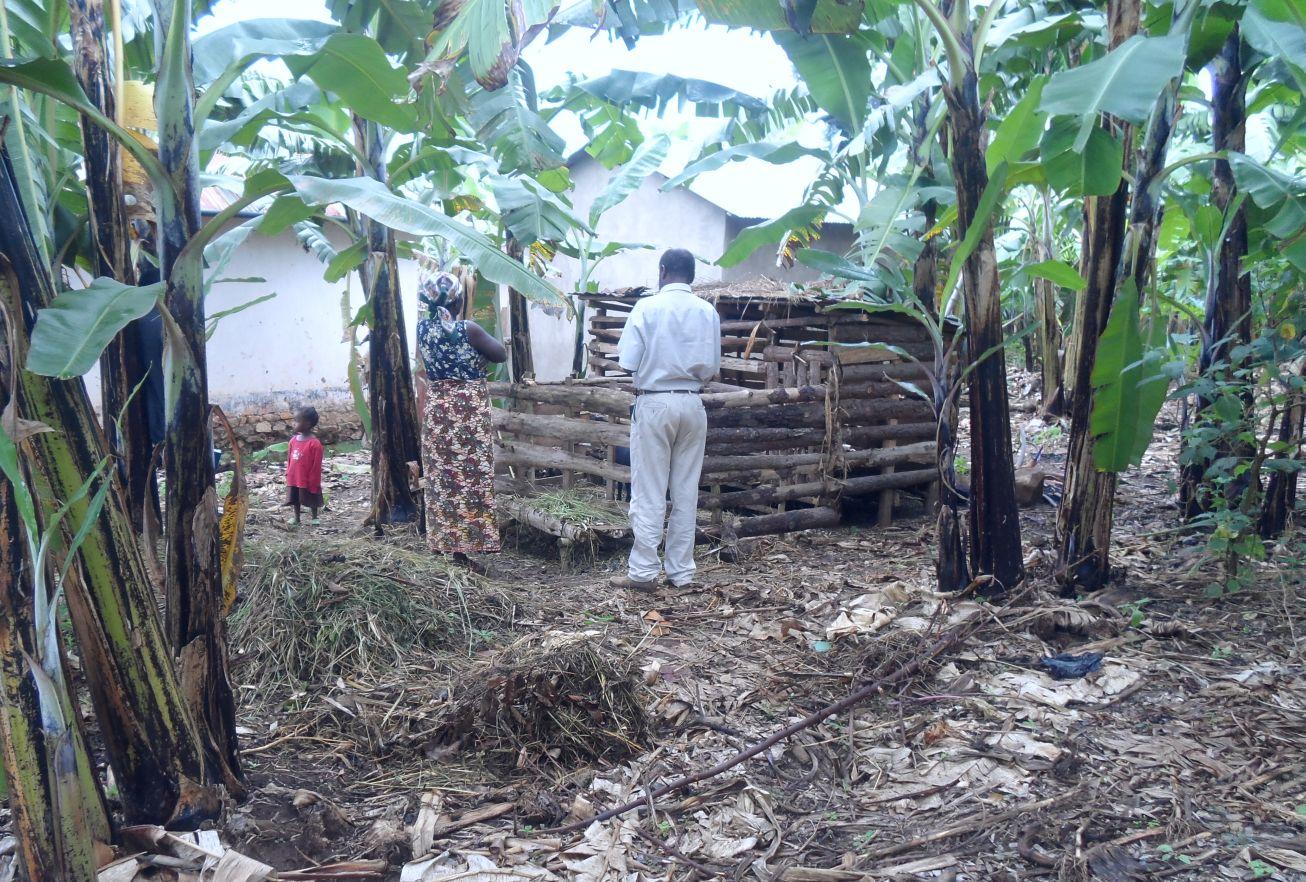
Multiplier banana fertilization is a system where rapid growing small ruminants (preferably dairy goats) of low gestation period are kept under zero grazing within a banana based (Kibanja) farming system and their excrement are used in complementing other fertilization of the banana fields. Dairy goats also improve diet of the rural poor and diversify their income. The animals were initially supported by SLM projects as quick win income generating motivation/incentives to farmer who spent their valuable time in SLM activities of long term benefit realization. In multiplier fertilization, a farmer starts only with a few numbers of animals (as kick start). Usually 2 female dairy goats and one improved male goat (buck) suffice. Goat dung collected from the shed is used to perform selective and on spot application of manure to banana plants. Because of their rapid growth and short gestation nature, goats multiplies and increase in number within few years and at the same time in multiplier terms farmers spread and apply manure to more banana plants. Farmers begin with a small animal shed of usually carrying capacity of 4 to 6 goats and can expand it as goat increases. Goats feed on products cut and carried outside or within the kibanja farm. Animals also feed on domestic residuals (e.g. banana peels), food supplements and water for their maximum performance. Goat dung is collected weekly from the shed and is piled in layers, covered with grass and kept shaded under banana canopies to allow microbial action and minimize nutrient loss through volatilization. Depending on the growth stage of banana, dry manure is applied on sport and selectively after every three months of microbial decay. The numbers of animal increases year after year at the same time farmer benefit from the use/sale of animal product (milk in the short term and meat in the long term) and in multiplier manner continue expanding manure application to other banana plants. Manure from goats contributes in improved banana productivity. Benefits accrued from goats also motivate and induce farmers’ patience in terms of their participation in SLM interventions of long term benefit realization.
Purpose of the Technology: Purposes: improved banana productivity, livelihood diversification, income of the rural poor and soil ecosystem through fertility and organic matter replenishment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities includes, kick start support of farmers with goats (two dairy goats and an improved buck), construction of the goat shed (100% borne by land user to inculcate self-initiative and ownership) and purchase of working tools (spade, rake, hand hoe).
Recurrent activities largely includes, fetching fodders and feeding the animals (cut and carry products outside or within the kibanja), weekly cleaning of the goat shed and manure collection, manure heaping and grass covering for microbial decay/reducing nutrient volatilization, spreading/cooling, monthly on spot and selective application of manure to banana plants, milking of the animals, disease control/deworming and providing supplements.
Natural / human environment: Multiplier banana manure application is used in kibanja farming system in sub humid tropical highland plateau/plains of 1000 -1500m a.s.l. with annual rainfall between 1000 – 1500mm, moderate soil depth and medium loam textural class.
Is used by small scale land users both men and women individual households. In Kibanja farm, land ownership is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial).
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tanzanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tanzania/Kagera
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Missenyi Disrict/ Kiziba division/ Kitobo ward/ Kyazi village
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Started in December 2012 as part of environmental sound income generating activities promoted and supported by the Trans-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (KAGERA TAMP).
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop: Coffee
Major food crop: Banana
Others: Maize, patatoes and yams

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Goats are kept under zero grazing for domestic consumption (milk and meet), are asset for sale to meet debts and commitments (e.g. health and education) and have significant impact on sustainable land management in terms of manuring and replenishment of soil nutrients.
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Without land conservation there will be inadequate/poor soil fertility and organic matter content, low soil moisture holding capacity, poor health of banana and their increased vulnerability to pest and diseases especially the most devastating Banana Xanthomonas Wilt (BXW).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Banana Xanthomonas Wilt, weak banana plants and low production.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
The technology is implemented in Kibanja cropping land use type by individual farmers who received support of diary goats from the Trans-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (TAMP) as quick win and environmental sound motivation for farmers who spend their valuable time in implementation of SLM intervention of long term benefit realization.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, green manure, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bl: perte de la vie des sols
- Bp: augmentation des insectes nuisibles (ravageurs)/ maladies, baisse des prédateurs

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Low soil fertilization/manure application), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor banana husbandry practces), population pressure (High land requirement and continuous utilization without fallowing.), poverty / wealth (low investment capacity), education, access to knowledge and support services (Shortage of staff, inadequate extension services and provision of subsidies.), governance / institutional (Low bylaws/law enforcements (e.g. on BXW control))
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
and rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Involve simple retraining of technologies already taught to staff in school/agricultural collages.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Have some elements of new skills and knowledge. e.g. a farmers must be taught of the principle behind zero grazing and manure preparation (microbial decomposition/control of mineral volatilization))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Banana, castrol oil, yams
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: scattered
Mulching
Material/ species: Banana thrashes and stems
Quantity/ density: 100m3/ha
Remarks: thinly pread seasonaly twice per year
Green manure
Material/ species: Various types of weeds
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: scattered
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: random
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Goat dung, grass and domestc residues
Quantity/ density: 222 m3/ha
Remarks: Assuming got dung is applied once per hactere
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tanzanian shillings
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
1700,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.20
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase goats (dairy goats) | Modes de gestion | |
| 2. | Build animal shed | Structurel | |
| 3. | Purchase tools | Modes de gestion |
Commentaires:
Lifespan of the goats and tools: 5 years
Lifespan of the shed: 3 years
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | Tools | piece | 5,0 | 2,8 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Goat shed | piece§ | 1,0 | 29,0 | 29,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Goats | piece | 3,0 | 70,33333 | 211,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 254,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fetching fodder (cut and carry) and use of domestic residuals. | Agronomique | Daily/annually |
| 2. | Cleaning shed and collecting manure | Agronomique | weekly/annually |
| 3. | Heaping manure and compost | Agronomique | weekly/annually |
| 4. | Tilling on sport and selective application around banana | Agronomique | March, June, Sept and Decemb |
| 5. | Disease control/de-worming | Agronomique | weekly/annally |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Fetching fodder (cut and carry) and use of domestic residuals. | person/days | 120,0 | 1,175 | 141,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Cleaning shed and collecting manure | person/days | 26,0 | 0,8848 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Heaping manure and compost | person/days | 26,0 | 0,8848 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Tilling on sport and selective application around banana | person/days | 16,0 | 1,1875 | 19,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Biocides | litres | 12,0 | 3,91666 | 47,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Labour: Disease control/de-worming | person/days | 26,0 | 1,1925 | 31,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 284,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, rake, hand hoe, machete and bucket.
The costs were calculated per unit of kick start animal flock (three dairy goats) needed annually per individual farmer household.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
September to December 120 days, March to Maya 90 days = 210 days . Average length of growing period is 210
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average temperature is 20°C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (about 60cm)
Soil texture: Medium (highly clay loam)
Soil fertility: Low (due to excessive nutrient uptake without replenishment)
Top soil organic matter: Low (low crop remains)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (no water logging)
Soil water storagce capacity: Very high (nature of soil is loamy)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: Medium (water is available in nearby natural water spring. There is reduction of water flow during the dry season)
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water as it comes from a natural spring
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Soil microorganisms e.g earthworms and ants.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
6% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
64% of the land users are average wealthy and own 64% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 6% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some have established small kiosk at the village center and most have additional income items of regular support, assistance and cash transference from children or family members who work or have big business in cities, town and in some cases in diaspora.
Market orientation: Mixed (Banana and goats/milk are produced for both sell and home consumption)
Level of mechanization: Manual work (land form and agroecological nature of the kibanja farm cause hand hoe to be the best means of cultivation)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
< 0.5 ha, Ranked 2, about 30% of household fall in this category
0.5-1 ha: Ranked 1, account for 60 % of the household
1-2 ha: Ranked 3, account for 10% 0f the household
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Commentaires:
Land is largely acquired by inheritance. Traditionally water is open accessed for public use through customary law.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
15-20kgs/banch
Quantité après la GDT:
35-40kgs/banch
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
manure application have contributed in increase of banana yield
production animale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0 goat per household
Quantité après la GDT:
3 goats per household
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
goats introduced through projects.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
385 usd
Quantité après la GDT:
200 usd
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
manure received from goat overshadow the costs of fodder, concentrates and waters for goats
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
3.5 usd
Quantité après la GDT:
6.5 usd
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
net income gain due to use of manure
diversité des sources de revenus
Quantité avant la GDT:
1 enterprise
Quantité après la GDT:
2 enterprises
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
additional income sources from goat keeping
charge de travail
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
237
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased labour needed for goat keeping
Impacts socioculturels
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmer use additional income generated from banana production to pay for debts and other commitments like school fee and health expenses. Goats act as moving banks and contributes in farmer income assurance during the sensitive time e.g. sending children to school or wives to maternal/birth services. There is also nutritional improvement to farmers (farmers attain a balanced diet from milk protein).
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
improved water holding capacity
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Quantité avant la GDT:
low N
Quantité après la GDT:
high N
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to application of goat dung
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to goat manure
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
espèces bénéfiques
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased soil micro-organism/insect
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to improved plant health.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas connu |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
Commentaires:
Storage of crop remains, hay making for animal to have enough food and produce more meat, milk as well as manure.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
goats give quick win benefits because have short gestation period, usually gives twin kidding twice per year. Their average lactation period is 250 days and a single goat can produce average of 750 litres of milk per year worthy about 441 American dollars.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
317 households and 23% of the area covered
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 10-50%
Commentaires:
4% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
317 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The project supported procurement of goats.
31% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
317 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: goat keeping is part of tradition and culture.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some neighboring farmers have started adoption.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The technology is simple and easy to learn and have a short establishment time due to the short gestation nature of the goats themselves (only two female goats and an improved buck, a goat shed and some concentrates suffice for initial investment). |
| In the long term has synergistic effect and complements other existing land fertilization, moisture conservation and erosion control methods e.g. the quality of compost is improved. |
| Improves livelihood (goats act as moving banks and contributes in farmer income assurance during the sensitive time e.g. sending children to school or wives to maternal/birth services) and nutrition to farmers (farmers attain a balanced diet from milk protein). |
| Increased banana production and continuous returns in multiplier terms. Goats also convert domestic residuals (e.g. banana peels) into useful products . |
| Maintenance activities can be covered by land users and this help in ensuring self-initiative and ownership |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High workload in looking for fodder | Introduce fodder within kibanja farm |
| Shortage of genetically improved dairy goats | Introduce genetically improved dairy goats. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Shortage in the number of field extension workers needed for effective extension service delivery | Government employ more extension worker |
| Limited reach ability of extension staff due to shortage of transport facilities. | Provision of reliable transport facilities to extension workers. |
| Agro-vert/input dealers services are not available in the rural premises. | Introduce agro-vert/input dealers in rural premises. |
| Goat provision and distribution to farmers done at a small pace | Expand goat provision and distribution to more farmers. |
| Rural urban migration of the youth searching for greener pasture leaving behind the less energetic elders. | Introduce attractive and decent income generating activities for youth in the rural areas. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé