Fodder provision to goats and sheep to reduce grazing pressure on natural vegetation [Chypre]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Michalakis Christoforou
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Παροχή σιτηρεσίου στα αιγοπρόβατα ως εναλλακτική τροφή με σκοπό τη μείωση της υπερβόσκησης στα φυσικά οικοσυστήμα(greek)
technologies_1247 - Chypre
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Cyprus University of Technology (Cyprus University of Technology) - Chypre1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/05/2014
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Use of different types of fodder in order to reduce grazing impact on natural vegetation
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
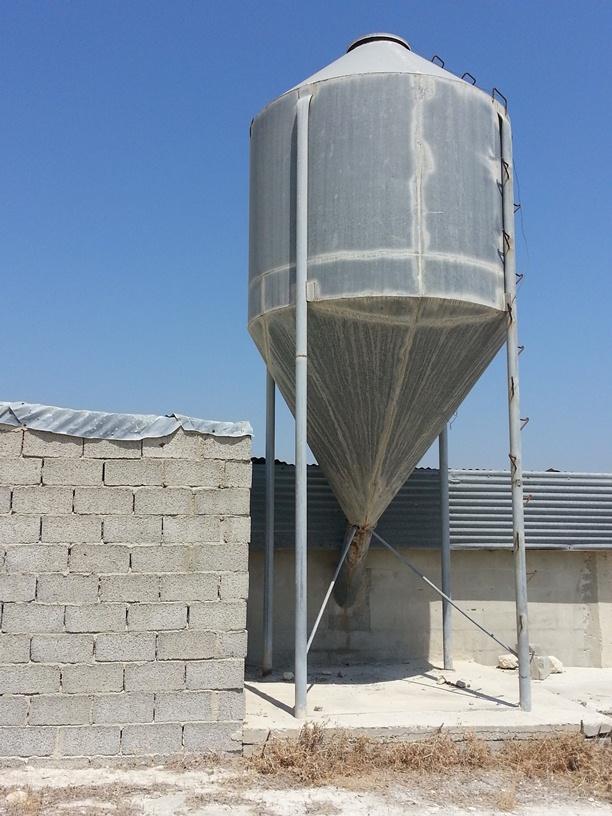
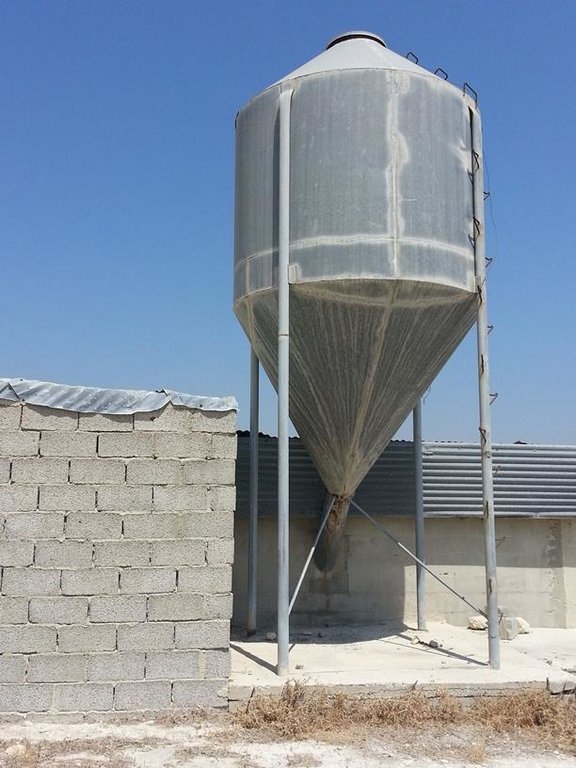
Goats graze on almost all plants even on thorny shrubs. The pastoralist in the past (some still do now a days) use to spread seeds on the grazing area in order to provide fodder for the animals. Another method is to provide fodder within the farm using dry seeds of wheat, barley, soya etc which can be stored in big silos.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is to provide to the animals with the food they need in order to minimize or even stop them from grazing on the wild flora such as shrubs, trees and annual plants. Within the study area, most of the vegetation is vanished and only traces of plant species can be found. Even the thorny shrubs like Callicotome villosa and Rhamnus oleiodes are suffering from overgrazing.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Fodder can be provided in-farm and out-farm. In-farm fodder is provided using a silo in which dry fodder can be store, mixed and deliver to the animals mechanically. Out-farm fodder is provided seasonally since the seeds should be seeded and plants must grow up before eaten by the animals
Natural / human environment: By providing fodder to the animals in-farm, grazing is avoided since the animals remain within the farm. This way, animal diseases transmission from one farm to another can be minimized. Also, animals may travel a long distance to find food whose energy miight be less than the energy they use.
Seeding on the hills will attract the goats and stop them from grazing on other wild plant species. Minimizing grazing will allow to the vegetation to recover and grow up providing good aesthetic view and also shelter for the wild animals. Furthermore, vegetation increase will contribute to the decrease of soil erosion and the increase of organic matter.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chypre
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Limassol
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Pissouri
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
EU funding gave the opportunity to some new farmers to buy new equipment for fodder provision. In this way the new farmers were able to feed their animals and increase their productivity
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Semi-nomadisme/ pastoralisme
- Ranching
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Main species semi-nomadism: Goats/rabbits/birds
Main species ranching: Goats
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): overgrazing due to a large amount of animals, drought, erosion
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): drought, poor calcareous soils, incomes are not enough to buy food
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: goats/ rabbits, birds
Ranching: goats
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 100Second longest growing period from month to month: September to December
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 10-100 km2
Commentaires:
The total area in which goat and sheep farmer are allowed to grow animals is around 400 Km2. The area affected by overgrazing is around 100Km2
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

structures physiques
- S11: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures, structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: Use of Silos in order to provide fodder to the animals
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, legume inter-planting
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (large number of animals), change in temperature (hot summers & cold winters force the animals to eat more in order to obtain water and energy from plants), change of seasonal rainfall (summers without rain and winters with some rain), droughts (heavy droughts every 3-4 years), poverty / wealth (farmers can not afford to feed the animals)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (about 90 years ago), urbanisation and infrastructure development (Urbanisation mostly at the coastal zone has forced the animals to move to the North. A large number of animals is concentrated in the northern site, increasing the overgrazing problem), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (A highway road split the area in two), war and conflicts (In 1974 many refugees moved from the North to the South due to the invasion of Turkish troops. Most of them who established in the area became farmers, and therefore increased the number of animals)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (animal feeding specialist with good knowledge on goat and sheep fodder)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (be able to follow the specialist advice and protocol for feeding animals)
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of animal feeding on natural vegetation
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: cereal seeds (wheat, barley, etc)
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: seeds should be seeded by hand during the rainy season
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: spread the seeds before the last rainfall in spring
Structural measure: Silo
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (other): stainless steel
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 9,42m3
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
euro
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
0,77
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
38.85
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy or make a Silo | Structurel | anytime |
| 2. | Buy cereal seeds (200kg) | Agronomique | |
| 3. | Buy legume seeds (200kg) | Agronomique |
Commentaires:
Inputs: Stainless steel
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 116,0 | 116,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Stainless steel silo | ha | 1,0 | 2589,0 | 2589,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Fodder transfer tubes | ha | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Agricultural | ha | 1,0 | 427,0 | 427,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 4132,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
Life-span of cereal seeds: 6 months
Life-span of legumes seeds: 3-4 months
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | spreading seeds | Agronomique | during rainfall (oct - Mar) |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 233,0 | 233,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 427,0 | 427,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 660,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Cost were calculated according to the farmers opinion which was confirmed by the agricultural department. Seeds and labor are calculated as units per ha and the silo per unit (farm)
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Cost for applying fodder is affected by 3 factors: a) the price of the Silo which is applied only once, b) the cost of the seeds and c) the labor needed for spreading the seeds. The slope in the area where the technology is applied is steep and makes the seeding difficult.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Annual rainfall for the year 2013 was 207 mm. From june to october rainfall was 0. In the last three years annual rainfall was between 207 and 540 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
- aride
Thermal climate class: tropics. Winter 0-25 °C, and Summer 20-45 °C
Thermal climate class: subtropics. During the winter, mean temperature can be 15-18 °C
According to the FAO, Cyprus is considered to be an arid to semi-arid area
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 100-500 m a.s.l (The area where the technology is applied is 1km far from the sea)
Landforms: Hill slopes (The area of interest consists of steep hill slopes)
Slopes on average are rolling (most common) and hilly (sometimes after soil erosion)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average is very shallow (the area is considered to be rocky) to shallow (only where soil is concentrated)
Soil texture is coarse (Analysis has shown that soil texture is 50% sand, 25% silt and 25% Clay)
Soil fertility is low
Topsoil organic matter is medium where some vegetation is, low where no vegetation is and high where vegetation is
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor (inter patch), medium (patch-interpatch) or good (plant patch)
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water is poor/none (there is no surface water available in the area)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Thorny shrubs, olive and carob trees, annual grass
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: no young women are involved with goat farming
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land (they make profit).
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (they barely survive).
Off-farm income specification: Some of the pastoralists who apply the SLM technology, have apartments which they rent to tourists during the summer season
Market orientation of production system: Equipment and structure subsidy (50% of the equipment and structures are funded)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial): Pastoralists receive subsidy from EU funds annually
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
The animal numbers are 10 times the amount permitted to graze in the area
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- individuel
Commentaires:
More than 70% of the land belongs to the government (forestry department) and the land is open to everybody. The pastoralists do not pay rent for using the land. The land which belongs to individuals is used by the owners or is been rented to the pastoralists
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Spreading cereals and legumes
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By providing fodder all year round
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By providing fodder all year round
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better quality of dairy products
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
During the first year, the cost of the Silo
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to production increase
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In-farm fodder provision. Labor hours are reduced due to the presence of fodder in the silo. Simplified farm operations through using the silo.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Animals from different farms are no more in contact
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Seeding on the hill reduces erosion
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Between pastoralists
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Shepherds who provide fodder and/or are seeding cereals and legumes on grazing land, produce more milk and meat. Therefore, they have higher incomes and a better life. They are able to send their children to school and provide a health care insurance to their families.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation cover
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation cover
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to vegetation cover
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to soil cover by cereals and legumes
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
May be in the near future, antagonism between cereals and legumes with other wild type species will appear
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Especially birds
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les champs voisins
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
On site since the animals will graze in the seeded area
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
On site since the animals will graze in the seeded area
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Commentaires:
Shepherds who apply the technology and are in a better socio-economical status are satisfied with their incomes but they believe that things could get better. Shepherds who don't apply the technology are poor, not satisfied with the incomes they receive and at the same time they are negative in applying the technology although they see other shepherds being in a better socio-economic status than them.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: New farmers-shepherds can have up to 60% funding from EU and government funds for construction and equipment
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The cost of buying fodder is extremely high. Also the equipments (silo) is considered to be expensive.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Using the Silo for providing fodder, they spend less hours in the farm. |
| By providing fodder, the quality and quantity of milk and meat is better |
| By keeping the animals in the farm, they save work hours and also the threat of animal poisoning is minimized |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
By providing fodder in and out of the farm the animals receive a better quality of fodder and the right quantities of fodder they need. How can they be sustained / enhanced? experts can give advices to the shepherds about the type of fodder, and the quantity during different seasons |
|
Through grazing in a specific area marked and seeded by the shepherd, the animals avoid direct contact with other animals. This minimizes the spread of diseases between animals of different farms. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Shepherds should come to an agreement about the area their animals graze and create borders |
|
Seeding cereals and legumes within the grazing areas decreases overgrazing on shrubs and annual plants How can they be sustained / enhanced? in the case where the shepherd is leading the animals, he should not allow the animals to graze on shrubs |
|
The presence of a Silo in a farm makes fodder provision easier and therefore less work is required How can they be sustained / enhanced? Government funding can cover the cost of the silo |
| seeding in the grazing area leads to improved soil cover which minimizes soil erosion |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| It is difficult to spread seeds on the rocky hills | |
| Buying fodder is expensive |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Not all shepherd are able to buy the Silo and large amounts of fodder to store in the silo | Government funding can cover the cost of the silo |
| The Randi forest area is suffering from prolonged droughts. Seeding cereals in the grazing land will not be achieved without rain. |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé