Humic acid application [Pays-Bas]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Jason Stuka
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Toepassing van humuszuur (Dutch)
technologies_1254 - Pays-Bas
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
Droevendaalsesteeg, 6708 PB Wageningen, Netherlands
Pays-Bas
Spécialiste GDT:
Rienks Willem
willem.rienks@rom3d.nl
Rom3D
Dorshorst 1, 7217 PH Harfsen, Netherlands
Pays-Bas
Spécialiste GDT:
Leever Henk
info@hoeduurzaam.nl
HOEDuurzaam
Pays-Bas
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
ROM3D - Pays-BasNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Hoe Duurzaam - Pays-BasNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - Pays-BasNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Provincie Gelderland - Pays-BasNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - Pays-Bas1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
20/03/2015
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Regional process, social innovation [Pays-Bas]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- Compilateur : Simone Verzandvoort
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Humic acid application is a technology that allows the farmer to supply organic matter to the soil, without supplying additional nitrogen and phosphorus.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The application of humic acids to the soil is a way to supply organic matter, without supplying additional nitrogen and phosphorus, which is disadvantageous for farmers under the current manure legislation, since this imposes a threshold for the entry of nitrogen and phosphorus.
Humic acids stimulate the binding of K, Mg, Na, Ca and trace elements to the soil complex, causing the soil to supply more nutrients to the plant roots. umic acids fix iron and calcium particles, preventing these to fix phosphorus. This enables the release of phosphorus for take up by plant roots.
Purpose of the Technology: Increasing grass yield and nutritional value of grass.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Solution is applied with a tractor sprayer approximately 33 metres apart. Only small strips are applied as this is a test by farmers. Strips are shifted and rotated each year. They spray with a density of 60 L/ha. Width of strip is only the width of the sprayer.
Natural / human environment: Humic acid is a by-product of the water company's treatment of drinking water.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Pays-Bas
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Gelderland
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
- Introduced by water company
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Ranching
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Prairies améliorées
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Decrease of soil organic matter content. Nutrient losses to ground water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area experience decreasing organic matter content in soils, soil moisture deficits and declining yields of grass and maize cultures.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 250Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Humic acid is applied on grassland fields in small strips. There are 344 ha of grasslands in the area spread amongst 44 farmers. Only 4 farmers applied this technology.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse

dégradation hydrique
- Hq: baisse de la qualité des eaux souterraines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing intensive grassland renewal)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (rotation with more corn and less grassland)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
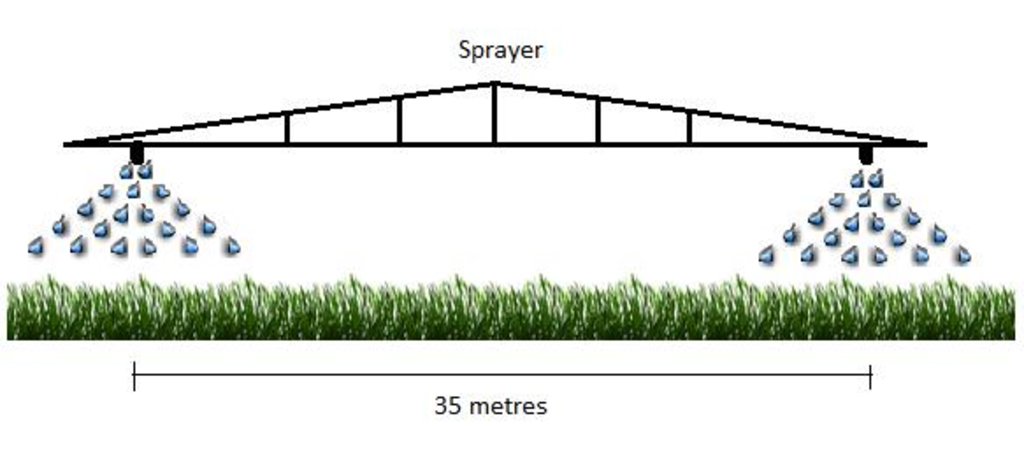
Sprayer on a tractor applies humic acid in short strips 35 metres appart.
Location: Wageningen. Gelderland
Date: March 20, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Quantity to apply is important.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Easy to apply.)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Humic acid
Quantity/ density: 60 L/ha
Remarks: strips 35 metres apart.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Euro
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
0,94
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
255.70
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Spray humic acid on grasslands | Agronomique | Once per year |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 36,17 | 36,17 | 50,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Humic acid | ha | 1,0 | 140,43 | 140,43 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 176,6 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor, sprayer.
March 20, 2015 - No new equiptment is needed for this technology.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Price of product - humic acid.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
182 days of precipitation annually.
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C (LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C)
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitidunal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm), deep (A and B horizons up to 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area). Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm depth. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm depth), shallow and very deep (deep topsoils rich in organic matter in the Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area))
Soil texture: Coarse/light (All sandy soils)
Soil fertility is medium
Topsoil organic matter (The purpose of the pilot project is to increase soil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep ground water. Sandy soils.) and medium (some shallow groundwater)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (Dependent on soil organic matter content)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (Contaminated. Requires treatment by water company (Vitens).)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm opersations are completed by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Market orientation is subsistence (Grazing and fodder for dairy cows)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
Average grassland is 7.8 ha per household.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
All agriculture land is owned by individual farmers. Some farmers lease their land to other farmers. There are some regulations on land uses set by communities.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Estimated. Not measured or proven.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Estimated. Not measured or proven.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Humic acids are provided by the company Triferto. In the future this will be on commercial basis.
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Created farmer's foundation
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmers understanding ecological impacts of farming practices, dairy farmers have learned more about soil health.
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmers collaborating with water company.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
qualité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Sols
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Expected. Not proven yet.
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
capacité tampon/de filtration
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas connu |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas connu |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Commentaires:
Slightly positive benefits are mentioned based on a test by Triferto (the company selling the humic acid) in 2014 in one cut of grassland. The yield was 8% higher and the grass contained higher concentrations of trace elements.
However, there is no evidence from farmers about improvement of their yields as a result of the application of humic cid. Increase in weight of grass production has not been measured and value has not been compared to application costs. The few farmers that are applying humic acid have only done so for two years and results are not measured yet. But farmers are subsidized for humic acid application until 2024.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
4
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It is too early to state this, since the technology is still in the test phase. Humic acid is applied on 29 ha of the 130 ha total surface on which measures to increase soil organic matter are applied in the pilot Gezond Zand. Results on the effects are only sparsely available, Farmers are being subsidized to apply the measure until 2024.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
The technology is likely to increase soil organic matter, to improve nutrient uptake by the crop and to improve the soil moisture retention capacity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Test the expected impacts in field implementations of the technology by farmers. Continue subsidy or payment for the humic acid until positive effects have been demonstrated. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
The technology is likely to increase soil organic matter, to improve nutrient uptake by the crop and to improve the soil moisture retention capacity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Test the expected impacts in field implementations of the technology by farmers. Continue subsidy or payment for the humic acid until positive effects have been demonstrated. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Farners are unlikely to pay for the application of humic acids until impacts are proven, but they know that the application of humic acid does no harm to their soils or crops, and ae therefore not reluctant to apply the humic acid as long as it is paid for by the subsidy arrangement or the drinking water company. | Continued financial support for applying the humic acid and proof of impact. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The drinking water company (supplier of the source material for the humic acid) and the company selling the humic acid raise big expectations about the technology, but thus far there is no scientifically based proof of impact on maize or grass yield. | Continued tests in real farm implementations. |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden Eibergen By Willem Rienks and Henk Leever 2014
Unravelling changes in soil fertility of agricultural land in The Netherlands Arjan Reijneveld 2013
RECARE_WP3 Report: CS_11_Ouden-Eibergen_v2 Annemieke Smit and Simone Verzandvoort 2014
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Free http://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdf
Wageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057
Free annemieke.smit@wur.nl
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Regional process, social innovation [Pays-Bas]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- Compilateur : Simone Verzandvoort
Modules
Aucun module trouvé