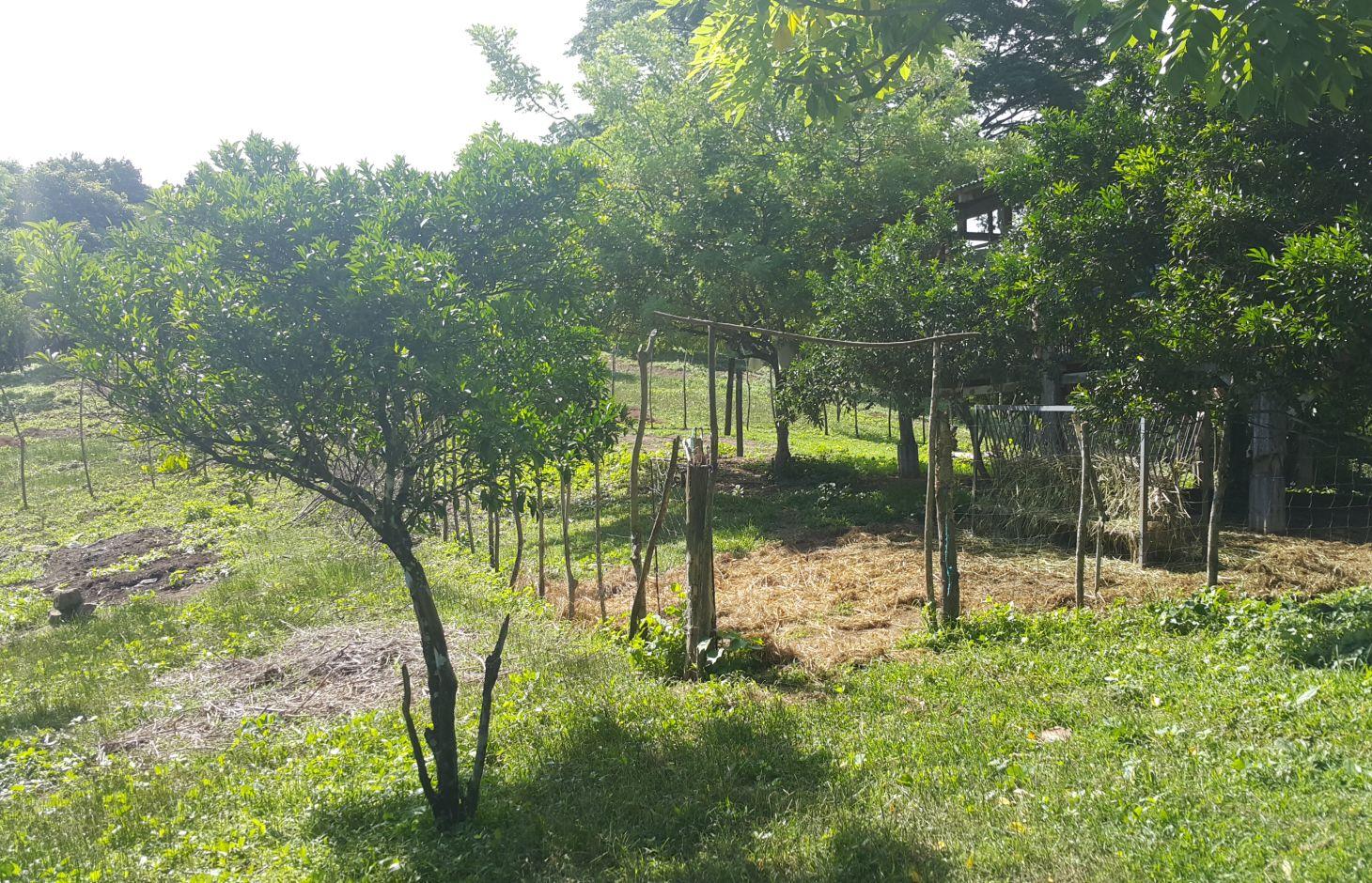
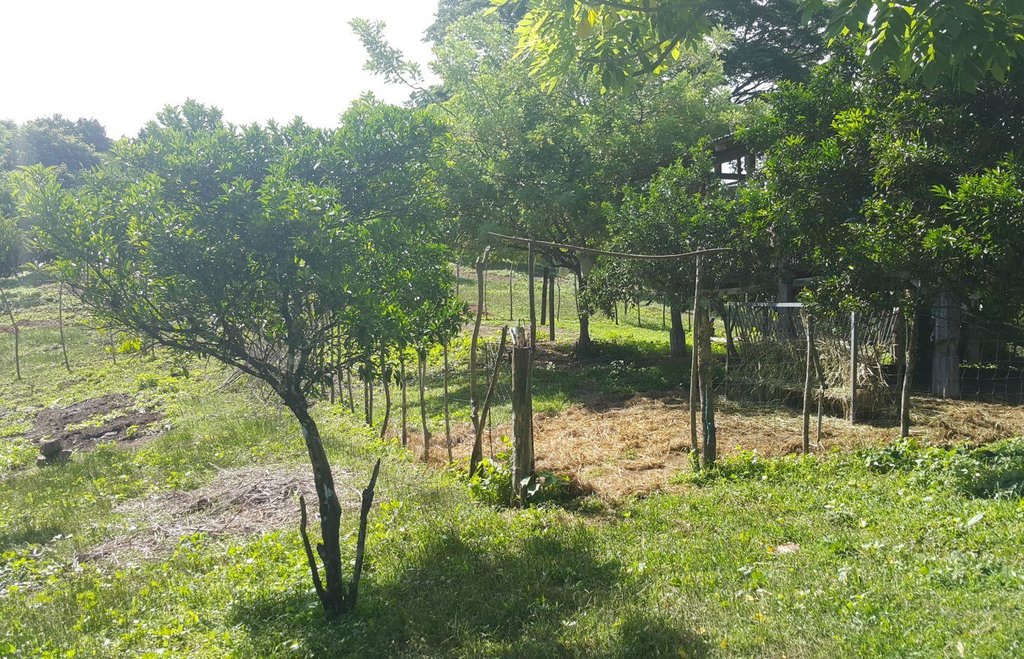
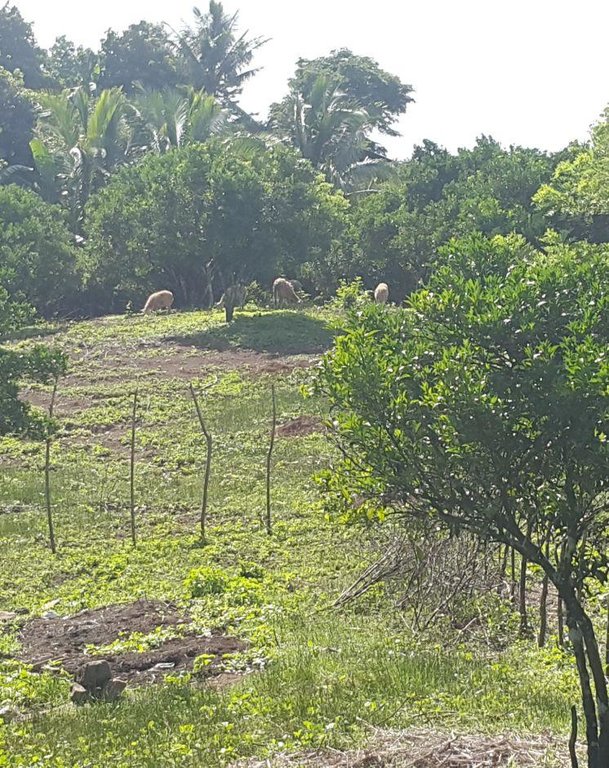
Improved pasture under citrus [Philippines]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Pastulan sa ilalim ng dalanghitaan (Filipino)
technologies_1321 - Philippines
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Rojales Jose
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Calonge Arsenio
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Millare Kirby
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Quinto Jasmin
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Gultiano Wilfredo
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Cornes Jennelyn Mae
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - Philippines1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
29/06/2016
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [Philippines]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
It is a farming system that integrates the growing of fodder crops under plantation crops.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
It is an integration of livestock and agronomic crop production of incorporating small ruminants in an existing citrus plantation. This technology was based on the private initiative of the farmer where he adapted it from other land users. He further improved it through study of reading materials and ad hoc monitoring of his environment.
Purpose of the Technology: After the adaption of the technology, the land user observed a decrease in the infestation of aphids. The land user observed and concluded that the decline in the aphids infestation was due to the presence of the small ruminants in the area. The small ruminants forage on grasses that were continuously growing, year-round, in the plantation area. The foraging of grasses improved the micro-environment of the plantation crop, which contributed to the decline and almost total eradication of aphids in the area, as observed by the land user. This promoted natural farming and improved the biodiversity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The area was first established as a citrus plantation inter-cropped with Vigna unguiculata, Cucurbita maxima, and Ipomoea batatas, as cash crop during the vegetative stage of the citrus crop. As the small ruminants increased in number, the land user decided to do “controlled grazing” by dividing the area into 3 paddocks. During lean days of forage grasses, the land user practices “cut-and-carry” system of feeding. In addition, the manure of the small ruminants serves as a source of organic fertilizer for the citrus and other crops grown by the land user.
Natural / human environment: Aside from the eradication of the aphids on the citrus crop, the technology aided in the financial needs of the land user. It increased the land user’s income by an increase in the fruits bore by the crop and the increase in the number of the small ruminants. The land user sells or sometimes suppliers of citrus fruit and goat meat would go to the area to do wholesale buying. As for the community near the area, they to benefit from the area, by wholesale buying the citrus fruit and be the one selling it to the market. The technology does not only contribute to the livelihood improvement of the land user but also to the community.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Philippines
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Bulacan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
City of San Jose Del Monte
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- experience from other farm land user
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
8 years
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop:
Citrus

Pâturages
- Silvo-pastoralism
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Goat and sheep grazing in combination
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Possibility of pollution in the area. The land user might have applied pesticide to the citrus crops to control the pest, but the land user did not mention of it. Application of herbicide to control the growth of grasses within and outside the area.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Without land conservation, there was an occurrence of pest in the citrus plants.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): silvo-pastoralism, goat and sheep grazing in combination
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: July to November
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée cultures-élevage
- lutte intégrée contre les ravageurs et les maladies (incluant l'agriculture biologique)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.08 m2.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

pratiques végétales
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bp: augmentation des insectes nuisibles (ravageurs)/ maladies, baisse des prédateurs
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intercropping planting), droughts (time frame of drought)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (grazing of small ruminants), overgrazing (no. of small ruminants), change in temperature (dry season time frame)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Third goal: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
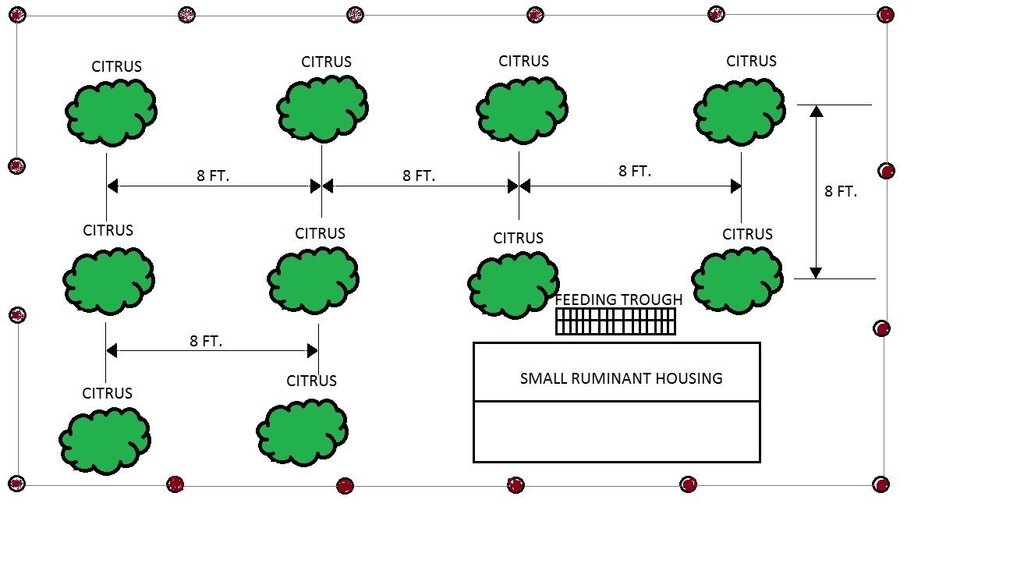
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Citrus plants are evenly distributed in the area, with a planting distance of 8 feet by 8 feet. The ground cover are forage grasses for the small ruminants.
Location: Barangay San Roque. San Jose Del Monte, Bulacan
Date: 06/29/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (technical assistance from agricultural advisory from other aspect in land degradation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land user is open minded with the technology introduced)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: pole sitao-squash-sweet potato/citrus
Agronomic measure: intercropping (1st Year)
Material/ species: pole sitao/citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (2nd year)
Material/ species: squash/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (3rd year)
Material/ species: sweet potato/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 8,800/188
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: goat manure
Quantity/ density: 5,000 kg
Remarks: .5 per square meter
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Philippine Peso
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
47,5
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.26
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | rotational grazing | Végétale | rainy season |
| 2. | cut-and-carry feeding system | Végétale | dry season |
| 3. | Buying pole sitao | Agronomique | |
| 4. | Buying sqaush | Agronomique | |
| 5. | Buying citrus | Agronomique |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 3160,0 | 3160,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 48,0 | 48,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Hog wire | ha | 1,0 | 397,89 | 397,89 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 3616,41 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
Life span of products:
Pole Sitao - 1 year
Squash - 1 year
Citrus - 50 years
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 10,52 | |||||
Commentaires:
The above costs usually occurs during the dry season when forage grasses are scarce. Lean months of availability of forages grasses are from the months April to June. This is the time the cut-and-carry method is applied and the start of the maintenance/recurrent cost.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Cut-and-carry method of feeding the small ruminants during lean months of forage grasses.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
2382,00
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Ridges (concave)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is: Good
Soil water storage is: High
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: It is the countries socio-cultural model, where men is the one working and the women stay at home. According to the land user it is the women who is record keeper.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income provides additional income to the land user during the dry season.
Market orientation: Subsistence (small ruminants are bought by the land user)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
3,000 kilograms
Quantité après la GDT:
8,000 kilograms
production animale
Quantité avant la GDT:
5
Quantité après la GDT:
5
diversité des produits
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
30,000
Quantité après la GDT:
80,000
diversité des sources de revenus
charge de travail
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It gave an opportunity to the neighbors of the land user to work at the field, with pay. Thus, an added income to the neighbor of the land user. According to the land user, he was able to send his children to a decent school for a quality education. It also gave the land user another source of income by purchasing a jeepney used as a public transportation through the increased income from the SLM technogy he adapted.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The increased in the income of the land user contributes to the food security of the family
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Daily chores of herding the small ruminants contributes to the good over health of the land user
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and-carry" style of feeding contributed to the possible overgrazing which is contributor to erosion
apaisement des conflits
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land user allows the member of his community to harvest some fruits and sell them to the market without the land user asking for something in return.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and carry" style of feeding contributes to the reduction in surface runoff, grasses are maintained on the soil surface
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduced soil in any form
encroûtement/ battance du sol
compaction du sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to nutrient recycling
salinité
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to the increased in soil organic matter content
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
espèces étrangères envahissantes
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further reduced alien species invasion
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further increased biological pest/disease control
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
risques d'incendies
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface improves soil tilth which further improves infiltration capacity
capacité tampon/de filtration
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Manure of the small ruminants improves the soil tilth, an improved soil tilth improves the buffering/filtering capacity of the soil
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduces erosion due to wind
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas connu |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Decreased in occurrence of pest |
| Increased land user's income |
| Helped the land user's neighbor by profit sharing during harvest of the citrus fruits |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Less labor input How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the varietal species of the forage grass |
|
Decreased in occurrence of pest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the existing micro environment |
| Rotational grazing |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| There was an inbreeding of the small ruminants | Putting another small ruminants of good genetic quality |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Variety of forage grass is of low quality in terms of crude protein content | Planting of improved variety with a high crude protein content |
| Species of small ruminants are not of good genetic quality in terms of meat quality | Putting of species with a good genetic quality in terms of meat produce |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [Philippines]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Modules
Aucun module trouvé