Combating of invader plants and bush packing [Afrique du Sud]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
technologies_1373 - Afrique du Sud
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Meyer Schalk
011 355 12 46
Gauteng Department of Agriculture
Afrique du Sud
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Gauteng Department of Agriculture and Rural Develo (Gauteng Department of Agriculture and Rural Develo) - Afrique du Sud1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
04/08/1999
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT
Awareness raising [Afrique du Sud]
To make the people aware of veld degradation, rehabilitation & the participation of the people
- Compilateur : Belly Mpoko Malatji

Technical and scientific support & Job creation in … [Afrique du Sud]
To make the community aware of precious resources like water and the preservation of it, the control of alien encroachment, creation of job opportunities and the training of the undeveloped communities.
- Compilateur : Philippe Zahner
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
The combating of Invaders to preserve water resources & the rehabilitation of the bare ground by means of brush packing to prevent soil erosion.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
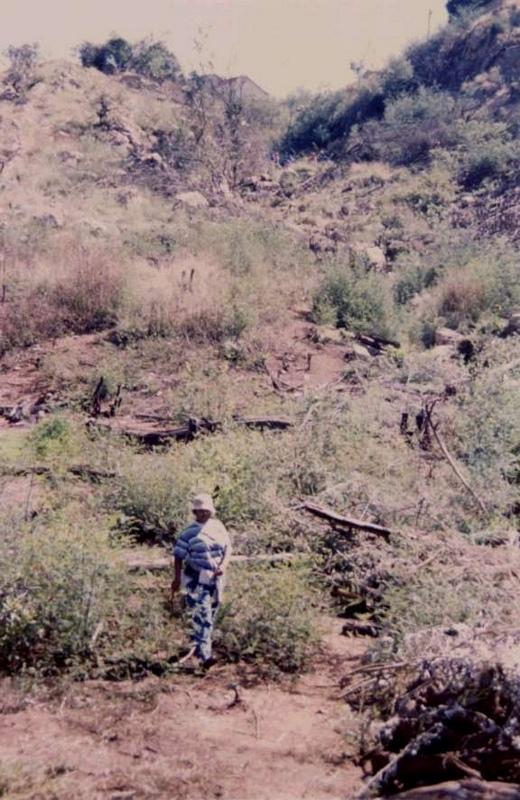
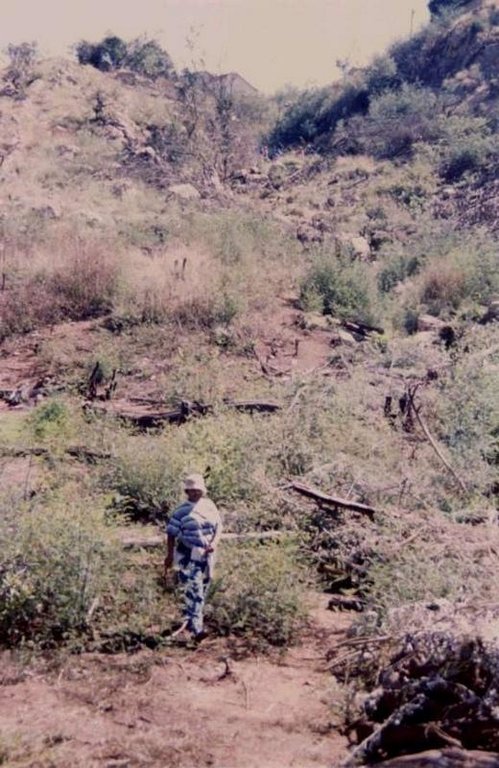
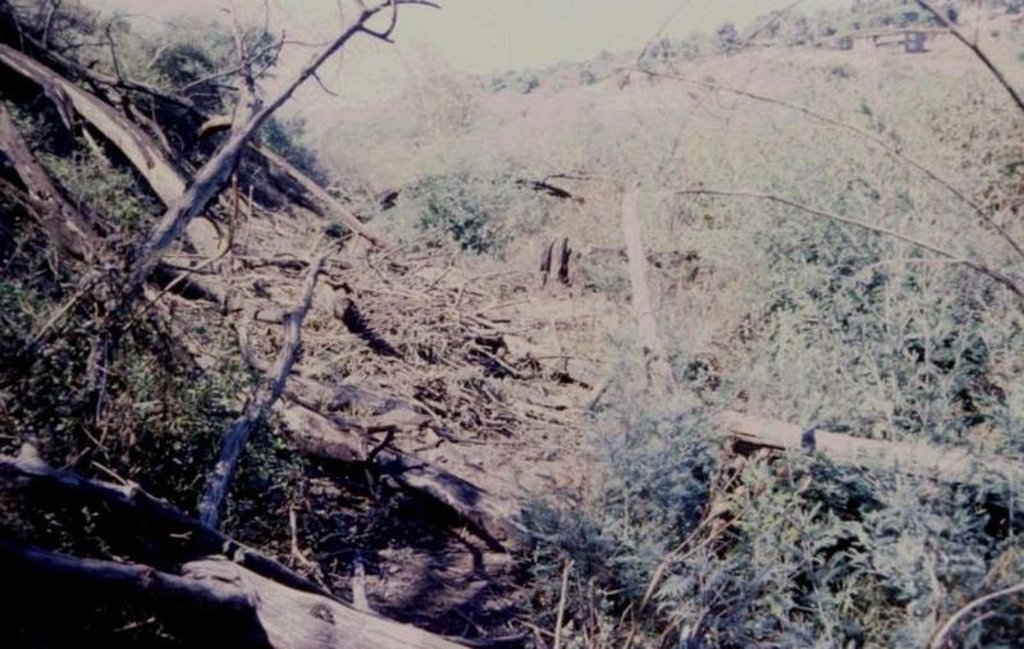
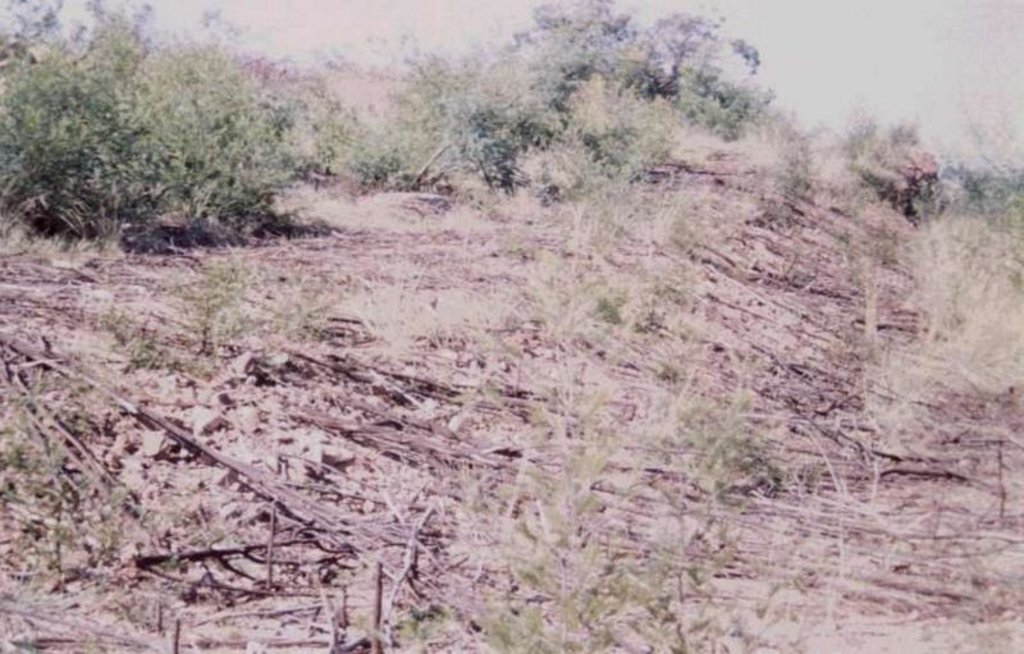
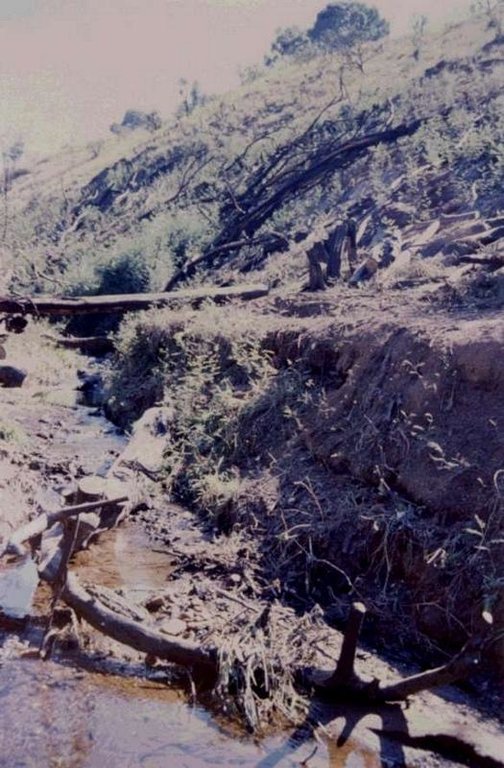
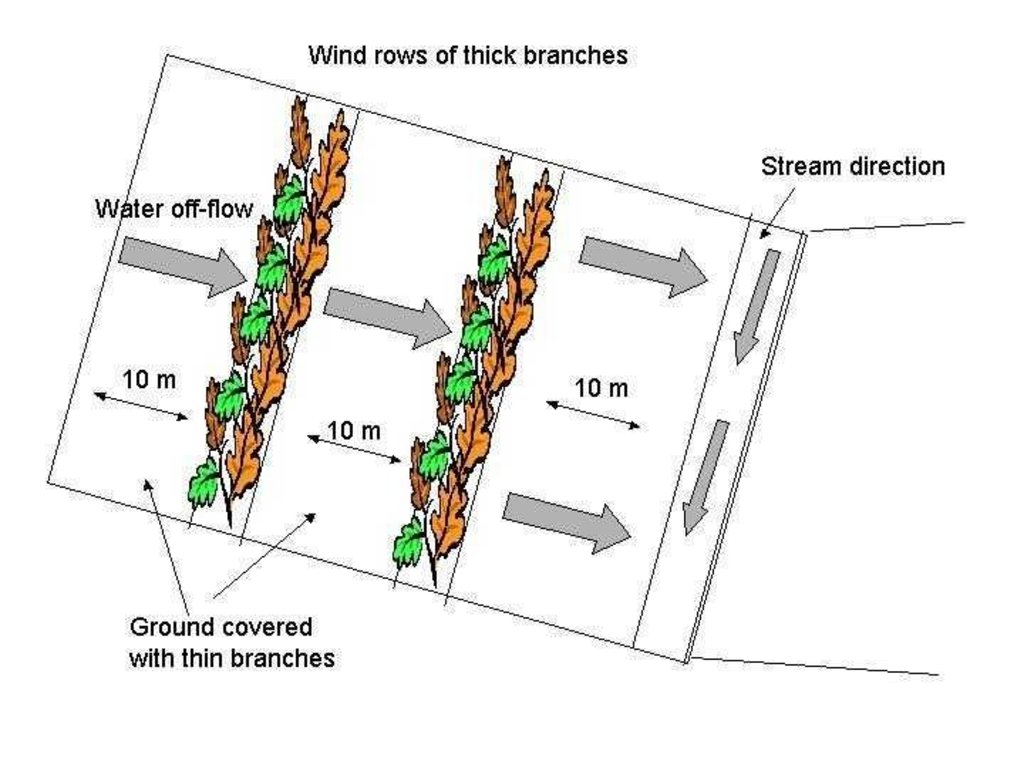
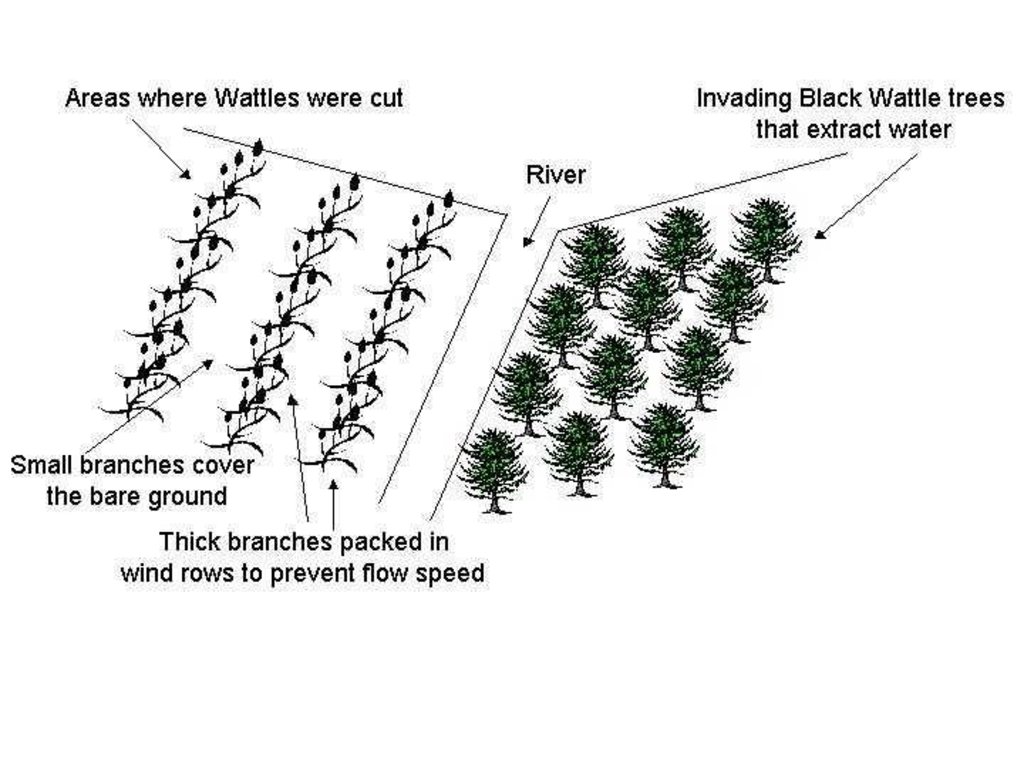
The technology is applied in areas under the 'Working for Water' projects that are run by the National Department of Water Affairs in South Africa, in the fight to combat invaders exhausting our valuable water resources. Catchment areas are fields that are infected by invader species on riverbanks, and catchment areas that extract enormous amounts of water out of the system. The trees (Black wattle - Acacia meansii) are cut or ring barked. After the trees are felled, large areas of bare ground are exposed. In order to prevent soil erosion until the natural succession processes are completed and the area is in equilibrium with the rest of the environment, soil needs to be stabilised and sometimes also rehabilitated.
These exposed areas must first be treated with a follow-up to prevent the coppice, re-growth and seedlings from growing again. Sometimes in agricultural grazing areas, the bare areas are re-seeded with natural climax grasses, and in urban areas left to be stabilised by successional species, or pioneers and aveads etc. The small branches of the felled trees are packed on bare areas, after the re-seeding to stop the topsoil from eroding. This reduces the off-flow and flow speed of the rainwater, lowering the raindrop impact, increasing the moist regime and preventing wind erosion. The thick stumps are either used for firewood or for the charcoal industry, as well as packed in windrows horizontal with stream flow.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Afrique du Sud
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Gauteng
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Gauteng
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology was experimented by the University of Potchefstroom and also applied at other typical Working for Water projects in the country and technical advise by experts of Water Affairs.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Ranching
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Not many cattle, people still poor - average
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Tremendous bush encroachment by wattle species or other similar invaders like blue gum trees, the area has no further land use after the bush encroachment.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The problem is similar, no land use in encroached areas, the trees are to close and no grasses grow underneath for cattle to feed on, and the bush provided shelter for criminal activities.
Constraints of settlement / urban: Preventing of fires in the dry trees
Constraints of recreation: Preventing of fires in dry trees/area
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 210; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2 km2.
2 Sites at Krugersdorp, one along a public rood where no development is done yet & the second at Kenmeare Kloof that divided two residential areas. Elandsfontein is bits & pieces that scatters over several farms.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V4: Remplacement ou suppression des espèces étrangères envahissantes

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
Commentaires:
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Clearing of alien plants
Working for Water
Gauteng
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: No grazing for first 3 years after reseeding
Control / change of species composition: Follow-up - eradication and control of regrowth
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rand
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
6,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.00
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting of trees | Modes de gestion | Summer |
| 2. | Packing of branches | Modes de gestion | Before winter (wind) & spring (rain) |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Cutting of trees and packing branches | persons/day/ha | 500,0 | 30,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | tools | ha | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 125000,0 | 125000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 140500,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Where reseeding took place the grazing must be maintained | Modes de gestion | 3 years after planting / 3 years |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
The total implementation of the technique: Costs of chemicals & tools, labour for the whole project, the cutting of the regrowth and the treatment of it (follow-up) and the packing of the branches.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour: The work team of 25 people is very expensive/costly. Chemicals for the invader eradication treatment is very expensive.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
600,00
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: Also rolling
Landforms: Hill slopes at Krugersdorp
Altitudinal zone: 1542 m a.s.l.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average : Very shallow at hillside at Krugersdorp more predominantly and shallow at more farm soils at the plains of Elandsfontein.
Soil fertility is medium in plains and low in hillsides
Topsoil organic matter: Not very fertile, no grasses to enhanced biomass
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium for the soil of plains of Elandfontein (not so compacted - better drainage) and poor for Krugersdorp (hillside highly compacted)
Soil water storage capacity is medium for Elandsfontein (less compacted) and low for Krugersdorp (more compacted)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (Elandsfontein, upcoming farmer).
60% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land (Communities that is not fully commercialized).
Off-farm income specification: Family members are working in the city, to provide for the family (the children and brothers etc.)
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence (self-supply) for Elandsfontein: workers that are living on the farm
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Where reseeding was done the bare soil will be replaced with grasses
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Where reseeding was done the bare soil will be replaced with grasses
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better grazing for cattle and selling of fire wood
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Selling of wood for fire wood & charcoal to charcoal industry
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Training and job creation
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better technologies and experience
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
90
Quantité après la GDT:
30
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
Autres impacts écologiques
soil fertility
biodiversity
conserve water resource while reducing invader bush
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No Wattle's to extract water, reduced runoff
envasement en aval
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Soil is stabilized
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Elandsfontein: prevent soil loss How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve farm soils - control overgrazing |
|
Elandsfontein: Improve grazing capacity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Rotational grazing and rest for first 3 years after rehabilitation |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Prevent soil loss How can they be sustained / enhanced? Packing of branches correctly and maintained - preventing of veld fires (wood from burning) |
|
Reseeding of perennial grasses that enhanced grazing capacity and biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Correct seed mix & seeding method; preventing from grazing and veld fires |
|
Conserve water resource How can they be sustained / enhanced? Eradication and control of invaders |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive | No recommendations |
| Time consuming | No recommendations |
| Expensive | No recommendations |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Business plan and work reports from government officers / officials & NGO's like universities
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Gauteng Department of Agriculture
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
NGO's and Universities
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Gauteng Department of Agriculture
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Awareness raising [Afrique du Sud]
To make the people aware of veld degradation, rehabilitation & the participation of the people
- Compilateur : Belly Mpoko Malatji

Technical and scientific support & Job creation in … [Afrique du Sud]
To make the community aware of precious resources like water and the preservation of it, the control of alien encroachment, creation of job opportunities and the training of the undeveloped communities.
- Compilateur : Philippe Zahner
Modules
Aucun module trouvé