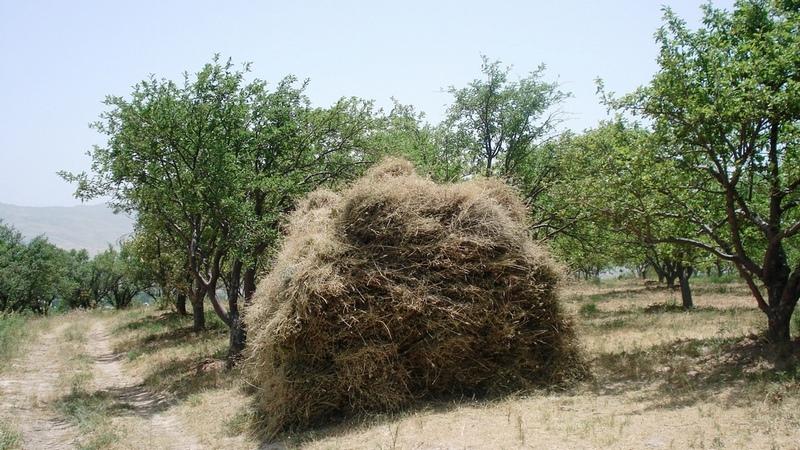
Combined cut-and-carry and fruit-production system with terraces [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Зина бох (tajik for terrace garden)
technologies_1406 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirghizistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
01/08/2008
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [Tadjikistan]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
A combination of fruit- and nut-trees together with seminatural trees and shrubs on one side with grass-communities on the other side provide for a diversified production system.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Fruit- and nut-trees give the production system the characteristics of an orchard, whereas sour cherry trees rather provide for a jungle atmosphere. They spread very quickly once they are planted. Hayproduction substitutes other uses of the lowest vegetation layer, since grazing is forbidden. The whole territory is concipied as a research station.
Purpose of the Technology: In general trees act against erosion: By their stabilising function they prevent soil from being washed out. Especially nut-trees with their 20 to 25 m long roots preserve soil moisture and by that consolidate soil structure. Terraces contribute to this moisture-preserving and production-enhancing function. They are very important in order to make rather steep land exploitable by reducing slope. Haymaking does not damage soils, but is only allowed after the end of June so that grasses can reproduce before.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Both the establishment of terraces and the planting of trees on such a big surface are costly in terms of labour and money. Maintenance means taking care of trees, taking measures against diseases and conserving soil fertility. Fertilisers are very costly and therefore dung has been substituting them in the last years.
Natural / human environment: From the two research stations of the orchard institute - one in the upper hill-zone and one close to the village Karsang - only the second one is assessed. This area is surrounded by two rivers in the West and in the East, with its main exposition to the South. It is in direct competition for irrigation water, especially needed for the trees, with the village. The orchard is situated on a ridge that is in the haymaking area, but is accessible for animals from the village.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Region of Republican Subordination
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
1961 the national orchard institute began with developing a research area in Karsang, which should be further enlarged from 1975 onward.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Access for livestock forbidden.
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problems are arid conditions and the loss of fertility, mainly by processes of water erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gully erosion by water and wind erosion together with droughts are the main problems. Gullly erosion may also be caused by
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Access for livestock forbidden.
Grazingland comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
Type of grazing system comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: post-flooding
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 270 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jul
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
< 1 LU/km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 m2.
Of the 70 hectares nearly half of the surface can be considered as unproductive with protective functions against erosion (many sour cherry trees planted).
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S1: Terrasses

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: scellage et encroûtement
- Pi: imperméabilisation des sols

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (According to agronomist and elderly persons steady decrease of rainfall Causing aridification..), droughts (No considerable precipitation for one and a half years. Causing compaction, crusting and aridification.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (The lack of fertilisers and other inputs is a consequence of the breakdown of URSS.)
Secondary causes of degradation: floods (Causing gully erosion and loss of topsoil by water.), war and conflicts (Many trees were chopped illegally during war to have energy (charcoal mines were occupied by armed men)), Unsuitable soils especially in the upper part (loe (Causing compaction, crusting and loss of topsoil by wind.), Steep topography with high sun inclination angle (Causing compaction.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
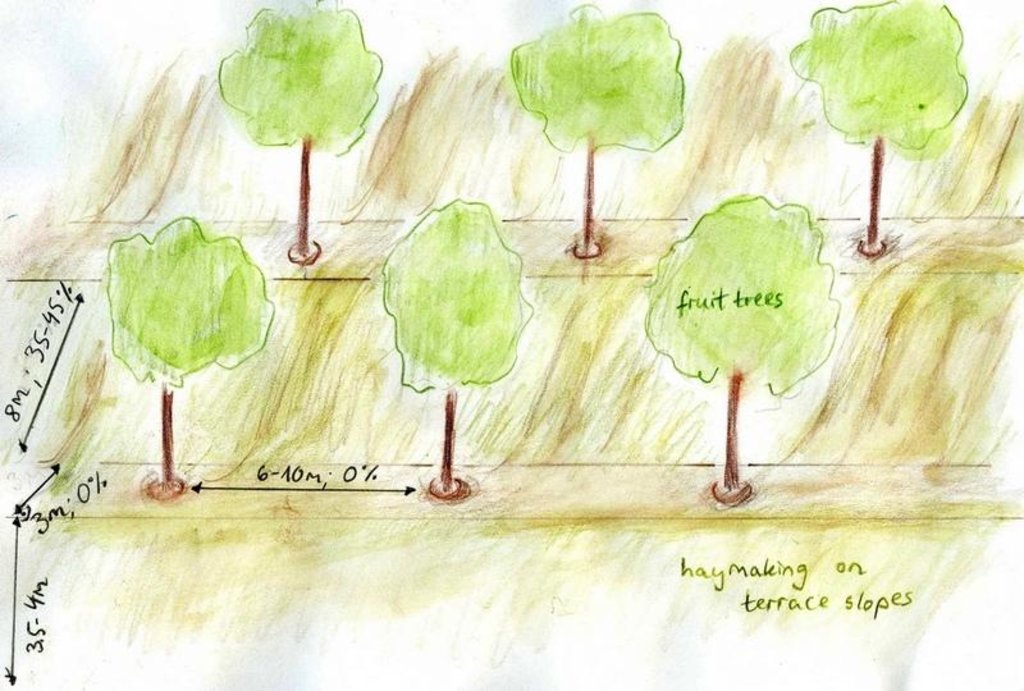
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Terraces with fruit trees.
Location: Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 25.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Cutting trees and maintaining tree nurseries)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Fieldwork such as haymaking)
Technical knowledge required for Research coordinator: high (Carrying out of workshops)
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, trees protect from snow
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 120
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Trees/ shrubs species: Apple, apricot, almond, walnut, quince, pear, peach trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Sour cherries, mostly through vegetative growth
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Terrace: bench level (earth)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 11
Construction material (earth): endogenous material used
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 33-45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Strictly regulated haymaking, only after the end of June.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.70
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of trees with provenance from Russia and Ukraine | Végétale | Tree plants |
| 2. | Tree-planting, grafting, giving dung | Végétale | 20 persons for 3 years |
| 3. | Terrace establishment | Structurel | 2 tractor drivers for 1 year |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Tree planting | ha | 1,0 | 714,0 | 714,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Autre | Terrace establishment | ha | 1,0 | 614,0 | 614,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1428,0 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
research stations of the orchard institute
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Yearly replacement of fruit-trees (10-15% per year) | Végétale | 10 persons plus brigadier, always employed |
| 2. | Aerating soils around trees, each spring | Végétale | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 3. | Applying animal dung and / or fertilisers | Végétale | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 4. | Seasonal workers for harvesting | Végétale | 10 workers, additionally |
| 5. | Planning of activities | Végétale | 1 director |
| 6. | Haymaking | Modes de gestion | 1 month |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Maintenance | ha | 1,0 | 93,0 | 93,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 28,0 | 28,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 121,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The data on the establishment of the orchard are an estimation of the director. The recurrent costs are based on the director's and other person's declarations and are rather a rough estimation than a precise list of the costs.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The costs today are strongly determinated by labour input, whereas during establishment and till the end of USSR costs for pesticides, fertilisers, new trees and equipment were very high.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
In the long-term average, 600-650 l, but in the years 2007 / 2008 only 200 l, since no rains in autumn.
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zonation: The orchard is located between 1300-1500 m.
Landforms ridges: A part of the area surrounds a ridge
Landforms hill slopes: Generally slopes are of moderate steepness.
Slopes on average gentle: The terraces themselves are quite flat.
Slopes on average hilly: A great share of the area are slopes, either natural ones or from terraces.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average shallow: In the higher part stony soils prevail.
Soil fertility low: When gypsum and loess soils.
Soil fertility medium: In the lower part soils with little humus.
Soil drainage / infiltration good: 3-4 m infiltration capacity.
Soil water storage capacity medium: Thanks to trees not low.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: Insufficient: only permitting to irrigate 5 ha of totally 30 ha classified as "irrigated cropland"
Water quality (untreated): According to expert, water contains iodine, but is otherwise "light" and clean, without calcium carbonate
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Typical plants of the foothills can be found in the area.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (all smallholders owning additional income by the work for the institute).
Off-farm income specification: Nearly all people have family members (mostly sons) in Russia, who send remittances.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
The employees produce hay on maximally 7 ha.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
Whereas land use rights are restricted to those employed by the research institute, water use is negotiated between the research institute and the village authorities.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The reason is the decision not to plant wheat anymore, partly because of droughts and partly because of the trees having reached a critical height (shadow).
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Animals eating this fodder give more milk.
production de bois
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
On the neighbour-ridge no irrigation water.
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Trees require more water than simple pastures, especially in the establishment period.
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Especially fruit production is important, to make jams, dried fruits etc. for winter.
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The milk is of better quality and leads to less sicknesses
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The institue is in conflict with the village for irrigation water.
Open-access pasture-area
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No strong effect, because it is a research territory.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Is especially a function of cover and infiltration capacity
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Plants are greener and less dusty thanks to moisture
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Plants are taller, wider and denser.
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Thanks to strongly reduced erosion, organic matter is conserved
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less crusting than without technology, but more than without droughts.
salinité
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to lacking drainage system
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More nutrients given, for example by the trees' leaves.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More than 50 pasture species
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Forest administration considers the proportion of trees to be one of the decisive factors of fire-risk.
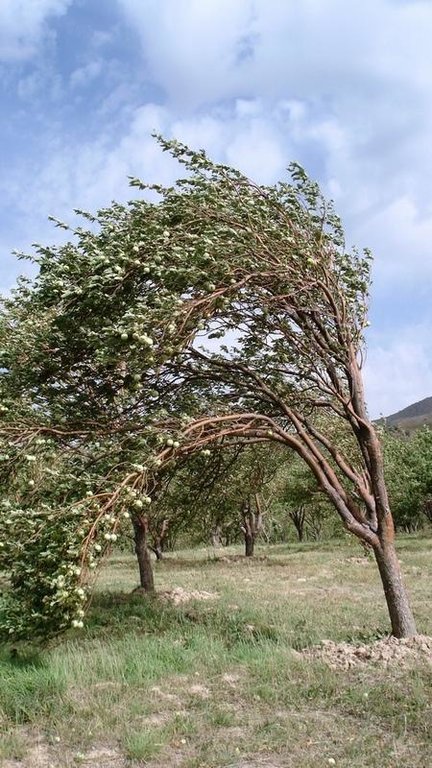
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
High proportion of trees leads to longer snow cover and thus soil protection in spring
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
Commentaires:
No damages by heavy rainfall in the orchard, whereas next to it there is damage. Especially winds cause damages by covering vegetation with dust and impeding them from making fotothynthesis. Plants can die therefore.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government wants more people to adopt the technology and their has effectively been an increase of such initiatives over the last years.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [Tadjikistan]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
Modules
Aucun module trouvé