Application of water by drip irrigation [Grèce]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Costas Kosmas
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
Αρδευση με σταγονες
technologies_1456 - Grèce
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Bardoulaki-Spanoudaki G
Organization for the Development of Western Crete OADYK Agia, Chania
Laboratory of Hydrogeochemical Engineering and Remediation of Soil Department of Environmental Engineering Technical University of Crete 73100, Chania, Crete, Greece
Grèce
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - GrèceNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Organization for the Development of Western Crete (OADYK) - Grèce1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
07/02/2011
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Sustainable use of water [Grèce]
Sustainable use of water
- Compilateur : Costas Kosmas
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
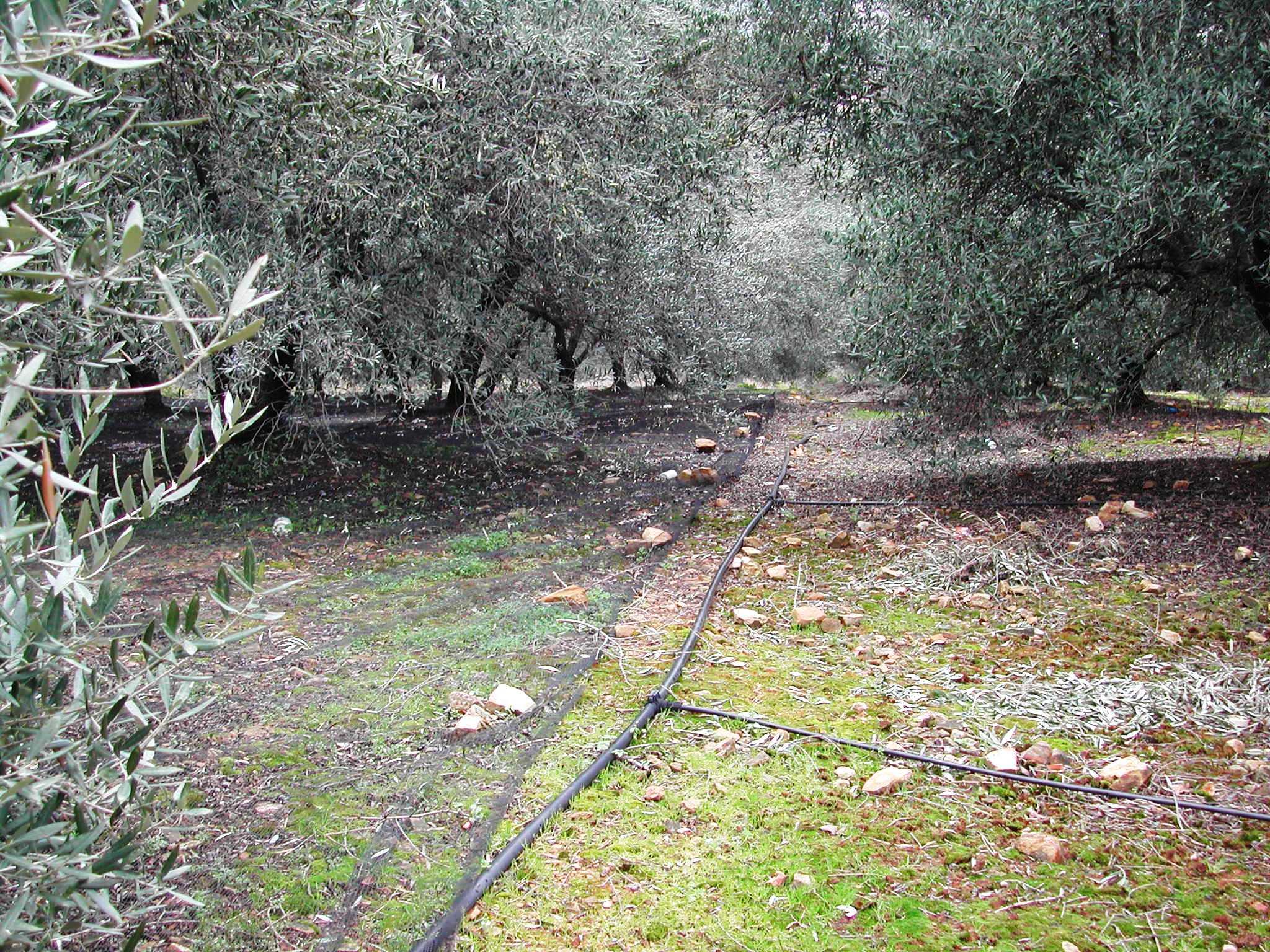
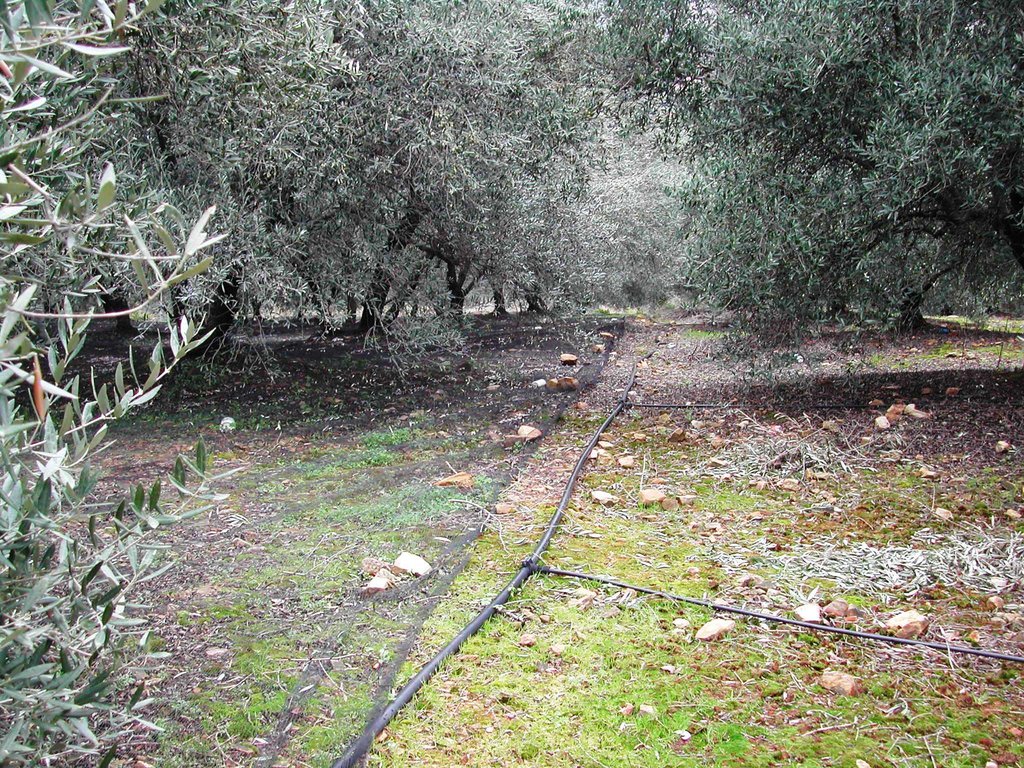
Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation is a method which minimizes the use of water and fertilizer by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either onto the soil surface or directly onto the root zone, through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Irrigation is very important for increasing crop yields in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid climates. The area of irrigated land has increased more than twice in the last decades in the study areas. In recent years, the considerable reduction of winter and autumn rainfall has caused a serious lack of water resources. The production of the various crops is substantially reduced if water is not provided during the summer period.
The high demands for water consumption or other economic activities have increased the price of water, forcing up the cost of agricultural production. In addition, in many cases, low quality (with high electrical conductivity) water is used for irrigation. The need for intensification of agriculture to meet the high cost of production, the use of poor quality of water, the lack of drainage systems are in many cases responsible for soil degradation resulting from water logging, salinization, alkalinization, and soil erosion.
Purpose of the Technology: Drip or trickle irrigation achieves the highest irrigation efficiency since about 90% of the applied water is available to the plants. This SWC technology is especially suitable for watering trees or other large plants keeping strips among trees dry. Application of water by drip irrigation can be considered more as more efficient method using low quality of irrigation water. Irrigation water of high salt content can be applied in higher quantities in spots leaching salts to deeper soil layers. Drip irrigation can be applied in any type of soil from coarse- and fine-textured and without any limitation to slope gradient requiring little labour during installation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In the study area of Chania trickle irrigation system includes mainly three branches from the outlet of main water network transportation system to the application in the trees. The last branch consists of plastic tube 12 to 32 mm in diameter that lies either on or just below the soil surface and applies the water either through small holes in the line or through emitter nozzle
Natural / human environment: In recent years the increasing awareness of farmers on issues relating to the sustainability of the environment and conservation of water by promoting SWC technologies has led to widespread of use of drip irrigation in the area of Crete and in many other parts of the Country. The categorization of the specific SWC technology according to the WOCAT questionnaire is defined as: CtWtA3.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Grèce
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Kidonia
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Chania Crete
Map
×2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Major cash crop: Olives
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): availability of irrigation water, loss of water in the network, conflicts between districts and economic sectors of tourism and agriculure
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): availability of irrigation water, conflicts between districts and economic sectors of tourism and agriculure
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 150Second longest growing period from month to month: March to June
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 480 m2.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol

structures physiques
- S11: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (lack of water), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (salinization)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
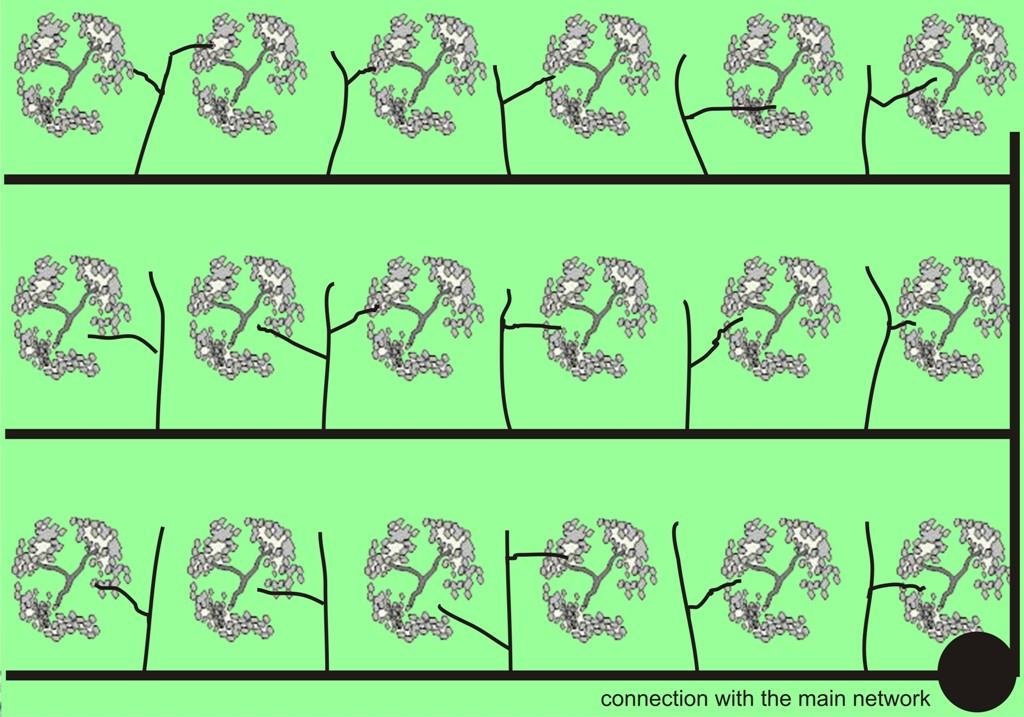
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
In the study area of Chania trickle irrigation system includes mainly three branches from the outlet of main water network transportation system to the application in the trees. The last branch consists of plastic tube 12 to 32 mm in diameter that lies either on or just below the soil surface and applies the water either through small holes in the line or through emitter nozzles.
Location: Kasteli. Chania
Date: March 2007
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (system installation requirements)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
In blocks
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 250
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Perennial crops species: olives
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 15.00%
Structural measure: irrigation system
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Construction material (other): plastic, plastic tubes 12-32 mm in diameter
Other type of management: Water distribution among farmers, water is provided under the control of local authorities
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting the olive trees | Végétale | 2 days/ha |
| 2. | transporting plastic tubes | Structurel | once during installation |
| 3. | Whole system of tubes, filters and system of fertilizers application | Structurel | once during installation |
| 4. | Main network of irrigation system | Modes de gestion | once per year |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | >Installation | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 1650,0 | 1650,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2000,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.1 month(s)
Life span of the irrigation network: 20 years
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | cleaning filters and replacing destroyied tubes | Agronomique | 3 hours every year/ha |
| 2. | Checking outlets and conectors | Structurel | once per year |
| 3. | Control of network for loss of irrigation water | Modes de gestion | once per year |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 60,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: hand tools, System of applying fertilizers through the irrigation water, filters for keeping various solid materials
per hectare of land affected
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
the reguired materials (tubes, filters, etc)
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
With six months of dry period
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is very high-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high-very high
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: 5-50 m, > 50 m
Water quality (untreated): good drinking water, for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women in rural areas are involved in other type of work
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are rich (cost for buying materials).
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: working in tourist business
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
1500 kg/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
2000 kg/ha
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cultivation of the land is hindered by the irrigation network
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
4500 euro/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
5800 euro/ha
charge de travail
Impacts socioculturels
opportunités culturelles
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Significant environmental benefit from the rational use of irrigation water
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
salinité
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Autres impacts écologiques
Waste
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
enviromental pollution due to presence of plastics not easely recycled
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Commentaires:
Control of flooding by adjusting river bed
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
3850
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 10-50%
Commentaires:
65% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1650 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Increase crop production in some cases up to 50% How can they be sustained / enhanced? providing more water |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Technologies on conserving soil and water resources and combating desertification in Crete are mainly related to land management. Olive groves are widely expanded in the island due to the importance of olive oil as one of the essential material for daily human food needs. Furthermore, olive groves can survive under adverse climatic and soil conditions supporting a significant farmer’s income under relatively low labour. Land management practices have been adopted in the area based on tradition and transfer knowledge by the local institutes and specialists. In addition, irrigation of the land by the drip system is considered as a very promising technique for conserving water resources in the area. Land terracing is a human intervention in sloping semi-natural landscapes, which have suffered losses, to some degree, in their sustainability and resilience. How can they be sustained / enhanced? by providing additional water resources in the area (build a water reservoir) |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High cost for buying materials, better education | subsidizing materials, technology transfer |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| increased cost for the first installation | subsidizing the system |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Sustainable use of water [Grèce]
Sustainable use of water
- Compilateur : Costas Kosmas
Modules
Aucun module trouvé