Sunken gully pits [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : SATYANARAYANA SAHU
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
khancha, Dhuda
technologies_1479 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Nayak Pradeep Kumar
Nuapada, Orissa, India
Inde
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/10/2006
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Participatory Watershed Development Approach [Inde]
Livelihood asset base development through participatory watershed developemnt keeping people at the center stage of development and promoting village level institutions.
- Compilateur : Narendra Kumar Panigrahi
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
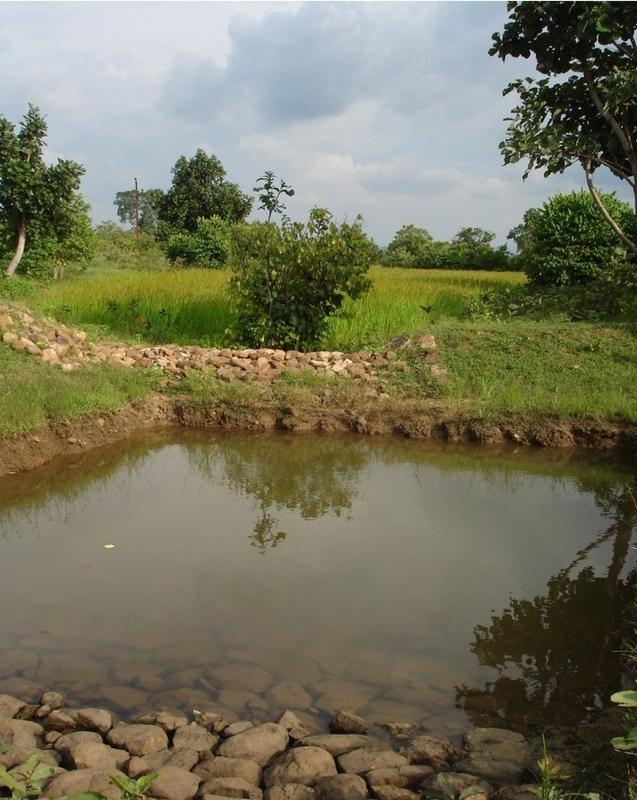
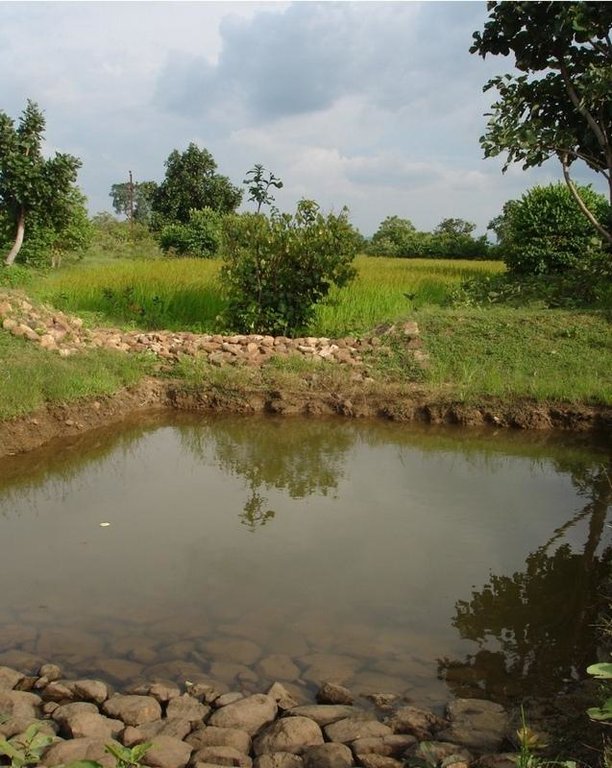
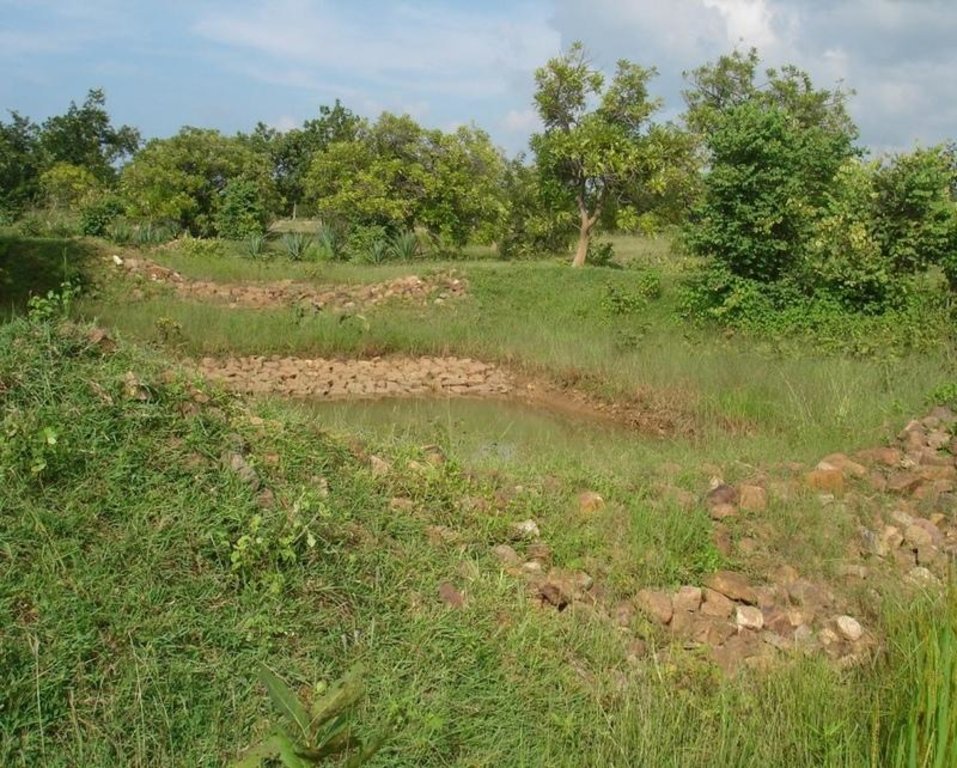
Runoff management pit in the gully with provision of waterway for excess runoff water.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Adopted in 4-8% sloped gully at an interval varying from 20 M to 30 M . Pits are dug on the upsteam of the bund with graded slope or the upsteam of the pits. Also having provision of safe water disposal. Purpose: 1. Reduction in flow velocity 2. Withheld and impound the flow water 3. Ground water recharge 4. Increase in soil moisture regime 5. For supplemental irrigation by the middle and lower reach structure. Establishment/maintenance: Turfing, Placing in position of displaced boulder. Excavation of deposited earth from the pit. Environment: User friendly, Low maintenance, Promotes vegetation,Eco-friendly
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
ORISSA
Autres spécifications du lieu:
ORISSA/NUAPADA/MAHANADI/CHAKAPADA
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
ANDHRA PRADESH By Hanumant Rao based upon Four- Water concept.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Mixte (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres), incluant l'agroforesterie
- Sylvo-pastoralisme
Principaux produits/ services:
Shrubs, trees and fodder cultivation. Also: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection, recreation / tourism
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Formation and development of gully in course of time.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Problem of sand casting in crop land and graduallly coverted into unproductive lands.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Animals reside in the Watershed area
Grazingland comments: Trend increasing towards livestock production. Trend to have stall feeding. Trend to produce better and improved quality fodder.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Other type of forest: Natural forest
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Management and protection of existing forest and species are increasing by providing watch and ward by the Watershed members through Vana Surakhya Samiti(Forest Protection Committee)
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 75 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Jan
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- gestion des eaux souterraines
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.4 m2.
Technology adopted following T.Hanumanth Rao's four- Water concept.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
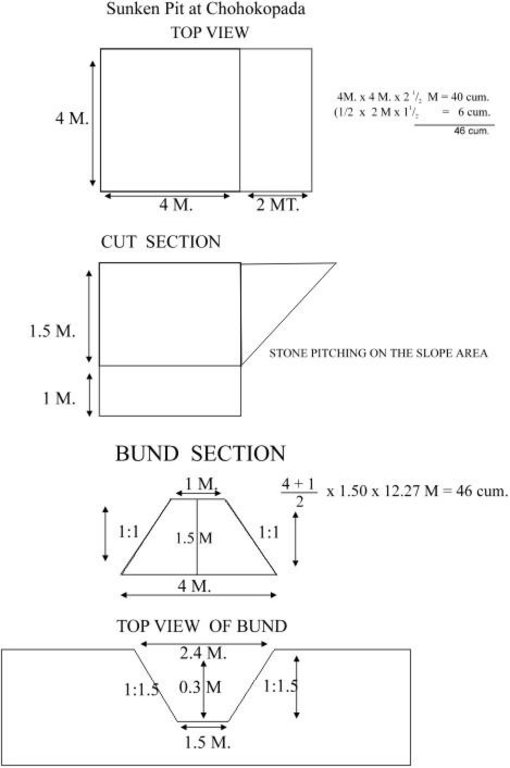
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Sunken pit technical drawing
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase in soil fertility
Vegetative measure: Turf on bund
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Local grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Structural measure: Sunken gully pit
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Construction material (earth): Excavated earth over 4.5 cum is utilised for construction of down stream bund
Construction material (stone): 1.08 cum of stone is used in upstream pit slope
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rupees
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
50,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.00
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Local grass collection | Végétale | Onset of monsoon(Jun-july) |
| 2. | Putting the turf on the bund | Végétale | Onset of monsoon(Jun-july) |
| 3. | Establishment of grass | Végétale | During monsoon |
| 4. | Survey and layout | Structurel | before onset of rain. |
| 5. | digging of pit & construction of earthen bund | Structurel | pre-monsoon |
| 6. | stone pitching on upstream slope of pit | Structurel | pre-monsoon |
| 7. | grass turffing | Structurel | monsoon |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 37,0 | 37,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 40,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replanting of grass in the dried out patches | Végétale | During rainy season(July-Sept) /When required. |
| 2. | stabilisatioin of bund with grass | Structurel | during rain/annual |
| 3. | de-silting of pit | Structurel | Before onset of monsoon/annual |
| 4. | Maintaing upstream & down stream bund slope | Structurel | Before onset of rain/annual |
| 5. | Re-arrangement of displaced stones | Structurel | before onset of rain/annual |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Length of structure , deapth of gully , stone availability
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour availability, stone transportation.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1250,00
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 40% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Income from offl farm activities like stone cutting, stone transporation, dry stone pitching
Market orientation of grazing land: Mixed (ranked 1, shrubs, trees and fodder cultivation) and subsistence (self-supply, ranked 2, to supplement the fodder requirements of watershed)
Market orientation of forest land: Commercial/market (ranked 1, sale of oil producing seeds), mixed (ranked 2, supply of excess fodder to nearby area/watershed) and self subsistence (ranked 3, trend increasing towards livestock production. Trend to have stall feeding. Trend to produce better and improved quality fodder.)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Low fertile and degraded soil
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cowpea, Stylo
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cowpea, Stylo
production de bois
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Private land
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Rs. 400/- per ha
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop area increased.
Awareness and willingness for maintenance required needs to develop
Autres impacts socio-économiques
On farm employment
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farm production
Off farm employment
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Stone cutting and T.C. of stone and dry packing
Input constraints
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
User group formation
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Communitymobilization is required to restore the conflicts.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
60
Quantité après la GDT:
25
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Retention of water in pit. But might lead to waterlogging
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Plantation of fodder crops
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
20
Quantité après la GDT:
18
Autres impacts écologiques
Soil fertility
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Top soil loss checked
Biodiversity
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Ecological changes/Eco. Dev./benefits to environment not assesed in short period of time.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Recharge to ground water
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
13
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
25% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
3 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Because this technology shows successful result in moisture retention, check soil erosioin and prevents sand casting.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Low cost & affordable. |
| Maintainable based upon traditional practices with some additional techniques. |
| Farmers friendly. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Best upon traditional practices, reducing runoff and soil loss How can they be sustained / enhanced? proper planning Water disposal at higher elevation Regular maintenance Adoption of proper cropping pattern depending on water availability Water disposal at higher alevation Regular maintenance Adoption of proper cropping pattern depending upon water availability. Water disposal at higher elevation Regular maintenance Adoption of proper cropping pattern depending upon water availability. water disposal at higher elevatioin regular maintenance Adoptioin of proper cropping pattern depending upon water availability. |
| low cost |
| Farmers can maintain and very less area is lost |
| Efficient soil & moisture conservation. |
| Protection of top soil, Increase Productivity and production of land |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Expected conflicts from adjecent farmers | Community mobilisation |
| Contribution mobilisation to have their ownership | Participatory planning |
| To be liable for its future care & maintenance | Awareness among the community |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Participatory Watershed Development Approach [Inde]
Livelihood asset base development through participatory watershed developemnt keeping people at the center stage of development and promoting village level institutions.
- Compilateur : Narendra Kumar Panigrahi
Modules
Aucun module trouvé