creation of meliorative plantings for struggle with erosion [Kazakhstan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Vladimir Kaverin
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
no
technologies_1482 - Kazakhstan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Salimov Abdul-Bari
SPC for forest facility
58 Kirov str. Shuchinsk city, Akmola region
Kazakhstan
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
SPC of Forest Facility (SPC of Forest Facility) - Kazakhstan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/12/2003
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Technology of creation of meliorative plantings for struggle against wind and water erosion
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
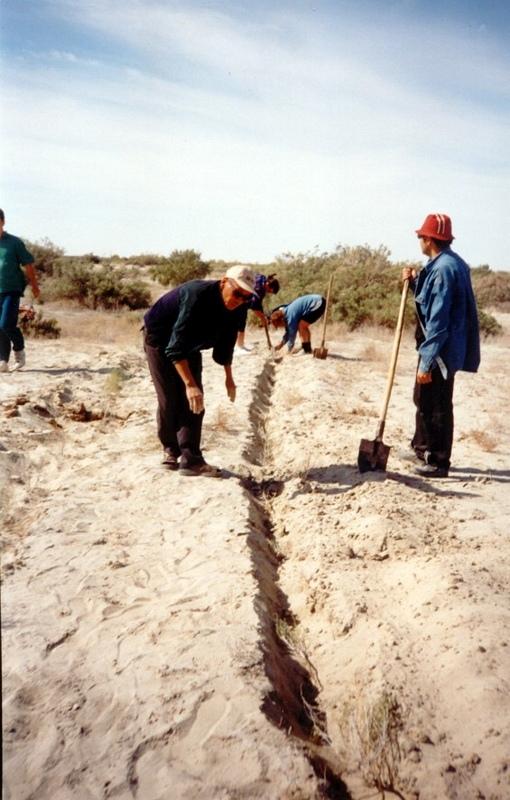
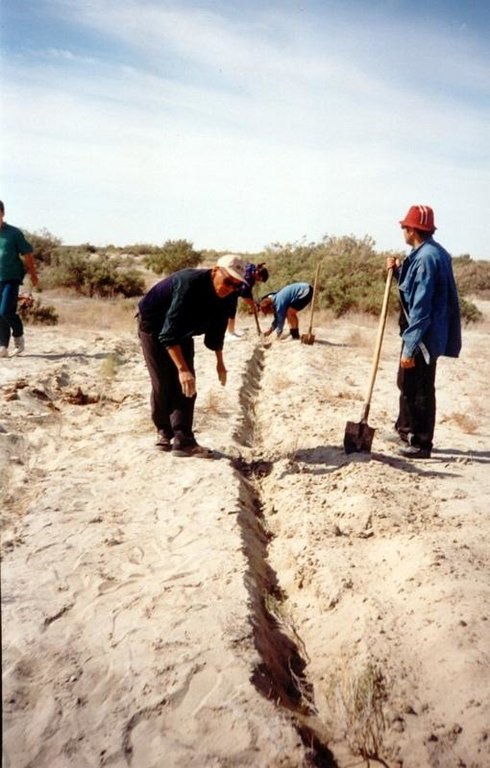
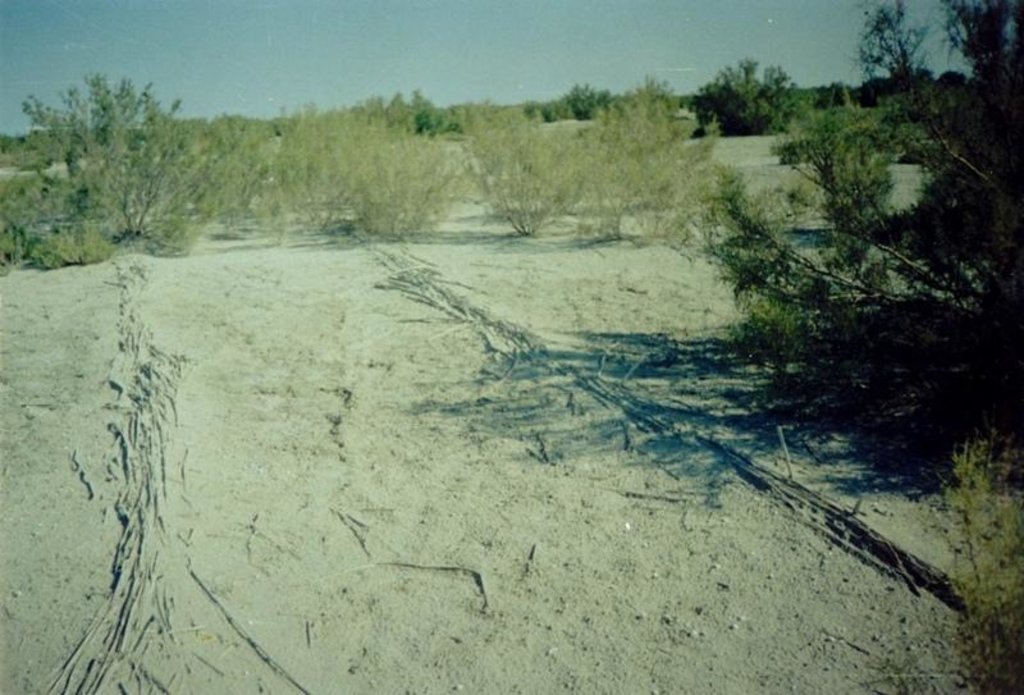
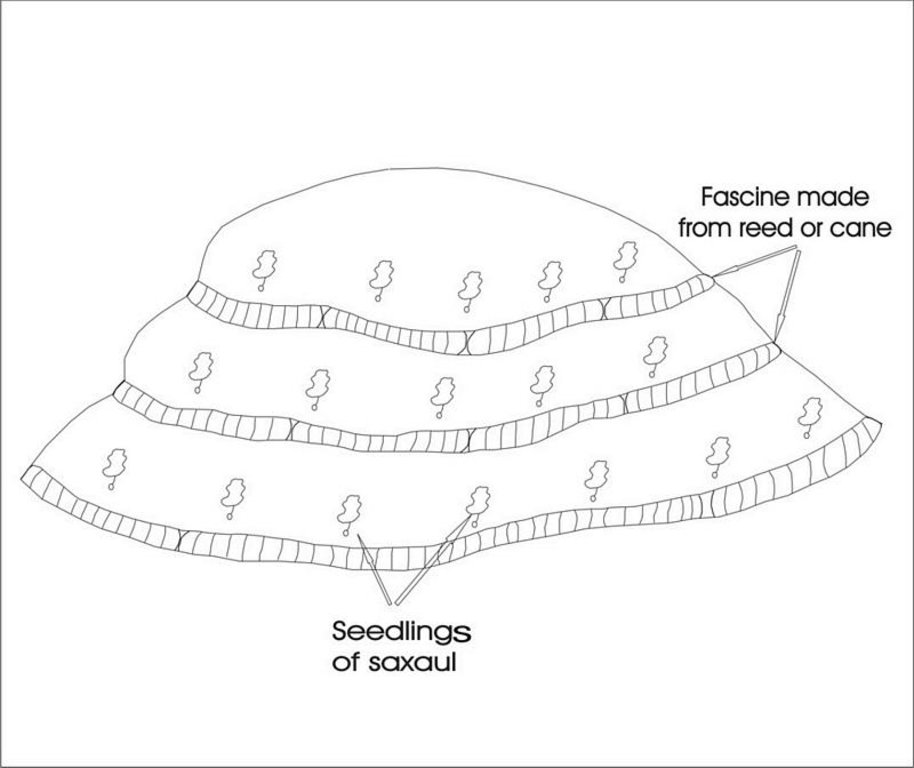
In Syrdarya river’s delta on alluvial drought sandy and loam sand soils processes of wind and water erosion become more active with a view of protection of the soils it is applied covering fascine made from a local cane or reed. Fascines thickness 12-15 cm settle down on a surface by lines in a 2-3 m. On distance of 20 centimeters it is carried out planting of a saxaul seedlings
-Planting of the saplings was done in holes and uninterrupted furrows, which were formed by hands.
-Depth of holes and furrows is 20-25 cm.
-Distance between holes was 1.5-2 m.
-Furrows were perpendicular to the prevailing winds (west-east) and placing mould in several optio0ns: 1- moulds on both sides; 2- the same from the southern side of a furrow; 3- the same from the northern side. Furrows alternated with holes rows.
-Length of rows variants in repetition was 100 m.
-Saplings were filled up by hands in rows in 1-2 meters, distance between rows was 2-2.5 meters.
Prevention of water and wind erosion on sandy and loamy sand soils of the Syrdarya delta.
Many farmers use the given technology for prevention of wind and water erosion on the lands.
The technology is applied on the area of 1.5 sq.km. Expenses per 1 ha make 99.2 $ USA or 14880 tenge.
Irrevocable water consumption in agricultural land use in the Syrdarya delta, development of the areas of irrigation, livestock grazing led to the contradiction between the agricultural industry and the ecological state of the region. It caused more intense processes of desertification, among them are soil salification and increase in the groundwater mineralization: degradation of vegetation cover; erosion and soil deflation; wind-blowing of the salts from dried bed of the Aral Sea; sand advance on the arable land, etc. At present about of 60% of irrigated areas within the Syrdarya delta are strongly salificated.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kazakhstan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Kyzylorda oblast
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kazalinsk
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
From Kazakh Research Institute of forest management at 1989-2002
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
major cash crop: Fire wood

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Semi-nomadisme/ pastoralisme
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
In deltoid meadows
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Loss of biological variety, degrodation of lands for agriculturing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Approach of sand to settlements and agricultural grounds
Grazingland comments: With a transitional economy and absence of market relations it is prevail a fine farms with a small amount of cattle on a farmstead
Type of grazing system comments: With a transitional economy and absence of market relations it is prevail a fine farms with a small amount of cattle on a farmstead
Constraints of mines and extractive industries: old system of landed property
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 208; Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- brise-vent/ plantations abris
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 1 000-10 000 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.5 km2.
Loamy sand and sandy alluvial desertification soils of delta of the river Syrdarya are subject to process of wind erosion Deflation-accumulative prosses create threat for settlement
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S3: Fossés étagés, canaux, voies d'eau
Commentaires:
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Excessive water-fence on an irrigation from the rivers Syrdarya and Amurdarya.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Destraction saxaul fuel.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (High wind activity in region (prevalence of winds with a speed up to 5 min/sec).)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Ameliorative plantings
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 3000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1,5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0,2
Trees/ shrubs species: saxaul seedling
Grass species: prostrate summer cypress, winterfat, corn
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,05
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (other): Reed fascines
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.00
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stacking of fascines | Végétale | summer |
| 2. | Slips' planting | Végétale | autumn, spring |
| 3. | Laying fascines | Structurel | summer |
| 4. | Slips' planting | Structurel | spring, autumn |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | persons/day/ha | 3,0 | 5,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 165,0 | 165,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Other | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 220,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Additional planting | Végétale | spring /1 |
| 2. | Supplementary slips' planting | Structurel | spring, autumn/1 |
| 3. | Supplementary fascines' setting | Structurel | spring, autumn/1 |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Reed fascines against deflation 100 m in length, 0,5 m in breadth 50 pieces per ha
Saxaul’s seedling every 2 m lines, distance between slips-1.5 m, 3300 pieces per ha
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Manufacturing of reed fascines, purchase and planting saxaul's seedlinfs
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
124,00
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Deserted
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 58-53 m abs. of hight
Landforms: Poorly wavy inclined plan
Slopes on average: Weakly wavy
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Depth of humus under 5sm
Soil fertility is very low 0,191 of humus
Topsoil organic matter: 0,13-0,26%
Soil drainage / infiltration is good ins sandy and loamy soils and medium in clay
Soil water storage capacity is very low - low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très pauvre
- pauvre
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Annual population growth: negative
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: With falling a level of Aral sea and degradation of the natural invironment in dicline there came all branches of agriculture and fishing industry
Level of mechanization: Fascines and planting of bushes are manually spread
Market orientation of production system: Rise of pastures' fodder capacity
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The projective covering increases
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase in effeciency of livestock
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Manual labour
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Fastening of surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Stoppage of blowing
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase of farmer's living level
Impacts écologiques
Sols
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Surface stabilization
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Blowing stops
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Times are occupied
Autres impacts écologiques
biodiversity
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Erosion of surface of the ground are stopping
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 10-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
15 households covering 20 percent of stated area
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
15 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The increase of deflated and eroded areas compels farmers to apply SWC
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Decrease in the areas of wind and water erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? For a long time enough depending on life cycle of wood-bushes vegetation |
|
Improvement of microclimatic conditions of settlements How can they be sustained / enhanced? During all time of existence of the green zone created with the help of SWC |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Stabilization of mobile sand How can they be sustained / enhanced? At rational use of technology the created ecosystem can be supported for some life cycles with help of the main wood breed |
| Elimination of drifts of settlements by sand |
| Returning the grounds in rotation of the pasture |
| Creation of additional workplaces |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Shortage of seedlings for the big areas | Creation of artificial nurseries |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Almost hundred percentage use of manual skills | Development of new machines and mechanisms |
| Probably low survival of seedlings and absence of shoots because the weather conditions are not good enough | The organization of post planting watering |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
"To develop scientific bases of forest amelioration of the grounds of a naked bottom of Aral sea, classification of types of growth conditions" Kaverin V.S.. 2000y.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
SPC for forest facility58 Kirov str. Shuchinsk cityAkmola regionThe Republic of Kazakhstan
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé