Polypit nursery [Népal]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Madhav Dhakal
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Plastic-Khalte nursery - Nepali
technologies_1498 - Népal
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Népal1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/11/2006
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
A simple, inexpensive and practical method for raising healthy plant seedlings
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
During the winter in Nepal’s middle mountains, the soil temperature generally remains at 5-10 degree celsius above the ambient air temperature. This principle was used to design a simple, inexpensive, and effective nursery technology for raising vegetable and horticulture seedlings in colder regions. The polypit technology allows seedlings to be raised by protecting them from the freezing temperatures that occur mostly
at night.
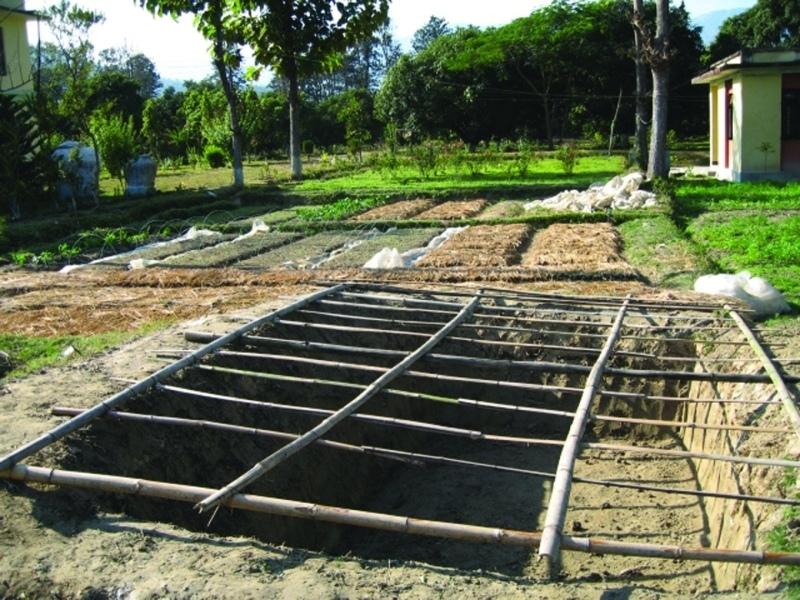
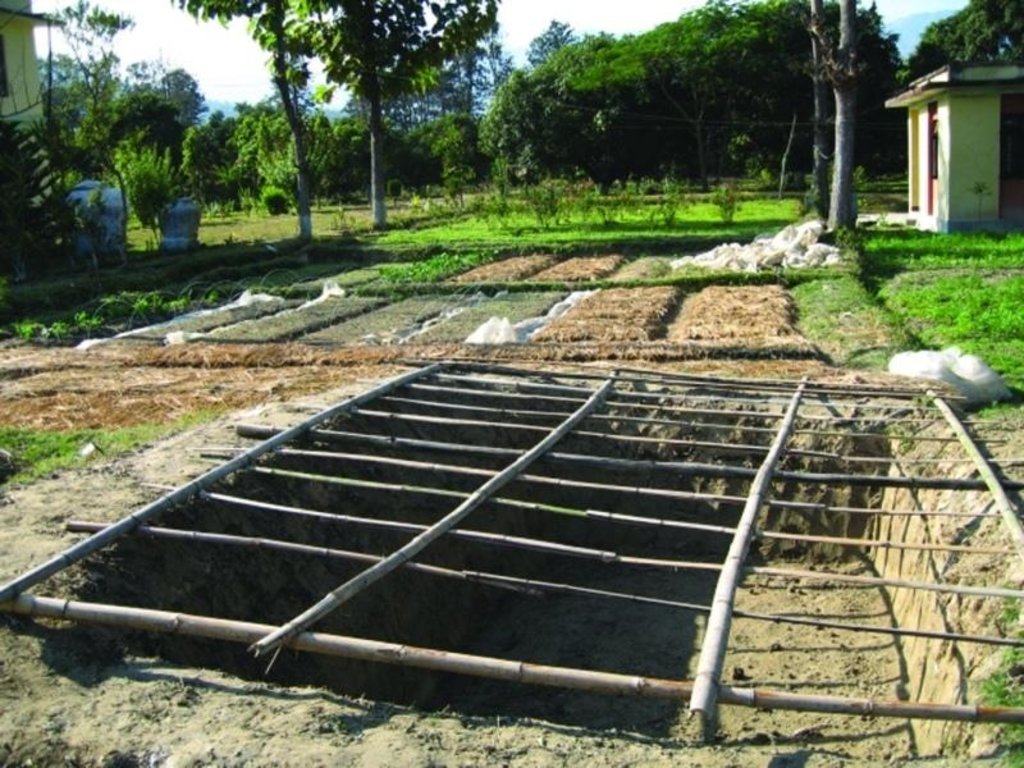
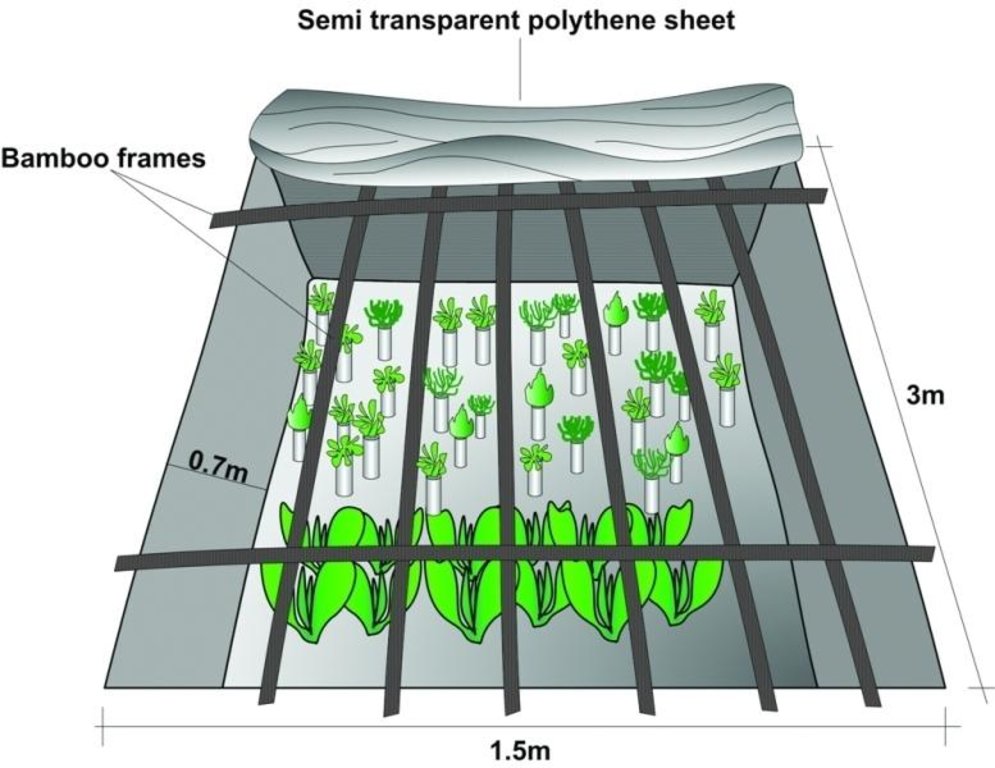
Polypits are about 1m deep pits dug into the ground and covered with semitransparent polythene sheets, preferably UV stabilised and supported on bamboo frames. A 30 cm high mud wall is built across the slope on the upper side of the pit. The polythene sheet is sealed on the upper side of the pit, leaving three sides unsealed but held down with stones that can be lifted to access the pit. The base and sides of the polypit are left as they are with no form of plastering.
The polythene sheet covering the pit reduces the photosynthetic photon flux (PPF) by around 30% inside the pit, still allowing sufficient sunlight to reach the plants inside. The polythene is usually removed during the day from 11 am to 4 pm to allow full sunlight to reach the plants except on rainy and very cold days. A modified version of these polypits - only 70 cm deep - were used in the Jhikhu Khola watershed to grow vegetable seedlings during the winter. The pits can be made of any reasonable size depending on the number of seedlings to be grown and the layout of the land. The Jhikhu Khola pits were about 3m long, 1.5m wide, and 0.7m deep.
Since the polypits are closed at night, the CO2 released by the plants and soil microbes accumulates and increases to well above levels outside the pit. In a completely sealed polypit, the CO2 concentration could reach up to 3000 ppm during the night which would be harmful for plants. Thus the polythene cover is only loosely sealed along the edges at night to regulate and maintain the concentration of CO2 at about two to four times the ambient concentration.
The warmer protected conditions and CO2 enrichment leads to extra growth and biomass gain for plants grown inside the pits during the winter. This technology is easy to maintain with the only maintenance costs being to repair damaged polythene sheets and frames.
The polypit technology is useful for mountain farmers where water scarcity and low temperatures limit the potential to raise quality seedlings. The technology is being promoted in the northwest Indian state of Uttarakhand, although only a few farmers have adopted it so far. It is a very promising technology and its use should be encouraged by hill farmers and research and development organisations engaged in raising seedlings. The technology needs more participatory action research to improve it and to encourage more farmers to adopt it spontaneously.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Népal
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kavrepalanchowk district/Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology is developed by G.B Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment and Development (GBPIHED) in Almora (India) for raising healthy plant saplings, named as polypit (Palni et al. 1994).
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
major cash crop: Vegetables
major food crop: Rice , wheat and maize
other: Legume and oilseeds
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Production is limited due to insufficient water during winter and the pre-monsoon season (from Nov-May); insufficient
farm income due to small landholdings; increased inputs of chemical fertilisers
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Irrigation shortage during pre-monsoon and monsoon months.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize -vegetables/wheat-vegetables
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 3
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- full year planting
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Commentaires:
The technology was tested in the farmers field at Lamdihi and Spice Crop Development Centre. atTamaghat.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Poly pit covered with semi transparent plastic sheet which is supported on a bamboo farme.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: protecting seedlings from frost, reduction of water loss, carbon dioxide enrichment
Structural measure: pit
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5 m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3 m
Construction material (earth): a mud wall is made about 30 cm high from the ground, sloping on the two sides.
Construction material (wood): to place semi transparent plastic on a frame.
Construction material (other): plastic sheet: to cover the pit, rope, wire: frame preparation
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Polypit nursery
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.10
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Determine the appropriate size (length, width and depth) of the pit | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 2. | Mark the area for soil excavation | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 3. | Excavate soil from the marked area | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 4. | Make a mud wall (~30 cm high) from the ground, sloping on two sides | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 5. | Make a bamboo fram of an appropriate size | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 6. | Lay the frame over the pit with one end resting on the mud wall | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 7. | Lay the plastic sheet over the frame | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 8. | Seal the polythene sheet on the higher side of the mud wall and leave three sides unsealed | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 9. | Lay the other three sides of the polythene sheet normally at ground level and weigh down with stones that can be removed to access the pit | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
| 10. | The base and sidesof the polypit do not need any form of plastering (even with mud) | Structurel | beginning of the winter season |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Construction of polypit nursery | Persons/unit | 1,0 | 2,1 | 2,1 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Plastic | unit | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Bamboo | unit | 1,0 | 1,3 | 1,3 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Rope | unit | 1,0 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 7,6 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The polythene cover is opened to acclimatized the plants to the outside environment | Structurel | 11:00- 16:00/Every day |
| 2. | Cleaning the pit | Structurel | After trasplanting the seedlings/ once or twice in |
| 3. | Replacing the frame and polythene sheet if it gets damaged. | Structurel | before raising nursery/In case of damage |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Maintaining the pit | Persons/unit | 1,0 | 2,1 | 2,1 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 2,1 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: wooden/iron peg, spade, shovel ,knife, and saw
The cost was calculated only for unit technology , and it can not be extrapolated on hectare basis as in 2006.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The plastic sheet , but it is easily affordable by the land users.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1200,00
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 850 m a.s.l.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Variable
Soil texture: Fine/ heavy (clay) is red soil with high clay content but medium (loamy, silty) is non red soil
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Water quality (untreated): Also good, but more in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: natural spring.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and
increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: About 50 percent of the product , especially vegetables are grown commercially.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for planting, irrigation, harvesting; Animals are used for field preparation and in valley bottom machines can be used for field preparation
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
the pit interrupted land preparation
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
About the polypit and their advantages
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Inside the polypit high relative humidity is maintained.
Autres impacts écologiques
Protection of seedlings against frost
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Quality of seedlings
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
customers prefer to buy seedlings grown in polypits compared to those grown outside
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The investment costs can be recouped within one season leading to positive results due to higher production.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
2 households
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There were not enough dissemination and awareness raising activities to inform farmers of the benefits of the technology and convince them to use it.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
The survival rate for vegetable seedlings is higher and seedlings mature about two weeks earlier than if grown outside where they take about one month to be ready, leading to additional income for farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Every aspect of the technology should be highlighted through experience sharing programmes |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Polypits are a simple, inexpensive, practical and effective technique for raising and protecting plant seedlings from severe winter temperatures.They can be called ‘poor farmers greenhouses’ How can they be sustained / enhanced? More dissemination and awareness raising activities are needed to inform more farmers about the benefits of this technology |
|
The high relative humidity in polypits means that watering only needs to be carried out once or twice a month in comparison to fi ve to six times for open nursery beds, thus saving labour and water How can they be sustained / enhanced? Every aspect of the technology should be highlighted through experience sharing programmes |
|
The more physical conditions and CO2 enrichment in the pits during the winter months are refl ected in the extra growth and biomass gain of plants grown inside the pits How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| In the demonstration, the bamboo frame to hold the sheet was too heavy making it diffi cult for the farmer to remove the frame and work inside. | Use a modifi ed frame with a space built in to allow a person to enter the pit easily without having to remove the frame. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| In completely sealed polypits, the CO2 concentration can become so high during the night that it harms the plants | Only loosely seal the sheet at night to regulate and maintain the CO2 concentration |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Bhuchar, S. (2004) Polypit: a Green-chamber for Poor Farmers, an article prepared for PARDYP Quarterly e-Newsletter-8, ICIMOD, Kathmandu
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
ICIMOD
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Palni, L.M.S.; Bhuchar, S.; Kothyari, B.P. (1994) ‘A Simple Polypit can Greatly Reduce Nursery Time of Tree Seedlings”. In Journal of HIMA-PARYAVARAN, 6(2):10-11
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
GBPIHED- Almora
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Vyas, P.; Bisht, M.S.; Bhuchar, S.; Sharma, S.; Palni, L.M.S. (1999) ‘Polypit: An Improved Technique for Raising Nursery Plants’. In Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 8(1): 43-59
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
GBPIHED- Almora
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé