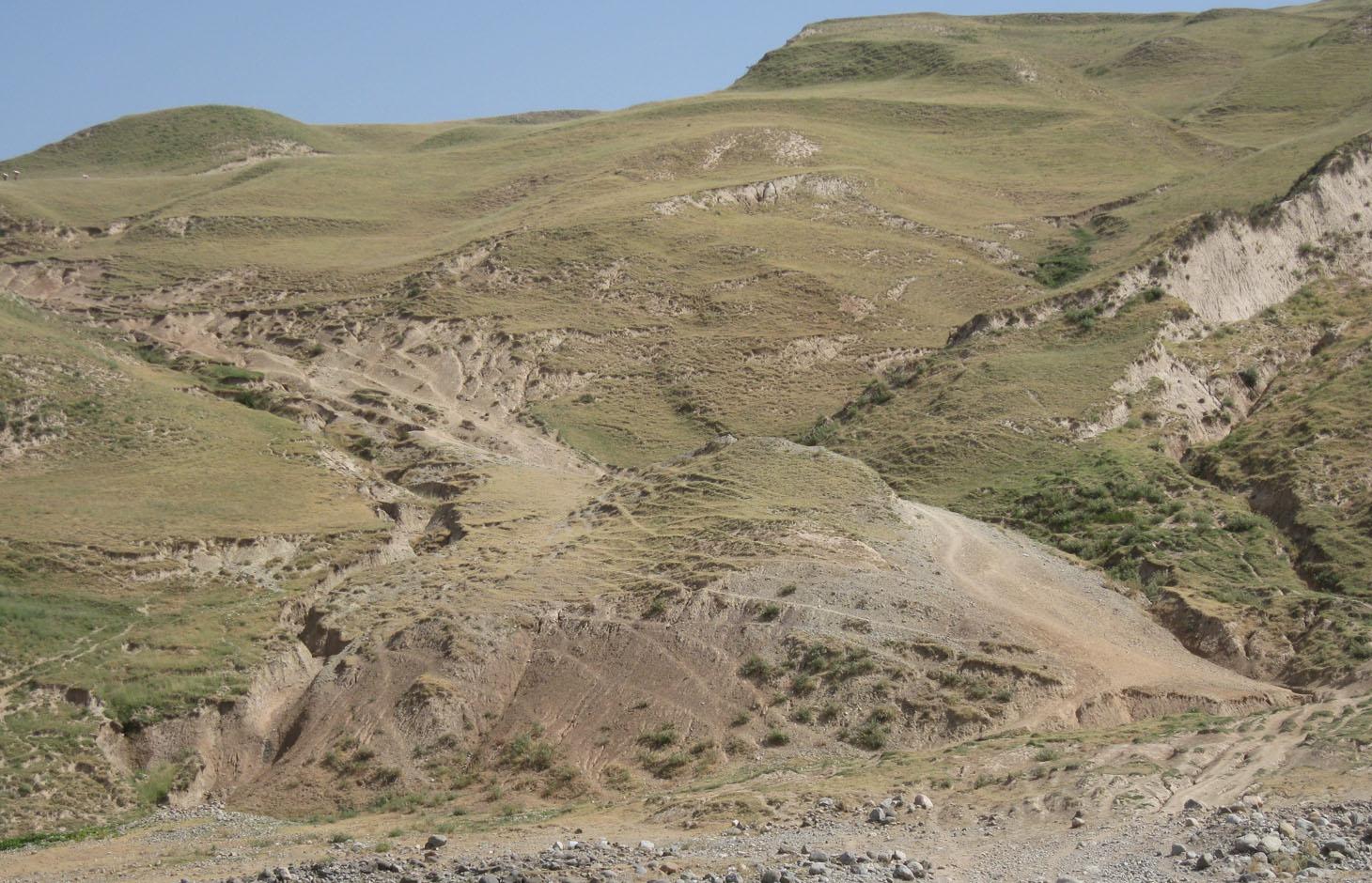
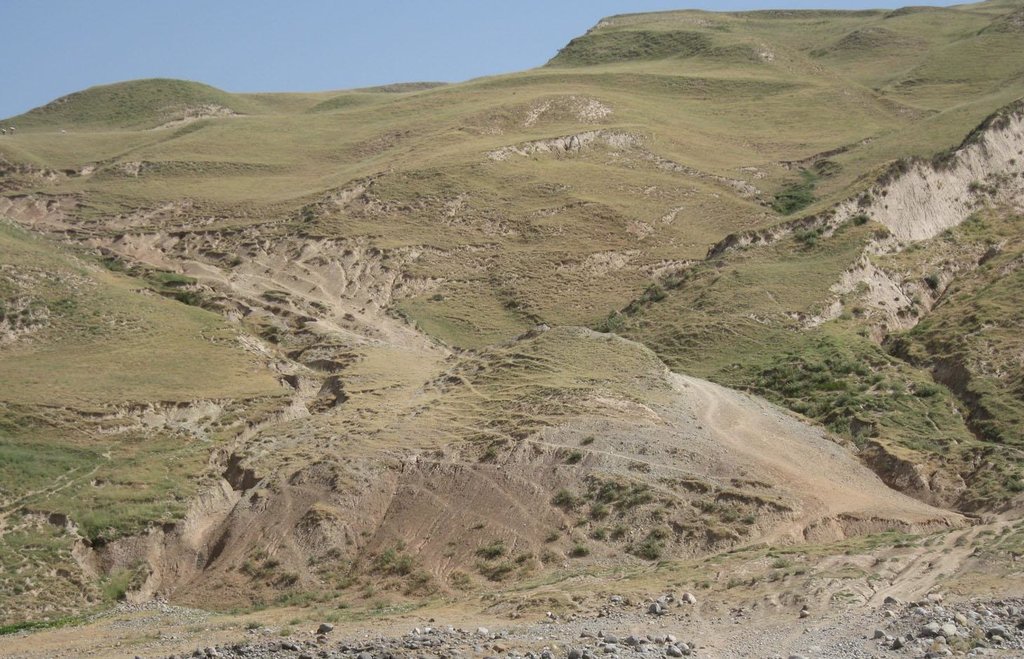
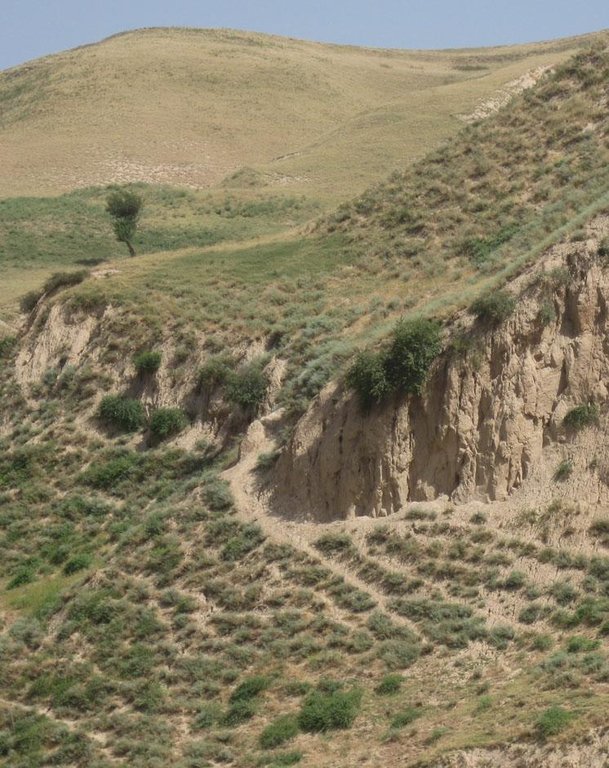
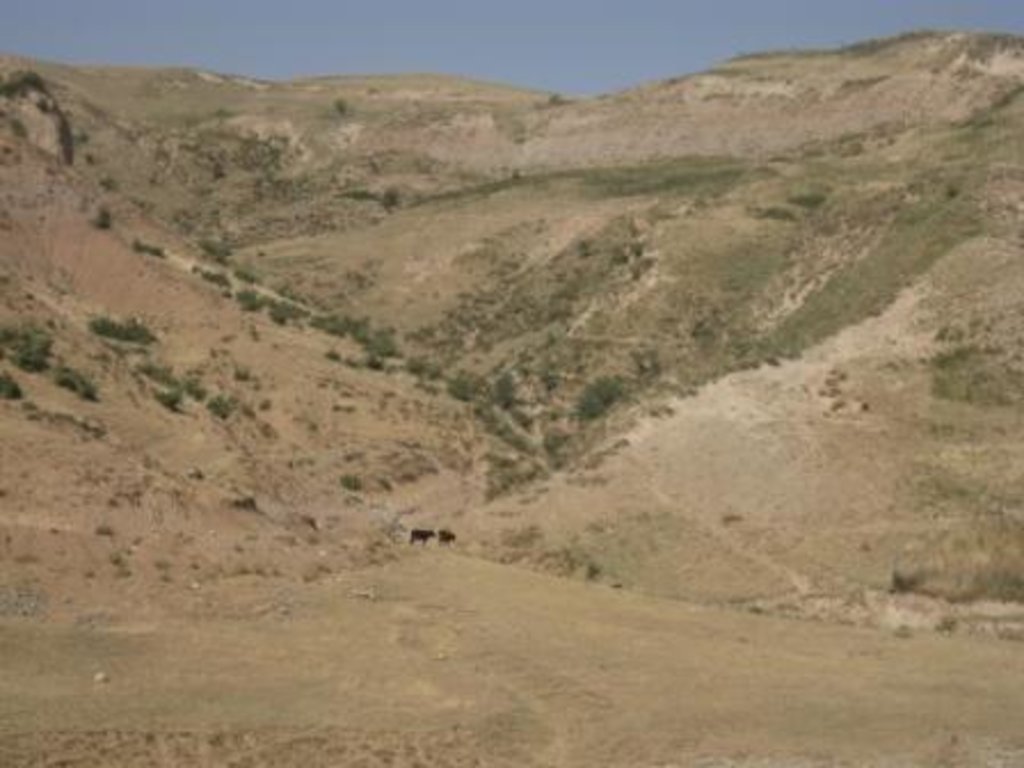
Degraded communal pasture Obishur [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Malgorzata Conder
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1545 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - KirghizistanNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
28/07/2012
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Degraded communal pasture without grazing management and sufficient waterpoints
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
On the communal pasture, located at the foothill around 85 households graze their livestock totally 500 cows and 100 sheep and goats. Half of the households of the village Momandion have livestock which is meant to graze at different places on that pasture. As there is no water point higher up in the pasture area, livestock grazes near the village where a water point is installed. The rolling zone is totally overgrazed and shows several deep gullies. Cows and the small livestock are divided for grazing. Every family is looking after a herd for a day every month. Although the families of the herding livestock communicate with each other, there is no planning for a sustainable grazing management.
Purpose of the Technology: The whole plot is overgrazed and livestock is increasing, so at least controlled pasture management could be expected to decrease the degradation process. Additionally, more vegetation would be available for feeding livestock. More water points have to be installed higher up in the pasture, to decrease pressure on soil and vegetation. More waterpoints would extend the area to be used for grazing. Another issue is that nobody really feels responsible for the pasture and its management. This explains why no pasture management exists at Jamoat level. Farmers are not organized in terms of pasture rotation and control. Livestock owners pay very small rent, which does not make them vakue the pastureland. Additionally, the tax is not enough for projects or investments (like installing water points).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Every household pays 12 Somoni per year for pasture rent, which is in total around 1000 Somoni. Rent is per household not per livestock number. No maintenance is done.
Natural / human environment: The pasture extends from the foothill to the upper parts of the hill with a high percentage of overgrazed, trampled, erosive area. Except for the water point near the village, there is no water and no shady points for livestock. 85 households graze their livestock, which total 1500 cows and small livestock. Every household is responsible for grazing the herd one day every month. Apart from that, no management exists between the families and Jamoat.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Muminabad
Map
×3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Main animal species: Cow, sheep, goat
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing, soil compaction, soil and gully erosion, increasing vegetation cover and hence lower resilience for disaster risks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): More livestock reduces vegetation cover through overgrazing and trampling. Gully formation. Not enough water acces in the pastureland.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cow, sheep, goat
Grazingland comments: Evtl. summer pasture
semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
Type of grazing system comments: Evtl. summer pasture
semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: March-Sept
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
50-100 LU /km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
- Water points
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- 0,1-1 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.94 km2.
Farmer (Vakil) did not know at all the area extent, data based on Google Earth
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
- M3: Disposition/plan en fonction de l'environnement naturel et humain
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Eo: effets hors site de la dégradation

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Eo: offsite degradation effects, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (No controlled grazing), population pressure (Increasing livestock), land tenure (Communal property=No individual responsibility)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (one or two decades ago), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), poverty / wealth
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Bare vegetation cover, no trees, soil erosion, trampled paths, rill building, no waterpoints are all calling for pasture management among the villages.
Location: Obishur watershed, Momandion. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Controlled access, staged grazing
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Somoni
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
4,83
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
12.40
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Possible solutions: Pasture ManagementWorkshops, Meetings, Round table | Modes de gestion | |
| 2. | Water points | Modes de gestion | |
| 3. | Reduce Livestock quantity | Modes de gestion |
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
It wouldn not be expensive to hold regular meetings between the livestock keeping families for a better organization of the grazing area. The installation of a water point is very costly and labour intensive in contrast.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: Steep (ranked 1, approx. 40%) and hilly (ranked 2)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau inutilisable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
2.4 ha, if 7.7 pers/household counted. In total 3040 ha pasture
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- loué
Commentaires:
Land ownership is based on Land user certificates
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less forage available for livestock due to reduce vegetation cover
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
important clear-cutting in the past
gestion des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
no organizational task without pasture management
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
no organizational task without pasture management
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
lack of water points for livestock
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
lack of water points for livestock
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
more fodder has to be bought, because grazing is insufficient
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less forage for livestock
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
no organizational task without pasture management / feeding animals
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More difficult to feed livestock
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
compaction du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
capacité tampon/de filtration
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Commentaires:
Pasture rotation would improve vegetation cover, infiltration, slope stabilization and natural disaster resilience
Rotate within the grazing land and less energy needed by livestock, which leads also to less consumption and hence overgrazing
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Establishment of rotational grazing is not expensive and does not require further equipment How can they be sustained / enhanced? Empower communication and decision-making also between the farmers |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Importance of rotational grazing depends on Jamoat and farmers level | Strengthen communication between Jamoat and farmers through consultancy, meetings etc. Farmer as tenants should get a voice. |
| Pastureland rent is too cheap and is not valued. There is no incentive to change, because nobody feels responsible for that area. | Increase the rent and discuss communally where money should go to (e.g. water points). |
| Pasture management does not show benefits immediately which makes it difficult to evidence good Technology. | Explanation/ education about short and long-term benefits |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé