Unexpected flood risk control in village [Népal]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Sabita Aryal
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Bhelbadi Niyantran
technologies_1590 - Népal
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Koirala Pratiksha
Népal
Gautam Bibhu
Népal
Mulmi Anjuli
Népal
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Kathmandu University (KU) - Népal1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
It is a technology used to control and reduce the effects of downstream flood by physical interventions like construction of spillway, ditch and stone dam on the wall of ditch.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
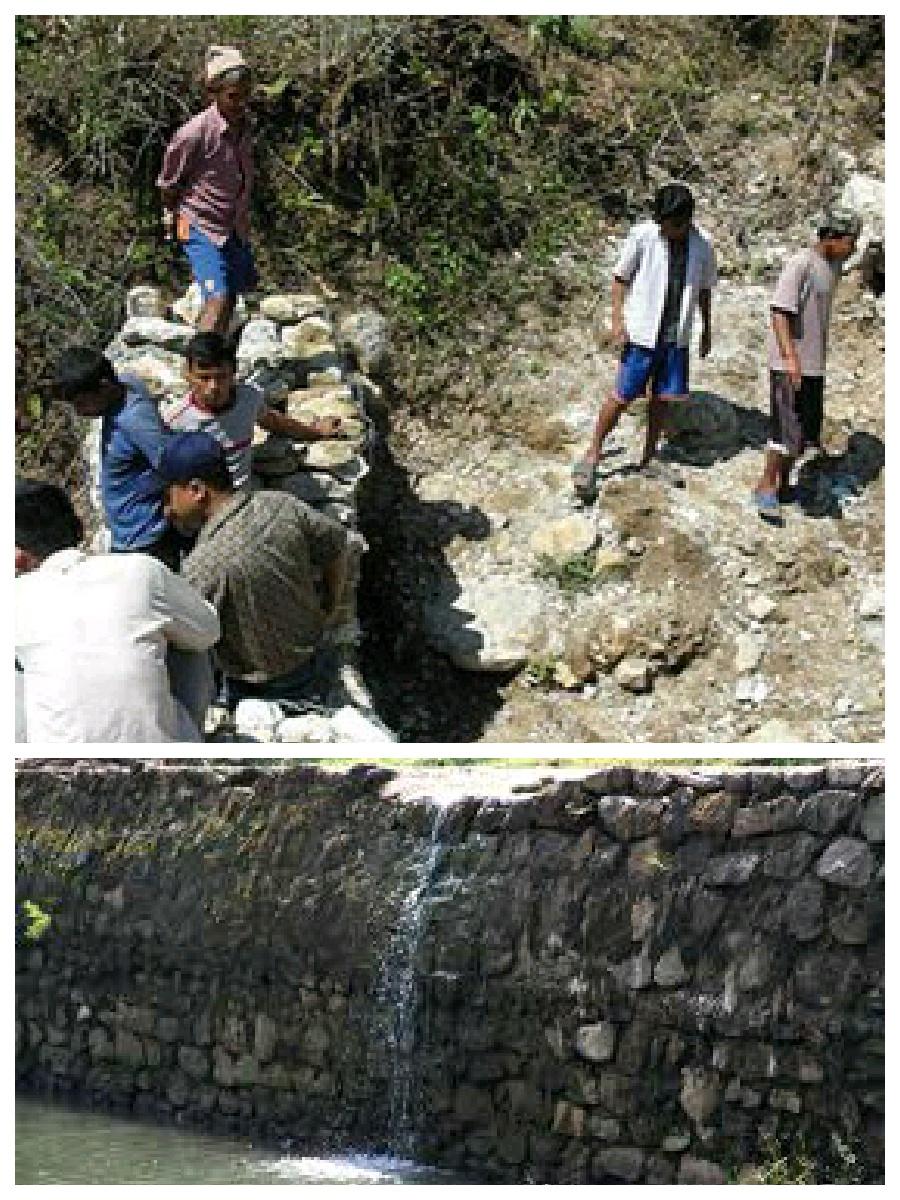
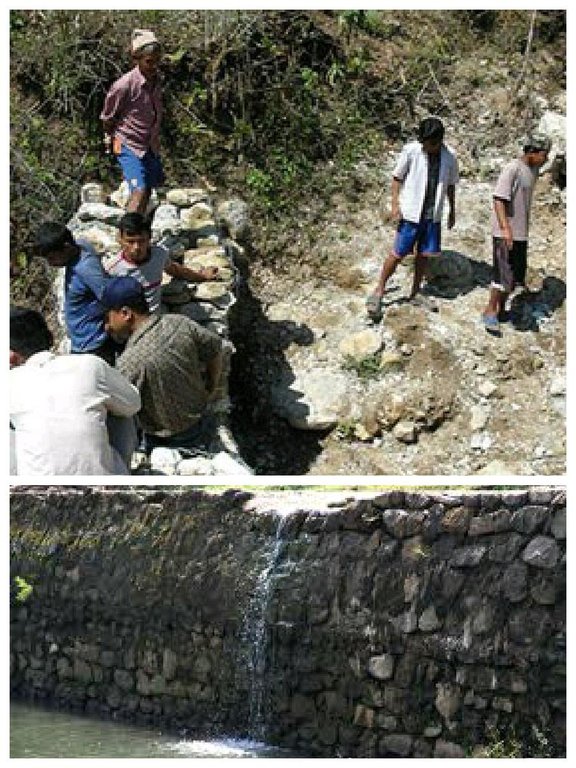
Hilly areas are prone to flash flood that occur with little warning. During rainy season, level of water rises in the stream due to which land mass field of around area was degraded. This technology is used to control the land mass and water flowing from upper region to the lower region of the hill. The natural stream was modified to deep and more sloppy. And surrounding walls were made by piling up stones dams and tighten them by metal wires. These dams decrease the slope gradient and reduce the velocity of water flow and promote the deposition of eroded materials.
Purpose of the Technology: There was no problem of landslide and downstream flood before. But after the road construction, soil became loose resulting in the occurrence of downstream flood. It caused massive destruction of agricultural fields and disturbed settlement areas. Also, stone and gravel during landslide and stream flood used to be deposited and block the flow of the water. So land user invented by this technology to control and reduce the effects of downstream flood.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Land users and other villagers took the initiative to carry out the technology. Stones were abundantly found in the stream that were utilized to make the dams on lining the stream. Dozer was used to deepen the stream and increase the slope of stream. Stones were piled up and tied by iron wires on the bank of stream by local farmers themselves with their own investment.
Natural / human environment: The area where this technology has been used is a hilly area. Soil fertility in that area is low or medium which differs according to the place. Due to landslide and downstream flood, sand and gravel get deposited in the cropland, so its fertility is very low. No crops can be grown in there. This technology helps to control further degradation of land but could't help to restore natural quality of land.
This area is semi arid area. Due to the proper supply of water the area is prevented from drying. People living in that area are mainly farmers and depend on agriculture for livelihood. Also the area is developing more after the road construction. People are now being more aware about health, education and development.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Népal
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Nepal
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kavre
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The problem of downstream flood was caused before two years after the construction of road. so technology was also developed before 2 years.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Waterway, ditch
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Cropland destruction
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cropland destruction, vegetation destruction, decreased soil fertility.
Constraints of waterway/ditch (Ditch for the flow of water): Big stone which block the water ways.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 3
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: june-november; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: march-june
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Commentaires:
The area occupied by SLM technology is approximately 28 km2. It includes area occupied by conversation measures and the additional area protected by them.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S3: Fossés étagés, canaux, voies d'eau
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development (Construction of road i.e infrastructure development), floods (Downstream flood during rainy season.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Road construction)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall during rainy season cause downstream flooding.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Auteur:
Bibhu Gautam, KUGH,Kavre
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
This technical drawing shows the constructed dam and gully which allow proper flow of downstream flood.
Location: Chyamrangbes. Kavre
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Technical knowledge required for labour: high (Through their experience to construct in a useful way.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing)
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): n'a
Spacing between structures (m): n'a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.13
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1000
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1000
Construction material (earth): Soil excavate from the ditches is used to build bank.
Construction material (stone): the cut off ditch is lined with stones, embankment with stones.
Construction material (other): iron wire was used to bind the stone together.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12%
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land user increased the width and slope of existing ditch for easy flow of water. | Structurel | dry seasonm |
| 2. | Land user embanked the bank with stones on either side. | Structurel | dry season |
| 3. | Stones are bind together by wires in some places. | Structurel | dry season |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Increase the width and slope of ditch | ha | 1,0 | 941,17 | 941,17 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 941,17 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: dozer, Dozer
The above mentioned cost is not given per unit/hectar. It is the total cost used for that technology.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most determinate factor affecting the cost is land structure. Land contains loamy soil which made it difficult for construction of ditch.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
monsoon rain, dry winter
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: The average slope is about 15%.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil texture: Sandy and graveled land
Soil fertility is medium - low and varies according to soil texture
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low, soil is sandy and contains gravel. So it cannot store water
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
en surface
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
excès
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau inutilisable
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: Infiltration is very low. Water only flow on surface.
Availability of surface water: During rainy season excess water flow through the steam.
Water quality (untreated): Some portion water is used in agriculture
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Soil is very infertile. So it is poor in biodiversity.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: More male because women cannot do such type of heavy labor work.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
(living standard is more than average).
(average life standard).
Off-farm income specification: Their land is protected from further degradation
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
The land where SLM technology is applied belongs to individual, but it land use right belongs to community.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
risque d'échec de la production
Quantité avant la GDT:
n/a
Quantité après la GDT:
n/a
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
protected the cropland from flood
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
n/a
Quantité après la GDT:
n/a
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
active participating people on land conservation.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
water travel in fixed path
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
improved water way for passage of excess water
Sols
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
soil loss due to flooding is reduced
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
the main benefits of this technology
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Commentaires:
Dame can be made more tolerant again flash flood by using wire to tighten the stone walls or making the concrete wall.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement négative
Commentaires:
This technology is not a investment purpose. People used their own money to construct it.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
14 households in an area of 10 - 100 sq km (50 - 100 persons per sq km)
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
14 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Iron wire was provided by Bagmati watershed.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: People have well accepted this technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Risk of downstream flood and landslide is reduced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If they had been more donation from government or any other projects, they would construct concrete or more flood resistance dams. As some parts are still unconstructed they would complete them with some more external support. |
| Agriculture land get protected so they can plant the crop without being at risk. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Proper water drainage system and water can get collected in the river following the fix path. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fodder plant could be grown on the stream banks which is now left and unused. This could be used to feed the animals and would also help to control flood and landslide. |
|
It reduced the risk of further land degradation by downstream flood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Dams can be made more strong by making concrete walls |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| N/A |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| N/A | N/A |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé