Alternate Wetting and Drying [Philippines]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
technologies_1725 - Philippines
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
DA-BSWM
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Raquid Jemar G.
DA-BSWM
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Martinez Mamerto F.
DA-BSWM
Spécialiste GDT:
Pascual Kristine
Philrice
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Sibayan Evangeline B.
Philrice
Philippines
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - PhilippinesNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) - Philippines1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
11/02/2016
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Palayamanan: Climate Change Adaptation Strategy for Lowland Ecosystem [Philippines]
Synergistic mix of farming ventures implemented by the farm family based on the existing environment and their resources to address food security, income instability, and sustainability.
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Alternate Wetting and Drying is a water-use management technique wherein irrigation water input could be substantially reduced to as much as 35% without significantly affecting rice yields.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
It was observed that most of the farmer’s irrigation practice of continuously flooding their rice fields is wasteful and uneconomical. The imbalance amount of water, either in deficit or excess, might affect the development and productivity of the crops.
With this inefficient water use and coupled by the increasing frequency of drought, vulnerability to water scarcity is inevitable. Furthermore, it has been recognized that poor water management practices contributed to the process of land degradation. Hence, there is a need to practice proper water management in rice cultivation. As an integral part of the Palayamanan system, the Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) introduced a water saving technology to the farmers called Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD).
The AWD modifies the irrigation scheduling and application and eventually the amount of water to be use in the field. Irrigation water is applied a few days after the disappearance of the ponded water in the so-called “observation well”. Hence, the field is alternately flooded and non-flooded.
Purpose of the Technology: The following are the purpose of this technology: (1)reducing water use for irrigation so that it can be used for other purposes, (2) reducing the use of irrigation water because there is less of it, and (3) reducing the use of irrigation water to reduce the cost. Emission of greenhouse gas (GHG) specifically on methane is reduced since this is caused by flooding of ricefields.
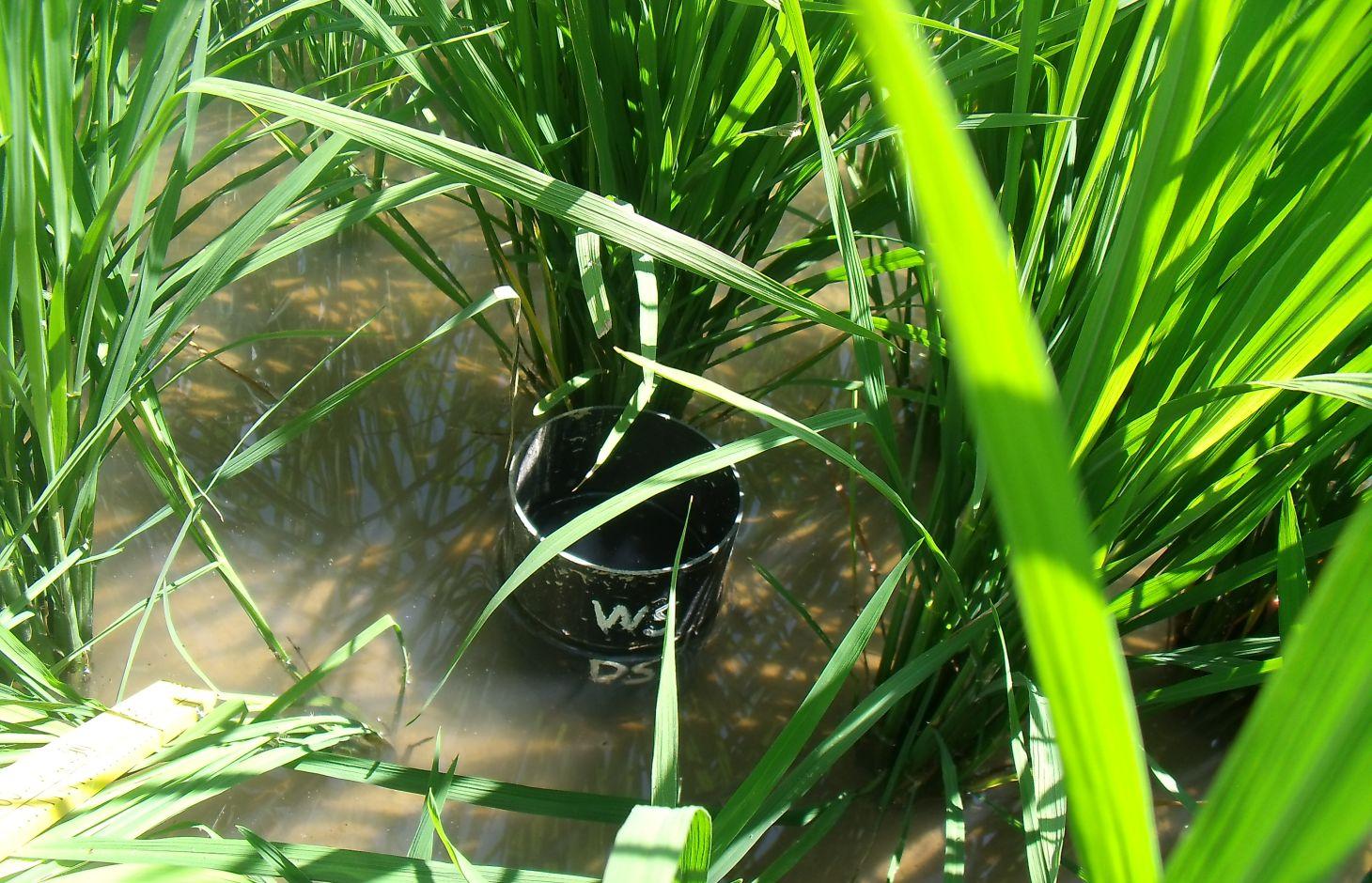
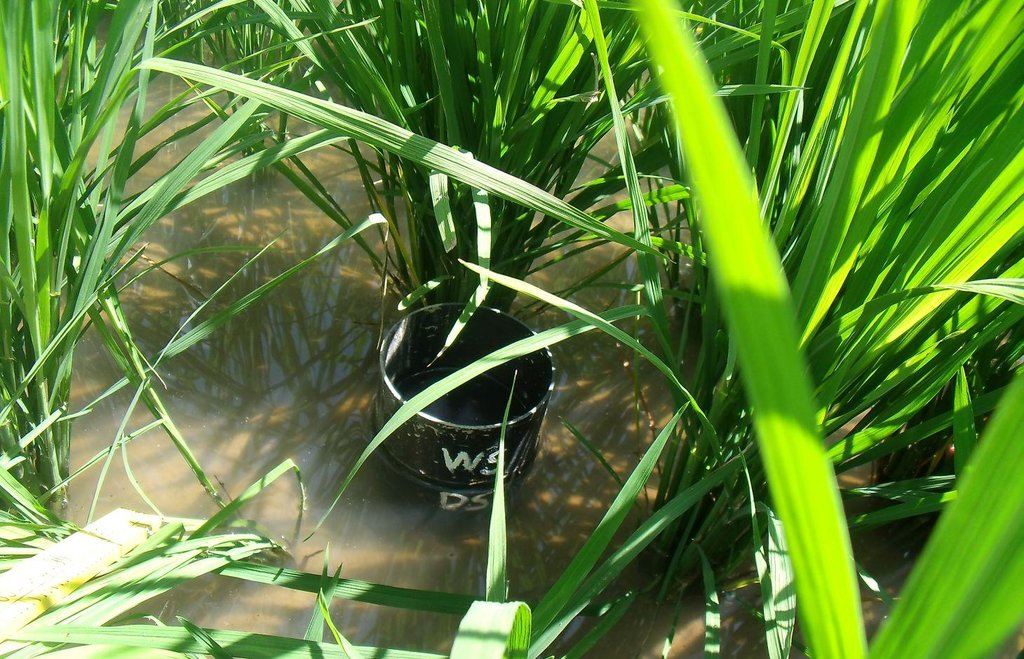
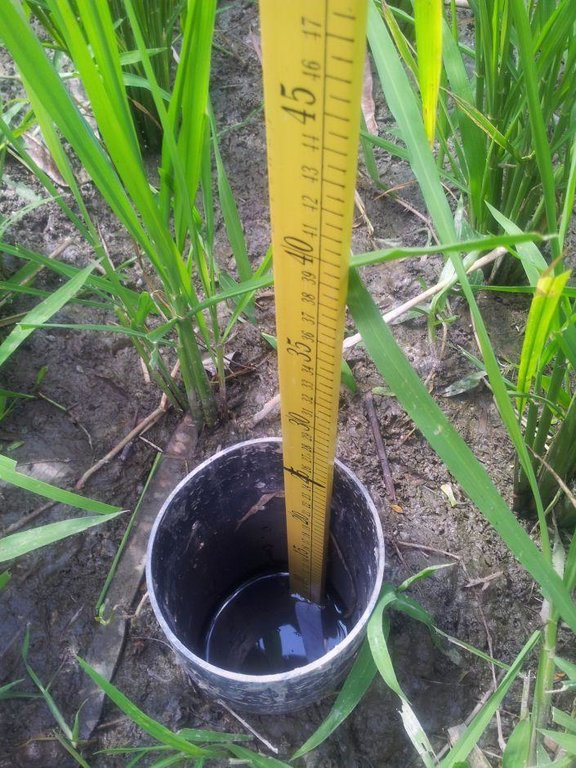
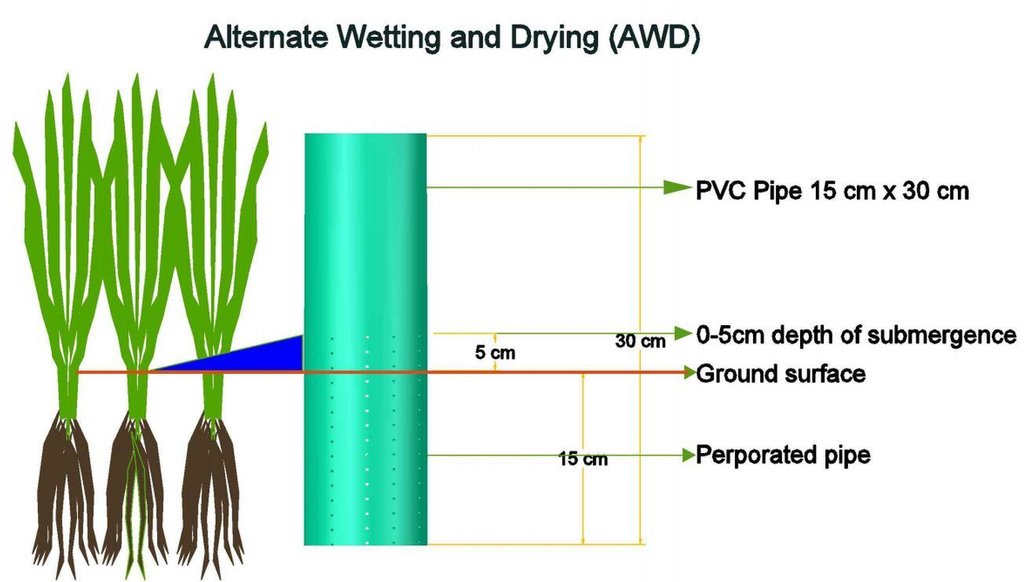
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Practical implementation of AWD is facilitated using a simple tool called a 'field water tube' as observation well, used in monitoring the water level in the field.It is made of a 25 cm long PVC pipe with a diameter of 10 to 15 cm. In some instances, bamboo can be used instead of the PVC pipe. The pipe is perforated with many holes on all sides to allow lateral movement of water in the root zone. It is installed into the soil by ensuring that 10 (dry season) or 5 (wet season) cm protrudes above the soil surface. Soil must be removed inside the tube so that the bottom is visible. During the first 21 to 30 days after direct seeding or transplanting, 2 to 3 cm of water is maintained to control weeds and to ensure that the crop has already
recovered from transplanting shock. AWD is imposed after 21 to 30 days where the water in the tube is monitored. Once the water inside the tube disappears, irrigation is applied to a water depth of 5 cm above soil surface. It is noted that during fertilizer application and flowering stage, sufficient water is maintained to avoid spikelet sterility. Terminal drainage from one to two weeks before the expected time of harvest is also done to promote uniform maturity of the crop and to facilitate easement of post-harvest operations in the field.
Natural / human environment: The area is under a humid climate experiencing wet and dry season with an annual average rainfall ranging from 1000-1500 mm per year. The technology was applied to irrigated rice field in flat and plain areas.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Philippines
Région/ Etat/ Province:
San Nicolas, Dingras
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Ilocos Norte
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
major cash crop: rice
major food crop: rice
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): lack of irrigation water
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
autre (par ex., post-inondation):
- controlled flooding
Commentaires:
The field is alternately flooded and non-flooded.
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
This is practiced in most of the "Palayamanan" sites in Ilocos Norte.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

modes de gestion
- M4: Changement majeur dans le calendrier des activités
- M7: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: management measures
Specification of other management measures: water use management
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), other human induced causes (specify) (water use management)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
PVC pipe used for the technology.
Location: Ilocos Norte
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: more efficient water use
Major change in timing of activities: AWD modifies the irrigation scheduling and application
Other type of management: Water use management on irrigation water is applied a few days after the disappearance of ponded water in the field water tube.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
3.33
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of the PVC/bamboo pipes | Modes de gestion | |
| 2. | Perforation with many holes on all sides of the PVC/bamboo pipe | Modes de gestion |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Perforation with many holes on all sides of the PVC/bamboo pipe | Person/day | 1,0 | 3,33 | 3,33 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Preparation of the PVC/bamboo pipes | piece | 1,0 | 4,44 | 4,44 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 7,77 | |||||
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of the PVC/bamboo pipe into the soil | Modes de gestion |
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Market orientation: Rice produced are intended for market and food consumption for the family
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha and1-2 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Autres impacts socio-économiques
weed growth during dry period
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
seen as disadvantage
Impacts socioculturels
apaisement des conflits
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
drainage de l'excès d'eau
évaporation
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: No exact data is available to determine the numbers of land user who adopted the technology but most of the "Palayamanan" farmer partners in the irrigated areas adopted and practiced it.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No exact data is available to determine the numbers of land user who adopted the technology but most of the "Palayamanan" farmer partners in the irrigated areas adopted and practiced it.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Most of the land users practicing "Palayamanan" in the municipality and province of Ilocos Norte is adopting the technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Positive outcome primarily in water savings without significant yield difference from the usual practice. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Simplicity of the technology's method. |
| AWD leads to firmer soil conditions at harvest, which is beneficial to operating machines in the field. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Prone to weed growth during the period when the soil is dry. | Proper weed management |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Palayamanan: Climate Change Adaptation Strategy for Lowland Ecosystem [Philippines]
Synergistic mix of farming ventures implemented by the farm family based on the existing environment and their resources to address food security, income instability, and sustainability.
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Modules
Aucun module trouvé