Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields [Viêt-Nam]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Justyna Sycz
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
technologies_1277 - Viêt-Nam
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 5 janvier 2017 (inactive)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 29 avril 2017 (inactive)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 3 mai 2017 (inactive)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 11 août 2019 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Land Use and Climate Change Interactions in Central Vietnam (LUCCi / GLUES)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Technische Hochschule Köln (TH Köln) - Allemagne1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
03/08/2015
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Vu Gia Thu Bon River Basin Information Centre [Viêt-Nam]
The VGTB River Basin Information Centre (RBIC) offers decision support tools for stakeholders and aims at providing comprehensive information and consulting services to the water and land users according to their demands.
- Compilateur : Justyna Sycz
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Return flow from paddy fields is strategically collected before being lost to rivers and is reused as an effective source of agricultural water.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
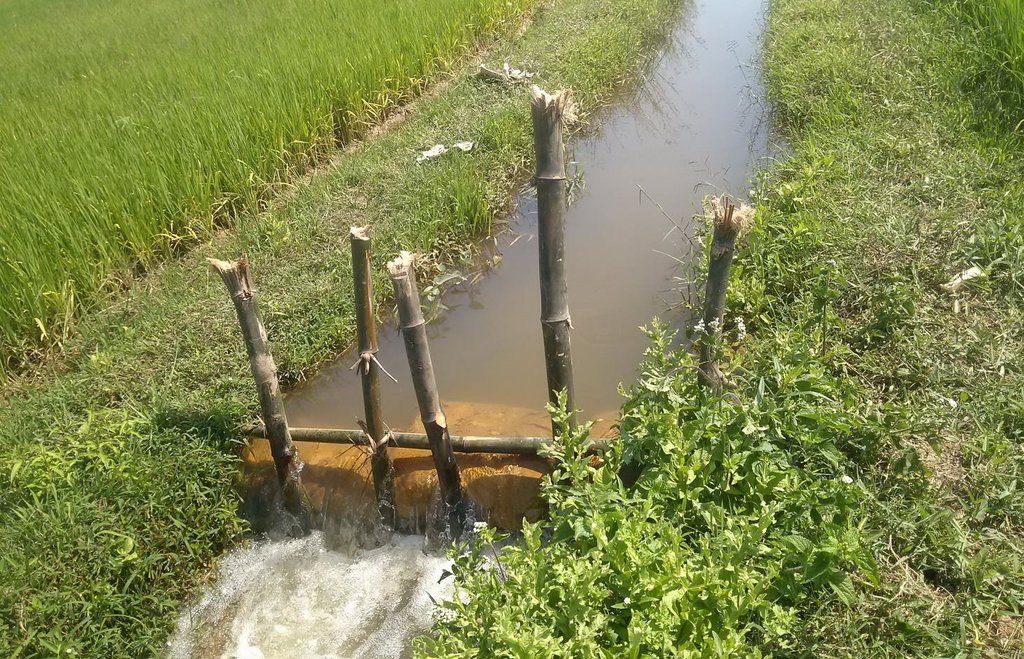
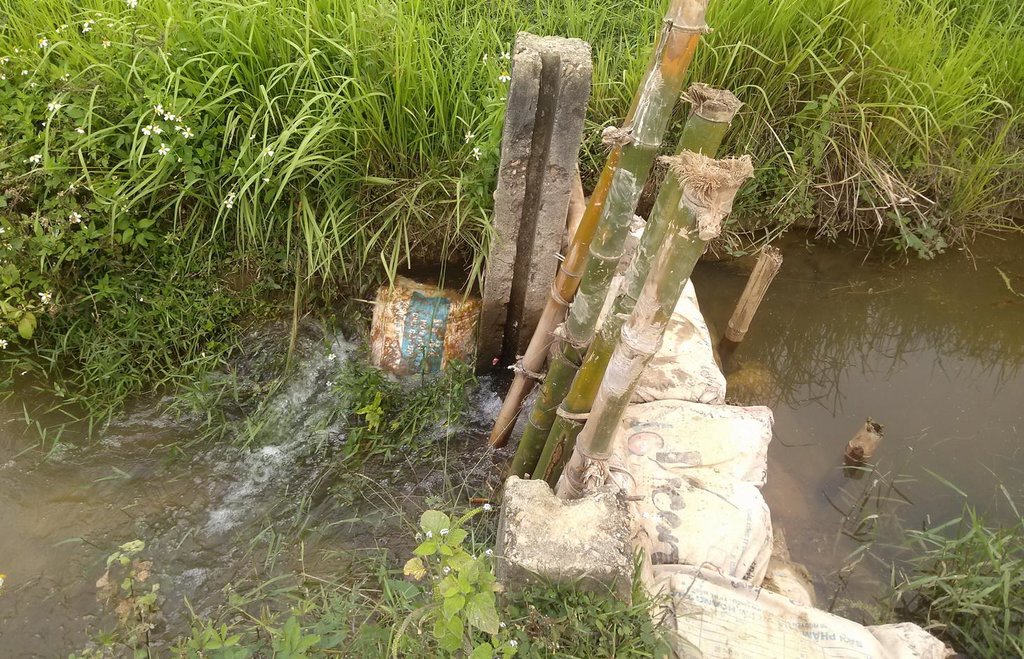
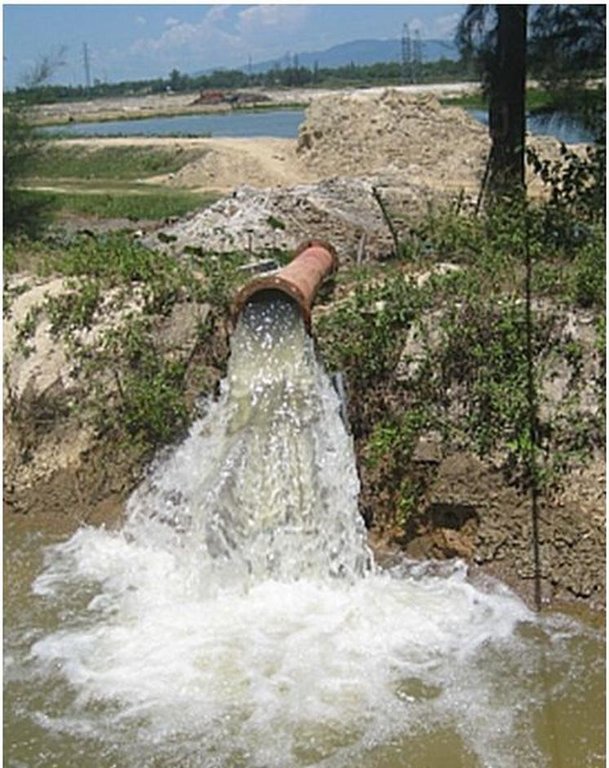
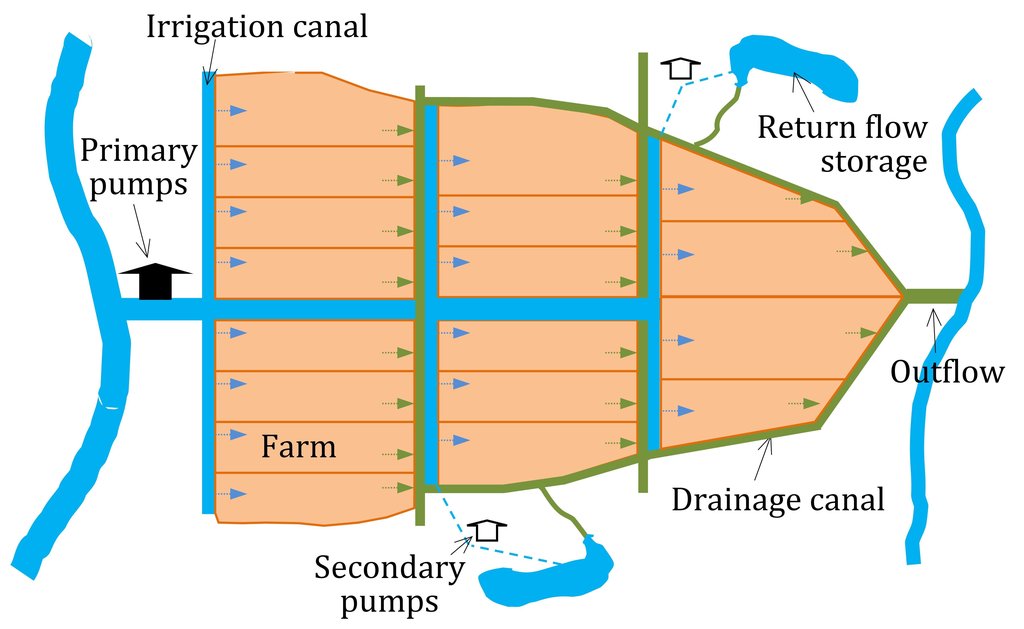
Return flow from paddy fields is defined as applied water that is not lost by evapotranspiration but returns to an aquifer or surface water body (Womach, 2005). The two types of return flow are surface and sub-surface. Surface return flow accounts for the major proportion. If surface return flow is strategically collected before entering rivers, it can be used as an ‘extra’ effective source of agricultural water supply (Phil King, 2008; Simons et al., 2015). Because paddies effectively purify water by absorbing nitrogen and phosphorus, this produces return flow of an acceptable quality for irrigation purposes. Return flow can be collected by drainage canals and stored in ponds and reservoirs, and then returned to pumps for reapplication. This technology offers one solution towards overcoming a deficit of irrigation water.
The goal of this technology is to store and reuse surface return flow from paddy farms to enhance irrigation efficiency. The purpose of constructing temporary barriers in drainage canals is to minimise water wastage and optimise the possibility of collecting and recycling surface return flow. Return flow from irrigation system is stored in surrounding ponds and reservoirs Return flow can only be used when it is captured in a storage structure or drain which has a hydraulic link to the irrigation source: thus an integrated framework for the reuse system consisting of both hydraulic, and management, links should be established. Within the scope of this study, the Water Management Unit (WMU) is understood as an integrated irrigation and drainage system consisting of four components: (i) the hydrological catchment which covers both non-irrigated and irrigated area; (ii) the source scheme generating return flow; (iii) the reuse scheme that is hydraulically connected with the source scheme; and (iv) a drainage system functioning as a harvesting as well as a supply structure.
Before implementing such a system it is recommended to analyse the correlation between irrigation efficiency and reuse of return flow, as well as developing a framework for managing and recycling return flow. Investigation aims at identifying the potential of return flow for irrigation; determining its quantity and quality; and developing an efficient and sustainable reuse framework. Water balance calculations, field measurements, water quality sampling and interviewing are all used for this purpose.
In the study area, long dry seasons cause severe water shortages and problems with saline intrusion. The study area is mainly covered by paddy, vegetables and other annual crops such as maize, sweet potatoes, peanuts and sugarcane. Paddy rice, which consumes a high proportion of the freshwater, is the dominant crop. Agricultural land in the downstream area is irrigated through gravity or pump irrigation systems. Here results indicate that the irrigation efficiency can be improved significantly: the irrigation efficiency of Tu Cau and Thanh Quyt irrigation schemes is projected to increase respectively by 1.8 and 1.4 times.
Reuse of return flow can be applied in all WMUs where the drainage canals are connected with storage tanks. Scientific and technical support tools are offered by the Vu Gia Thu Bon River Basin Information Centre. The centre was established in Danang providing a comprehensive information service to farmers and other water users – it includes capacity building and consulting services also.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Viêt-Nam
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Quang Nam
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Dien Ban
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- préserver l'écosystème
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The lowland part of Vu Gia Thu Bon is an intensive agricultural area. Rice cultivation, which consumes a high proportion of fresh water, accounts for 70% of total agricultural land (Ribbe et al., 2011). Since 2005, due to the impacts of droughts and saltwater intrusion, water for irrigation during the dry seasons has become an increasing problem in the lowland area of this basin. Simultaneously, the irrigation efficiency of this region is relative low. Various measures are applied to address water scarcity for irrigation. Reusing return flow is regarded as a potentially new measure to reduce the severity of the irrigation deficit in dry periods.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Based on the information provided by the Department of Natural Resources and Environment (DONRE) for Quang Nam Province, this basin now faces the problem of temporarily insufficient irrigation water. This situation is caused by droughts, insufficient reservoir capacity, salinity intrusion and ineffective irrigation management.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pleine irrigation
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 130, Longest growing period from month to month: 20th December to 28th April; Second longest growing period in days: 110, Second longest growing period from month to month: 20th May to 06th September
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.916 m2.
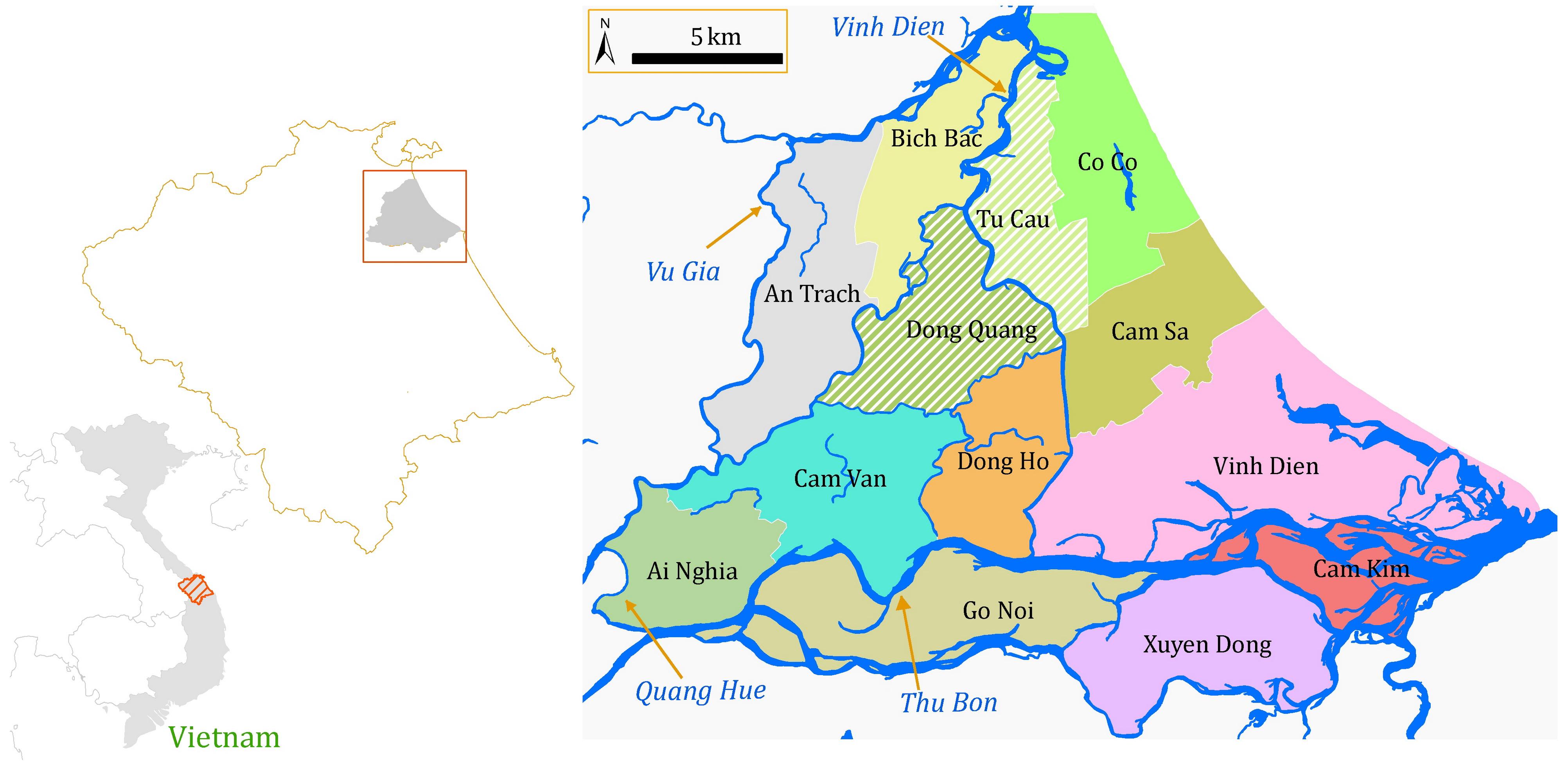
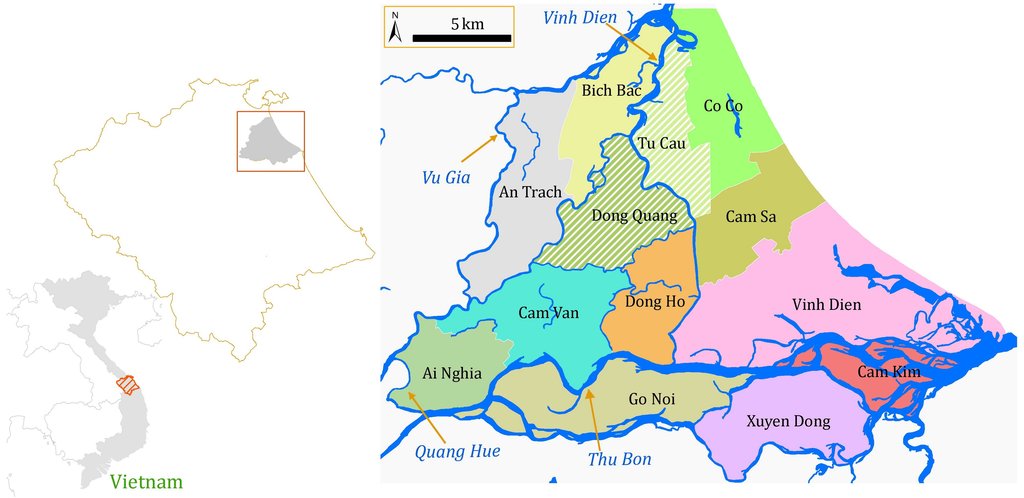
The research area is located in the downstream of the Vu Gia Thu Bon Basin (VGTB), Central Coast of Vietnam. Based on the hydraulic connectivity, the lowland of the VGTB is divided into 13 Water Management Units (WMU) (Viet, 2014). Of which, the Dong Quang and Tu Cau WMUs are selected to conduct the field survey and water quality sampling.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Paddy rice requires huge amounts of water. Meanwhile, the coefficient of irrigation return flow from paddy field is also quite high.), industrial activities and mining (Hydropower construction reduces water availability for irrigation), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (It causes water waste and reduces irrigation efficiency.), change of seasonal rainfall (It affects the paddy water balance and actual irrigation need.), droughts (It causes saltwater intrusion.)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (It relates to evapotranspiration.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …), governance / institutional
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Methods of recycling return flow from paddy fields: The surface return flow can be captured by drainage canals and stored in tanks: return water from these reservoirs is pumped back into irrigation canals.
In 2012, the first on-farm irrigation structure was initially implemented in the Tu Cau WMU in order to use return flow for irrigation purposes. The existing Sen Pond was enlarged and a temporary pumping station was installed to pump water into the irrigation canal system.
According to the pumping diary of Tu Cau station (in Winter-Spring crop 2013), there were totally 7 irrigation periods (8-11 days/period). Total input water (including effective rainfall) during the measuring period from 01 March to 10 April was about 28,000 m3. Meanwhile the total volume of return flow of the Tu Cau site was 16,176 m3. This amount of return flow has the potential to irrigate the agricultural area for about 16 days, equivalent to one and a half irrigation periods. The overall efficiency of the irrigation system will be significantly improved.
Location: Lowland area of VGTB Basin. Quang Nam Province
Date: January 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 194.9
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 399.4
Wall/ barrier
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.25
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.26
Construction material (other): Stone, sandy bags and bamboo sticks
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 116764.59m3
Catchment area: 77860 m²m2
Beneficial area: 30 ham2
Other type of management: Return flow is the part of drainage flow, it is necessary to enhance the institutional link to develop the reuse framework for the study area. Think about reforming IMC to IDMC with D is drainage.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
VND
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
20828,0
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building temporary barrier in drainage canal | Structurel | |
| 2. | Dredging and expanding Sen Pond | Structurel | 12 months |
| 3. | Installing and operating the temporary pump at Sen Pond, P is 15KW (Q=520-600m3/h) | Structurel |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | 1,0 | 3046,52 | 3046,52 | ||
| Equipements | machine use | 1,0 | 5344,09 | 5344,09 | ||
| Equipements | hammer, iron wire | 1,0 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 100,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone,sandy bags,bamboo sticks | 1,0 | 6,45 | 6,45 | 100,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Earth, concrete | 1,0 | 1335,8 | 1335,8 | ||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 9735,26 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Temporary barrier | Structurel | each cropping season |
| 2. | Temporary pump | Structurel | annually |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | 1,0 | 24,0 | 24,0 | 30,0 | |
| Equipements | machine use | 1,0 | 38,41 | 38,41 | ||
| Matériaux de construction | Stone,sandy bags,bamboo sticks | 1,0 | 3,22 | 3,22 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 65,63 | |||||
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Prices of the material and equipment; the approval procedure and disbursement process of the project of “Dredging and expanding Sen Pond”; the compensation cost for the farmers; the cost of operating and maintaining temporary pump; the cost of reinforcing the drainage canals.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Average annual rainfall in period 1978-2010 of research area is 2105mm. February to April is driest period as rainfall in this period accounts only 3-5% of annual rainfall.
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics. humid tropical monsoon climate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 3% of the land.
2% of the land users are rich and own 7% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
2% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is a large industrial park located near the study site and a large part of the working population in the region is earning income by working in the factories.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- farmer, individual
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- farmer, individual
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
A small farming area within an irrigation scheme will be used to store drained water.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology helps to minimise negative impacts of saltwater intrusion on irrigation
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology helps to reduce water abstracted from river in dry periods when saltwater intrusion occurring
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Increased irrigation efficiency
Quantité avant la GDT:
37%
Quantité après la GDT:
68%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The irrigation efficiency is improved significantly (increasing about 1.8 times) in the case of recycling return flow
Impacts socioculturels
apaisement des conflits
contribution to human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
This technology helps to minimise the damage to agricultural production caused by excess salt during the dry periods. It brings the benefits for the farmers by increasing the crop yields and helps to improve their livelihoods.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less freshwater is used for irrigation purposes
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Sols
humidité du sol
salinité
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
50/270 ha of the Tu Cau Irrigation scheme is additionally supplied water in the dry periods as rivers are affected by saltwater intrusion
Autres impacts écologiques
Loss of land for enlarging the Send Pond
contamination of reused water by agro-chemicals
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 50-90%
Commentaires:
By applying the technology, the potential reuse area of return flow is estimated about 33% of the study area (30.4ha of agricultural area is potentially irrigated by return flow). However, estimating the number of land user families that have implemented the technology is not the initial aim of the study. Therefore, it requires further detailed investigation and social survey as well.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Increases the water depth in paddy fields which helps to improve paddy productivity |
| Beneficial/ endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Using return flow is helpful to improve irrigation efficiency. The amount of extracting water for irrigation and the cost of operating an irrigation system can be reduced. |
| The measure contributes to mitigating negative impacts of drought and salt intrusion. During the dry season the river water becomes more and more saline due to salt water intrusion. Salinity also builds up from not leaching out salts in the subsoil |
| Take advantages of available drainage canals, ponds, reservoirs to reduce the investment costs |
| Acceptable water quality because of the purification function of paddies which removes nutrients from the water |
| Low costs of conveyance systems because of short distance. More flexibility of allocation because of stable return flow. Less conflict between sectors. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Temporal and spatial variation causes difficulty in using return flow. The differences in soil type, terrain, storage capacity of the paddy fields and irrigation method (e.g. irrigation techniques, the amount of input water and pumping intervals) are major factors influencing the quantity of return flow | Constructing temporary barriers in the drainage canal helps to minimise the water wastage and optimise the possibility of collecting and recycling surface return flow. |
| Using return flow might spread diseases, and weed seeds from affected farms to safe farms | Encourage farmers to comply with the principles of prevention and control diseases in agricultural production. It is necessary to implement preliminary tests and analyses the quality of return water before recycling for irrigation purposes. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Kim, H. K. et al. (2009) Estimation of irrigation return flow from paddy fields considering the soil moisture
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Agricultural Water Management, 96(5), 875–882.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Phil King (2008) Return Flow Efficiency
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Simons, G.W.H. et al. (2015) Water reuse in river basins with multiple users: A literature review
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Journal of Hydrology. 558–571
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Ribbe et al. (2011) Annex 2 to Milestone Report 2011 - Description of the Study Region including an updated stakeholder analysis,
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
LUCCi project. ITT, Cologne University of Applied Sciences
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Vu Gia Thu Bon River Basin Information Centre [Viêt-Nam]
The VGTB River Basin Information Centre (RBIC) offers decision support tools for stakeholders and aims at providing comprehensive information and consulting services to the water and land users according to their demands.
- Compilateur : Justyna Sycz
Modules
Aucun module trouvé