Rock catchment [Kenya]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Fredrick Ochieng
- Rédacteurs : Nicole Stolz, Boris Orlowsky
- Examinateurs : Boris Orlowsky, Renate Fleiner, Alexandra Gavilano
Rock catchment
technologies_580 - Kenya
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Fredrick Ochieng:
Kenya
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
21/09/2016
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology has instead addressed the perennial water shortage among the beneficiary households.
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Partnership with beneficiary communities in project implementation [Kenya]
The approach focuses on community engagement on a partnership basis. The model is a departure from the traditional approaches where the community mostly is reduced to being a beneficiary of project services without substantive responsibility.
- Compilateur : Fredrick Ochieng
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
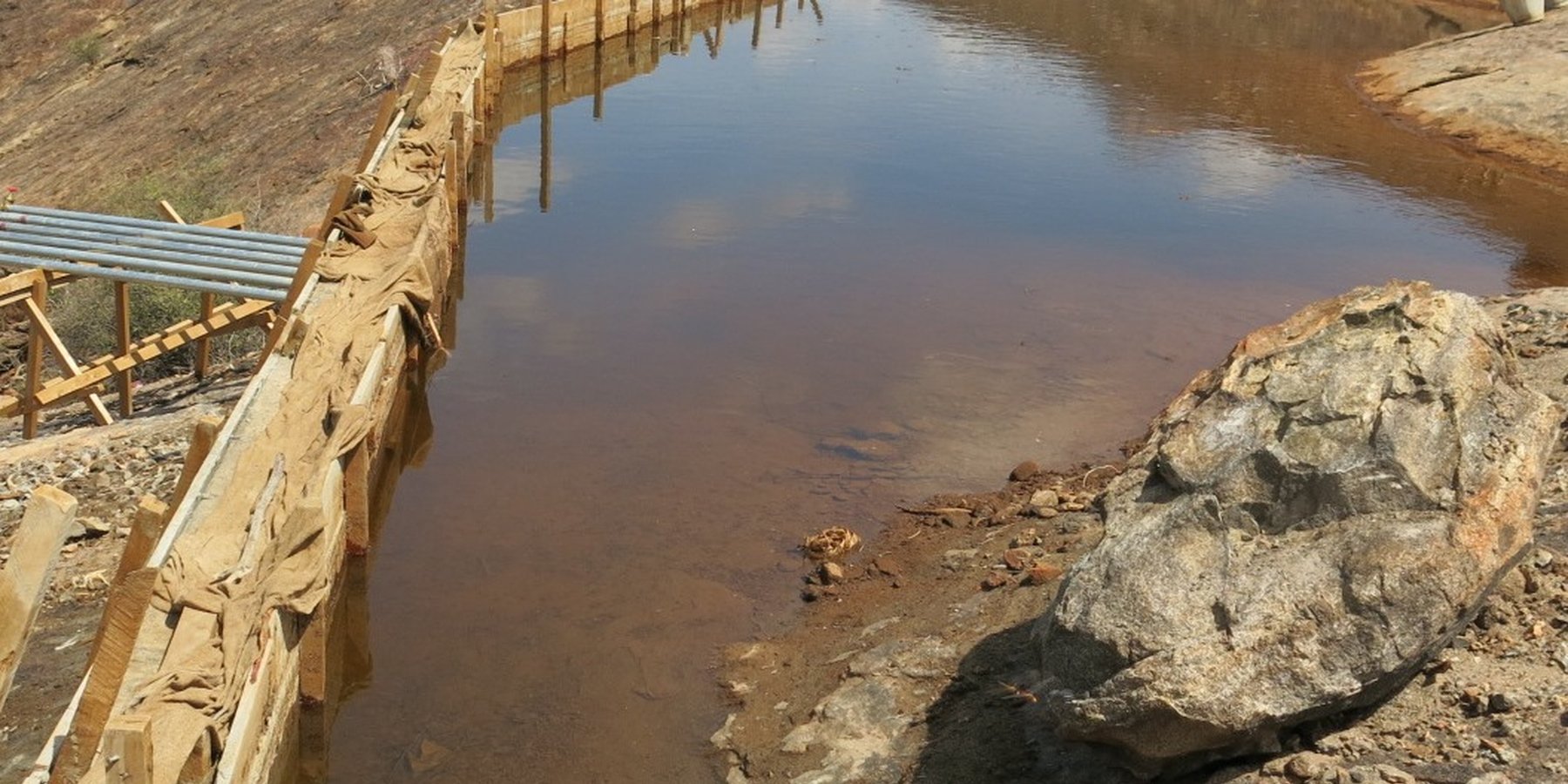
A rock catchment system is a water harvesting structure comprising a bare
sloping rock surface (impounded area), a constructed concrete wall at a
strategic point (weir), pipeline from the weir to the storage tank(s),
storage tanks and water kiosk(s) connected to the water tanks by pipelines.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The Technology is built on a gently sloping outcrop on the hillside. The bare
rockface is the surface from which rainwater is harvested. A weir is constructed at a
strategic point for maximum collection towards the foot of the hill. The weir dams hold
harvested water in the rock catchment and channels the water through a piping
system to reservoirs, generally masonry tanks, located below the hill. A weir is
usually a concrete wall constructed and reinforced with iron bars to give it
adequate strength to withstand the weight of the dammed water. The length, height
and thickness of a weir varies with the size and the slope of the rock catchment area.
On average, a weir will be 10 meters long, 2 meters high and 0.5 meters thick. At
the base of the weir, an infiltration box of approximately 1 square meter is
constructed and filled from the bottom with fine sand, coarse sand and gravel (in that
order) for the purpose of sieving out impurities before the water reaches the tanks.
Metal piping is recommended for connecting the weir to the storage tanks
downhill due to the high pressure exerted by owing water. The piping distance
ranges from 15 to 300 meters from the weir to the storage tanks. Provision is
usually made for additional pipelines in case there is need for expansion of the system.
At the bottom of the hill, masonry tanks are constructed, ranging from 100 cubic
meters capacity, or greater, depending on the impounded area,
population, and available resources. The pipes join the tanks through a control
chamber meant for regulating water flow into the tanks. Adjacent to the tanks are
water 'kiosks' where the community draws water. To gauge how much water is
issued, a meter is fitted inside the kiosk. Metering the water is a measure for
accountability and control. Construction of a rock catchment system needs
heavy investment in materials - cement, quarry stones, ballast, iron bars, sand,
hard-core stones, water, metallic (galvanised iron) pipes and plumbing
installations. Construction of the system is labour intensive in terms of both
skilled and non-skilled personnel. The main purpose of the rock catchment
system is to harvest, and store rainwater for domestic - and some livestock -
use. In the case of the documented project, the benefiting communities are
pastoralists who live in northern Kenya, a region characterised by chronic
droughts, seasonal floods and acute water shortages. The water situation is
aggravated by increasing drought frequency and severity. On the other hand, the
little rain received has often been destructive downstream, cutting through roads
and causing massive soil erosion due to high water velocity. During the dry
periods when open water sources such as earth pans dry up, women travel long
distances to search for water from hand dug shallow wells within dry seasonal
riverbeds ('sand rivers').
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
The weir which dams rock surface runoff when it rains channelling the water into the piping system which takes the water into masonry storage tanks.
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
Rock catchment showing how the system harvests water and channelled down to water storage tanks.
Date:
08/12/2014
Lieu:
Ndikir village, Marsabit County, Kenya
Nom du vidéaste:
Fredrick Ochieng
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kenya
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Laisamis sub county, Marsabit County, Kenya
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Implemented with three different communities in three locations, Ndikir, Manyatta Lengima and Mpagas.
Commentaires:
The Technology was implemented with three different communities in three locations, Ndikir, Manyatta Lengima and Mpagas.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2015
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology was introduced after technical assessments which looked at areas that had rock catchment potential with willing communities to participate in their construction.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- préserver l'écosystème
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
- The common hazard in the region where the Technology has been implemented is drought. The Technology aims at reducing the drought impacts among the pastoralists
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Semi-nomadisme/ pastoralisme
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
Camels, cattle, donkeys, goats, sheep
Commentaires:
The pastoralists practice sedentary to semi-nomadism way of living. However, even for those who are sedentary, they do not cultivate land. They entirely rely on livestock and relief assistance.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Précisez:
Do not apply as the communities to not grow crops. However, there is a bi-modal rainfall season with more rains received between October to December.
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
The livestock owners constantly move with their livestock from one location to another.
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
- mesures en travers de la pente
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
- S7: Collecte de l'eau/ approvisionnent en eau/ équipement d'irrigation
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
- Hp: baisse de la qualité des eaux de surface
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
A Rock catchment consists of the following main components:
Catchment area - vary between more or less than 100 square meters
Infiltration box - concrete box with approximately one square meter and 0.5 meters deep
Weir - a wall approximately 20 meters length, approx. 0.3-0.5 meters width, and 1.5 meters height; depending on the site the catchment can store between 150 and 700 cubic meter above the weir
Pipes - Galvanised steel pipes of varying diameters and length depending on catchment size and storage location and capacity
Tanks - tanks with varying capacities, of the same order of magnitude as the catchment storage capacity above the weir. Together, tanks and catchment can store some 10-20% of the annual precipitation falling over the rock catchment, which is enough to sustain water use during a normal year, but not during a year of exceptional water scarcity.
Here is a link where you can see a sketch of typical rock catchment: http://www.climatetechwiki.org/sites/climatetechwiki.org/files/images/extra/media_image_3_22.png
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
A unit comprises the key component of the Technology. The rock catchment technology has four components - the weir, piping, tanks and water kiosk
Spécifiez le volume, la longueur, etc. (si pertinent):
N/A
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
15 dollars per day for skilled labour and 3 dollars per day for unskilled labour.
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Surveys - topographical, environmental impact assessment | Autres mesures | no specific time |
| 2. | Drawings and bill of quantities | Autres mesures | no specific time |
| 3. | Procurement of materials | Modes de gestion | advisable should be done during the dry season when roads are passable without difficuities |
| 4. | Recruitment of artisans | Modes de gestion | no specific time |
| 5. | Start of construction works | Structurel | no specific time |
| 6. | Continuous technical supervision and completion | Structurel | Continuous throughout the year |
Commentaires:
The key activities are not generally affected by the seasonality or any other type of timing with exception of procurement, for which it is advisable to do it when roads are passable.
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Si possible, ventilez le coût de la mise en place selon le tableau suivant: spécifiez les intrants et le coût par intrant. Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de ventiler le coût, donnez une estimation du coût total de la mise en place de la Technologie:
1,0
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Skilled labour | Days | 607,7 | 15,0 | 9115,5 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Unskilled labour | Days | 1973,0 | 3,0 | 5919,0 | 40,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Construction materials for all the four components together | 1 catchment system | 1,0 | 75407,0 | 75407,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 90441,5 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Caritas Switzerland
Commentaires:
The project was implemented with funding support from Caritas Switzerland to assist the community recover from the 2011 devastating drought experienced in Kenya and the entire Horn of Africa
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Periodic washing of tanks and scooping out of sand and silt at the weir | Structurel | Twice a year |
| 2. | Repairs of broken parts - valves, pipes, taps etc.. | Structurel | Through the year |
Commentaires:
Rock catchment systems generally have minimal maintenance and repairs
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Si possible, ventilez le coût de l'entretien selon le tableau suivant: spécifiez les intrants et le coût par intrant. Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de ventiler le coût, donnez une estimation du coût total de l'entretien de la Technologie:
1,0
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autre | Seasonal scooping of sand and silt from the weir | seasons/year | 2,0 | 100,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Broken parts and repairs | lumpsum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 500,0 | |||||
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
1. Availability of parts, whether they can be bought locally or from far
2. Quality of parts
3. Extent of the system exposed to vandalism and/or destructive weather events
4. Early detection of broken/spoilt parts
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The are two rainy seasons annually. The long rainy season start in March to May and short rainy season begins in October and ends in December. There has been however variations in the recent years mostly seen on rainfall variability in distribution, amounts and seasonality.
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Amount of rainfall received annually coupled with high rates of evapotranspiration cannot sustain crop farming.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The Technology applies where there is adequate gradient of a rock surface.
5.3 Sols
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
The technology is implemented on a rock surface.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Oui
Précisez:
The community currently benefiting from the rock catchment have reported health problems (kidney stones) due to use of salty borehole water. The water is saline.
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
The borehole which has been the main source of water is strongly saline and the community only use it when they can no longer find water from nearest (approximately 5 kilometres away) shallow wells. In addition, the borehole is run by diesel generator attracting high operations and maintenance costs. Earlier, breakdowns would necessitate water relief from NGOs and the government.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The area is covered with arid and semi arid type of vegetation mostly characterised by acacia trees and other thorny shrubs. There is limited variety of wild animals, insects and birds. This could be due to harsh climatic conditions.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
- Semi-nomade
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- enfants
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Not applicable. The land use system is communal and without clear demarcations from one community to another. The herders constantly move from one area and region to another in search of pasture and water resources.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
Quantité avant la GDT:
600 cubic meters
Quantité après la GDT:
3800 cubic meters
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The community almost every year would need emergency water trucking. This is not so anymore.
qualité de l'eau potable
Quantité avant la GDT:
Borehole water was the only alternative source during dry season
Quantité après la GDT:
Water free of salt is now available and adequate for domestic use
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
They no longer use the the highly saline water which has been reported to have adverse negative health effects. The harvested water is easy to treat for microbial contamination at the household level.
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Quantité avant la GDT:
N/A
Quantité après la GDT:
N/A
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The harvested water from the rock catchment is mostly for household use.
qualité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Quantité avant la GDT:
N/A
Quantité après la GDT:
N/A
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The harvested water from the rock catchment is mostly for household use.
Revenus et coûts
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The time women used to spend in search of water has drastically reduced. They are now freer to engage and participating in social local networks and small businesses.
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Women have benefited hugely from this Technology. Before the intervention, they would walk up to 5 kilometres in search of water for domestic use. This was particularly worse during drought or an extended dry spell as they also had to queue for many hours a day to get the water from available water points.
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Reduced conflicts over scarce water resources
Quantité avant la GDT:
N/A
Quantité après la GDT:
N/A
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The pastoralist communities have in the recent decades experienced resources-based conflicts. These conflicts happen at regional, communal and family scales. The communities and families benefiting from this intervention no longer have to fight over the resource because it is adequate.
Impacts socioculturels
situation sanitaire
Quantité avant la GDT:
Little water available for hygiene practices such as handwashing
Quantité après la GDT:
Additional of 30 litres per day now available for good hygiene practices
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The availability of water have drastically improved hygiene practices.
institutions communautaires
Quantité avant la GDT:
No properly functioning water managment committee
Quantité après la GDT:
There is a vibrant and dedicated water management committee
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The implementation of the Technology has invigorated the community members and they have shown better organisation to prudently manage the water system. The management committee was existing before the technology was implemented when they managed other water sources. However, the motivation then was low coupled with low capacity to operate and maintain the water sources they had.
apaisement des conflits
Quantité avant la GDT:
Several occurences of conflict over water
Quantité après la GDT:
No more reason for conflict
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The pastoral communities have in the recent decades experienced resources-based conflicts. These conflicts happen at regional, communal and family scales. The communities and families benefiting from this intervention no longer have to fight over the resource because it is adequate.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Quantité avant la GDT:
About 6 hours spent a day in search of water especially during the dry season
Quantité après la GDT:
A maximum of 30 minutes spent by a woman to fetch water
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The Technology benefits women most who traditionally are socially and economically disadvantaged. Now they have more time to engage in other profitable activities. The Technology has also taken away the burden of proving water for the households, freeing them for greater social engagement
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Water that would normally be lost almost after it has rained is now stored and kept for future use.
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
All rainwater from the developed catchment was lost each time it rained.
Quantité après la GDT:
About 3500 cubic meters of water is retained within the locality of the community
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
There is increased control of surface runoff reducing its damaging effects on soil, vegetation and infrstrature. However, the the scale to which this is realised is low.
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Quantité avant la GDT:
N/A
Quantité après la GDT:
N/A
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The rock catchment do not in any way lead to increased groundwater recharge.
Sols
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
N/A
Quantité après la GDT:
N/A
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to reduced amount of water flowing from the hillside downstream, the ability of water to erode soil downstream is reduced though at very low scale.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts de la sécheresse
Quantité avant la GDT:
Water emergency supply at least two a year during the two dry spells.
Quantité après la GDT:
No single water trucking done in the last two years
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Water has been the most affected livelihood commodity during drought events among the benefiting community. The impact had been acute water shortage leading to external emergency interventions. It was also happened that sometimes when food aid was provided, the community would have no water to cook. There is no longer need for water emergency in these communities.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The high velocity water from the hills have been a constant menace in cutting or blocking roads downstream with debris. The harvesting of water has reduced the impact of this water at some sections of the hilly landscape.
Commentaires concernant l'évaluation des impacts:
Some aspects of information are difficult to establish and could be best evaluated by a household survey.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures saisonnières | saison sèche | augmente | très bien |
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | modérément | |
| précipitations saisonnières | saison sèche | augmente | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | très bien |
| orage local | très bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | très bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The benefits are instantaneous as soon as the structure is completed and especially if it is during a rainy season. The technology has minimum to near zero maintenance costs which remains relatively the same in the long term. The main tasks for maintenance is seasonal removal of silt at the weir and the washing of the tanks.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- plus de 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
This is a one Technology which is benefiting the entire community. At the time of project implementation the estimated total population was 1000 people.
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 90-100%
Commentaires:
N/A
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
1. Relatively low cost of operation and maintenance. 2. The technology does not require specialised technical skills for the day to day operations |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| 1. Relatively high initial investment cost that is unlikely to be raised by communities themselves. Without external financial support it is therefore unlikely that the system can be expanded when water needs increase. |
1. A long term plan that includes savings from fees from water sales. 2. Funds could also potentially be acquired from the county government or NGOs |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
A field visit was done by the data compiler to meet with the land users
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
One meeting (Focused group discussion) was done with the beneficiaries of the Technology
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
Filling in some sections for the questionnaire required input from technical/specialist personnel who implemented the project. These are technical staff of Caritas Switzerland.
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
reference was made on technical documents of the project - proposals, technical reports (narrative, photos, videos).
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
A Handbook of gravity-flow water systems for small communities; Thomas D. Jordan Junior; 1980; 978 0 94668 850 0
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
CACH office library, Nairobi
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Rock Catchments for Community Water Supply in Eastern Equatoria State, South Sudan
URL:
http://waterconsortium.ch/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Poster_Rock_Catchments_Caritas_South_Sudan_2016.pdf
Titre/ description:
Adopting locally appropriate WASH solutions: a case study of rock catchment systems in South Sudan
URL:
http://wedc.lboro.ac.uk/resources/conference/37/Leclert-1935.pdf
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Partnership with beneficiary communities in project implementation [Kenya]
The approach focuses on community engagement on a partnership basis. The model is a departure from the traditional approaches where the community mostly is reduced to being a beneficiary of project services without substantive responsibility.
- Compilateur : Fredrick Ochieng
Modules
Aucun module trouvé