Backyard fish farming in tarpaulin ponds for improved livelihood [Ouganda]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Aine Amon
- Rédacteurs : Drake Mubiru, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- Examinateurs : Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Okutunga Ebyenyanja omu ntundubale
technologies_3391 - Ouganda
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
David Mawanda
Uganda, Bushenyi, Kagoma
Ouganda
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - Ouganda1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
23/01/2018
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
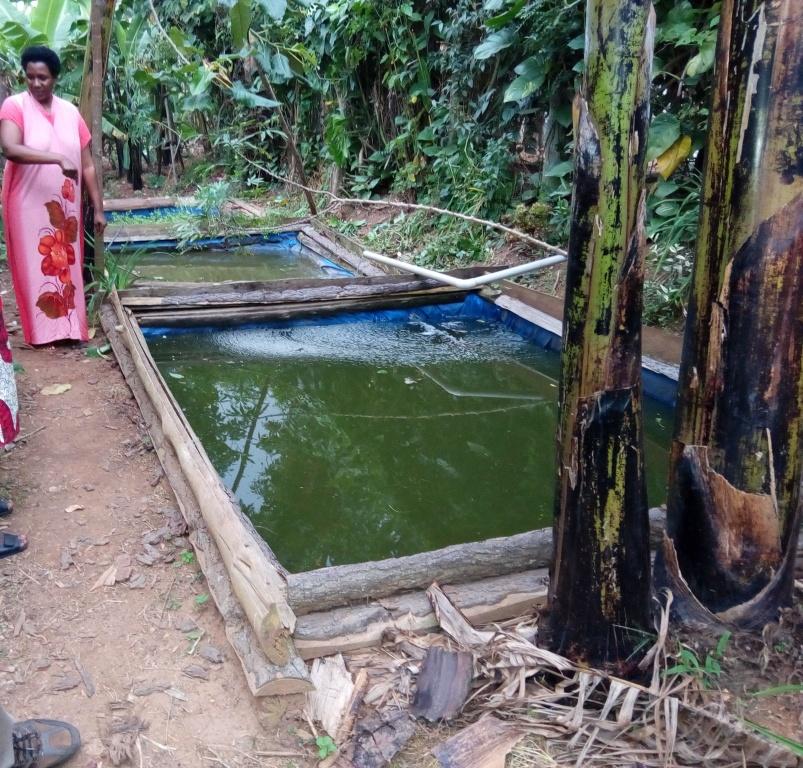
A fish pond for intensive commercial fish farming is constructed in the backyard of the farmer's home for easy management. The pond is lined with a tarpaulin interior and is connected to a water source for water supply during the seasons of water scarcitiy.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
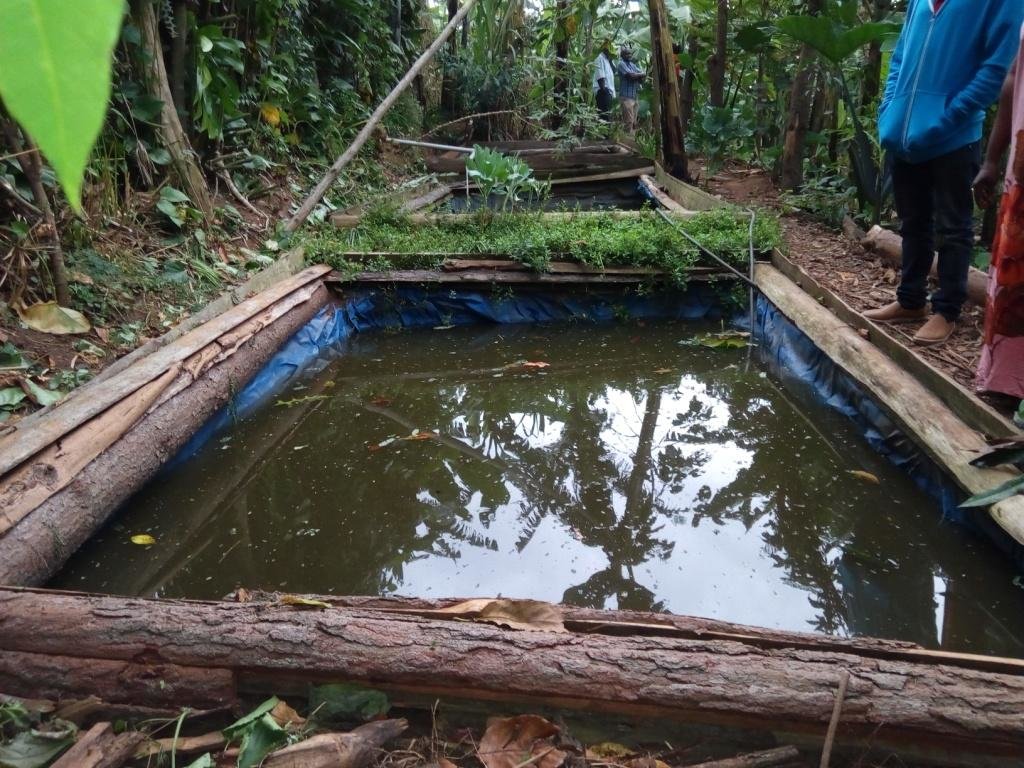
The backyard fish pond farming system is a simple commercial fish farming system established close to the farmers’ home stead. It is planned to ease management of rearing the fish and to minimize maintenance costs. The system is also designed to harvest rain water and overflow which eases filling and emptying of the pond with water. The walls of the ponds are lined with tarpaulin and the banks are strengthened with timber or brick work to prevent breaking of the walls. The three ponds in Bushenyi-Kigoma are located on a gentle slope and designed with a trench that feeds them with rain water from the rain harvest reservoir up slope. They were constructed in 2013 and are located a meter away from a live fence enclosing the farmer’s house. This makes it easy for the farmer to access, monitor and manage the fish ponds.
The establishment process for each pond is simple and may not require technical skills to set up the system. The activities involved include:
i.Excavation of the pond, which is best done during the dry season to avoid interruption by runoff.
ii.Strengthening of banks using timber and nails (some farmers use brinks, cement and sand)
iii.Lining of the water proof tarpaulin on the interior of the pond.
iv.Construction of a water channel from the water reservoir to the pond and fixing of overflow pipes at the deeper end of the ponds.
v.Filling the pond with water and applying animal dug to fertilize the ponds. This creates a favorable environment for growth of microorganisms and algae on which fish can feed.
vi.The fish fingerlings are introduced into the pond two weeks after fertilization with animal dug.
The maintenance activities include; cleaning of ponds from contamination of objects, changing of the pond water on a monthly basis to avoid contamination that may lead to infestation and application of organic fertilizers.
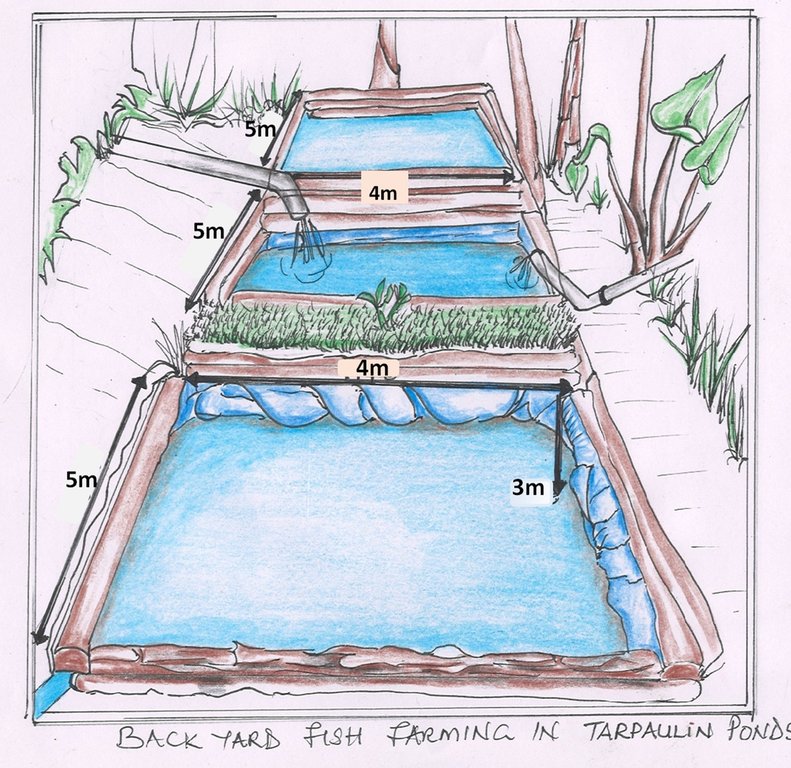
Establishment requires a hoe, panga, dibber, spade, wheel barrow, hammer and the trowel. The inputs include; timber, tarpaulin, cement, garters bricks, sand, nails, plastic pipe, water, animal dung, fish pellets and fish fingerlings. These where used to construct a pond 5 m × 4 m × 3 m i.e length × width × depth respectively, with a maximum carrying capacity of 500 cat fish.
The costs of setting up the system are relatively affordable to the average local people according to the farmer. The key determinants are hiring labor to excavate the ponds, construction of a water channel and stocking fish fingerlings which are all locally available. The maintenance activities involve daily feeding of fish, cleaning in case of contamination, changing the pond water every 3 months and harvesting of fish at 7 months of age. The farmer spends USD $ 164.65 on establishment of the pond system including, exaction costs, equipment, materials and stocking fingerlings (USD $ 0.033 each). The farmer spends USD$ 21.99 on premixed feeds before harvesting the fish after seven months. The cat fish are harvested with 3-5 kg liveweight after 7 months and sold at USD$ 2.75 to wholesale buyers from Kasese District.
The intensive fish farming system is designed to demand minimal labor for feeding the fish, cleaning the pond, replacing water and harvesting fish. The system is also adapted to water scarcity in the dry season since it is connected to a rain water harvest system; regular changing of pond water improves visibility, removes algae, replenishes oxygen and minimizes possible infections in the pond.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
The Video shows the set up of the ponds but does not include the farmer's house because of the live fence separating the ponds from the house.
Date:
24/01/2018
Nom du vidéaste:
Amon Aine
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ouganda
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Western Uganda, Bushenyi District
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Nyabubare Sub county, Kigoma town
Commentaires:
The farm is 6Km from Ishaka Bushenyi along Bushenyi-Rubirizi highway.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2016
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Intensive back yard fish farming.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
- Beauty
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
Bananas, yams and shrub fence
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
The farmer harvests roof top water and channels it into the ponds during times of water scarcity
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
March - May & Sept - Nov
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
500 fish per 5m×4m×3m in length, width and depth respectively
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- apiculture, aquaculture, élevage de volailles, de lapins, du ver à soie, etc.
- Jardins/ potagers familiaux
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation physique des sols
- Pu: perte de la fonction de bio-production en raison d’autres activités

autre
Commentaires:
The intensive method utilizes small space for high quantity fish production and therefore reduces the conversion of large pieces of land to fish farming
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
The design promotes intensive methods to utilize small space for high quantity fish production and therefore reduces the conversion of large pieces of land to fish farming.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
The water ponds are constructed with 5m × 4m × 3 m i.e length × width × depth. The ponds are on a gentle slope a meter away from a live fence. The ponds are lined with a water proof tarpaulin. The banks are strengthened with wood fixed together with nails.
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Pond
Spécifiez le volume, la longueur, etc. (si pertinent):
5m × 4m × 3 m i.e length × width × depth respectively
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ugandan shilling
Indiquer le taux de change du dollars en monnaie locale (si pertinent): 1 USD= :
3650,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
10,000
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation | Structurel | In the dry season |
| 2. | Fixing of tarpaulin and timber on the banks | Structurel | After excavation |
| 3. | Filling pond with water and fertilizing with animal dug | Modes de gestion | After fixing walls |
| 4. | Stocking the pond | Autres mesures | 2 days after filling pond with water and fertilization |
| 5. | Connecting a water channel from the water reservoir with a pvc pipe at end the end leading to the pond | Structurel | After excavation. |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Construction labour | man day | 5,0 | 50000,0 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hoe hire | per day | 500,0 | 5,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Panga hire | per day | 500,0 | 5,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spade hire | per day | 500,0 | 5,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hammer hire | per day | 500,0 | 5,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Wheel barrow hire | per day | 500,0 | 5,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Metallic tray | per day | 500,0 | 5,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Fish fingerlings | pieces | 500,0 | 500,0 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Animal Dung | kg | 50,0 | 120,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Tarpaulin | pieces | 1,0 | 45000,0 | 45000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Timber | pieces | 8,0 | 3000,0 | 24000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Nails | Kg | 0,5 | 8000,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Hose Pipe | Pieces | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Water | Liters | 500,0 | 10,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 609000,0 | |||||
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Feeding | Modes de gestion | Once daily |
| 2. | Cleaning | Modes de gestion | Once a week |
| 3. | Changing the water | Modes de gestion | Every three months |
| 4. | Harvesting | Modes de gestion | Every 7months |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Cleaning | man day | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Feeding | man day | 1,0 | 600000,0 | 600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Replacement of water | man day | 1,0 | 100000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Harvesting | manday | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Slasher | piece | 2,0 | 8000,0 | 16000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hoe | piece | 2,0 | 15000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Bucket | piece | 2,0 | 6000,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Cow dug | tones | 1,0 | 250000,0 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1023000,0 | |||||
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Excavation of ponds and stocking of fish fingerlings. Excavation is done once at the start of the project. The labour required for operation and maintenance is minimal compared to conventional fish farming methods.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The rain seasons are two i.e March-May, Sept-ov
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Oui
Précisez:
Cat fish doesn't thrive well in saline waters, the longer the water stays in the pond the more salts it accumulates due to waste from fish and feeds being used hence need for replacement every three months.
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The project belongs to a household of 5 children and parents in their 45-50 years
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Water from pond used for irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less labour cots for the operation & maintenance
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farmer has many other projects (piggery, bananas, yams)
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Water collected in ponds
ruissellement de surface
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
impacts de la sécheresse
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Harvesting of water for fish farming reduces the runoff and hence a reduction in the water volumes flowing down hill
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | très bien |
Commentaires:
During the dry season, the water harvested from the roof top is used to replenish the water in the ponds
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 10-50%
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 50-90%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- la disponibilité de la main-d'œuvre (par ex., en raison de migrations)
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
The system is designed to harvest water on roof tops and deliver it in the fishponds, Some of the harvested water is reserved for replenishing of water in the ponds during times of scarcity
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Easy management since most of the tedious work is at establishment |
| Easy to harvest the fish since many fish are keep in a small pond/tarpaulin |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| There is rady market for the fish |
| Rain Water harvesting reduces impacts of climate change on the fish production especially in the dry season/times of scarcity |
| Source of proteins for the public that buy the fish for sauce |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| At times of extreme dry season, the farmer may face challenges of water scarcity | Establishment of big enough water reservoirs |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Due to high stock ratio, the fish are prone to diseases/parasites in case of any break out | Reduction in the stocking rate, the farmer should farther maintain the hygiene and precaution in management |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
1 farm
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
1 farmer
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
1- a news paper that wrote about a similar pond system, in Masaka District
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes disponibles en ligne
Titre/ description:
Rear fish in your backyard with harvested rainwater
URL:
http://www.monitor.co.ug/Magazines/Farming/Rear-fish-backyard-harvested-rainwater/689860-2997914-vacgkk/index.html
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé