Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China [Chine]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Christian Rumbaur
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
膜下滴灌 (Chinese)
technologies_1305 - Chine
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 mars 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 mars 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 4 avril 2018 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 13 mars 2019 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Müller Joachim
+49 711 459-22490
joachim.mueller@uni-hohenheim.de
University of Hohenheim
Allemagne
Spécialiste GDT:
Zia-Kahn Shamaila
+49 711 459-23119
shamaila.zia@uni-hohenheim.de
University of Hohenheim
Allemagne
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Universität Hohenheim - Allemagne1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
14/05/2015
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Drip irrigation under plastic mulch, associated with drainage, to reduce water demand and improve cotton yields in Xinjiang Province, China.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
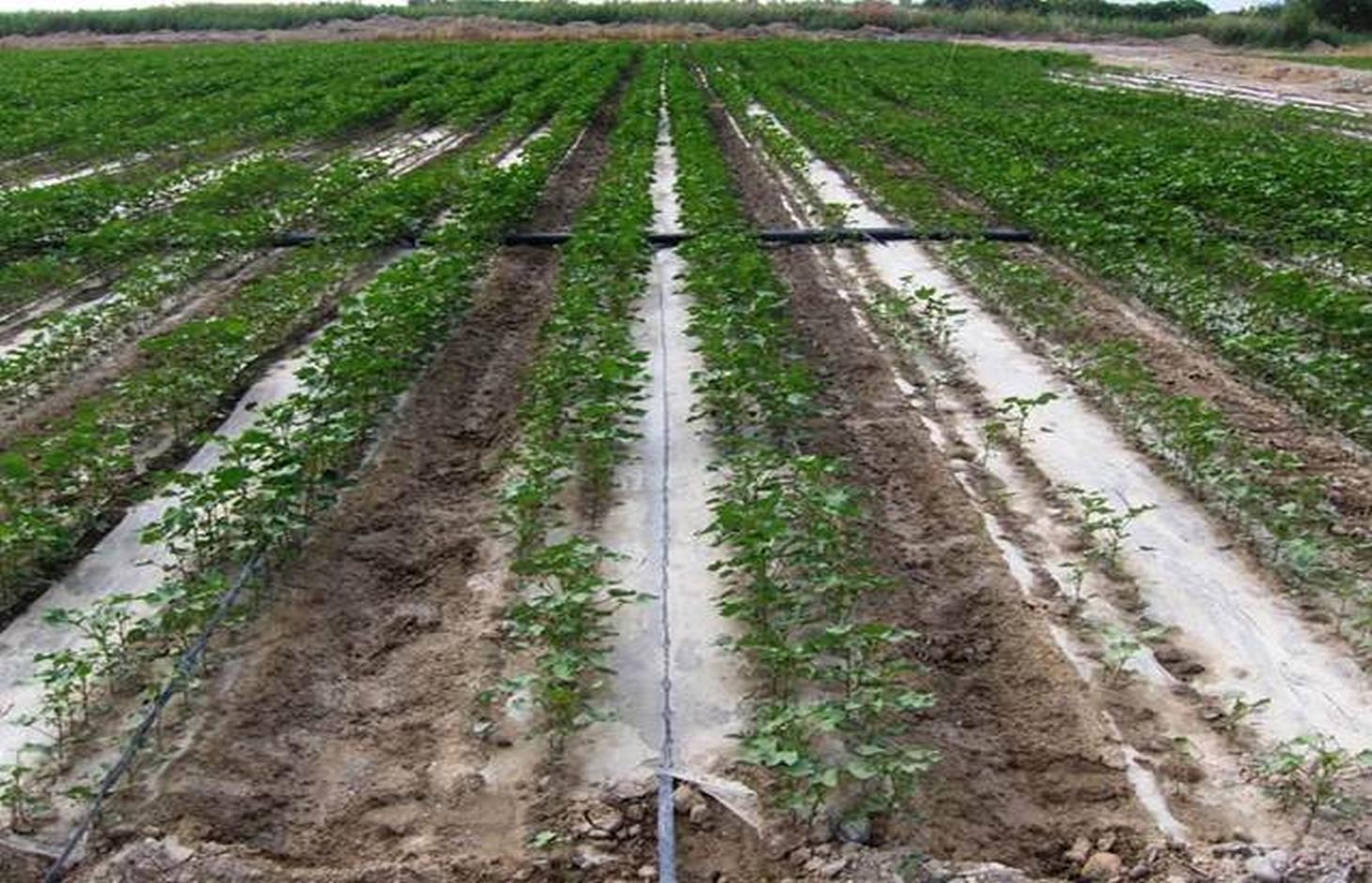
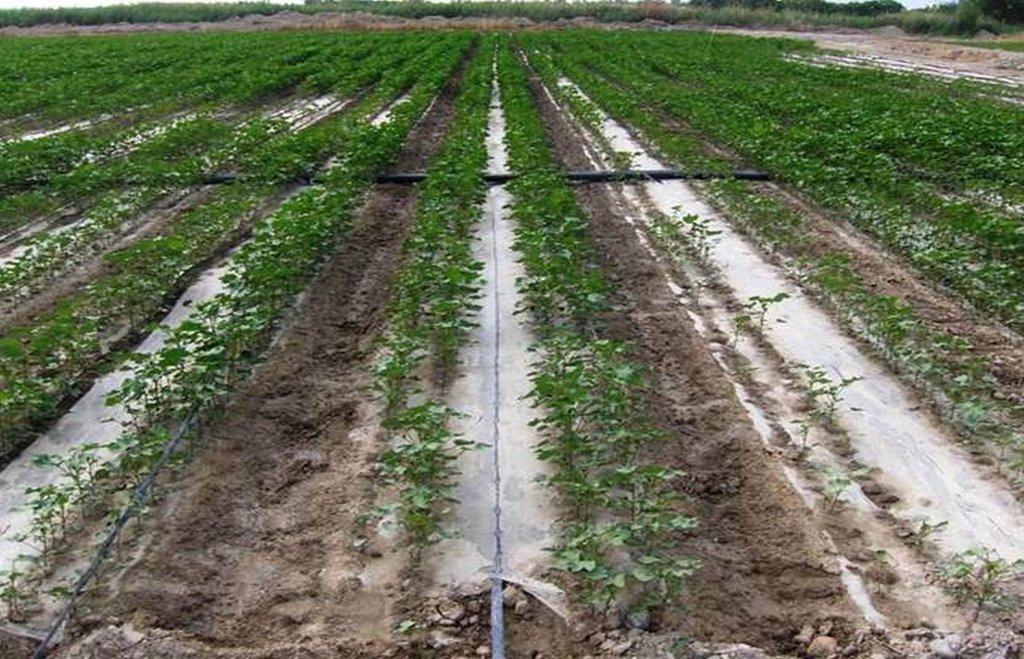
The dry climate and the long hours of sunshine make Xinjiang especially suitable for production of high quality cotton, and as a result some 40% of China’s cotton is grown here. But there are two main problems: shortage of water and salinization of the soil. Farmers who use the traditional flood irrigation method, and don’t have a drainage system, tend to abandon their fields when they become too saline - and then they look for new land to cultivate. A combination of mulching and drip irrigation can be very effective but still needs careful management. Drip irrigation helps to save water for farmers - and for the environment. But it is still very important to install a drainage system to dispose of surplus water in order to reduce the risk of salinization of the soils. Every four cotton rows are covered with transparent polyethylene film and as a result approximately 80% of the ground surface is covered by the plastic mulch. Plastic mulch and drip lines are placed with a specially equipped tractor.
Purpose of the Technology: Low temperatures and dry soil at sowing, in combination with soil salinity, hinder early plant growth. Plastic mulching increases soil temperature, reduces the need for irrigation, and also helps control salinity in the root zone and suppresses weeds, thereby increasing yields by 10–30% (and improving quality also) (Wang, R. et al., 2011). In the first stages after sowing the climate is particularly cold. With plastic mulching the cotton plants can be sown earlier, because the soil will not cool down during the night as much as without plastic mulch.
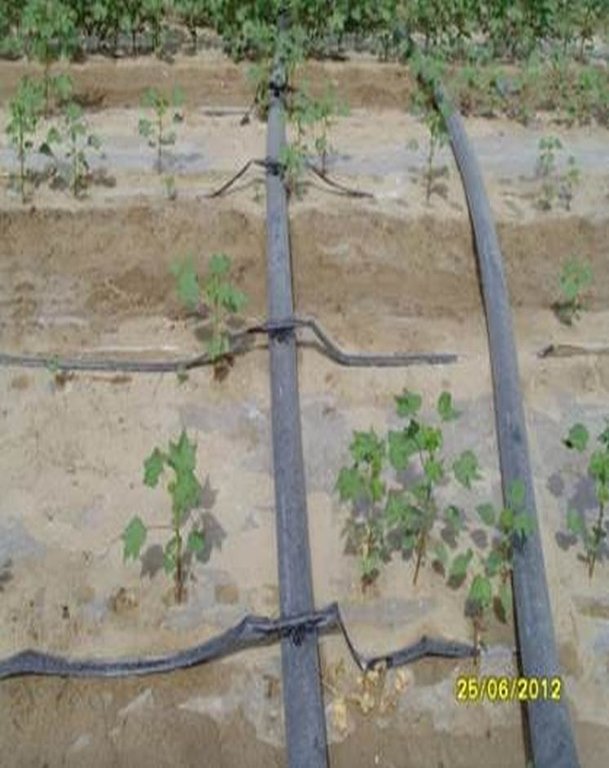
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the new technology of drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is simultaneously essential to install a drainage system to avoid raising the groundwater level and causing salinity. For the installation of the drip lines, the transparent plastic film and the seeding, a tractor and a special tool for the installationis needed: one acre can be installed in a day. After the emerging of the cotton plants, holes must be cut in the plastic film so that the cotton plants can emerge. After harvesting, the drip lines and the plastic film must be collected and recycled. If the plastic is left behind it will pollute the soils and injure livestock if they eat it. Furthermore plastic residues in the soil can reduce subsequent yields, as roots are physically inhibited. After the collection of the plastic residues, if there is no adequate drainage system, the field needs to be flooded to flush the salt layer, which has accumulated below the root zone, deeper into the soil. If the field is not flooded the salt will negatively affect the next years’ cotton plantation.
Natural / human environment: Southern Xinjiang is an arid region with 50 to 90 mm per year. Most precipitation occurs between June and August. It is classified as a temperate cold desert climate. For drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is principally surface water that is used, which is delivered to the field via channels from reservoirs to the fields. The reservoirs are filled in summer with the floods along the Tarim River. The untreated surface water is of poor quality - for agricultural use only. For drip irrigation, the water needs to be treated to avoid blocking the drip outlets. The overall technology is expensive, and only land user groups and communities can afford the machines and the materials.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chine
Région/ Etat/ Province:
China / Xinjiang Province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Tarim River Basin
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
It is not clear how the technology was invented.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
major cash crop: cotton
major food crop: wheat
other: fruit trees
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water use conflicts between agriculture and natural vegetation, soil salinization, desertification.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil salinization and water shortage.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: water availability, evaporation
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Forests / woodlands: Fn: Natural
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pleine irrigation
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, indiquez la superficie couverte approximative:
- > 10 000 km2
Commentaires:
It might be used also in other provinces. But this not known to the author.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
- M4: Changement majeur dans le calendrier des activités
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
Commentaires:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cs: salinisation/ alcalinisation

dégradation physique des sols
- Pw: saturation en eau des sols

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pw: waterlogging
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage - Increase of groundwater - salinization of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (cotton monoculture), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation to gain new arable land), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), wind storms / dust storms (Dust storms, blow out of top soil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (Doubling of population during the last thirty years.), land tenure (Land belongs to the state), poverty / wealth (Family farmers are poorer than city dwellers), education, access to knowledge and support services (Poorer farmers have less access to extension services.)
Secondary causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining (There is oil production in the region, but it was not studied), discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (use of surface and ground water for large scale irrigation), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests))
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
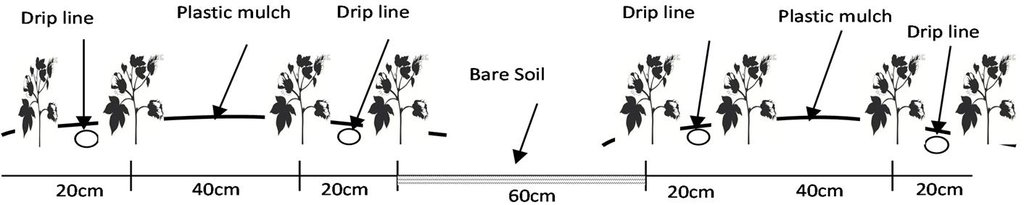
There are double rows of cotton 20 cm apart, with a drip line between. 40 cm then separates each double row. Two double rows are covered by one length of plastic mulch. There is a small strip of bare soil between each length of plastic mulch. Mulch covers around 80% of the soil surface.
Location: Korla City. Xinjiang Province / China
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (For the easy and fast installation a tractor is needed)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity), increase of water use efficiency
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: transparent plastic (Polyethylene), thickness: 0.08 mm
Quantity/ density: 7100 m/ha
Remarks: 1.4 m width in lines with spacing of 20 cm between lines
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Change from flood irrigation to drip irrigation
Major change in timing of activities: Plastic mulch enables early sowing of cotton
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor | ||
| 2. | Drip line installation, plastic mulch and seeding tool | Agronomique | At sowing |
| 3. | Making holes for the (cotton) plants in the plastic mulch.Maintaining hoses | Agronomique | After emerging |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Drip line installation | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tractor | Piece | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | seeds | kg | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Plastic mulch | 1,0 | 32,0 | 32,0 | 50,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Black dripe lines | Set | 1,0 | 380,0 | 380,0 | 50,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 5510,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.33 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing and leveling of field. | Agronomique | Before sowing |
| 2. | Irrigation | ||
| 3. | Removal of the drip lines and the plastic mulch |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Collecting mulch | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 98,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Irrigation and flooding water | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 13,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: tractor with installation tool for the drip irrigation under plastic mulch, other tools: hoe
The costs for the machine, the plastic hoses and the plastic mulch are calculated above are for 1 ha and were calculated on the basis of 2013 (subsequently costs have risen). Water price: 0.019 CNY/m3. Farmers need 3000 m3 per ha.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
90 mm per year. Jan, Feb, Apr and May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5 mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- aride
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: altitudes of 800 to 1300 meters
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium high
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: also < 5 m and the installation of drip irrigation under plastic mulch should be installed with a drainage system. If the groundwater table is too high salinisation of the soil will be the result
Availability of surface water: For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch mostly surface water is used. It is diverted by channels to the agricultural fields. There must be a good water availability at the fields.
Water quality (untreated): For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch the water quality must be quite high, otherwise the small holes of the drip lines will be blocked soon.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
- très riche
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the earth works in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land (income from large fields of cash crops).
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have not implemented the drip irrigation under plastic mulch also generate off-farm income.
Manual labour: harvesting
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
5-15 ha: state farms
< 0.5 ha: family farmers
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- loué
Commentaires:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
15% of more cotton yield
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Impacts socioculturels
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
évaporation
Sols
couverture du sol
perte en sol
salinité
Autres impacts écologiques
salinization below root zone
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
No number on households
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The government gives subsidies to the farmers who are installing the drip irrigation under plastic mulch.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government want to spread the technology in the whole region by giving subsidies to the farmers.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
helps to save water thus saves costs. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is subsidies by the government. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
It helps to save water during the vegetation period and thus helps to reduce the conflicts between the upstream and downstream farmers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology (drip + mulch) needs to be supplemented by installing a drainage system in the fields otherwise there will be a build-up of salinity and farmers will abandon land and move on. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Salinization of the soils is increasing The consequence is that the fields are flooded after harvest in November/December to leach out the salt. The water used for drip irrigation plus the water to flush the salts to lower soil layers add up to almost the same amount as if farmers were using the original flood irrigation technology. | drainage system in the fields required. |
7. Références et liens
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Zia-Khan,S., Spreer, W., et al. Effect of dust deposition on stomatal conductance and leaf temperature of cotton in Northwest China.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Water 2015, 7, 116-131; doi: 10.3390/w7010116. www.mdpi.com/journal/water open access.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé