Afforestation with mangrove plants to protect land degradation [Bangladesh]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Fazlay Arafat
- Rédacteurs : Mutasim Billah, Md. Arfanuzzaman
- Examinateurs : Nicole Harari, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Upokuliyio Bonayon
technologies_4300 - Bangladesh
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Hossain Md. Kamal
Bangladesh Forest Department
Bangladesh
exploitant des terres:
Hussain Md. Jobair
Bangladesh Forest Department
Bangladesh
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
FAO Bangladesh (FAO Bangladesh) - BangladeshNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bangladesh Forest Department (Bangladesh Forest Department) - Bangladesh1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
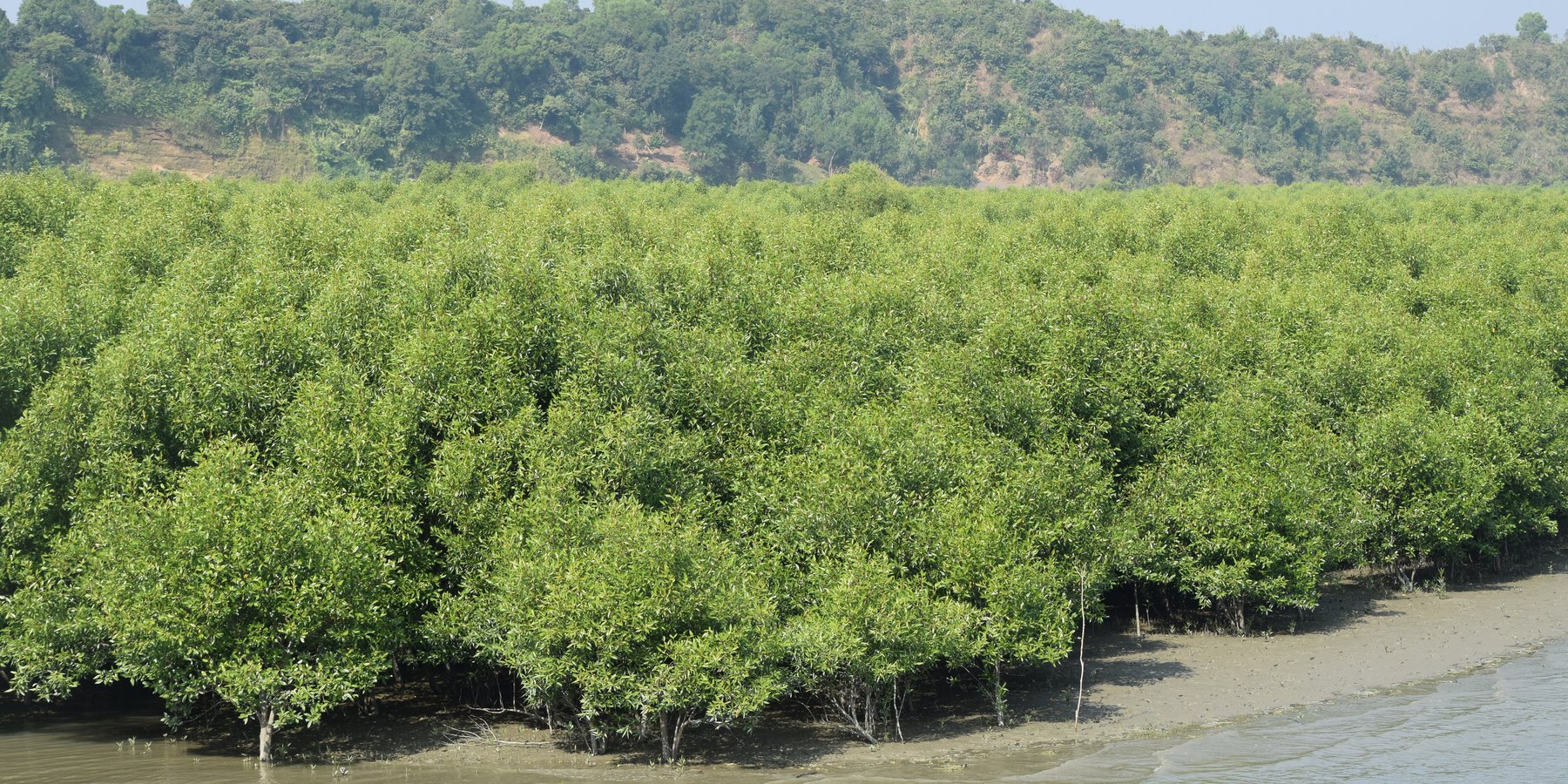
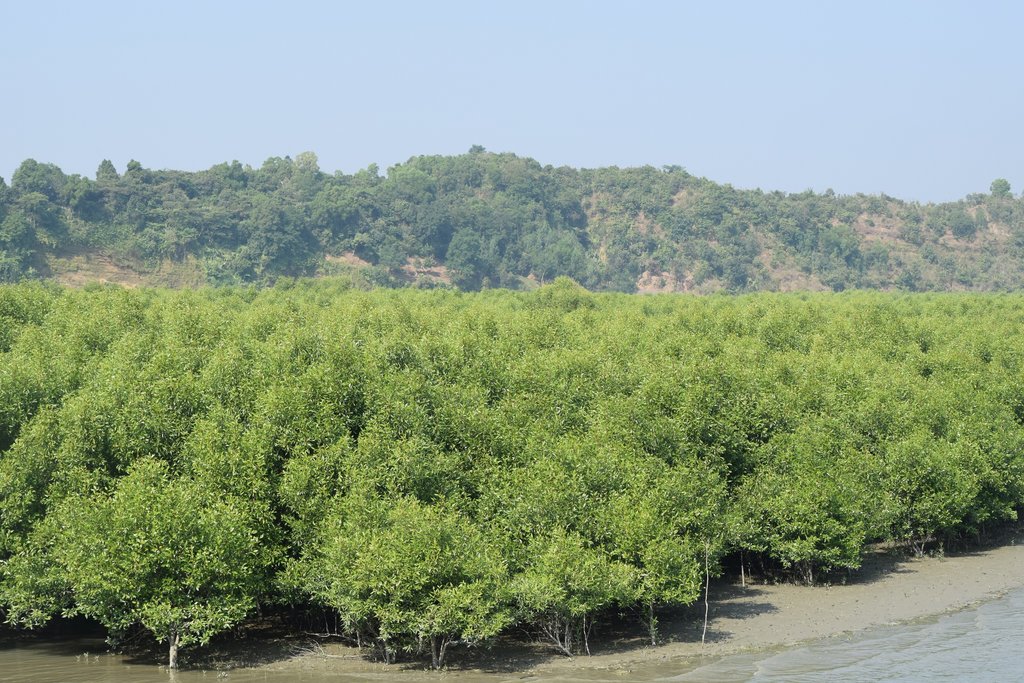
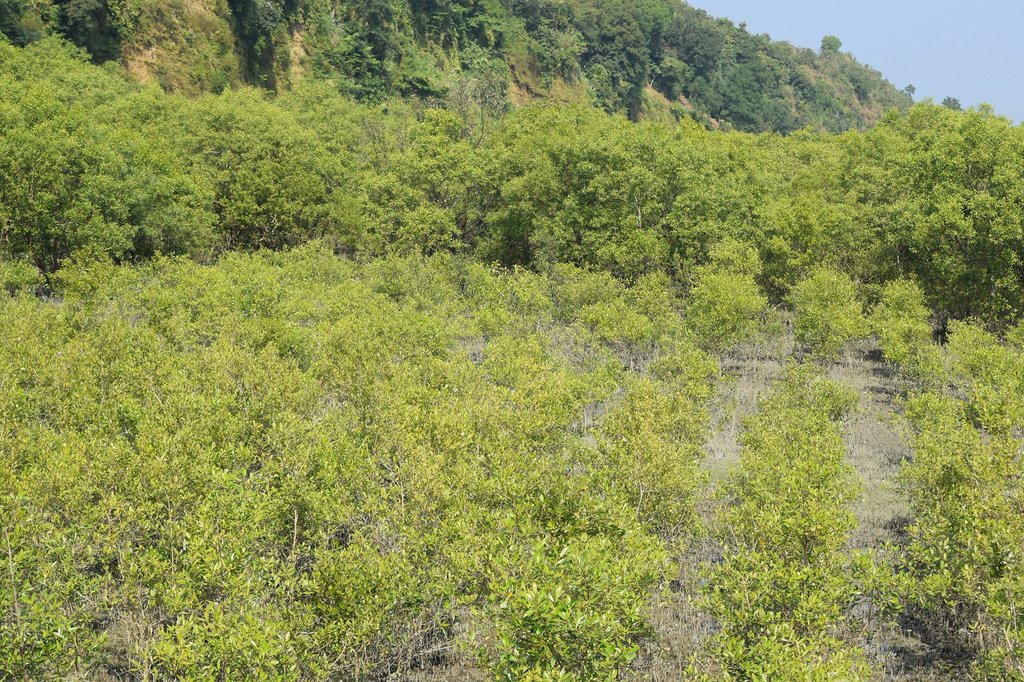
Mangrove afforestation in newly accreted land along cooastal regions accelerates the process of land stabilization, creates new forest resources, and enriches biodiversity.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
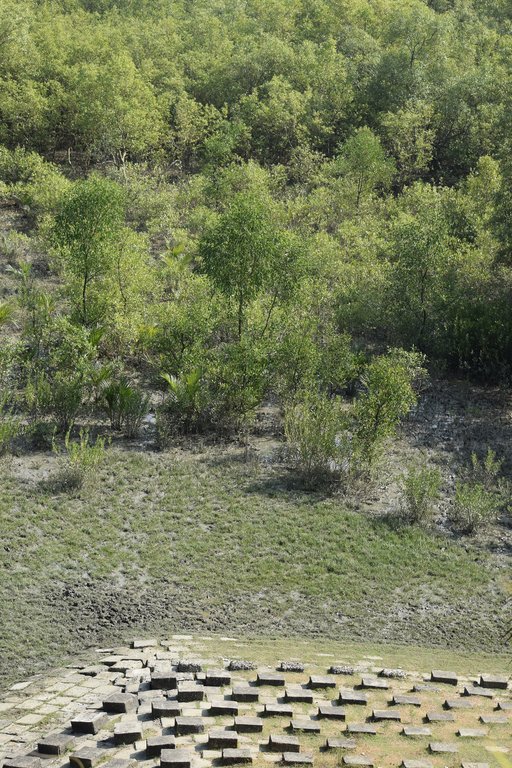
Maheshkhali is the only hilly island of Bangladesh and situated in northwest of Cox’s Bazar. This island has become a tourist destination for its mangrove plantation and ancient Adinath Temple situated at the hilltop. Historically the island had suffered from coastal erosion and structural measures like building blocks along the coast were implemented in some places to protect the Adinath hill from erosion. The Maheshkhali channel have deposited sediments in the near-shore zone and formed mud banks along the coast. This newly accreted land and other lands were used for mangrove plantations, which stabilized the land and provided protection against coastal erosion, storm damage, flooding, and siltation of adjacent seagrass beds. Mangrove plantations can provide a long-term and cost-effective solution to coastal erosion while at the same time improving the landscape aesthetically and increasing ecological habitats. Before the mangroves were planted, the existing shrub and tree vegetation along the coastline of Maheshkhali was scattered. The barren and exposed coastline is now converted to a green shelter-belt and protecting the soil. Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and the mangrove plantation was carried out with the support from World Bank through "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP)" project in 1997. Later, some new plantation also carried out in 2016 on newly accreted land through "Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project (CRPARP).
The mangrove plant species Baen (Avicennia officinalis) was used to create the plantation. Salinity in coastal regions increased as consequence of global warming and Avicennia officinalis is among the most salt tolerant species that prefer clay soil. The young tree forms a low, dense bushy crown. When it matures, it forms a columnar tree up to 15 m and may grow up to 30 m. The spreading root system of the plant also provides stability in shifting substrates. When planting mangroves, site selection and proper nursery management is crucial. Geo-morphological changes in coastal areas can be rapid and unpredictable, making it difficult to identify suitable sites correctly. Accreted land with grasses and crab burrows indicating a stable site, ideal for planting. The experience of field staff is a key factor in identifying suitable sites. Nursery management is carried out by forest department. Seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation and weed control are the major activities of nursery management. Proper care of seedlings needs to be ensured while transporting from nursery to plantation site thorough boat. Gunny bags can be used to carry the seedlings while transporting. The spacing between each plant was 1.5m x 1.5m and 4444 seedlings/ha were planted in the visited site. Compost fertilizer was used both in nursery and while planting in pit. After planting, each seedling was tied up with a bamboo stick for support and to prevent from washing away in tides. The plantation activities were carried out by the staff of forest department. As mangrove afforestation is carried out in unstable environments, there is always a risk of losing some plantation during the time it takes for trees to reach maturity.
Coastal afforestation accelerates the process of land stabilization, and by creating new forest land it enriches biodiversity and natural resources. It also protects the lives and property of the coastal population against cyclones and tidal surges. The plantation develops suitable habitats for wildlife, fish and other estuarine and marine fauna. It produces timber for fuelwood and industrial uses. However, the local community people can only collect fuelwood and other non-timber forest products like honey, crabs and fishes from this plantation site. The mangrove plantation increased the aesthetic beauty of the area and also create employment opportunities for remote rural communities through eco-tourism.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bangladesh
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Chittagong division
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Moheskhali, Cox's Bazar
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Plantation was carried out from the support of World Bank project "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP) project in 1997" and "Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project (CRPARP) in 2016"
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Forêts/ bois
- Plantations d'arbres, boisements
Plantation d'arbres, afforestation: Précisez l'origine et la composition des espèces. :
- Variété locale en monoculture
- Mangrove plantation
- Avicennia officinalis
Est-ce que les espèces d’arbres précisées ci-dessus sont des espèces d'arbre arbres à feuilles caduques ou à feuilles persistantes ?
- forêts à feuillage persistant
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Bois de chauffage
- Fruits et noix
- Autres produits forestiers
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
- Loisirs/ tourisme
- Protection contre les aléas naturels
Commentaires:
Due to the establishment of mangrove plantation, the degraded land is now covered with vegetation and protected from land degradation
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- fellow accreted land
Principaux produits/ services:
Fish and crabs
Commentaires:
The areas were inundated regularly by the tide and physical barriers were imposed to protect the land from degradation
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion des plantations forestières
- brise-vent/ plantations abris
- réduction des risques de catastrophe fondée sur les écosystèmes
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
Commentaires:
Plantation of mangrove species in newly accreted land to stabilize the soil to protect from land degradation
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wc: érosion côtière
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
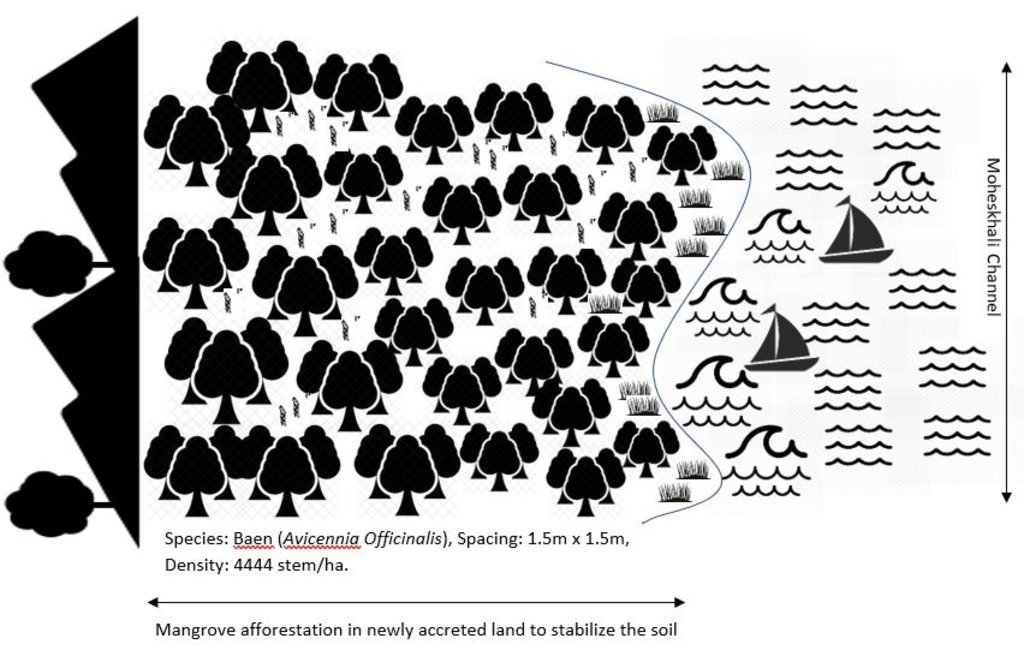
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Planted species: Baen (Avicennia officinalis)
Soil condition: Accreted land with grasses indicated a stable site and suitable for planting Baen plant.
Spacing: 1.5m X 1.5m
Density: 4444 stem/ha.
Vacancy filling: 3 consecutive years after plantation
Auteur:
Md. Fazlay Arafat
Date:
21/04/2019
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
1 ha
Si vous utilisez une unité de superficie locale, indiquez le facteur de conversion vers un hectare (p.ex. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha = :
2.47 acres
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
BDT
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
84,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
BDT 500
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery preparation (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control) | March-April |
| 2. | Survey plantation site and prepare site map | August |
| 3. | Transportation of seedlings | September-October |
| 4. | Plantation | September-October |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Nursery preparation (seed collection, site clearing, leveling and fencing, drainage arrangement, bed preparation, making overhead shed, poly-bag preparation, potting seeds, manuring, irrigation, weed control) | person-days | 20,0 | 500,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Plantation site survey | person-days | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Transportation of seedlings | person-days | 4,0 | 500,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Plantation | person-days | 10,0 | 500,0 | 5000,0 | |
| Equipements | Boat rent for seedlings transportation | lump-sum | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | |
| Equipements | Poly bags | pieces | 4500,0 | 1,0 | 4500,0 | |
| Equipements | Rope for tying up seedlings with bamboo stick | lump-sum | 1,0 | 1500,0 | 1500,0 | |
| Equipements | Gunny bags (to carry seedlings to the plantation pit) | lump-sum | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Bamboo sticks to support seedlings | pieces | 4500,0 | 2,0 | 9000,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost fertilizer (to apply in pit) | kg | 50,0 | 10,0 | 500,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 35900,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 427,38 | |||||
Commentaires:
Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and the costs was borne from the project "Forest Resource Management Plan (FRMP)"
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1 year old plantation replanting nursery 40% ( 2 bed/ha) | March-April |
| 2. | 2 year old plantation replanting nursery 30% ( 2 bed/ha) | March-April |
| 3. | 3 year old plantation- replanting nursery 20% (1 bed/Ha.) | March-April |
| 4. | 1 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 40% (1777 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
| 5. | 2 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 30% (1333 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
| 6. | 3 year old plantation- replanting (VF) 20% (888 seedling/Ha.) | September-October |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Nursery work | person-day | 18,0 | 500,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Replanting work | person-day | 10,0 | 500,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Boat rent for seedlings transportation | Lump-sum | 1,0 | 6000,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost fertilizer | kg | 25,0 | 10,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 20250,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 241,07 | |||||
Commentaires:
Bangladesh Forest Department is the land user and borne the maintenance cost of the technology
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labor cost
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
3700,00
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Cox's Bazar
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
Mean annual temperature is 25.6 °C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
excès
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau inutilisable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Oui
Précisez:
Due to regular tidal inundation the soil become saline and only support to grow mangrove plant species
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
épisodiquement
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
- personnes âgées
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Non
Précisez:
Land use rights based on forest management type
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production de bois
qualité des forêts/ bois
production forestière non ligneuse
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Honey, fish and crab production increased
risque d'échec de la production
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The mangrove plantation support production of timber, fuel wood, crabs, fruits for wildlife, honey, etc.
surface de production
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Promote alternate income through ecotourism
Impacts socioculturels
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The mangrove plantation saved one ancient temple (Adinath Mondir) of Hindu religion from destruction by land degradation.
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The mangrove forest now become a tourist place
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Forest department now replicating the practice in other degraded areas
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
surface runoff decreased due to canopy coverage and accretion of sediments in plantation site
Sols
accumulation de sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
soil accumulation increased as the plantation promote soil accretion during tides
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
the plantation site support habitats for birds and crabs
espèces bénéfiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Honey bee and various birds living here and add benefits in pollination and pest control
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The plantation develops suitable habitats for wildlife and fish
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The plantation protect the debris flows of Adinath hill from washed away in water. The Adinath hill is on the edge of coast and now protected from bank erosion.
impacts des cyclones, pluies torrentielles
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
capacité tampon/de filtration
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The plantation act as a buffer to reduce the saline water flow of high tide towards terrestrial land
impact des gaz à effet de serre
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | saison des pluies/ humide | augmente | bien |
| autre changement climatique progressif | water salinity in coastal areas due to global warming | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| tempête tropicale | modérément |
| orage local | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| onde de tempête/ inondation côtière | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
Commentaires:
Forest Department is the land user here
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Protect the lives and property of the coastal population against cyclones and tidal surges. |
| Conserve and stabilize newly accreted lands and protect from land degradation |
| Produce fuel wood for local people |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Develop ecotourism facility for local communities |
| Develop suitable habitats for wildlife, fish and other estuarine and marine fauna |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Vulnerable to natural calamities specially in initial stage | Proper management and vacancy filling |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Risk of low production due to unstable environment for plantation | Proper monitoring and management of plantation |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
number of field visits: 02
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
number of informants: 04
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
number of informants:02
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
16/01/2019
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Macintosh, D.J., Mahindapala, R., Markopoulos, M. (eds) (2012). Sharing Lessons on Mangrove Restoration. Bangkok, Thailand: Mangroves for the Future and Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. ISBN: 978-2-8317-1558-2
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
www.mangrovesforthefuture.org
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Mangroves for the Future
URL:
www.mangrovesforthefuture.org
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
The WOCAT questionnaire covers all the aspect of this technology
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé