Closed Pipe-conduit [Chine]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Mei Zhao
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Rat tunnel tillage
technologies_1556 - Chine
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Lingqin Meng
Division of water and soil conservation, Songliao water resources commission, ministry of water resources P.R. China
Chine
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Songliao Water Resources Commission (Songliao Water Resources Commission) - Chine1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
A Rat tunnel is a kind of subdrainage. It is a drainage duct formed through extrusion or oscillation in soil layer by pulling a mole plough with a tractor. The rat tunnels in a field should be used together with a concealed conduit drainage system in order to safely and quickly drains the water in the rat tunnels and avoid field collapses incurred by poor drainage and washings on the rat tunnels.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
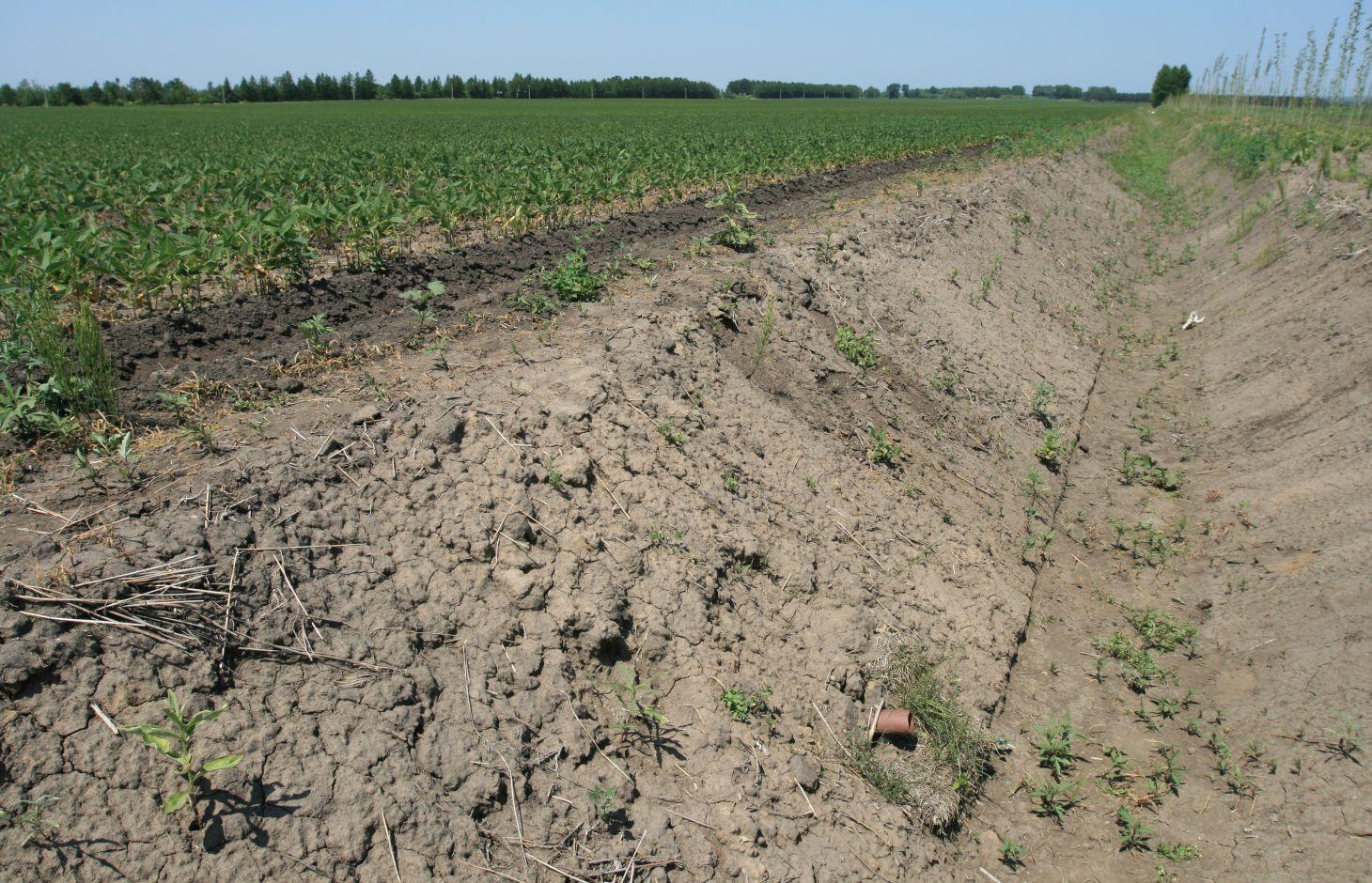
Rat tunnels are suitable for the regions with sticky and heavy soil, thick soil layer, and lower infiltration rates, high underground water level and where waterlogs are very likely to happen. By applying the rat tunnels, infiltration can be increased, soil salinization can be prevented without affecting the growth of the crops and occupying croplands. Good effect can be achieved by combining rat tunnels with closed conduits in application. Closed drainage refers to burying the drain pipes underground and letting the underground water flow along the fissures between the pipes and penetrate into the tubes and drained. In a field, if rat tunnels and closed conduits are combined for use, the rat tunnels constitute the first-grade drainage system, the closed conduits constitute the second-grade drainage system; the stagnant water in the plough layer penetrates through the soil and rat fissures and converges into the rat tunnels; While draining the water inside themselves to the outside, the rat tunnels collect the inside stagnant water and guide the water into the closed conduits, through which the water is discharged. In this way, the surface water can be discharged in a relatively thorough way.
Increase of soil infiltration, rapid discharge of direct surface runoffs, prevention of soil salinization.
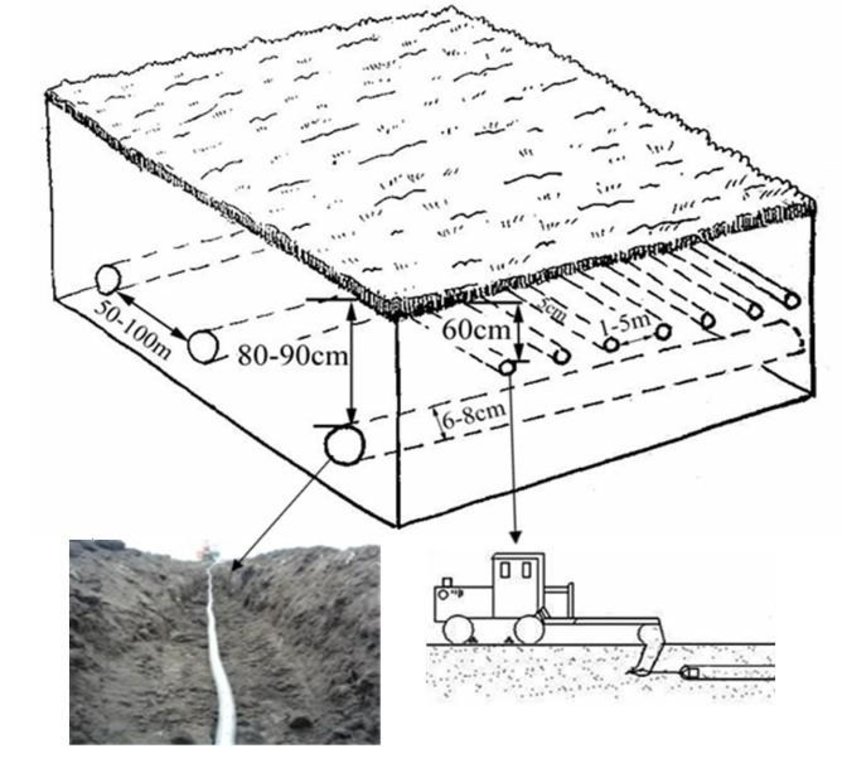
In building such a project, the closed conduits should be built first, followed by the building of the rat tunnels; the closed conduits should be under the rat tunnels, the included angle between a closed conduit and a rat tunnel should be 90°.
The gap between two neighboring laid closed conduits should be 50m-100m. The burying depth of a closed conduit should be 80cm-90cm, the area around the closed conduit should be evenly laid with a layer of coarse gravels 5-8cm in thickness. After the project on the closed conduits in a field is accomplished, restore the flatness of the field surface, then undertake the operation on the rat tunnels.
In building the rat tunnels, a tractor is directly applied to pull the mole plough in accordance with the designed distances. When the tractor moves forward, the mole plough goes deep into a specified depth(generally 60cm) of soil layer and generates through piercing the soil along the direction of the forward motion of the tractor a tunnel(rat tunnels) whose diameter is equal to bullet diameter and which is in parallel with the ground surface. The separation distance between two neighboring rat tunnels is 1-5m. The service life is generally 2-5 years. If the rate of flow of a field obviously decreases, new rat tunnels should be built by averting the original routes.
After a rainfall, check whether the rat tunnels have collapsed. The service life of the newly laid closed conduits is over 20, however, new rat tunnels should be built every two years.
Rat tunnels are mainly distributed on the Three River Plain, which is the largest marsh distribution area. It has a total population of about 8.625, with the population density being about 79/km2. With the annual average temperature being 1℃-4℃,being warm in summer with the average temperature being over 22℃, having an annual amount of precipitation of 500-600 mm with the rainfall seasons mainly concentrated in the hot seasons from June to August, the Three River Plain is suitable for the growth of crops. The area is affluent in water resources, with the total quantity reaching about 18.764 billion/m3. In this area, the per capita cultivated land area is about 5 times of the average level in China. There are also about 2.52 millions of theropencedrymion distributed in the terrains with low mountains and hills.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chine
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Hei Longjiang
Autres spécifications du lieu:
San Jiang Plain
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- > 10 000 km2
Commentaires:
This technology is widely used in San Jiang Plain.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150, Longest growing period from month to month: From April to September
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): high underground water level, lower infiltration rates,Soil salinization
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): It's hard to drainage excess water. Lower soil fertility
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S11: Autres
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wm: mouvements de masse/ glissements de terrain

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
Commentaires:
Causes of degradation: soil management (Backward management modes), change of seasonal rainfall (The rainy seasons mainly focus on summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (The land can't drainge the excess water after downpours), population pressure (Population pressure makes extensive cultivation in this region), land tenure (As the lands are owned by country or by peasant communities, the peasants will not protect their land initiatively.), education, access to knowledge and support services (The channels for the local peasants get knowledge are few, and they will not learn knowledge initiatively.), governance / institutional
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
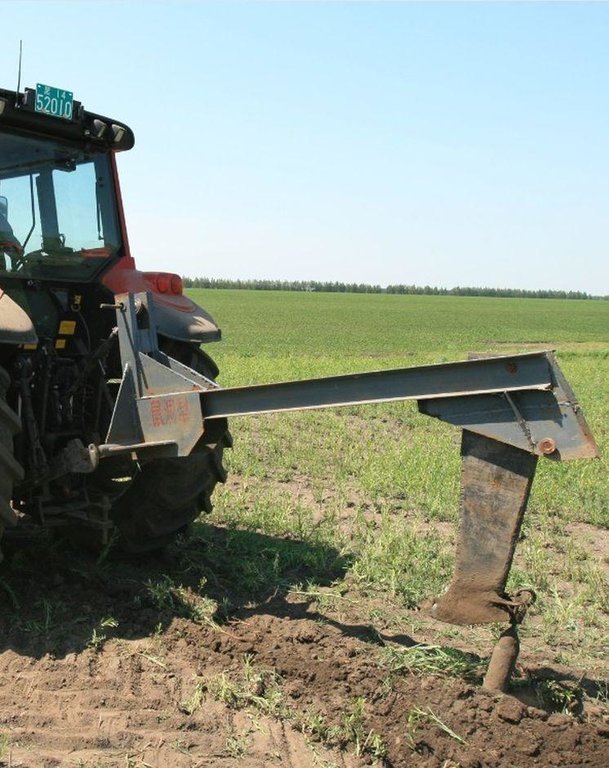
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Diameter of closed conduit: 6-8cm, separation distance between two neighboring closed conduits: 50-100m, burying depth: 80-90cm: Diameter of rat tunnel: 5cm, separation between two neighboring rat tunnels: 1-5m, depth: 35-100cm(generally being 60cm). If the depth of the rat tunnels is >60cm, the depth of the closed conduit should be adequately increased.
Location: Hong Xing Farm. Hei Longjiang Province
Date: 2012-7-19
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (It's complicate to constructe this technology)
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Structural measure: Closed conduit
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 50-100
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 8-9
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.06-0.08
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): >50
Structural measure: Rat tunnel
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 1-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.05
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): >50
Construction material (other): A closed conduit is a kind of corrugated plastic conduit with the diameter generally being 6-8cm and
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Auteur:
Zhao Mei, Beijing Normal University
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ren Min Bi
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
6,25
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
60.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layout the line of Closed Conduit | Spring |
| 2. | Laid closed conduits | Spring |
| 3. | Build rat tunnels.The tractor is directly applied to pull the mole plough in accordance with the designed distances. | Spring |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | ha | 1,0 | 64,0 | 64,0 | |
| Equipements | first machine | ha | 1,0 | 224,0 | 224,0 | |
| Equipements | second machine | ha | 1,0 | 24,0 | 24,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | corrugated plastic conduit | ha | 1,0 | 640,0 | 640,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 952,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 152,32 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Build rat tunnels. | every two years |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | second machine | ha | 1,0 | 24,0 | 24,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 24,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 3,84 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Mole Plough, refer to the photo of technical drawing.
The accounted costs for each hectare are as follows: Depth, diameter and spacing on closed conduit: being 90cm, 8cm and 80m respectively, the closed conduits with a total length of 200m are required for each hectare. 1. Costs of closed conduit laying: Tractor cost is 224$US ; Expense of the conduit materials is 640$US; Labor expense is 64$US. 2. Costs of rat tunnel building: Machinery cost: 24$US/hectare (the operation efficiency: 30 hectare/day). No maintenance cost. However, new rate tunnels should be built with the same costs(24$US) every 2 years. The service life of the closed conduits is over 20 years.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most determinate factors is the cost of corrugated plastic conduit.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate, boreal
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
excès
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
10% of the land users are very rich.
45% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Apart from farming, the main works of the local people involve doing works for others in cities and towns or doing business.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
The lands are owned by country or by peasant communities.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production animale
production de bois
diversité des produits
surface de production
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
disparités économiques
charge de travail
Impacts socioculturels
opportunités culturelles
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
contribution to human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Local peasants learn some knowledges of soil and water conservation though this technology.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
perte en sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
salinité
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
capacité tampon/de filtration
dommages sur les champs voisins
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
95% of all households
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
This technology only be implemented by farmers, because it's too expensive for peasant to afford it. If farmers implement the technology, the local government will organization peasants to help farmers, the government pay for the wages.
A few of land users will implement the technology without any external material support.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Fast drainage of surface water |
| Prevention of soil salination |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| New rat tunnels should be built every two years |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Complicated in construction, big investment | seeking other substitutes |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
28/02/2013
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Techniques standard for comprehensive control of soil erosion in the black soil region, Author: Shen Bo; Meng Lingqin, Years: 2009
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Internal book
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé