Carob tree protection from rats [Chypre]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Michalakis Christoforou
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Προστασία χαρουπόδενδρων απο προσβολές αρουραίων και ποντικών
technologies_1703 - Chypre
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Governement official:
Costas Michael
Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Environment, Cyprus
Chypre
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Cyprus University of Technology (Cyprus University of Technology) - Chypre1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Carrob tree protection from rat attacks include protection of trees directly by using aluminium layers as rings on the neck of the carob trees in order to keep rats away from climbing on the threes and thus causing problens on fruits and new branches. Furthermore, poisonus rat baits are attached on the trees in case the aluminium layers can not be used.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
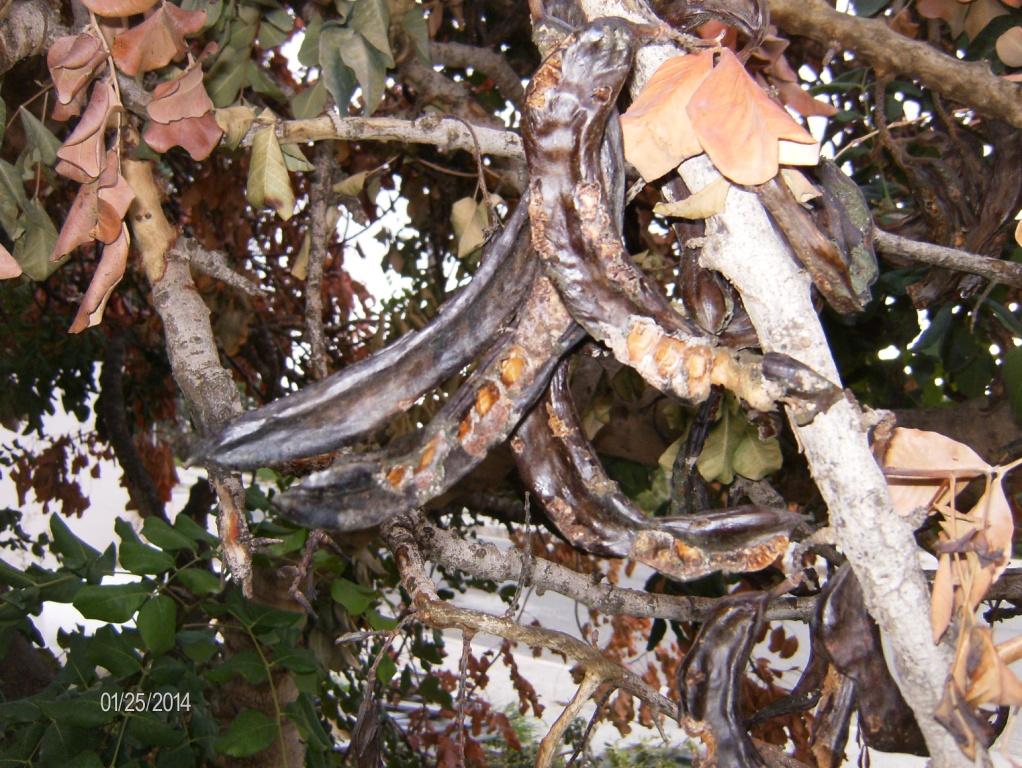
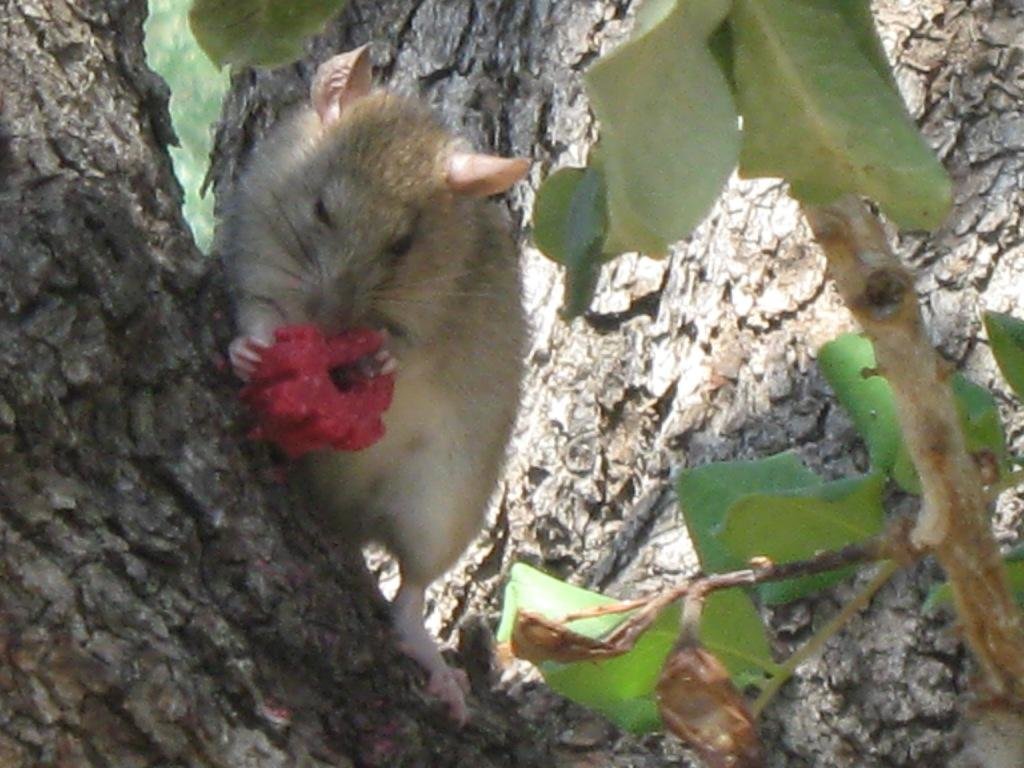
Carob trees are attacked every year by rats who nibble the trunk stem of the tree, remove the bark of the trunk and the branches sucking the juice and eat the mature fruits. Rats nibble the bark of the tree in order to reduce their teeth size which tends to enlarge year by year. This results in the death of the tree branch or even of the entire tree. The tree may also show symptoms of hemiplegia. Rats run on the tree through the trunk. Apart from the direct effect of rat attacks on carob trees, rats also cause other problems to humans and animals. Rats are vectors for serious pest and diseases
Purpose of the Technology: The rat population increases rapidly when there is enough food (such as carobs) available, and the population grows even faster in the absence of natural enemies. . Through interrupting the access from the ground to the tree trunk, or by pruning the branches which are connected to the ground, the rats are hindered from climbing the trees. Rats can also be controlled through the use of chemical baits. However, these baits should only be used by experts who know where and how to place them in order to avoid that other animals come in contact with the baits. Natural enemies such as cats, snakes and birds (e.g. Bam owl (Tyto alba)) should be breeded and established on the carob trees, and farmers, hunters and locals should be informed not to kill the natural enemies of rats.
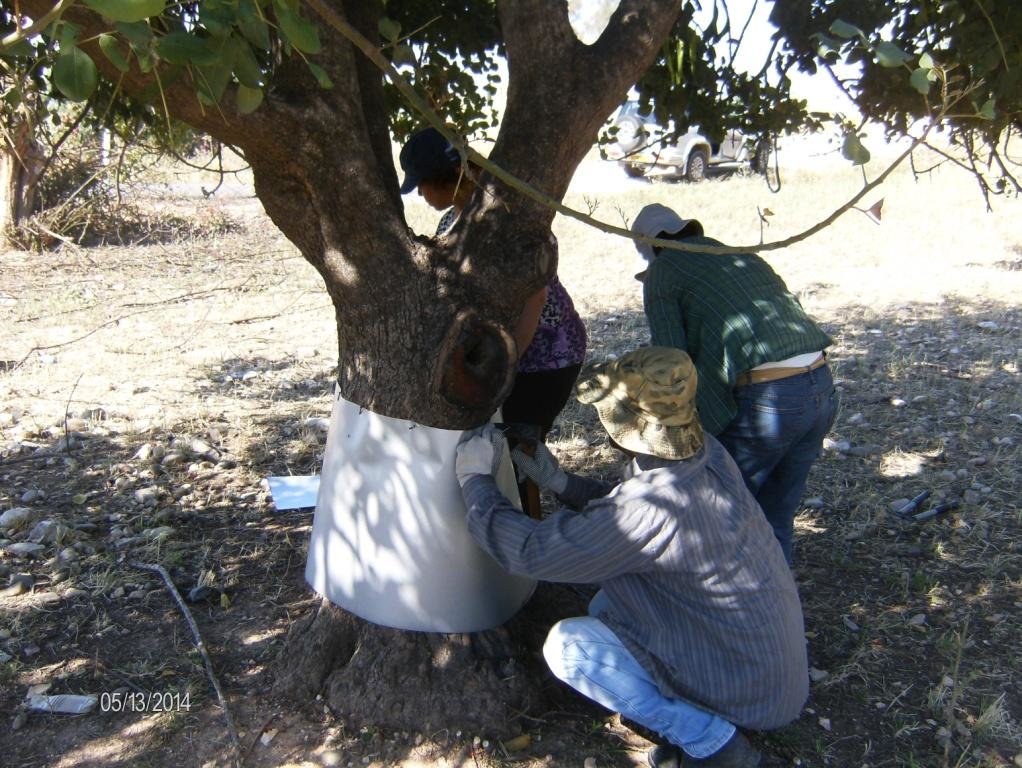
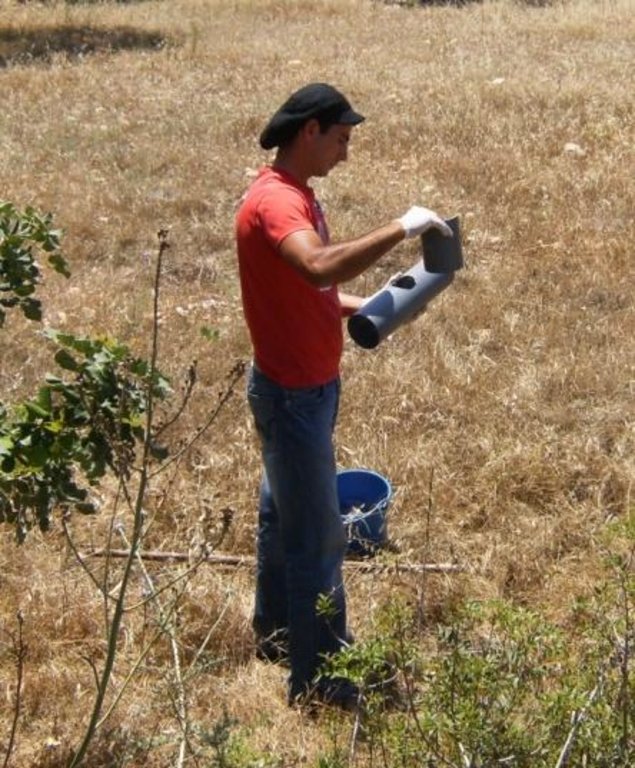
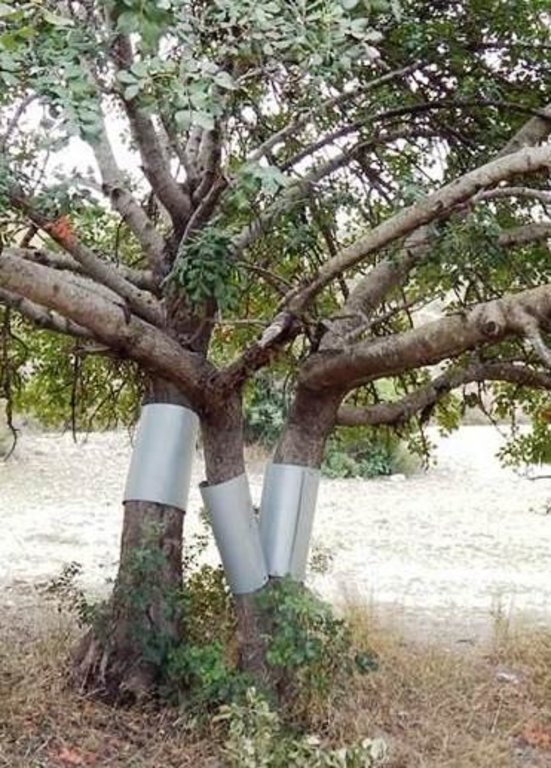
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The carob trees can be protected from rats by covering the tree neck and trunk from the ground up to 1 meter with a hard material such as aluminium with a slippery surface. This way the rats are not able to climb the trees since they will slither on the ring layer.
Natural / human environment: The carob tree protection will increase the production of carobs and therefore the income of the growers. Already established carob trees could provide a good income to growers with low production cost. The population of rats will decrease since the major source of food will not be provided anymore. Educating farmers, hunters and the local population about the benefits of natural enemies will allow that the environment regulates the rat population by itself.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chypre
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Limassol
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Pissouri
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
50,0
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50 km2.
Carob trees are grown in dry lands such as Pissouri and its sorrounding villages. In Cyprus a total of 4000 hectares with 300'000 carob trees are cultivated. The annual production of carobs is around 9000 to 12000 tons. Carob growers use minimum agricultural practices such as mechanical weed control and pest control (insects and rats)
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The use of aluminium layer covering the trunk of carob trees was applied in an EU project called Agrolife which started in 2014, http://agrolife.eu/
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- caroube
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: mid October to mid May
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Rat attacks on carob trees cause severe problems for plants health and the fruit quality and production.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Carob growers: Rats are attacking the carob trees causing the death of the trees and damage of fruits.
Locals: The rat population increased during the last 30 years especially in areas where carobs are grown.
Agricultural officer: Rat population increased rapidly causing serious problems in carob production due to heavy rainfall in 2012 and to the hunting and killing of the natural enemies such as snakes and birds by the locals and the farmers.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- lutte intégrée contre les ravageurs et les maladies (incluant l'agriculture biologique)
- Tree protection
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A7: Autres

structures physiques
- S11: Autres

modes de gestion
- M7: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: covering the tree trunk with aluminium layer
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation biologique
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bp: augmentation des insectes nuisibles (ravageurs)/ maladies, baisse des prédateurs
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Hunting and killing the natural enemies such as snakes and birds)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Rat popuation increases rapidly after rainy year)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
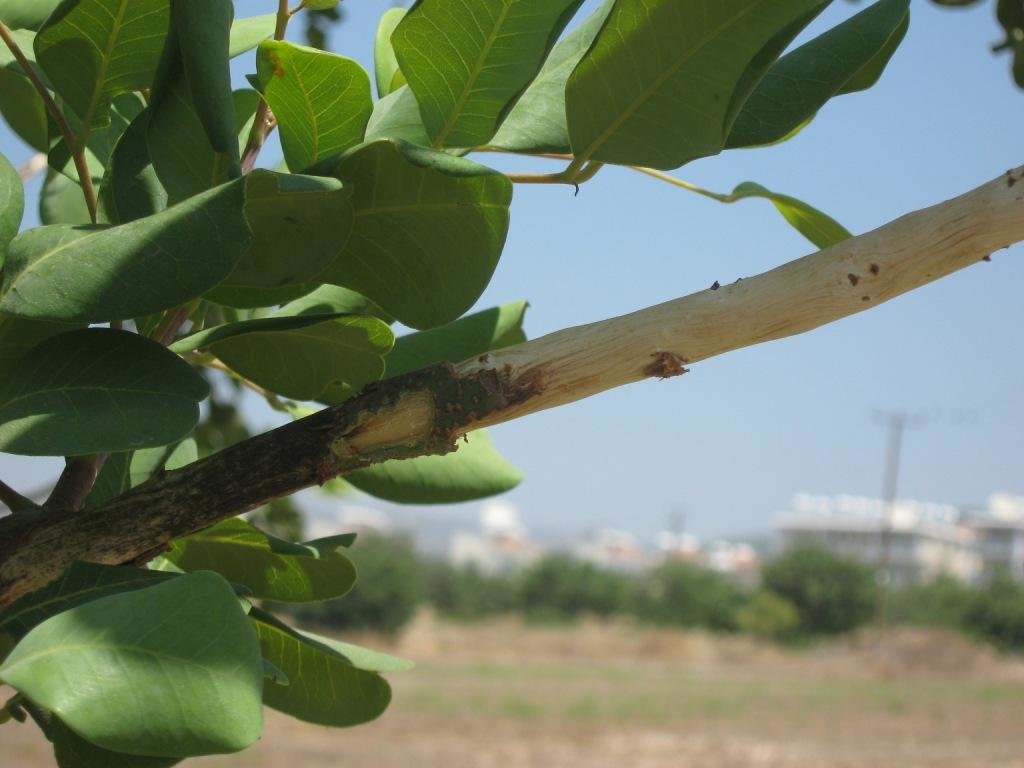
Aluminium layers are placed aroud the bark of carob trees as a ring. The aluminium is thin and light thus does not affect the growth of the tree. The hight of the aluminium is more than 50cm so that the rats can not climb or jumb on the bark of the tree
Location: Pafos. Pafos
Date: 10/3/2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Agricultural advisors will inform the land users about the rat life cycle and their charactiristics in order to understand the use of the technology)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land users will implement the technology by installing the zinc or alluminium layers around the tree trunk)
Technical knowledge required for wildlife department: low (will release natural enemies such as the bird Tyto alba)
Main technical functions: reduction of rat population, protection of carob trees and fruits
Structural measure: tree trunck cover with aluminium layer
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (other): aluminium layers 1m X 1m X 0,01mm
Auteur:
Costas Michael
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
euro
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
0,91
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
33.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | covering the tree trunk with an aluminium layer | winter, spring |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 265,0 | 265,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Aluminium layer | ha | 1,0 | 1116,0 | 1116,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Iron nails | ha | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1393,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1530,77 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of aluminium layers | once a year |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: hammer, nails
The costs were calculated for 8 persons working 8 hours per day and per ha. The costs were calculated on the 28th of August 2015.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The costs are affected by the trunk diameter and the plant height
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Total annual rainfall in 2013=255mm
Total annual rainfall in 2014=363mm, and in 2015=300mm from Jan to May
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: subtropics. In Jan and Feb the temp can go below 5 C for few hours in one or two days.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l (most of carob trees areas)
Landforms: Plateau/plains (most trees are planted in plateaus. The technology is not affected by landform)
Slopes on average: Flat (most of the plantations), gentle (some fields) and moderate (few plantations, old age carob trees)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (plateaus, flat areas) and shallow (hills with aged carob trees)
Soil texture: mdeium (in plateaus and flat areas) and fine (mostly on the base of the hill)
Soil fertility is medium in plateaus and flat areas and low mostly on the base of the hill
Topsoil organic matter is medium (in plateaus and flat areas) and low (mostly on the base of the hill)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low (due to lack of rainfall, when it rains the water is immediately absorbed by the soil)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table is 5-50m (if a field is near a river) and >50m if a field is far from rivers
Availability of surface water is poor/none (When it rains it does not last long enough in order to cause floods)
Water quality (untreated) is for agriculutral use only ( ground water analysis showed that in some cases the water is contaminated with boron)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Few species grow within the carob trees and those are mostly weeds. Once a year the growers remove the weeds from the fields. Fauna is also poor and consists of rodents, snakes, few birds and insects
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most of the land users are old men and women. Very few young men are involved in the carob tree production.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
80% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Since rat attack is the most damaging factor affecting the growth of carob trees and the quality of the product, the land users who apply the technology have more income with unsignificant yield losses caused by other factors.
Level of mechanization is manual labour (pruning, irrigation and harvesting) and mechanised (cultivating, weeds control, pesticide applications)
Market orientation is mixed (farmers either sell their products individually or sell them as a group)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
35 Kg/tree
Quantité après la GDT:
45-50Kg/tree
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Trunk and branch protection lead to yield increase
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Although other factor like fire, frost, pests and diseases can cause production failure, rat attack is considered as the most damageable
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
1,5 euro/tree
Quantité après la GDT:
1 euro/tree
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
During pruning, large dead branches should be removed
charge de travail
Quantité avant la GDT:
50 trees/day
Quantité après la GDT:
65 trees/day
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
During pruning,
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Carob fruits are free from infectious diseases transferred by rats
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduction of rat populations within the production area minimizes the risk of man diseases infection like typhos,
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology improved both livelihoods and human health. The growers income has increased more than 10-20% due to the reduction of the damage caused by rats every year. The reduction of the number of rats minimized the risk of human pathogens such as typhus which was very common in these areas.
Impacts écologiques
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase of predators in the areas around the carob trees since rats can not climb on carob trees
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fields with carob trees being attacked by rats are more sensitive to fires since they are abandoned by their owners
Autres impacts écologiques
Control of rat population
Quality of carob trees and fruits
Plant growth
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
On small trees the aluminium layer is pressing the trunk in a way the tree can not grow normally. In this case the aluminium layer must be replaced with a layer once every few years
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les champs voisins
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
rat population around the SLM technology is decreased therefore the damage caused by rats to the neighbours is also decreased
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Decrease in rat population rear farms also decrease the damage caused on the farm infrastructure (wires, wood, plastic equipment), by rats
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
Commentaires:
The use of aluminium layers covering the trunk of carob trees is not affected by the climatic conditions. Climatic conditions such as heavy rain could affect the use of plastic tubes which include poisonous bait or the direct poisonous cubes placed on the tree branches.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
Due to the damage caused on the carob trees by rats already, the trees will need some time (2-3 years) to create new branches able to produce fruits. Furthermore no new damages occur on trees.
During the first 3-5 years the aluminium layer can remain on the trees. After this period the aluminium should be replaced with a larger one due to the enlargement of the tree trunk.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
10
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Due to the lack of effective and cheap ways for controlling rat attack on carob trees the land users are adopting the technology, and so far they get positive results.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Few other land user are interested in adopting the technology. Many other land users are not adopting the technology because they inherited the land and they are not actually working on the land in order to make profit.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| easy to install |
| the technology can be used over a long time |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
the technology can be used over a long time How can they be sustained / enhanced? use of non-oxidizing material |
|
the aluminium layer can be bent easily How can they be sustained / enhanced? both vertical edges should be hold each other by the use of a spur |
| low cost |
| easy installation |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| the aluminium layer can be a target for thieves who steal metal |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| the aluminium layer should be replaced in time because the trees are growing in size | install larger aluminium layers and lold it with spring |
| The aluminium (metal) can overheat during summer time | Spray the layer with white paint |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé