Kitui Sand dams [Kenya]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Mung'eeto (KIKAMBA)
technologies_1486 - Kenya
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

SASOL community approach - for sand dams in … [Kenya]
Community based water resource development
- Compilateur : Donald B. Thomas
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
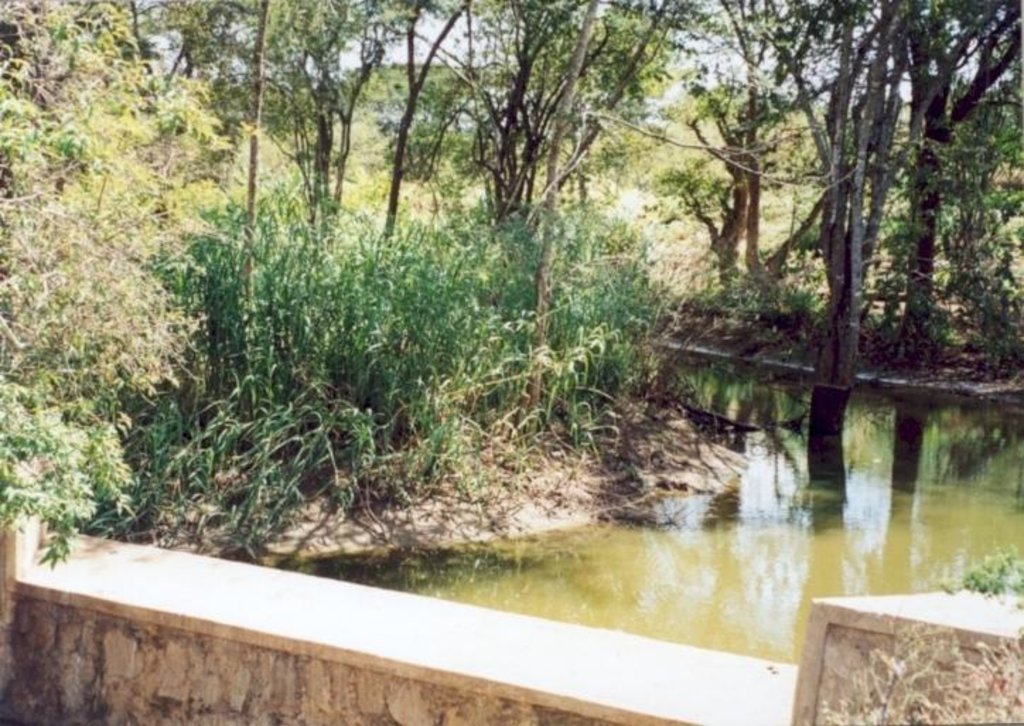
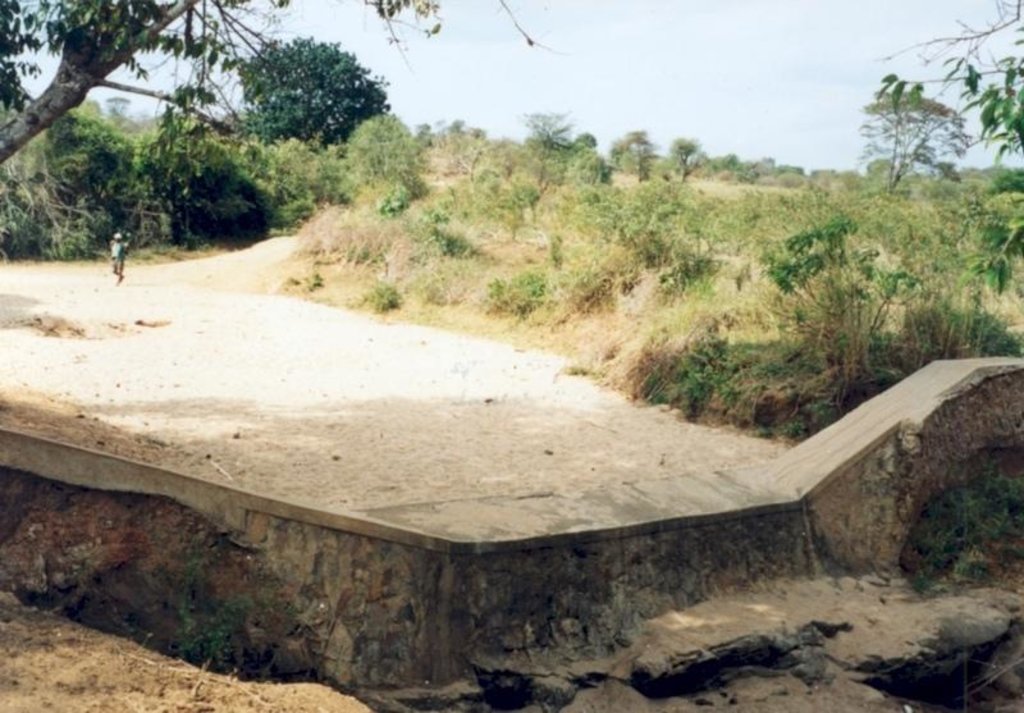
Masonry dam in seasonal watercourse or river that stores water in the sand which accumulates above it.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The dams are usually constructed where there is a rock bar in the river bed. The dam wall is raised 1.5 - 2.0 M above the level of sand.They fill up quickly with sand in which water is stored. The sand reduces the rate of evaporation and about 30% of the volume can store water for use in the dry season. If the dam is well constructed, maintenance is minimal. The dams are especially useful in semi-arid areas with catchments that provides plenty of coarse sand to fill up the reservoir.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
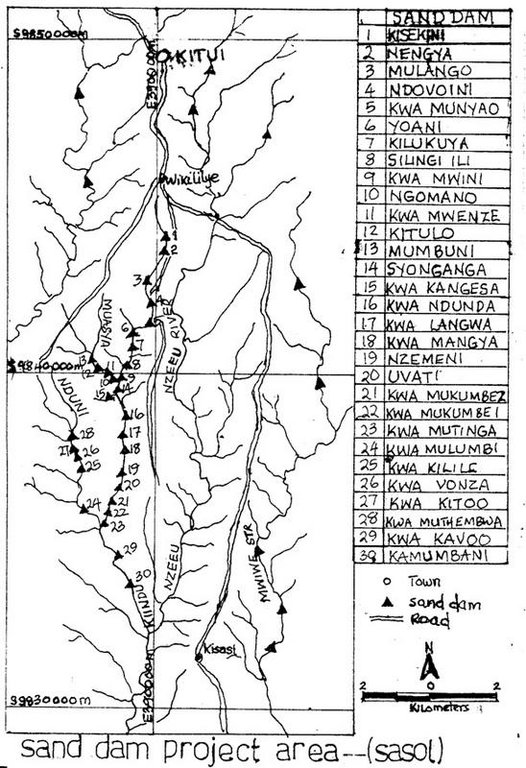
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kenya
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Eastern
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 200 m2.
The area was selected because of the need for water in the dry season and the density of population to implement the sand dam construction
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Introduced in semi arid regions of kenya by the colonial government to increase water availabilty during the dry period through construction of masonary barrier across ephemeral rivers.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Etangs, barrages, retenues d'eau
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Semi-arid conditions with frequent failure of rains and experience water availabilty problems during dry period. High incidence of both on-farm soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): drought , insufficient rains, water scacity.
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - JanSecond longest growing period in days: 58 Second longest growing period from month to month: Mar - May
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wr: érosion des berges
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Semi-arid climate)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (reduced infiltration and drying of springs), overgrazing, poverty / wealth (Lack of captial), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - incidence of water borne dieseases)
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Construction material (concrete): Masonry structure using rocks & stones with some reinforcing bars and wires
Construction material (other): reinforced bars and wires
Lateral gradient along the structure: 5%
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Kenya shillings
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
78,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging out riverbed to reach rock bar | dryseason |
| 2. | Laying concrete foundation | dryseason |
| 3. | collection of materials (rocks, sand) | dryseason |
| 4. | construction of dam and wing walls | dryseason |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | inspection of dam for leakages | after the rains/each cropping season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
depth of the foundation, valley width.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
depth of foundation trench to the rock bar, the width of the river valley and the height of the banks.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: Also gentle
Lanforms: In riverbeads
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Most areas have shallow soils with unweathered rocks.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium and soils are prone to surface sealing
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
1% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land.
55% of the land users are poor and own 45% of the land.
14% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: A large proportion of the adult male population is working outside the district
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
23000 Households in an area of 200 sq km
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
70% of land user families have adopted the Technology.
23000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: self help groups have started pooling together their resources for implementation of the technology especially in areas where there has never been an NGO or such a project.
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
"Where there is no water" SASOL and Maji na Ufanisi 1999
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Maji na Ufanisi Nairobi or SASOL Kitui
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

SASOL community approach - for sand dams in … [Kenya]
Community based water resource development
- Compilateur : Donald B. Thomas
Modules
Aucun module trouvé