Sugar Mill Wastewater Re-use for Irrigation [Philippines]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1914 - Philippines
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Perater, Jr. Feliciano
BUSCO Sugar Milling Co., Inc.
Philippines
Spécialiste GDT:
Betonio Gloria
Department of Agriculture-Regional Field Office 10
Philippines
Raquid Jemar
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Adel Dianne Michelle
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Benavidez Ryan
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Philippines
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - Philippines1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Re-using of wastewater to support agricultural crop production, as well as, to help in environmental protection
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
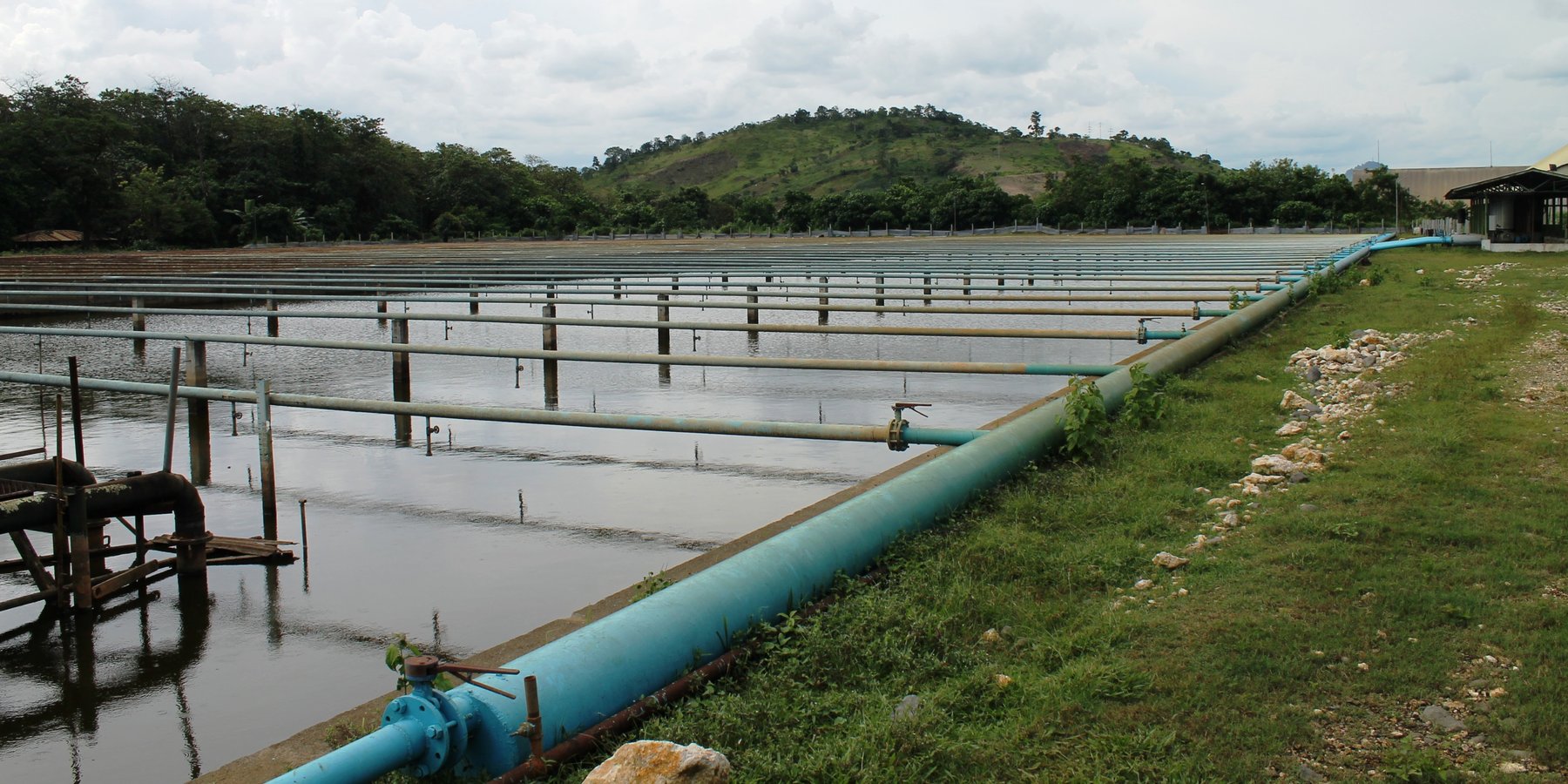
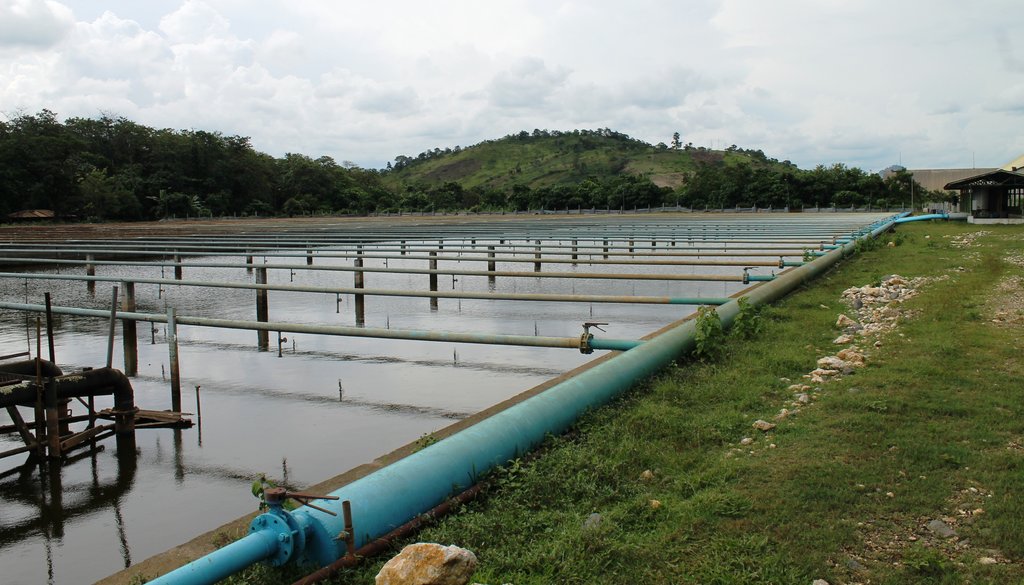
With increasing water demand and with the changing climate, water availability or water security is critical for the agriculture sector as this resource is a fundamental prerequisite in crop production. Various solutions are tapped and one of it is harnessing the potential of wastewater to be used for irrigation.
In the Philippines, one of the companies that utilize their treated wastewater is the BUSCO SUGAR MILLING CO., INC. located in Brgy. Butong, Quezon, Bukidnon. This treated wastewater is currently being re-used as irrigation water for the BUSCO Cane Farms areas, adjacent to the Mill Site covering 493 hectares and also to their leased adjacent 323-ha agricultural land.
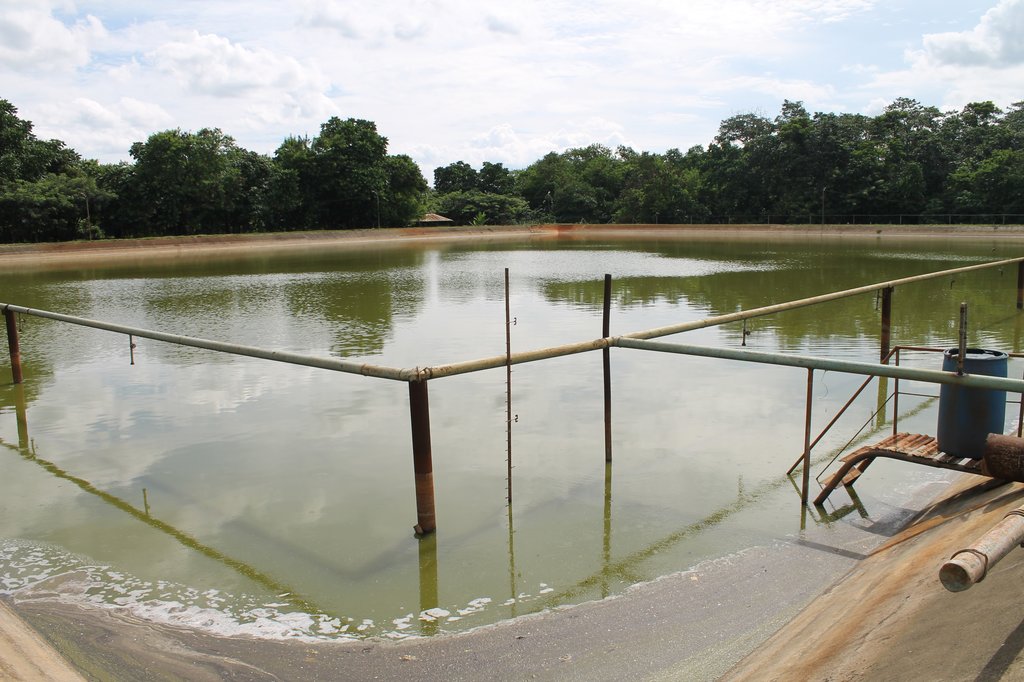
Primarily, water as an industrial by-product is evident in both raw and refined sugar milling process. Volume of wastewater can be generated in the following sources or stations of sugar production: mill and cane handling station, process and/or boiling house, refinery house, and boiler house. In BUSCO, this wastewater all goes to their common wastewater treatment plant with a capacity of 100,000 volumetric meter and uses primary and secondary treatment.
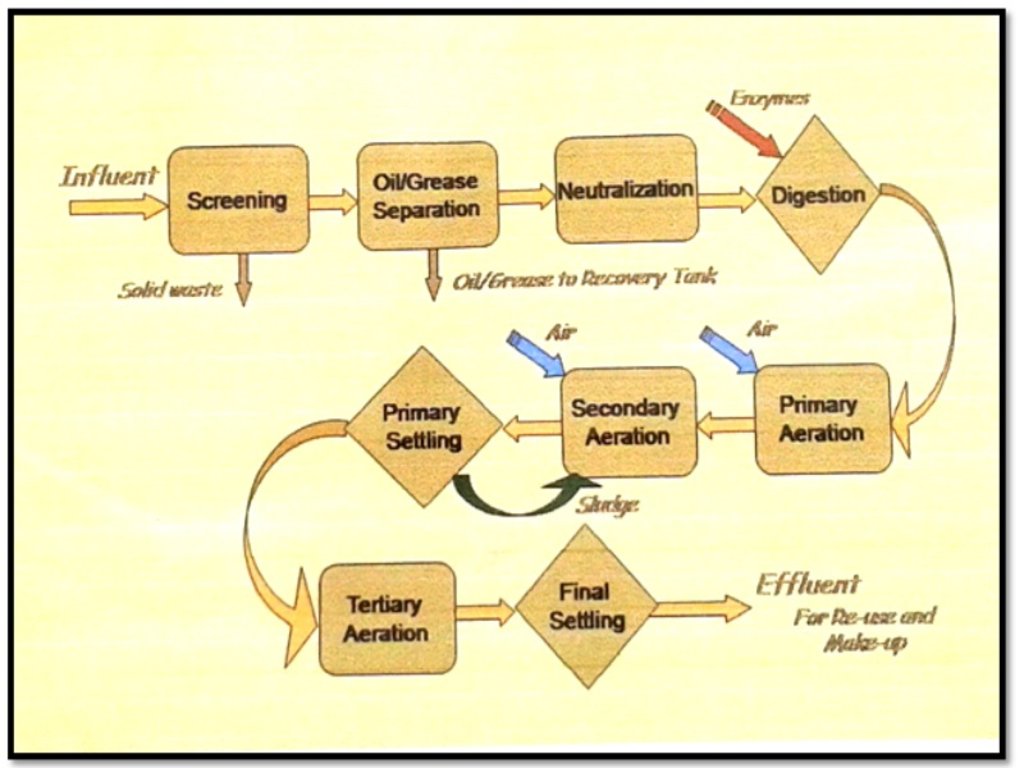
The treatment started with the screening of influent (waste water) which passes through a motor driven conveyor type system to separate the solid waste such as bagasse, bagacillo, silt/mud, sand, and trash canes. After the screening, it now proceeds to the oil/grease separation at the separator tank. Oil and grease that usually floats were removed via manual skimming. The next treatment process is called neutralization wherein the acidic influent (phof 4.0–5.0) will be added with chemicals (i.e. Lime and/or caustic soda) to neutralize and maintain the pH at 6.0–8.0. The neutralized wastewater is then impounded in a digester tank to undergo the process of digestion. Enzymes or bacteria are being introduced to enhanced biodegradation. Aeration is also applied to minimize suspended solids and scum formation. After this, wastewater is transferred to the lagoon for primary aeration process. Lagoons are belted with air diffuser membrane to produced fine bubbles and efficiently dissolved oxygen. Waste water was aerated and polluting substance decomposed. Further, the wastewater and the activated sludge are again mixed and aerated in the secondary and tertiary aeration where the polluting substances are further decomposed by oxidation and are absorbed. Finally, it will store in the final settling pond which will then be utilized for irrigation. The treated wastewater in BUSCO has a Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) value of 50mg/L which is within the prescribed standard BOD parameters of wastewater quality to be used for crop irrigation (< 150mg/L).
Irrigation is done through the hand move spray irrigation system. It uses aluminum pipes backed by centrifugal pumps and spray nozzles. Aside from supporting the sugarcane water requirement particularly during dry months, the treated wastewater/effluent contains nutrients (Nitrogen- 2.5mg/L; Phosphorus- 3.8 mg/L; Potassium- 3.8 mg/L) which reduce fertilizer requirements of the sugarcane farm.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Philippines
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Bukidnon
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Butong, Quezon
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- canne à sucre
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion des déchets/ gestion des eaux usées
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S8: Structures d'assainissement/ de gestion des eaux usées

modes de gestion
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation hydrique
- Hp: baisse de la qualité des eaux de surface
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Wastewater treatment flow diagram of BUSCO. The treatment started with the screening of influent (waste water) which passes through a motor driven conveyor type system to separate the solid waste such as bagasse, bagacillo, silt/mud, sand, and trash canes. After the screening, it now proceeds to the oil/grease separation at the separator tank. Oil and grease that usually floats were removed via manual skimming. The next treatment process is called neutralization wherein the acidic influent (phof 4.0–5.0) will be added with chemicals (i.e. Lime and/or caustic soda) to neutralize and maintain the pH at 6.0–8.0. The neutralized wastewater is then impounded in a digester tank to undergo the process of digestion. Enzymes or bacteria are being introduced to enhanced biodegradation. Aeration is also applied to minimize suspended solids and scum formation. After this, wastewater is transferred to the lagoon for primary aeration process. Lagoons are belted with air diffuser membrane to produced fine bubbles and efficiently dissolved oxygen. Waste water was aerated and polluting substance decomposed. Further, the wastewater and the activated sludge are again mixed and aerated in the secondary and tertiary aeration where the polluting substances are further decomposed by oxidation and are absorbed. Finally, it will store in the final settling pond which will then be utilized for irrigation. The treated wastewater in BUSCO has a Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) value of 50mg/L which is within the prescribed standard BOD parameters of wastewater quality to be used for crop irrigation (< 150mg/L).
Auteur:
BUSCO Sugar Milling Co.
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of Waste Water Treatment Facilities |
Commentaires:
information not available.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
information not available. The Company bore 100% of the cost.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
Commentaires:
information not available. The Company bore 100% of the cost.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
information not available. The Company bore 100% of the cost.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soils are not relevant for this Technology.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
- personnes âgées
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- entreprise
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Sols
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts de la sécheresse
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
The BUSCO Sugar Milling did it spontaneously without receiving payments. Reduction in the wastewater discharge fee since the BOD level of the treated wastewater is within the allowable range.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
•Source of irrigation during water shortage on dry months •Additional source of nutrients thus decreasing the dependency on chemical fertilizers •Eliminate/Reduce wastewater discharge on water bodies thus reduction of water pollution •Complying to the environmental standards •Savings on wastewater discharge fee of the industrial company |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Contribute in the elimination or reduction of water pollution in the near-by water bodies. Complying to the environmental standards. Water availability particularly during dry months. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| none |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Investment cost. |
Optimizing the operation of the treatment facility; possible utilization of other wastes like sludge, mill ash, and mudpress into soil conditioner or fertilizer |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
05/10/2016
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
not available
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé