Pasture management through rotational grazing [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Malgorzata Conder
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Deborah Niggli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1585 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Rotational grazing on private grazing land used as daily pastures
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
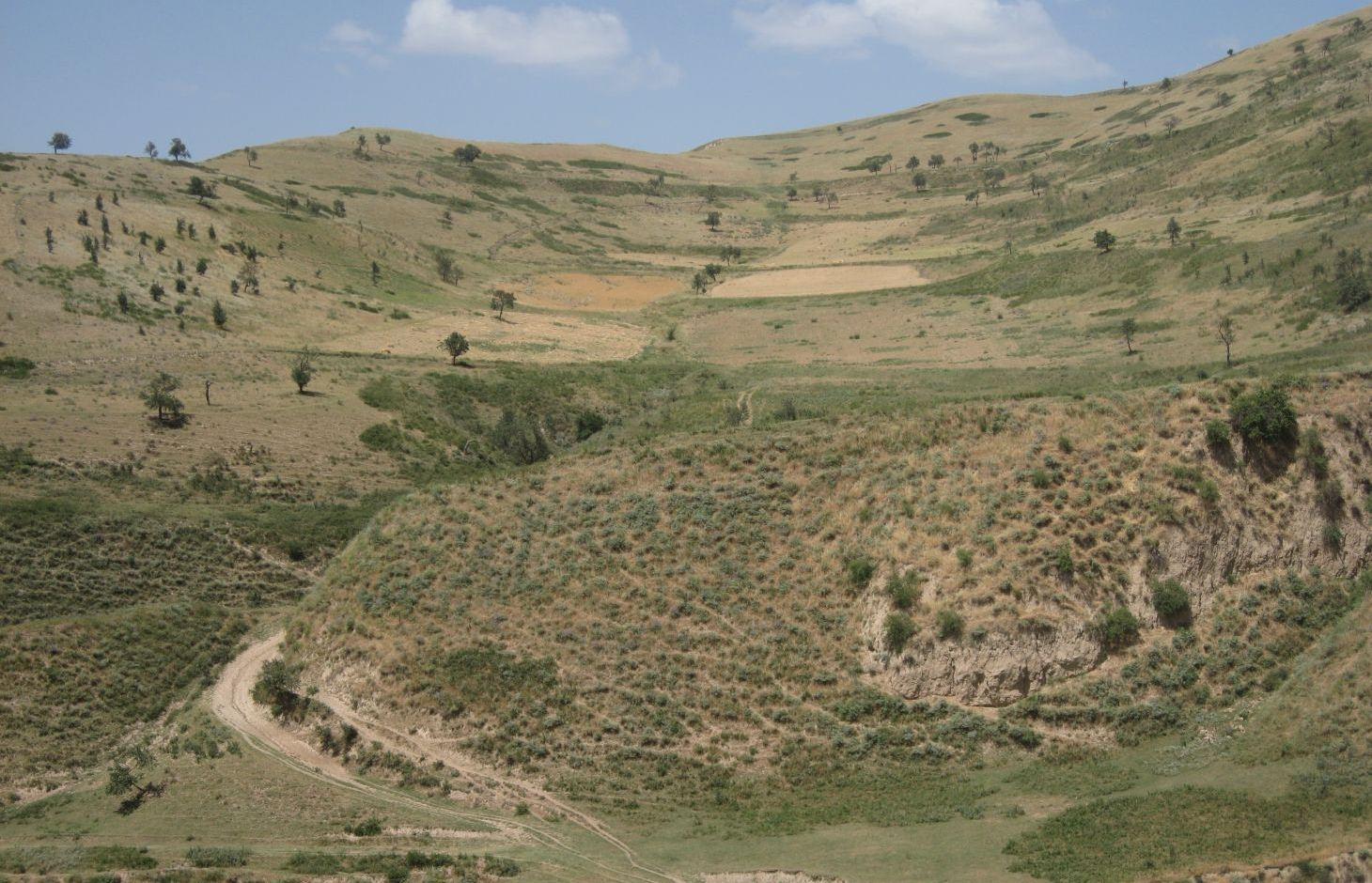
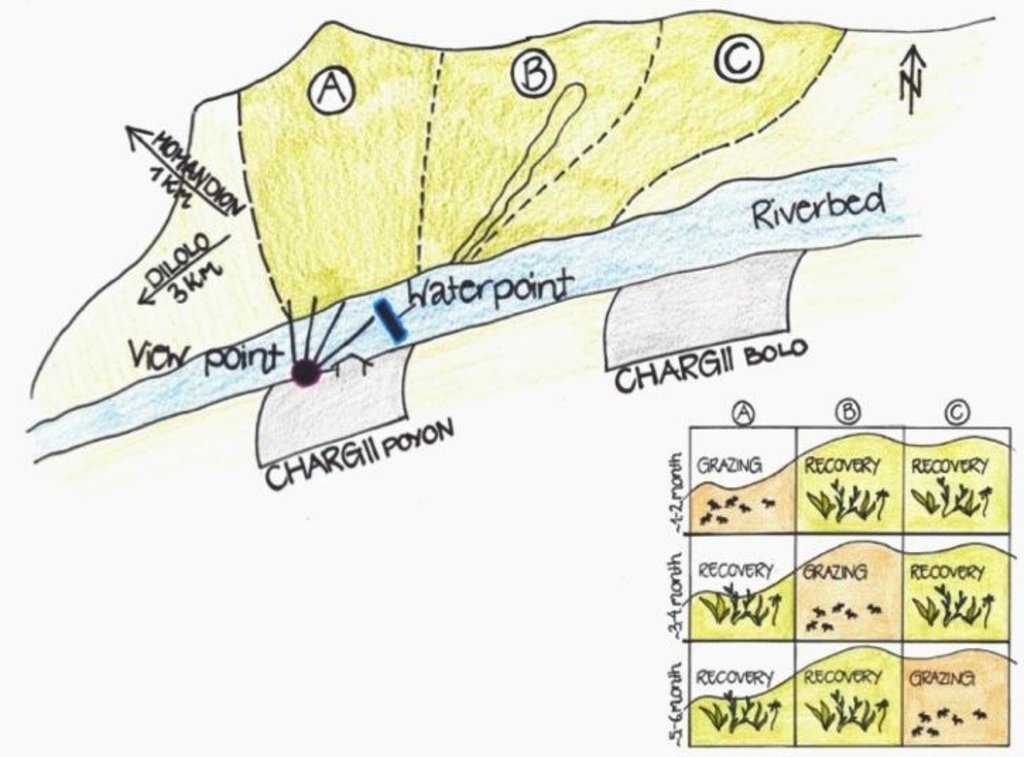
A riverbed divides the pasture where rotational grazing is practiced with the village Chargii poyon, where the certified land user and owner of the pasture lives. From a view point nearby his house, he has a good view on and hence a good control over the pasture area. This allows him to keep intrusive livestock outside, having a limited number of grazing livestock in the pasture. The area encompasses 119 ha, from which 5 ha are rented out as crop land.
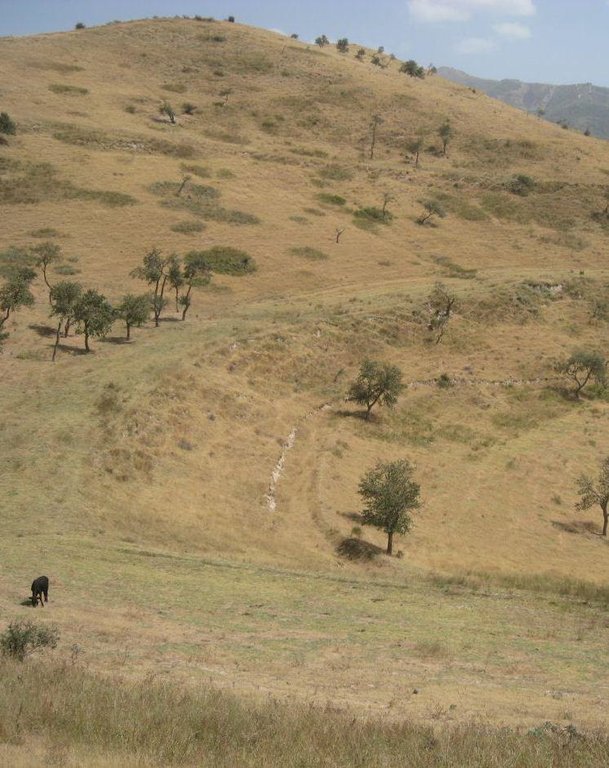
Land tenure conflicts about this pasture existed over many years, because there wasn’t declared any owner. The certified land user of Chargii poyon claims to possess the pasture since 1999. It is unclear how he got the land transferred. Being aware of the ongoing degradation of this land, the certified land user divided the area into 3 parts and introduced controlled grazing in 2007. While one part is being grazed the other two lie fallow. After one to two months of grazing in one area, the herds move to the next area. The rotation phases depend on the availability of grass. In June 2012, at the moment of documentation, there were 145 cows and some 30 goats and sheep. The number of animals is varying seasonally, with a higher amount of animals in summer than in winter. Compared to other pastures in summer, more grass in available on the pasture with rotational grazing. In winter grass availability is comparable between the pastures. This may explain why a higher number of livestock is recorded on the pasture with rotational grazing in summer.
The pasture is controlled by the farmer and further 4 people to avoid livestock intrusion.
In a seminar organized by Caritas Switzerland, the farmer learned about increasing long-term productivity of pastures by vegetation recovery. The idea of pasture rotation convinced him in order to raise productivity on long-term. The main reasons for changing the pasture management were the advanced stage of deforestation, increasing overgrazing, and the additional source to get the land taxes paid. The management of the pasture by rotational grazing on three areas allows the non-grazed areas to rest and recover. Less grazed and trampled areas result in an increase of the vegetation cover and thus to higher fodder quality, as well as increased soil stability and therefore a reduced risk of disasters, such as floods.
The farmer expected that the implementation of land conservation measures would stop the on-going pasture degradation and would assure long-term and sustainable use of the land. Despite the rotating system, the grazing land is still overgrazed and shows signs indicating moderate erosion, but it is less degraded than other pastures in the watershed. The area being the most far away from the settlement is in best conditions. The closer to the riverbed the more degraded and eroded the pasture is.
Additional measures are necessary to reduce soil erosion and gully formation in the area
Livestock owners have to pay a fee to the farmer for grazing cows, but not for grazing sheep and goats. The amount of the fee depends on the provenance of the herder. Fees vary greatly between the villages. Because of solidarity, Chargii villagers pay much less than herders from villages located further away. Momandion villagers pay 3 times, Dilolo villagers even 9 times more than Chargi villagers. But the certified land user claims to be flexible in the amount of fees for poor herders. He has to pay taxes to the government for the property and salary to the surveillants. If more money is available, also generated by the fees, the certified land user claims to invest a part of the money into the pasture. He would like to build another water point and to plant trees in the upper area. Livestock could graze in more remote areas which would reduce the pressure on the pastures in the lower area and decrease the soil compaction.
The pasture is located in the middle zone of the Obishur watershed and on the foothill above the riverbed plain. This pasture, located between the villages of Chargi poyon, Chargi bolo and Momandion and not far from Dilolo village, is a reachable place for many livestock of private households. In the riverbed, the only water point is installed where livestock is watered at midday. Due to tree cutting in the past, only a few shady places exist. Vegetation cover varies depending on the exposition of the slopes and the accessibility of the pasture. North-facing slopes have a more abundant vegetation cover. Some flanks are difficult to reach because of dense thorn bushes. A big gully, hardly accessible by livestock, is about to be covered again by naturally re-growing bushes and trees. Nevertheless, signs of erosion and rill building can be observed. Due to the closeness to the villages and to the pressure on natural resources it is crucial to sustain a controlled pasture management.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Muminabad
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.14 km2.
Total area is 119 ha, but 5 ha out of it are rented for cropping
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Idea of how to improve ground cover was initiated by a workshop from Caritas, but the rotational grazing was introduced by the farmer himself in 2007
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
- rotational grazing
Type d'animal:
- caprine
- ovins
- cows
Commentaires:
Livestock density (if relevant):
> 100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazed pasture with frequent big gullies, rills and trampled areas. Almost complete deforestation of the grazing land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water availability and water points for grazing livestock. Gradual degradation and erosion of the pasture which has to be stopped.
Grazingland comments: Rotation within 119 ha of grazing land
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- système de rotation (rotation des cultures, jachères, agriculture itinérante)
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

modes de gestion
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, governance / institutional (No/ Insufficient management planning and control), livestock pressure (Due to subsistence of the population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (impact of overgrazing and deforestation), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The hilly pasture of 114 ha in total is divided more or less vertically in 3 areas. In each area, the pasture between the ridge and the riverbed is covered. After having grazed one area for approximately one to two months, the herd moves to the next part. This means that two areas rest and grasses recover, while one is being grazed.
Location: Chargii poyon. Muminobod, Kathlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (When benefits of pasture management are known and understood, high technical knowledge isn't required)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (When benefits of pasture management are known and understood, high technical knowledge isn't required)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Change of land use practices / intensity level: In 2007 controlled and rotational grazing was introduced where no pasture management existed before
Auteur:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
12.40
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Introduction/information of pasture management among the herders | once in 2007 |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Introduction/information of pasture management among the herders | - | 1,0 |
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Salary for 5 people to guard pasture and herders: Monthly salary 70 Som/pers, pers d unknown | every day, from spring until autumn |
| 2. | Annual Rent | once a year |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Guarding pasture and herders | Persons/6months | 5,0 | 86,96 | 434,8 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Annual rent | ha | 114,0 | 1,359649 | 155,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 589,8 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 589,8 | |||||
Commentaires:
Costs which concern the information transfer to the herders is not calculated, as it is done informally. Only guardening by the employed people is monetarised.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The farmer already owns the land user certificate for the property and only has to pay annual taxes and the people who control the pasture. He covers these costs with the rent he gets for the grazing livestock.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Totally 800mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200mm asl, wheater station Muminabad). Precipitation increases 60mm per 100m of altitude in average.
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average: Some flanks over 40%
Slopes on average: Also rolling
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Low-medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: Poor-medium
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Water quality (untreated): For livestock, surface water in spring (because of snow melting and rainfall), in summer ground water at one water point
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Tree cutting, due to grazing more and more uneatable species
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men are taking decisions and administrating the property whereas women are working on the field. Privileged land user because he owns a big area.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2% (Farmer owns a big property of 119 ha).
Off-farm income specification: Additionally bee-keeping
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
3.2 ha if 7.7 pers/household for totally 4100 ha pasture
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
surface de production
gestion des terres
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
disparités économiques
charge de travail
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
institutions communautaires
apaisement des conflits
Livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The farmer possessing the user certificate of the land states that even poor families are allowed to graze their livestock for a low rent and thus this pasture management seems to lead to more equity among the farmers of different economic classes. The better the livestock is fed, the higher the value of livestock and the wealthier the households are. But this statement could not be verified and should be taken with precaution.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
ruissellement de surface
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
compaction du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
diversité des habitats
Autres impacts écologiques
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
Thanks to a better vegetation cover, the infiltration of rainwater is facilitated which results in an increase in soil moisture and thus to a higher resilience to droughts or higher temperatures.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Establishment and maintenance cost are low. Input consists mainly of the establishment of a pasture management which is based on dissemination of knowledge and information
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1 Household
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
At the time of documentation it wasn't known if there exist other land users with a similar technology. There are more farmers grazing on that rotational pasture than in the very beginning.
Precondition is a big grazing land property, but only a small amount of farmers do own such a property.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Equity amongst the farmers through flexible renting prices |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| No high establishment and maintenance cost |
| No high physical inputs required |
| Economic (better fodder quality) and ecological benefits (grass recovery, erosion reduction) can be seen as a direct result of pasture rotation |
| It is a good platform to share and spread knowledge of good practices, as over time many farmers come regularly to graze |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Other cost intensive investments required like building another waterpipe and planting trees |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Precondition for such a setup is that one farmer owns the user certificates for a big grazing land, which is unusual. It is not clear how he got the user rights. | Ideally communal grazing land would be divided among several households sharing access to pastures |
| The pasture shows still a lot of signs of erosion and degraded areas. | Less livestock or division into more parts to allow the vegetation cover to rest for a longer time span. Enhance a homogeneous grazing of upper and more distant parts of the pasture. Control if pasture management is adhered consequently. Additional conservation measures such as resowing of specific areas, or fencing of badly degraded areas such as gullies. |
| This system works when there are communal pastures in the surrounding area. On the here documented pasture, less livestock is kept than on communal pastures. This lower density of livestock is not realistic at watersheds level, because it might raise the pressure on land in the other pastures. | Rotating within the grazing land just combats the fact that there is too much livestock compared to the available area |
| It is not clear whether the main motivation of this private pasture is to stop degradation or to collect the renting fees | Elaborate an investment plan showing how the collected fees will be reinvested into grazing land infrastructure and how much is taken for reimbursing the efforts of the certified land user. |
| It is not known whether the different fee levels according to the herders provenance does not create discontentment | Transparent price structure |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
03/09/2012
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé