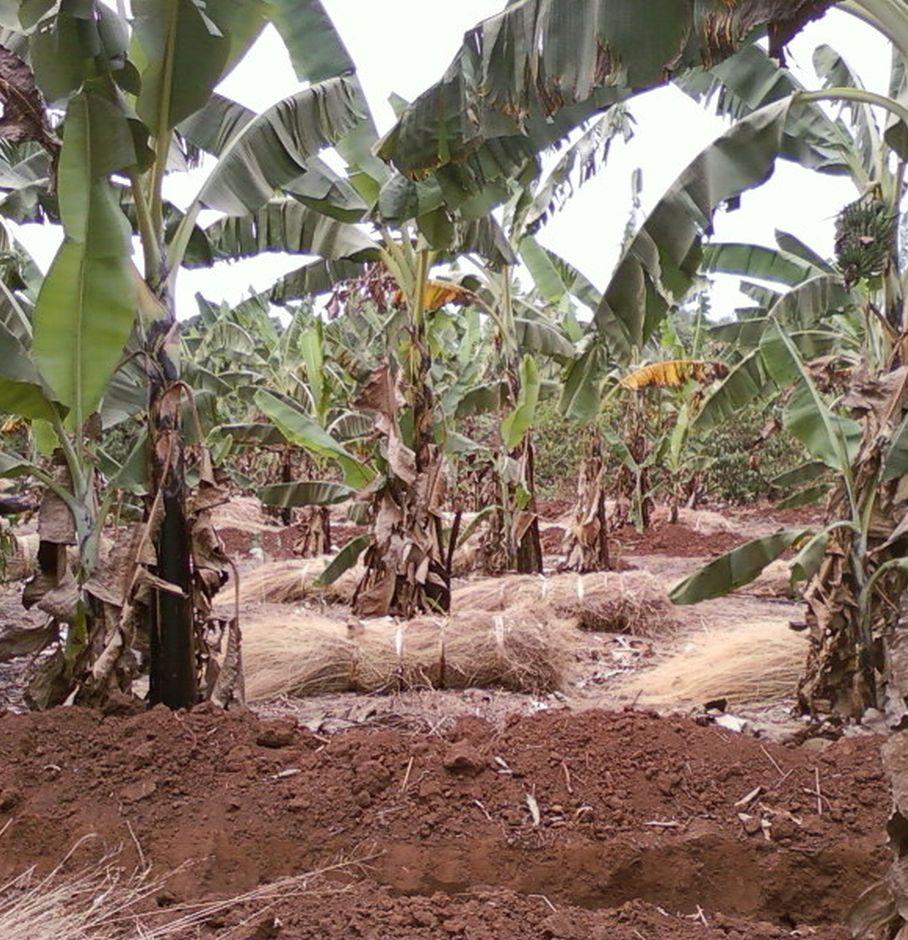
Contour ditches combined with manures and mulch grass in banana production. [Tanzanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Godfrey Baraba
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
makinga maji ya kati
technologies_1215 - Tanzanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - TanzanieNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - Tanzanie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Is a cross slope berier characterised with 2m widith by 2m depth furrow, farm yard manures and grass mulch in banana production.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
The level ditches combined with farm trushlines, farm yard manure, and grass mulch technology in banana production is the digging of a furrow measured 2m wide by 2m deep along the contour in the banana plantation. The technology is applied on a perennial cropland by combining structural, vegetative and agronomic measures. The climatic zone is sub humid in a gentle to moderate slope with medium to deep loam clay soils. The hand cultivation is done manual using hand hoes in a mixed production system. The establishment procedures contour demarcation using a local made A-frame, digging a furrow along the contour, digging the banana holes spaced at 3.6m by 3.6m between the structures, mixing farm yard manure with top soils and planting banana suckers after restng the mixture for not less than 60 days. The maintenance procedures requires, weeding the field, desuckering, detrushing, planting beans, topical manure application, grass mulch application and filling the contour furrow with farm trushlines. The land ownership is individual not titled. This technology was introduced in 2012 by Kagera TAMP using the FFS methodology. In case of sensitive climatic extremities
Purpose of the Technology: The major purpose for technology application is reduced moisture stress, increased soil water retention, reduced soil erosion to increase crop productivity in a sustainable land management.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment activities included; first to clear the field and demarcate the contour line using a local made A-frame done at the end of short rains. Second is to plough and harrow the field done in the early dry season. Third is to space and dig holes for planting banana suckers done in mid of dry season. Fourth is mixing farm yard manures with top soils and cover the hole for not less than sity days before planting, this is done in mid of dry spell. Fourth is to plant certified banana suckers done in late dry season. Fifth is to dig the contour ditch done in at the onset of long rainfall. The maintenance activities includes; first to weed the entire field done twice before the onset of rainfalls. Second is to apply farm yard manures concurrently with grass mulch done once in the late dry period. Third is to desucker and detrush banana plants done twice before planting beans. Fourth is to plant beans done once before the onset of long rainfalls.
Natural / human environment: The natural environment in the location is 750-1000 mm rainfalls, foots lopes valley floors landform, gentle slope, shallow to meium soil depth (50-80)cm and (80-120)cm characterised with two growing periods. The social economic persisting are small scale land users farming on( 0.5 to 2)ha per house hold. The land ownership is individual not titled while the water use rights is open access. The importance of off-farm incomes is less than 10% and the market orientation is mixed while soil cultivation is manual and livestock are not fed on farm residues.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tanzanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tanzania
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Karagwe District Council
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Three host farmers of FFS allocated a total of 1.5 acres (three different sites) as a leaning sites. While 22 group members implimented the technology with modifications in their farms with average of 0.5ha X22 =1.1ha
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Introduced by TAMP -Kagera, Tanzania in 2012 using FFS methodology.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - patates douces, igname, taro, colocase, autres
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- bananier/plantain/abaca
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- café, cultivé en plein champ
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 90; Longest growing period from month to month: October to December; Second longest growing period in days: 60; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem related to soil and vegetation in the area were soil erosion, soil moisture stress and fertility decline and reduced organic matter content.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): moisture stresss and soil erosion.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol

pratiques végétales
- V5: Autres

structures physiques
- S2: Diguettes, digues
Commentaires:
Specification of other vegetative measures: lemon grass
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mulching, temporary trashlines, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bl: perte de la vie des sols
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (cultivating along the slopes), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (continous banana production without soil fertilization.), change of seasonal rainfall (dry spell prolonged), droughts (the area experienced a six months dry period.), population pressure (High population growth rates had forced to cultivate slope lands to feed the population.), poverty / wealth (community cant afford to invest in soil conservation.), education, access to knowledge and support services (inadequate staffing reduces extension services rendered to farmes.), governance / institutional (Agriculture policy had a narrow focus on environmental issues.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Basic agronomy principles, farm structures and vegetation management are taught at colleges.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (most of material required to implement the technology are common to them.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Pumpukins and water melon
Remarks: spaced at 3m in the space between the contour bunds.
Mulching
Material/ species: hyperhamia spps
Quantity/ density: 1500
Remarks: spread across the slope with 15cm thick covering the soil surfaces where banana and coffee are plant
Temporary trashlines
Material/ species: banana dry leaves and psodstems.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: farm yard manures
Quantity/ density: 48979
Remarks: 60kg per plant during planting and 36kg for maintenance.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 1666
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 18
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 778
Structural measure: contour bund
Spacing between structures (m): 18
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (earth): soils excavated from the furrow.
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.64
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | To plant lemon grass | March |
| 2. | To plant water melon | april |
| 3. | To gape fill lemon grasse | september |
| 4. | Dermacating the contour lines using simple made tool (A-frame) | June |
| 5. | To dig a furrow and excavating the soils to be placed on either lower side or upper side of the furrow. | August |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 609,45 | 609,45 | |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 114,71 | 114,71 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 420,17 | 420,17 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost / manure | ha | 1,0 | 756,3 | 756,3 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1900,63 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1900,63 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding in the space where coffee and banana are planted. | january and June |
| 2. | desuckering | February and August |
| 3. | Detrushing | February and August |
| 4. | manure application | July |
| 5. | Spreading mulch grasses | September |
| 6. | Harvesting banana and coffee. | routeenly |
| 7. | To harvest lemon grass | routeenly |
| 8. | To remove soil sedments from the furrow and place them along the contour lines. | june and January. |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 416,91 | 416,91 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 88,24 | 88,24 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost / manure | ha | 1,0 | 252,1 | 252,1 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Grass mulch | ha | 1,0 | 441,18 | 441,18 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1198,43 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1198,43 | |||||
Commentaires:
Labour calculated per ha of land protected, Farm yard manure calculated per plants applied, mulch grass calculated per ha of land protected, seedling and seeds calculated per ha of land protected.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most determinate factor affecting the cost is labour
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
excès
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: Excess during short rainfals and medium because two permanent river tributaries (misheke and Charuhanga) flows throughout the year.
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water when gravity water supply from Kasunkuni river tributar and poor when over-flooded Mwisa river during short rains.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Mchwa, sisimizi, vipepeo and earth worms
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
99% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
1% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Land users who applied the technolgy can meet hie/her cost of living (mainly food) from farm income while land users who have not applied the technology can not the household cost of living from the farm.
Market orientation of production system: Coffee are for sale while banana only excess is for sale.
Level of mechanization: Hand hoes use during farm establishment, but late local made tool (vihosho) are used for weeding and desuckering purpoes.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
< 0.5 and 0.5-1 ha: 75 % of landusers
2-5 ha: 25 percent of landusers
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not yet harvested the first yield
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch grass have reduced moisture stresses
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farm yard manures, mulch grasses, lemon seedlings, certified banana suckers and water melon seed
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Lemon grasses and pumpukins sales
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Additional activies should demamnd more labours
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased food production should ensure availability, while sale of coffee should ensure accebility to balance the diet
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
FFS group members
institutions nationales
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Out-soucing of activities to TCRA
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Udelt learning using FFS methodology
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Three group members have no land, male and female have equal chances in the group
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch grasses and contour bung
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch grasses
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch grasses
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch grass and pumpukins
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Lemon grasse planted along the contour bunds
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Farm yard manures application
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mulch grass and trushlines
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Use of certicefid banana suckers
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Attention for grasses collection before fire seting on has increased
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les champs voisins
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Water run-off reduction
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No longer concentrated run-off
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Commentaires:
The technology can be modified of metre drain and the collected water to be used for small scale irrigation.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
In the short term returns banana harvested should equate the establishment costs, while in the long term retuns there will be no further establishment, therefore returns are very positive.
in the short term retuns negative compared to maintenance because all returns equate establishment costs, while in the longterm returns should be positive due to complimentary effects of protected land to improve productivity.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
70 households in an area of 10 ha
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
Commentaires:
35 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Three host farmers were provided with farm yard manures and mulch grasses.
35 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The FFS started late due to inadequate council staffing.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Still early to give any comments (actual implimentation started September 2013.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The technology is easy to learn and simple to implement. |
| Production results are of short gestation period when considering test crop (banana) for land users to make the decisions. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The technology increased the farm input (farm yard manures and grass mulch) costs of which average land users (peasants) can not afford from his farm income on top of meeting his daily cost of living. | Introduce zero grazing to provide farm yard manures and quick income generating activities. |
| Big land area is require to realise the ecological benefits. | Sensitize political will to stimulate and support technology up scaling through multiplier effects. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
30/07/2014
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé