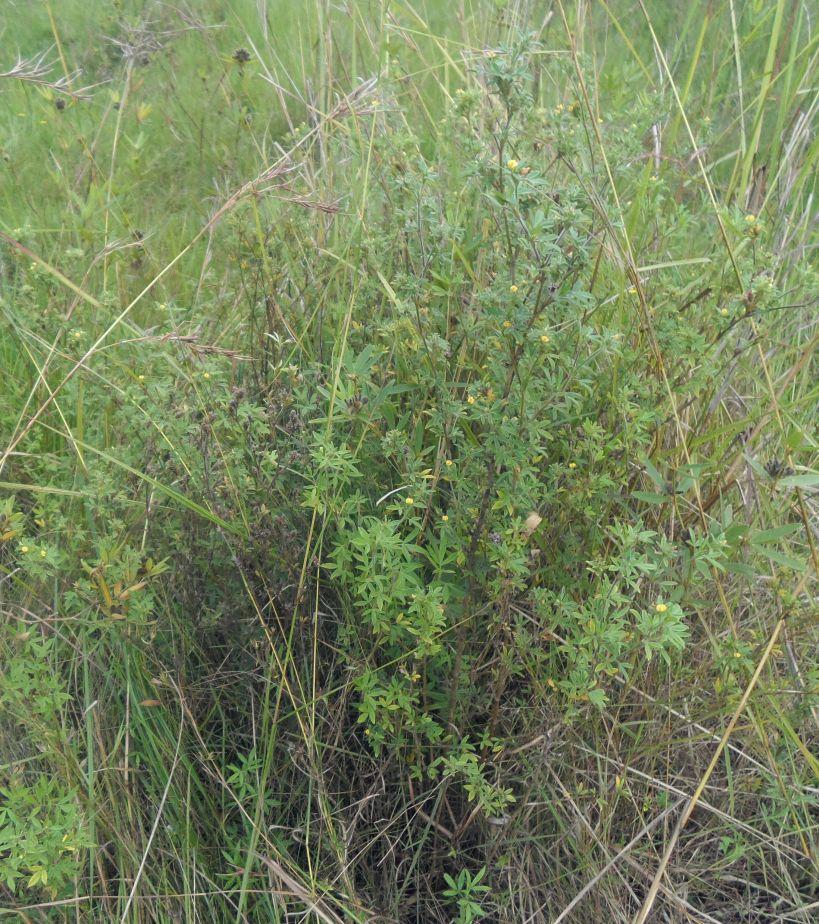
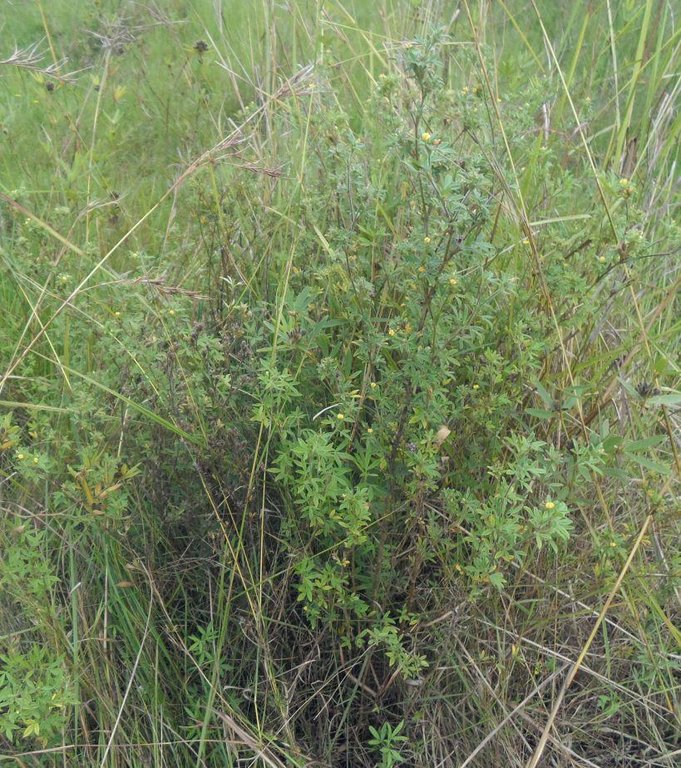
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and regeneration of cut and carry materials. [Tanzanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : ALLAN BUBELWA
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Eneo lililotengwa na kwa ajili hifadhi ya mto na kuvuna malisho na matandazo
technologies_1607 - Tanzanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Member of the district council:
Egidius Pancras
Missenyi Disrict Council Kagera Tanzania
Tanzanie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - TanzanieNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - Tanzanie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [Tanzanie]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- Compilateur : ALLAN BUBELWA
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and purposeful regeneration of mulching and pasture materials for cut and carry
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Area enclosure is done in low grazing range lands of average slope 2 – 5%. Enclosure is done by demarcating the fragile land that has direct impact to the riverine ecosystem. The land is exposed to degradation through overgrazing and soil compaction by livestock, bush fire, river bank erosion and reduced quality of pasture spps. Demarcation is done by planting trees in identified area situated about 300 meters from the riverine buffer zone. The preferred plants are Ficus thonigii. The average space between trees is 2 meters. Physical enclosure is supported and enhanced by use of protective bylaws. Reseeding of nutritious pasture species is also done and the area is left under protection for growth and regeneration of mulch, pastures and other vegetation to take place. The common pasture species reseeded are Leucaena spp, cannavaria brazile, clitoria tenatea, sesbania sesban, stylothensis, cajanus cajan, chloris gayana, branchalia spps . Direct grazing is prohibited and mulch and pasture materials are accessed through controlled and organized cut and carry.
Area enclosure is meant for rehabilitation of the riverine ecosystem and prevention of further degradation. Mulch and high nutritious pasture materials that are accessed through organized cut and carry procedures improve crop and animal productivity and have both direct and indirect impact to diversification of income sources and thus play significant role in putting the triple win solution into reality.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose: 1) To improve vegetative cover, reduce soil erosion and prevent and rehabilitate degradation of the riverine ecosystem 2) Ensure sustainable availability and accessibility of mulch and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity 3) Promote use of environmental friendly exploitation of land resources (i.e. mulch, pasture, grass carpeting and other materials) and 4) Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment and recurrent activities includes: area identification and measurement; slashing and land preparation for boundary tree planting and pasture reseeding; collection of planting materials and planting along defined boundaries for demarcation; procurement of seed and reseeding of nutritious and palatable pasture species; selective weeding; area reshaping and gap filling.
Natural / human environment: Bio-physically the area is semi natural grassland with grasses and shrubs trees. The technology is a combination of management and vegetative measure (area enclosure, demarcation using ficus thonigii and reseeding of nutritious pasture). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture is fine heavy (clay) with medium soil depth.
Social economic wise the area is dominated by handy tools typology of mechanization. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, pasture seeds and tree planting materials with average annual costs of 1084.3 USD per hectare. Land ownership in technological area is communal.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tanzanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tanzania/Kagera
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Missenyi distict/Minziro ward/Minziro village
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Includes enclosed and demarcated area closer and around the riverine ecosystem.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology is a result of the recent SLM participatory dialogues made between land users and SLM specialist (external experts). In these dialogues both endogenous and technical knowledge based were given equal weight and were combined in a complementary manner. Land users alos were empowered to take self initiative and ownership of the decision making process.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Nomadisme
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
Type d'animal:
- caprine
- ovins

Forêts/ bois
- Ficus thonigii
Commentaires:
Livestock density (if relevant):
50-100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion due to downstream run off exacerbated by loss of vegetation cover due to bush fire and soil compaction caused by overgrazing, degradation of the riverine ecosystem caused by River bank erosion, land bareness and exposure to direct sunlight and excessive unproductive loss of both green and blue water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): River pollution, erosion of the river bank, land bareness and reduction of mulching and pasture materials.
Nomadism: People with large herd of animal move with their animals in search of adequate pasture
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Exercised with people with few stock.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: done by farmers who usuall keep dairy goats and cattles.
Grazingland comments: Area enclosure is largely meant to control land degradation of the riverine ecosystem through overgrazing by people who own large number of stocks at the same time promote organized, sustainable and environmental friendly exploitation of the fragile land lands (e.g. controlled cut and carry rather than direct grazing in the riverine ecosystem).
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- fermeture de zones (arrêt de tout usage, appui à la réhabilitation)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

modes de gestion
- M7: Autres
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Specification of other management measures: Area enclosure to promote vegetative regeneration and organized use
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wr: érosion des berges

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale

dégradation hydrique
- Hs: changement de la quantité d’eau de surface
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Compaction due to overstocking, accerated runoff and erosion.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Reduction of mulching and pasture materials), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Rampant bush fire), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Un0rganize exploitation of mulching materials), overgrazing (Uncontrolled grazing), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Loss of green water through unproductive evaporation and blue water through ruoff as well as evaporation), population pressure (Exessive eploitation of the grassland and forests in the riverine ecosystem), poverty / wealth (Reliance on wood as the sole source of fuel), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate acess to extension service due to shortage of extension staff), governance / institutional (Weak and inactive institutions to deal with environmental issues)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), change of seasonal rainfall (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), droughts (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Is simply retraining on some principles of sustainable land management, law and rules guiding the fragile ecosystems, participatory training skills and grassroots facilitation skills.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Largely exposure to act and policies guiding the fragile ecosystems and learning by doing on the job,)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): various
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Trees/ shrubs species: ficus thonigii planted arround the boundary and leguminous pasture shrubs planted within the area (stlothensis, lucaena spps)
Grass species: Randomly planted (chloris gayana, desmodium spp and Calliandra)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2 - 5%%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Introduction of organized cut and carry exploitation of mulching and pasture materials
Other type of management: Boundary enclosure, law enforcement
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tanzanian shillings
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
1700,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.12
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site/boundary identification | October |
| 2. | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | October |
| 3. | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | November |
| 4. | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Once |
| 5. | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | once |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Site/boundary identification | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | |
| Equipements | Tools | Number | 5,0 | 3,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 235,29 | 235,29 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 117,65 | 117,65 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | kg | 125,0 | 0,588 | 73,5 | |
| Autre | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 651,9 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 0,38 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective weeding and gap filling | Once |
| 2. | Supervision and monitoring | monthly |
| 3. | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Weekly |
| 4. | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Weekly |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Selective weeding and gap filling | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,76466 | 26,47 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Supervision and monitoring | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,53 | 52,95 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 432,36 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 0,25 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: machete and sickles.
The costs were calculated per unit of ha as per 13/06/2014.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
labour is the most determinant factor.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Short rains (september to December), March to May long rains. Length of dry periods January, February, June, July and August.
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics. Temperature grater than 20°C, LGP is 210 days
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (ranked 1, is largely applied in extended cancave lower range land pouring water to the river) and footslopes (ranked 2, partly includes the convex the convex hill slopes)
Slopes on average: Gentle (The area is largely extended gentle sloppy lower range land plateau receiving water from the the upper landscape and draining into the lower Ngono river which drains into Kagera river)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1, The lower range land is moderately deep it receives eroded soil from the upper and mid sloppy landscape) and shallow (ranked 2, largely include the the area between the upper and lower mid landscape)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, the lower side is largely light sandy soil) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, some patches fine clay soil)
Soil fertility: Low (Nutrient eroded by runoff into the river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (top soil eroded by runoff into the river)
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium (ranked 1, caused by the dominance of sand soil) and poor (ranked 2, due to trampling by animals)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (due to the dominance of sand soil)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
en surface
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, along the flowing river Ngono) and <5m (ranked 2, the area is within the riverine ecosystem)
Availability of surface water: Medium (The main water source is Kagera river with water flows all year round)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, Kagera river receives partly receives water drained from the upper kibanja, Kikamba and other distant places. Kagera river water therefore is contaminated can not be consumed untreated)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Overgrazing has left the area with disappearance of some palatable and nutritious pastures, bushfire and deforestation also has disturbed tree and shrub composition and the soil microbiology.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 35% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor.
and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Generally 90% relies on agriculture as their main source of livelihood. Only a few are engaged in off-farm activities like petty trading, kiosk, brick making e.t.c.
Market orientation: Mixed (Livestock are largely kept for domestic use e.g. milk, meat and manure and parlty for commercial purposes)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
There is shortage of grazing land. People with large animal herd move with their animals in search of better pasture.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Commentaires:
In Tanzania land is a state property. Land use right is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance or purchase through traditional or customary procedures.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
5.0 ton/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
6-7.0 ton/ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to the availability and use of mulching by some farmersmaterials
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
2 acres/annum
Quantité après la GDT:
10 acre/annum
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
area enclosure and decline of forest fire
qualité des fourrages
Quantité avant la GDT:
3
Quantité après la GDT:
8
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increase in the number of nutritiuos pasture species due to reseeding
production animale
Quantité avant la GDT:
1200litres/cow/yeer
Quantité après la GDT:
2000litres/cow/year
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Contribution of nutritious cut and carry pastures
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
availability of manure from animal kept under zore grazing
diversité des sources de revenus
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Income accrued from sell of mulching and pasture materials.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
improved diet due to varied food availability (avalability of milk)
institutions communautaires
Quantité avant la GDT:
weak
Quantité après la GDT:
strong
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
empowerment and capacity building of environmental committee.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Knoledge over controll of riverine resources.
apaisement des conflits
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology has contributed to availability and accessibility to mulching and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity. This has both direct and indirect impact on the income of the community and hence livelihood (e.g. ability to meet education and health expenses).
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduction in uproductive loss of both green and blue water.
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Resultant of vergetation cover
évaporation
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduce uproductive evaporation due vegetation cover
Sols
couverture du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved vegetation cover
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cotrolled soil erosion due to runoff
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
compaction du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Controlled fire burning
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Controled bush fire
risques d'incendies
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
harzards due to bush fire but reduced due to enclosure, fire break and use of bylaws.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
envasement en aval
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas connu |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
Commentaires:
The technology was modified to become more tolerant through organized cut and carry of mulching and pasture materials.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
Mulching and pasture have short maturing period and this causes land users to realize rewards right from the beginning of the technology and the benefit increases more with time.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As a result of benefit realization of the use of technology, there a growing acceptance and spontaneous adoption by the whole community
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The technology prevent degradation of the river bank and disappearance of palatable and nutritious pasture |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Area enclosure complimented with reinforcement of bylaws reduce fire incidences and helps in sequestration of carbon both above and below the ground and reduce the effect of green gas emission. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of feed to animals kept in farm under zero grazing (e.g. dairy goats and cattle) and control unproductive loss of manure. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of mulching materials needed in production of banana and other crops. |
| Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources to the rural poor. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Time consuming and labour heavy especially to environmental committee members. | Device motivation and incentive system at the grassroots. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Emergency and dominance of invasive species | Liaise with research to find alternative and beneficial use of invasive species. |
| Needs committed people who can spend their valuable time in promotion of the technology. | Use SLM related incentives and promotion e.g. support with dairy goat to people who actively participate in promotion of the technology (as part of crop livestock integration) . |
| Takes time to inculcate self initiatives and ownership | Systematize and Operationalize into existing systems |
| Needs attitude and behavioral change (is not normal traditional for rural people to cultivate grass). | Encourage change of mindset by enabling farmers understanding of the principle behind pasture establishment. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
03/06/2014
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [Tanzanie]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- Compilateur : ALLAN BUBELWA
Modules
Aucun module trouvé