Sub-surface water harvesting for an efficient use of water resources [Pakistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Eveline Studer
- Rédacteur : Munawar Khan
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, Nicole Harari, Hanspeter Liniger
Infiltration gallery
technologies_540 - Pakistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Engineer-Water conservation:
Muhammad Khan
+923349915556 / +92915702450
khanm@helvetas.org.pk / mkkhattak@helvetas.org.pk
Water for Livelihoods Project-Intercooperation Pakistan
Peshawar- Pakistan
Pakistan
Water Management specilist:
Rehman Nasib-ur
+923469757756
On-Farm water managment, department of Agriculture
Peshawar Pakistan
Pakistan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
31/12/2015
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology promoted sunstainable water conservation. It is cost effective and requires no external energy supply as it is based on gravity flow.
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT

Water Use Management Plan (WUMP) [Pakistan]
The overall purpose of WUMP is to compile an inventory of available water ressources in a particular geographical or administrative area, to identify communities' priorities in order to achieve an effective, equitable and efficient use of water resources at local level. This approach promotes a participatory and inclusive analysis and …
- Compilateur : Eveline Studer
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
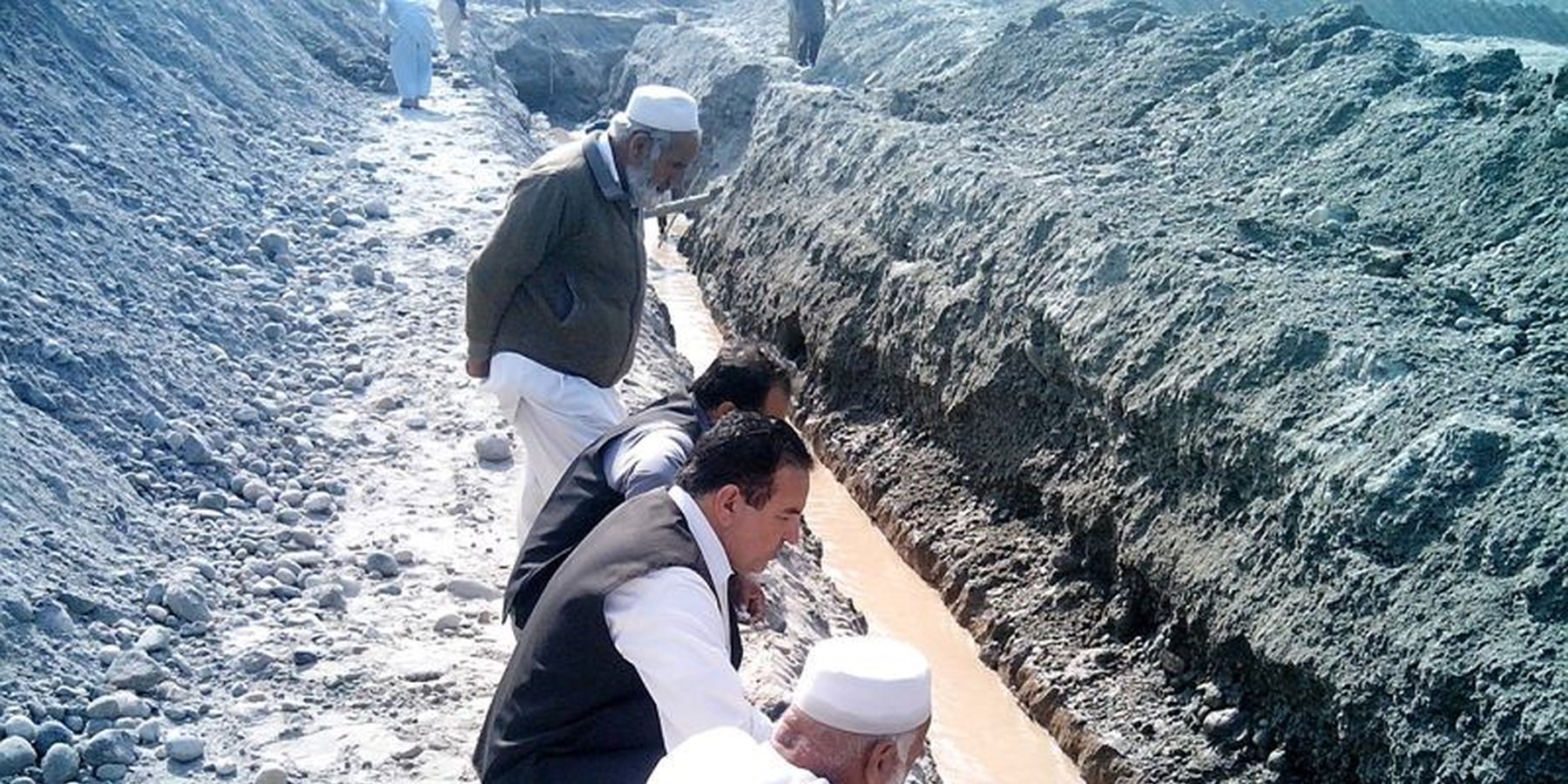
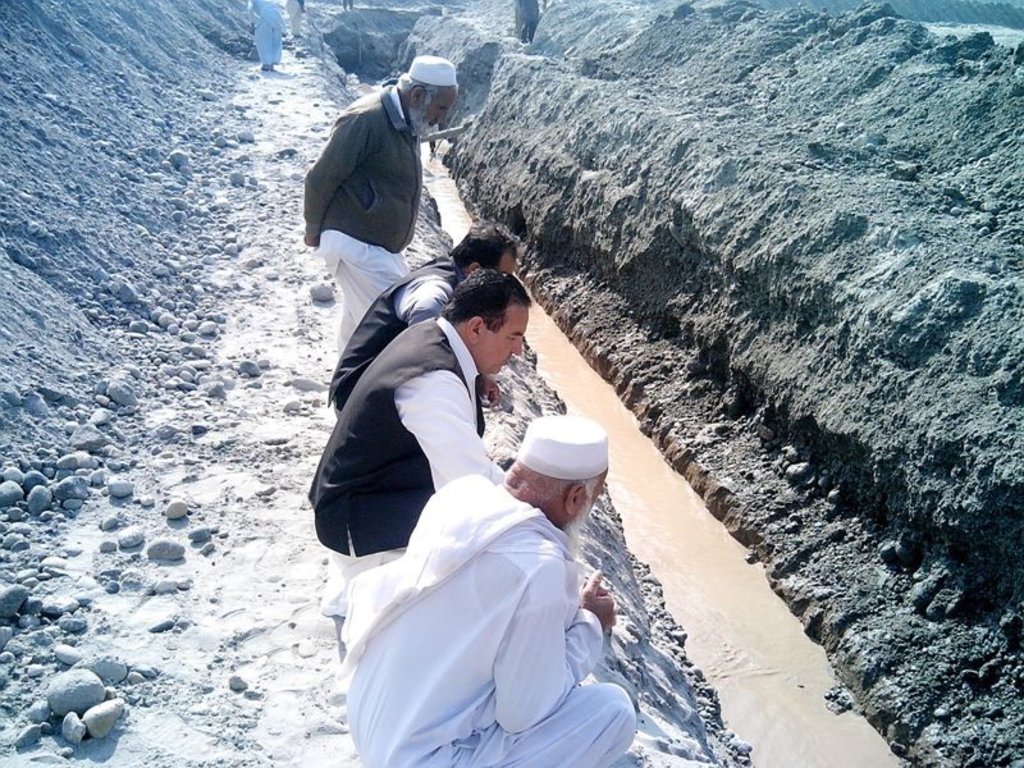
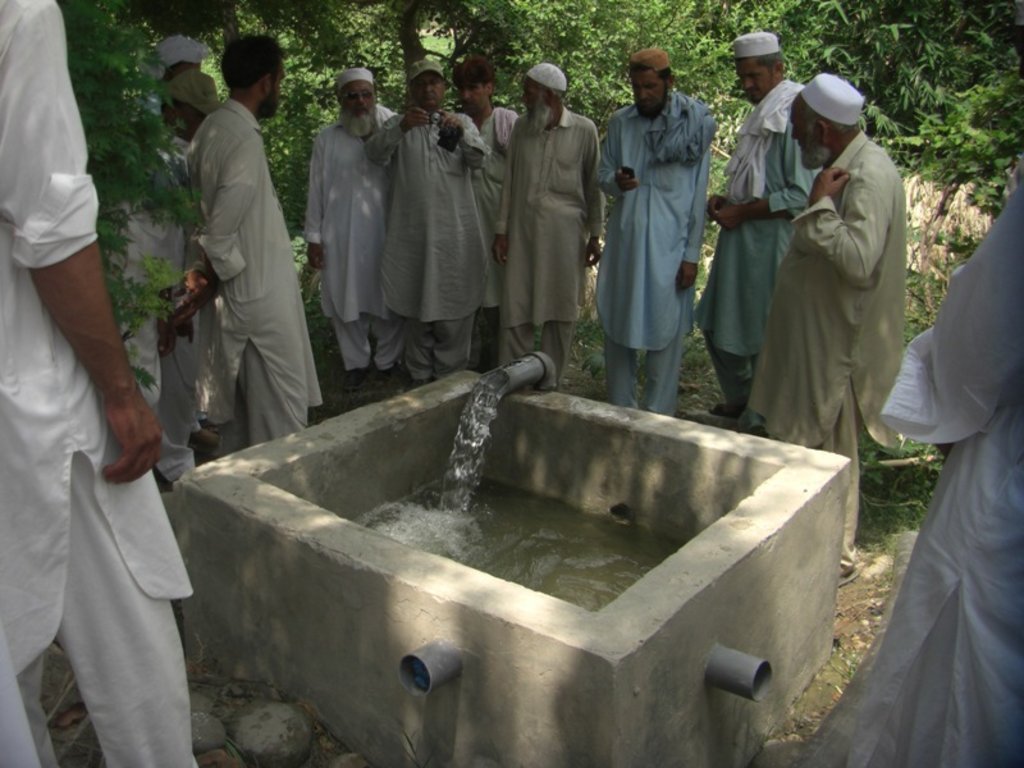
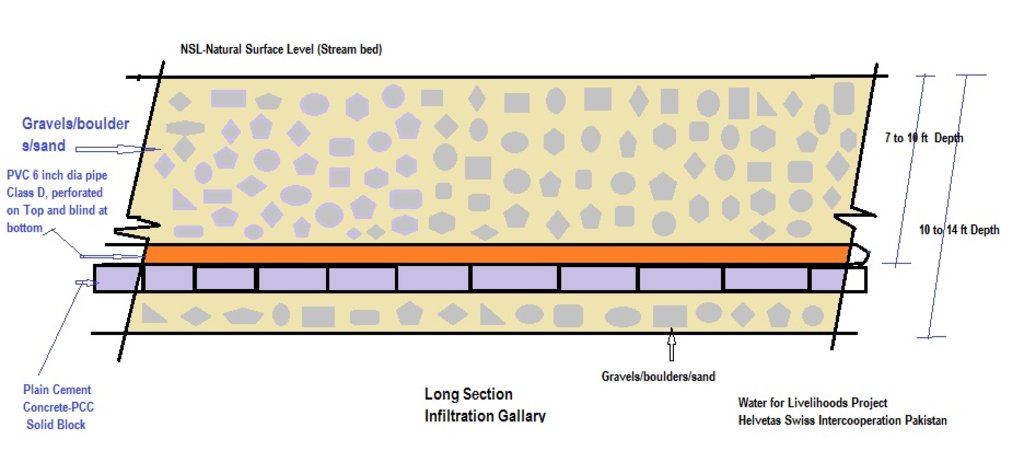
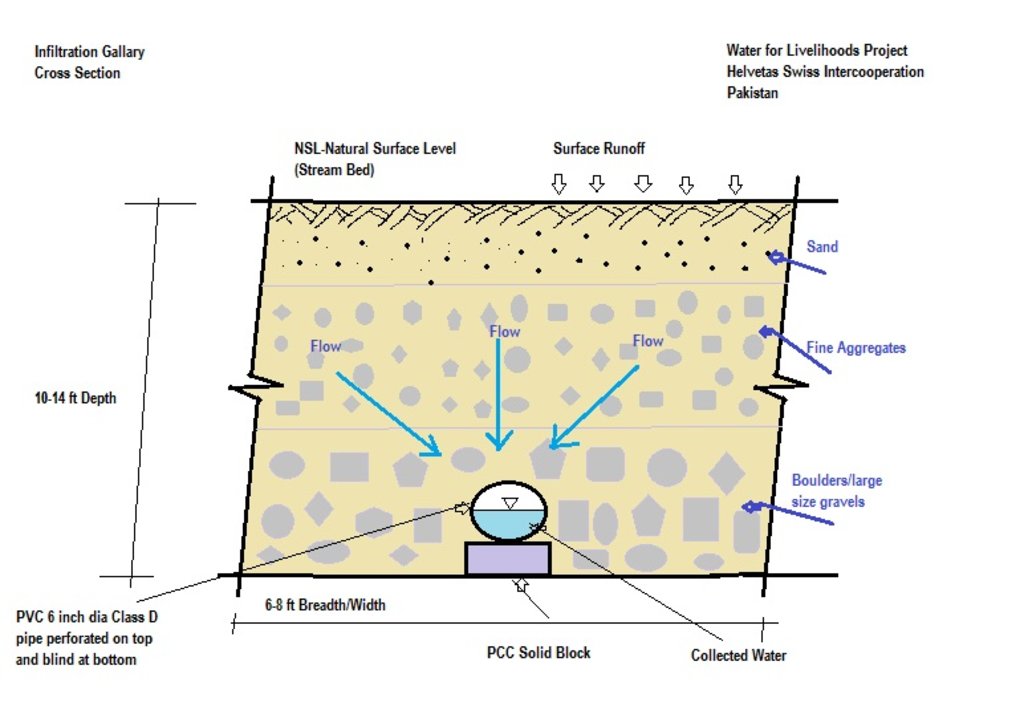
The purpose of this water harvesting technology is to capture, collect and distribute sub-surface water. First, an infiltration gallery is developed, which allows the percolation and collection of sub-surface water through perforated pipes at a depth of approximately 3-4.5 metres. Sub-surface water is filtered by gravel/sand underground and infiltrates into the gallery. The harvested water is used for household needs as well as for livestock and irrigation through gravity flow.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
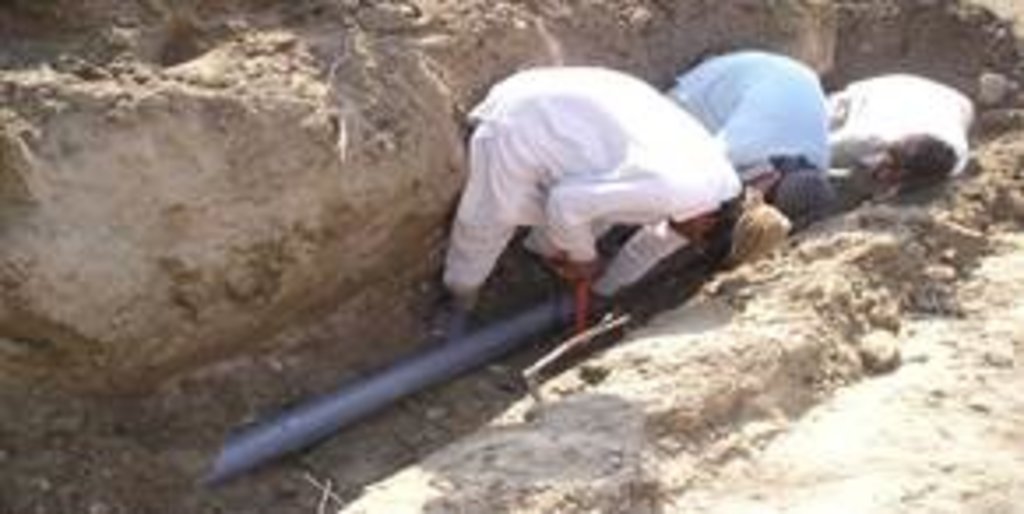
This method is applied in areas with low rainfall, where soils have a sandy-gravelly texture and where the sub-surface water can not percolate deeply, but instead flows laterally in shallow sub-surface channels. The technology consists of the following main elements: filtration materials (sand / gravel), collection chambers, perforated pipes, conveyance lines made from solid blocks, and storage tanks. Construction includes the following main activities and inputs:
• Excavation of rectangular trenches with machinery or by hand
• Construction of a solid base line with PCC (plain cement concrete) blocks on the top of
boulders
• Installation of perforated and blind pipes - and storage tanks where necessary
• Coverage of the trench first with boulders and then sand on top.
Once the gallery is constructed there is no further need for intervention; this means that maintenance costs for the user (farmer, households of the local community) are minimal. Traditionally, the technology has been implemented by local farmers for many years. Where improvements are required, support by local technicians is provided. The technology is based on local knowledge, and locally available construction materials. The method is technically simple, cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Farmers and other users consider this technology as very efficient as there is no need for external energy supply, and it can be easily replicated. Furthermore, it requires a minimum of external construction material and the operation costs are minimal. The captured water is filtered through the subsurface layers and - as long as there is no specific external contamination - it is safe and can be used for various purposes as already noted. This extra water supply is particularly effective for irrigation, contributing to increased production and allowing diversification of crop production (potentially also of high value crops), thereby improving the livelihoods of remote rural communities. The primary impact of this technology is to reduce risks related to droughts or water scarcity as natural phenomena or consequences of climate change effects. Additionally infiltration of water into the galleries reduces surface erosion of fertile soil, hence it lessens soil degradation.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Pakistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Karak, Laki Marwat & Dera Ismail Khan
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2013
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Water for Livelihoods Project (rural development project)
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Principales cultures (vivrières et commerciales):
- Wheat, maize/corn, millet
- Tomato and other vegetables
- Fruit trees: guava etc.
Commentaires:
As a result of the introdued technology, farmers can now produce multiple crops and have increased the cropping efficiency.
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Prior to the establishment of the infiltration gallery, cropland was mainly rain-fed and only a single crop was produced with 50 % cropping efficiency.
The cropping efficiency increased up to 150 % (growing 3 crops instead of 1 crop in a year.
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
- The technology is simple and not costly to establish.
- It further contributes to adapt to climate change, especially in areas where water becomes increasingly scarce.
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Rabi (October to March) & Kharif (April to September) season
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- gestion des eaux souterraines
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Commentaires:
This technology is suitable for area with little slope to retain a maximum amount of water. when the stream bed has a higher gravel content, it provides more water. The technology is suitable for strata with no/ low vertical percolation, such as underlying hard rocks.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S3: Fossés étagés, canaux, voies d'eau
- S7: Collecte de l'eau/ approvisionnent en eau/ équipement d'irrigation
- S10: Mesures d'économie d'énergie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- s'adapter à la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Further the technology contributes to reduce risks and losses linked to droughts as natural hazard and/or the effect of climate change.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Dimensions of the cross section:
- Depth: 10 to 15 feet, width: 6 to 8 feet, length: 300 to 1000 feet
- Slope: 3% on 200 feet
- Volume of storage tank: 30 x 30 x 4 feet
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Infiltration gallery: conveyance, collection chamber and tank
Spécifiez le volume, la longueur, etc. (si pertinent):
600 feet gallery (including 3600 feet conveyance lineconveyance line to the tank/water user's end point (adduction section without wholes for infiltration))
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
Skilled labour: 12 USD/day, unskilled labour: 6 USD /day
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation | Structurel | 2 weeks |
| 2. | Dry stone packing | Structurel | 1 week |
| 3. | Laying of PCC block (plain cement concrete) | Structurel | 2-3 days |
| 4. | Installation & fixing of perforated pipes (6" diameter) | Structurel | 2-3 days |
| 5. | Establishement of filtration media (boulder, gravel, sand packing)at gallery's end point/ water user's access point (if required) material: concrete | Structurel | 2 weeks |
| 6. | Construction of water collecting chamber | Structurel | 1 week |
| 7. | Convayance line (3" diameter) | Structurel | 3 weeks |
| 8. | construction of storage tank (if required) | Structurel | 4 weeks as parallel activity |
Commentaires:
Totally, it takes 3 months to complete the construction of the infiltration gallery unit (600 feet) including the conveyance line and storage tank. Some of the activities can be carried out in parallel.
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Skilled Labour | Days | 109,0 | 12,0 | 1308,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Un-Skilled Labour | Days | 465,0 | 6,0 | 2790,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Machinary (Excavator) | Hour | 118,0 | 25,0 | 2950,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Bricks (Number) | 1000 | 12,5 | 95,0 | 1187,5 | |
| Matériaux de construction | PCC blocks, rough stone (cubic foot) | 100 | 44,5 | 50,0 | 2225,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Cement (50 kg bags) | 50 | 275,0 | 5,0 | 1375,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | sand, crush, boulder, gravel (cubic foot) | 100 | 63,0 | 35,0 | 2205,0 | |
| Autre | PVC pipe perforated (6" diameter filter section class D) (ft) | 1 | 590,0 | 5,0 | 2950,0 | |
| Autre | PVC blind pipe (3" diameter class B) (ft) | 1 | 3600,0 | 1,0 | 3600,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 20590,5 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Project / Government partner - i.e. on Farm Water Management department & public Health engineering Department, shared the cost at the ratio of 80 % : 20 %.
Commentaires:
Total cost of the technology is basically proportional to the length of gallery and futher dependson the size of the storage tank.
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
Commentaires:
This technology is based on a single cost investment. Except minor repairs of storage tank, there are no relevant maintanance costs.
The filter function of the boulder layer and the perforated pipes reduce sedimentation problems. Minor amounts of silt and fine sediments in the storage tank can be removed with minor effort by the user (unskilled labo no tools required),
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
- Length of the infiltration gallery
- Length of the conveyance line
- Size of storage tank (not alway included)
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
300,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
rains in both season (monsoon & winter)
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Kohat & Bannu & DIKhan Met Department Automatic Weather Station
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Min. /max. temperatures: 9°C / 42°C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Due to floods in monsoon season, the discharge capacity increases.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- mixte (de subsistance/ commercial)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased crop production efficiency due to additional and year-round water avalability for irrigation.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
with the additional water for irrigation, water is no limiting factor anymore, with allows an improved crop productin in terms of quality and quantity.
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
1
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
water for irrigation can reduce risk of production failure due to drought/water scarcity.
diversité des produits
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
with additional water through irrigation, additional crops might be cultivated, which contributes to production and income diversification.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
with additional water through irrigation, additional areas can be used for agriculture.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
qualité de l'eau potable
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Quantité avant la GDT:
-2
Quantité après la GDT:
3
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
3
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
the technology directly contributes to additional water for irrigation
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Irrigation allows improved, diversified crop production. Water access for lifestock ensures animals health. Both crucial aspects for the income of local farmers
diversité des sources de revenus
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
-1
Quantité après la GDT:
2
droits d'utilisation des terres/ de l'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
1
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts de la sécheresse
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
reduced consequences of droughts/water scarcity, in terms of production failure/lost harvest and reduced production
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Type de changements/ extrêmes climatiques | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | été | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 10-50%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- changements/ extrêmes climatiques
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Design of infiltration galleries (diameter of pipes, size of perforation, slope etc.) was adjusted to local conditions including the consideration of local rainfall / amount of water.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Low cost measure, which requires only a one-time investment, low/no repair or maintenance costs are required. |
| Well assimilated and replicated by local farmers of the area since it is a simple and traditional technology. |
|
No requirement of external energy (no pumping). |
| Allows harvest of sub-surface water for different purposes (domestic use, irrigation, livestock). |
| Environmentally friendly, making use as much as possible of local construction material (gravel, sand). |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The technology can be replicated in areas of similar conditions, as well as up-scaled with little efforts in other areas with a similar environment. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| If the land, where the sub-surface water is harvested is communal property, the distribution of water rights may be an issue. | Involvement of farmer organizations, distribution of water rights based on land holdings have to according check water rights. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Filtration media might clogge in the long run in case silt content is high. | Filtration media should be prepared with graded materials (sand, gravel, boulder). |
| Considering the initial investment cost, the measure cannot be done by an individual alone. | It requires an organized (group of) community. Though this pre-condition can also be interpreted as a strength for a coordinated and efficient use of water. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
5-10
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
20-30
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
2-3
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Water Use Management Plan (WUMP) [Pakistan]
The overall purpose of WUMP is to compile an inventory of available water ressources in a particular geographical or administrative area, to identify communities' priorities in order to achieve an effective, equitable and efficient use of water resources at local level. This approach promotes a participatory and inclusive analysis and …
- Compilateur : Eveline Studer
Modules
Aucun module trouvé