Soil Bund with Contour Cultivation [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Unknown User
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Ditchira, Kab (Amharic)
technologies_1073 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Spécialiste GDT:
Tafese Berhanu
Hadiya zone
Ethiopie
Spécialiste GDT:
Watchiso Adibacho
Hadiya zone
Ethiopie
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
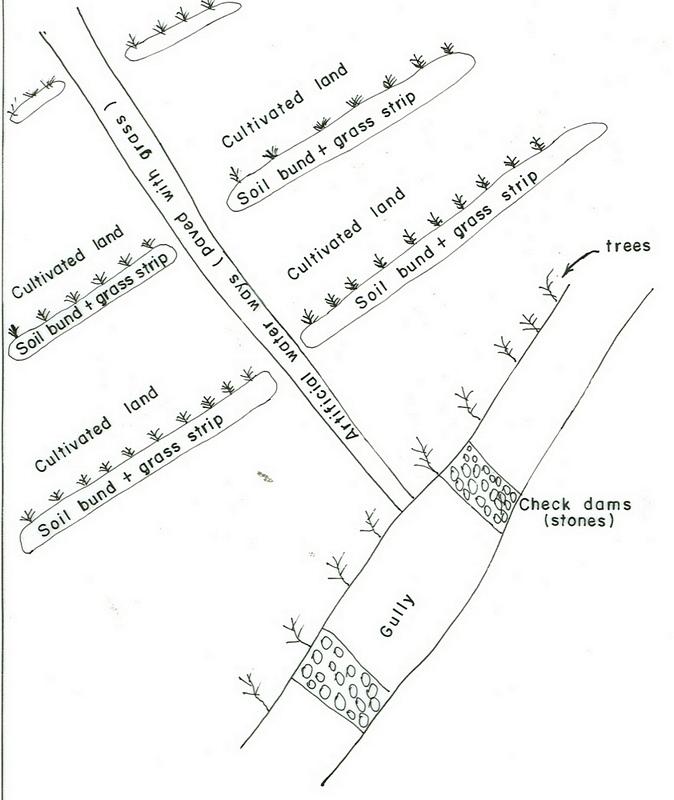
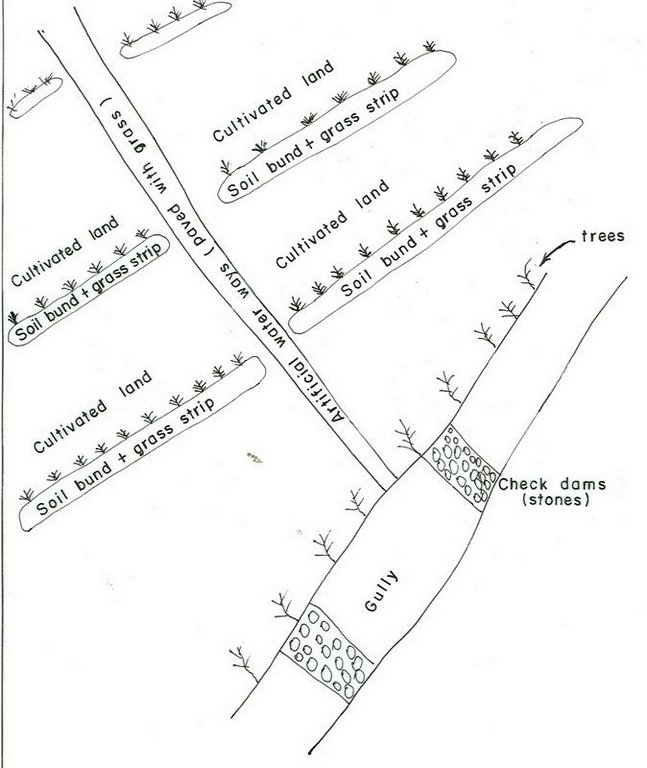
It is a structural measure with an embankment of soil or stones or soil and stones, constructed along the contour and stablized with vegetative measures (grass and fodder trees).
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Applied on different land uses on slope of more than 3%. This practice is widely used by farmers in the area. Stone and stone faced bunds height depends on the availability of stones. On the average the width is 1-1.2m and hieght is 0.6-0.7m.
Purpose of the Technology: Bunds reduce the velocity of runoff and soil erosion, retains water behind the bund and let it infiltrate. It further helps in ground water recharging.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Planning is made by community/group and individual discussion and reach a consensus on layout, spacing, implementation modalities and management requirments is reached before implementation.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applicable in areas where soil is moderately deep and stones are available
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
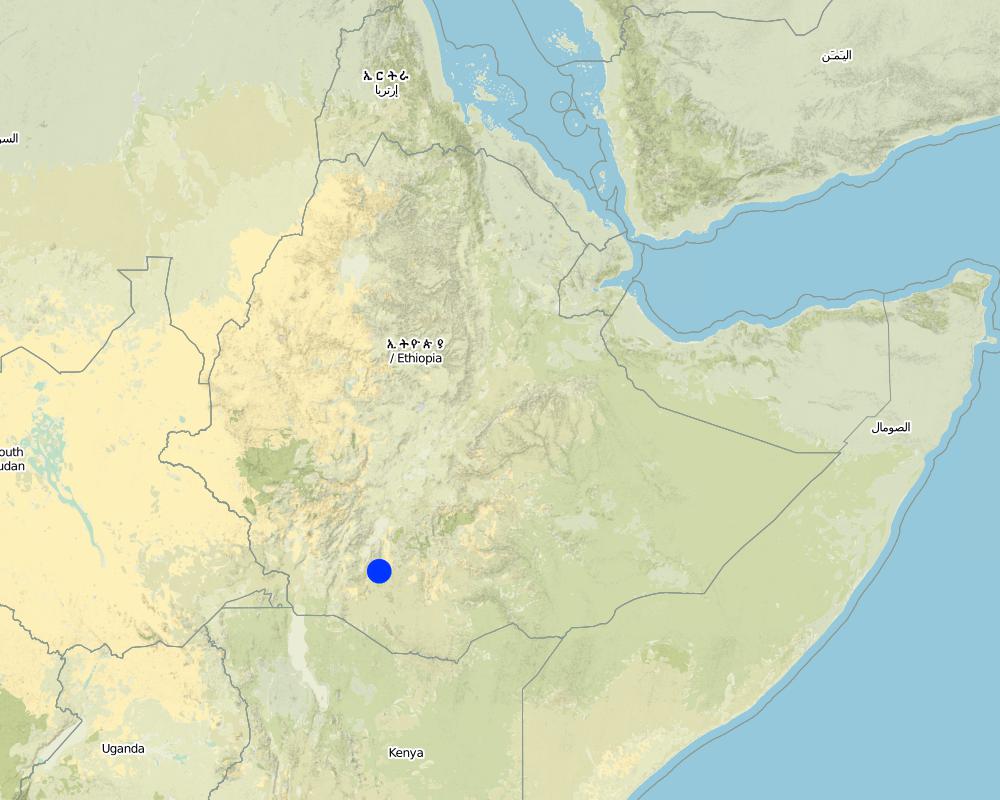
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
SNNPR/Hadiya/Lemo
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Lemo
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 173 km2.
Nowadays communities have developed positive attitudes towards SWC technologies implemented and the results obtained by practicing measures, which have reduced runoff and soil erosion reduced and land increased productivity.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Other countries and also other woredas in the country.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- céréales - autres
- céréales - sorgho
- légumineuses et légumes secs - autres
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - pommes de terre
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
- wheat, haricot beans
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- canne à sucre
- Enset, Desho, Phalaris
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- avocat
- café, cultivé en plein champ
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
- papaye
- Cordia, Croton, Ficus, Casmir
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Nov Second longest growing period in days: 150
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
maize + haricot beans
coffee + cabbage

Forêts/ bois
- Plantations d'arbres, boisements
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Bois de chauffage
- Pâturage/ broutage
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Absence of land use policy, low level of awarness, shortage of farm lands.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Continous cultivation, poor soil fertility, poverty, shortage of cultivated lands.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Many peasant kebeles have earned money by selling eucalyptus grown on plantation areas of the community. Some have built schools from the proceeds. Some kebeles have shared sizable money from the sales of trees.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Cereals - legumes - cereals
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mixed cropping / intercropping, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, breaking compacted topsoil, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Secondary goals: Rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
SNNPR
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Early planting
Material/ species: maize, potato
Remarks: row and broad casting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: sorghum + haricot beans
Remarks: row planting
Agronomic measure: mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize + haricot beans
Remarks: row planting
Agronomic measure: mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: coffee + cabbage
Remarks: row planting
Legume inter-planting
Remarks: row and broad casting
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: animal dung
Remarks: broad casting
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: once, along the contour
Contour tillage
Remarks: 3-6 times, along the contour
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 10-15
Vegetative measure: scattered/dispersed
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40-60
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia, Croton, Ficus
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Casmir, Avocado, Mango
Perennial crops species: Chat, Coffee, Sugar cane, Papaya
Grass species: Desho, Phalaris
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 10.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
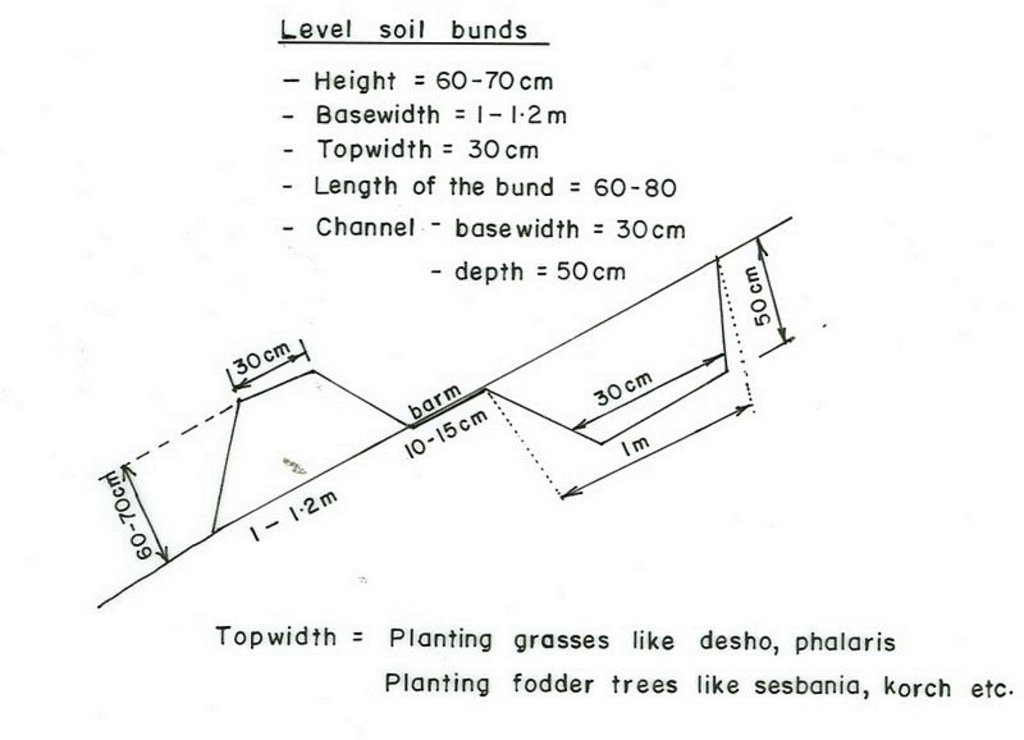
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6-0.7
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60-80
Construction material (earth): Soils excavated from the ditches is used to make the embankment.
Construction material (stone): Stones collected to construct stone/stone faced bunds.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 10%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: cut and carry system practiced
Other type of management: change of management / intensity level - Follow up and evaluating the performance
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Birr
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
8,6
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.70
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Production of planting materials | beginning of rains |
| 2. | Planting on the bund | during rains |
| 3. | Survey | dry season |
| 4. | Excavating the ditches and constructing the enbankment | dry season |
| 5. | desho grass transportation | during rains |
| 6. | Planting Desho grass on the bund | during rains |
| 7. | Group formation | dry season |
| 8. | Follow up and evaluating the activities | throughout the year |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 156,0 | 156,0 | 5,0 |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 27,8 | 27,8 | |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 32,1 | 32,1 | 70,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 27,0 | 27,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 29,0 | 29,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Grass | ha | 1,0 | 306,0 | 306,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 577,9 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 67,2 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contour tillage | dry season / annual |
| 2. | Contour tillage | dry season / two to three times |
| 3. | Sawing | during rains / annual |
| 4. | Weeding | during rains / one or twice a year |
| 5. | Harvesting | dry season / annual |
| 6. | Replanting | during rains /once |
| 7. | Reconstruction | dry season/annual |
| 8. | Replanting | rainy season/annual |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 18,84 | 18,84 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 81,39 | 81,39 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 100,23 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 11,65 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Shovel, hoe, water level, string
The cost is culculated per length of structure and other agricultural activities undertaken and the cost is in a hectare of land.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Type of hand tools, Slope of the land and soil depth.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
1001-1500 mm (Ranked 1): 900-1400 mm, rains are tremendously variable.
751-1000 mm (Ranked 2): 900 mm, Parts of the SWC area receives on an average 900 mm.
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Very suitable to agricultural activities with variety crops grown.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 2001-2500 m a.s.l. (Ranked 1, below 2400m asl, very suitable to wheat, barley and horse beans.) and 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (ranked 2, over 1900m asl, very suitable to cereal crops including maize)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, dominant land forms with flatter village areas at the top) also, ridges (ranked 2) and plateau/plains (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Rolling (Ranked 1, the technology is mostly implemented here), moderate (ranked 2, dominantly cultivated) and hilly (ranked 3, area enclosures) as well as gentle and steep (both ranked 3)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Also moderately deep (ranked 2, dominant soil depth in the SWC area) and shallow (ranked 3, degraded hillsides)
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (ranked 1, clay loam nitisols and vertisols) and medium (ranked 2, soils with high productivity)
Soil fertility: medium (ranked 1, most of the cereal cropped areas) and high (ranked 2, soils in the homestead)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (ranked 1, for all cereal cropped lands) and medium (ranked 2, land with perennial crops and homestead areas)
Soil drainage/infiltration: good (ranked 1, croplands on hillslopes ) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: High (vertisols and soils on flat slopes)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
6% of the land users are rich and own 19% of the land.
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 45% of the land.
45% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
12% of the land users are poor and own 7% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Land users who have SWC measures on their land have better income compared to others who do not have and they have better scope to get engaged in small trade.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (cultivation and weeding of perennial crops done by hoe and weeding manual) and mixed (tillage is done by oxen)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Most land users have 0.50-0.25 ha of land.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
soil loss reduced, fertilizers loss controlled
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
bund stablization increased feed availability
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
bund stablization increased feed availability
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
tree plantation
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
area occupied by the bund
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
production per unit area increased
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
SWC activities organized and planned by communities
institutions nationales
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
government & NGOs involvement increased
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
more land users acquired knowledge on SWC
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
uphills planted with forest trees
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
82
Quantité après la GDT:
8
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
integrated measures
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
25600 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers have acquired some technical skills that enables them implement SWC measures by themselves on their own land with little external support.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
increased crop production How can they be sustained / enhanced? use high yielding varities and better farming systems. |
| soil erosion reduced |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
soils protected from erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? more awarness creation and strengthening maintenance |
|
sources of income diversified How can they be sustained / enhanced? introduce more productive multipurposive activities |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé