Jatropha curcas hedge [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Simon Bach
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Agulo Keter
technologies_1524 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Ayele Habtamu
Haramaya University
Ethiopie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Haramaya University (HU) - Ethiopie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
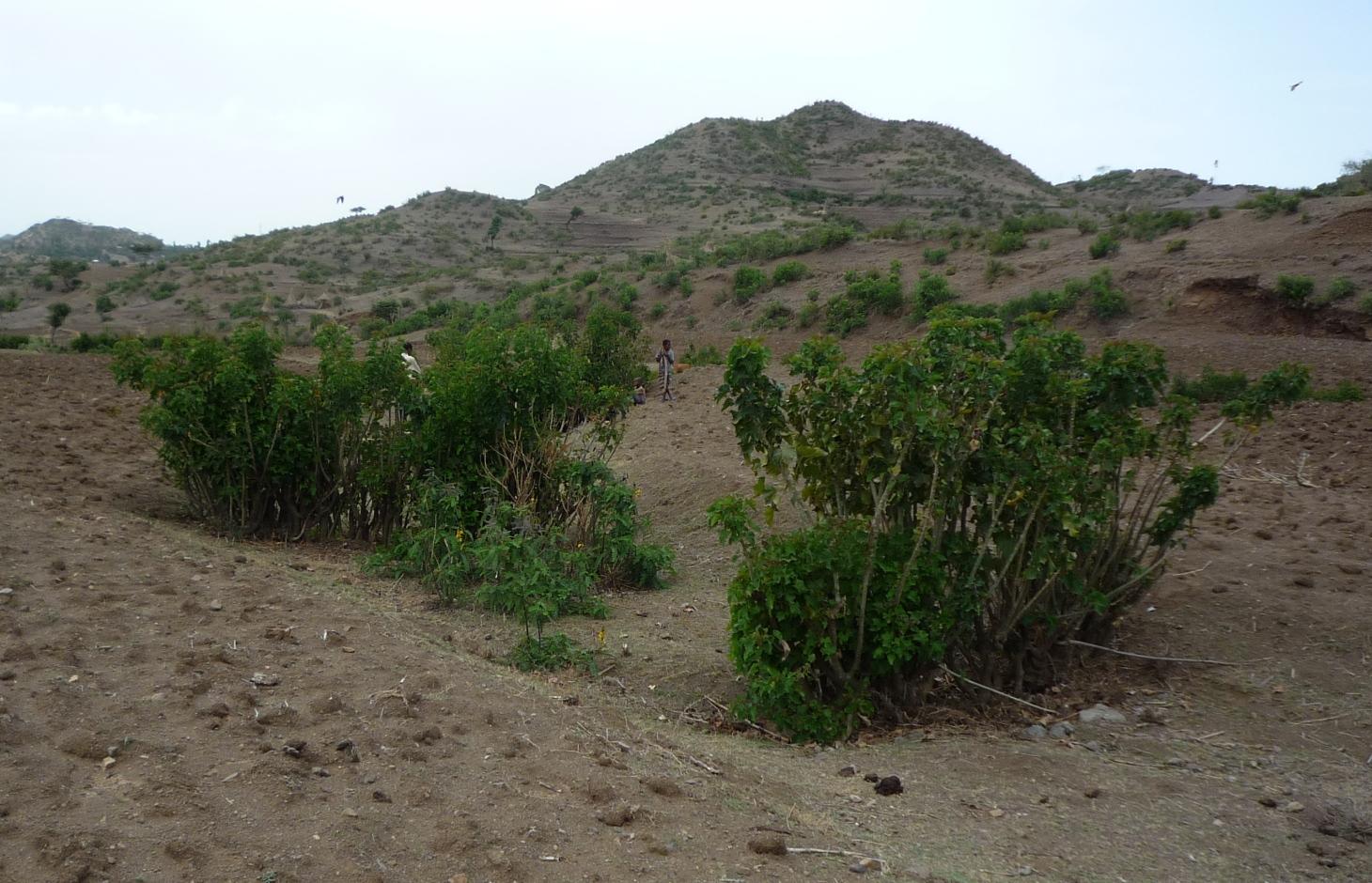
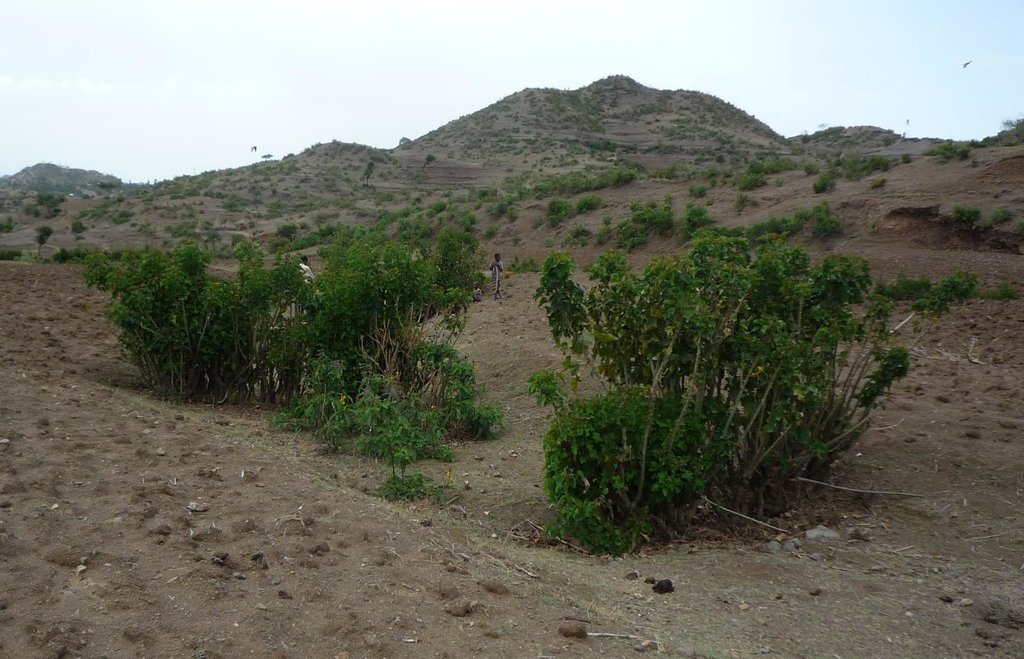
Gully rehabilitation and hill stabilization with Jatropha hedges.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
In the area around Bati in Ethiopia, Jatropha is used to stabilize hills ore to rehabilitate gullies. The technology was introduced during the last decade by local farmers on their plots. The advantage of Jatropha against other shrubs is that it is poisonous and therefore not browsed by animals. Additionally the seeds can be collected by household members and sold on the local market. The seed's oil can be used as a lamp oil or even for the production of bio-fuel.
Purpose of the Technology: Besides hedges and living fences, Jatropha is used for combating sheet or gully erosion. To stop erosion processes the Jatropha cuttings are planted across a gully or along hill sides to stabilize them in the same manner as check dams or terraces do. The plant is chosen because of its very tolerant character, rather high accessibility in the area and because it is easy to propagate by cuttings. Often Jatropha is used in combination with traditional stone check dams or terraces aiming for an increased stability of the technology itself. For that purpose Jatropha is planted in front of the stone walls or also on top of them.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In earlier times Jatropha was planted by seeds but nowadays, since there are a lot of plants in the area, propagation by cuttings is the more prominent form. Since the plants are pruned every year anyway, the cuttings are accessible almost in any case for free. At markets further away, the cuttings cost around one cent per piece. In order to rehabilitate a gully Jatropha cuttings are planted as near as possible in the selected area in a row across the gully. After rooting, the spaces between the plants are filled up with litter, shrubs or stones. In order to have a thick stem and avoid competition with crops, the plants are pruned every year. The thick main stems reach a height of approximately one meter which delineates the maximum height of possible soil collection. If the area behind the filled up gaps and the cuttings has silted up, the height is increased by adding new litter in the higher up gaps. In off farming season, the Jatropha seeds are collected and sold on the market to create additional income.
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. The area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Ethiopia / Amhara Region
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Bati
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 km2.
Size of the case study watershed.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Farmers are using Jatropha curcas since approximately 30 years in the research area in Bati mostly for fencing. Innovative farmers started using the plant for stabilizing existing physical structures (stone walls, terraces, gully check dams) or using it as a complete substitute for these physical structures.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - sorgho
- corn
- jatropha curcas
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: June until September

Pâturages
Type d'animal:
- chameaux
- bétail - laitier
- caprine
- volailles
- ovins
Commentaires:
Livestock density (if relevant):
> 100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation, overgrazing, cultivation of erosion-sensitive areas or steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Too much soil loss and land degradation, no vegetation cover and poor soil moisture.
Grazingland comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S1: Terrasses
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation for the past 30 years.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Wood collection for cooking and construction.), overgrazing (60% of the watershed area are cultivated - big grazing pressure on remaining land), other human induced causes (specify) (Cultivation of very steep slopes.), change of seasonal rainfall (Erratic rainfall.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (If there is rain, it is intensive.), population pressure (High population pressure.), poverty / wealth (Poor facilities.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices and lack of awareness.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Annual cropping.), droughts (The research area is considered rather dry.), land tenure (If the land is rented, it is poorly managed.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Poor access to fertilizer. Bad infrastructures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of awareness for soil degradation.), Low productivity of the land (As a consequence seeking for new/larger areas to increase production.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
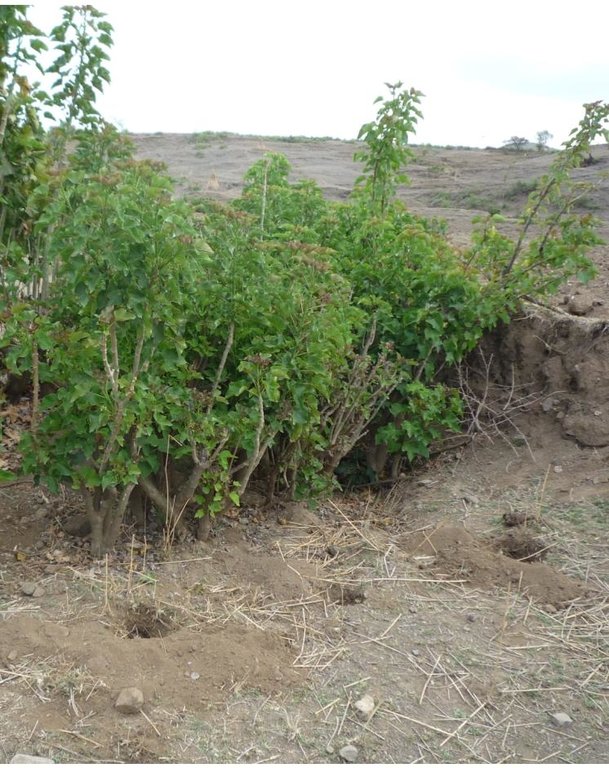
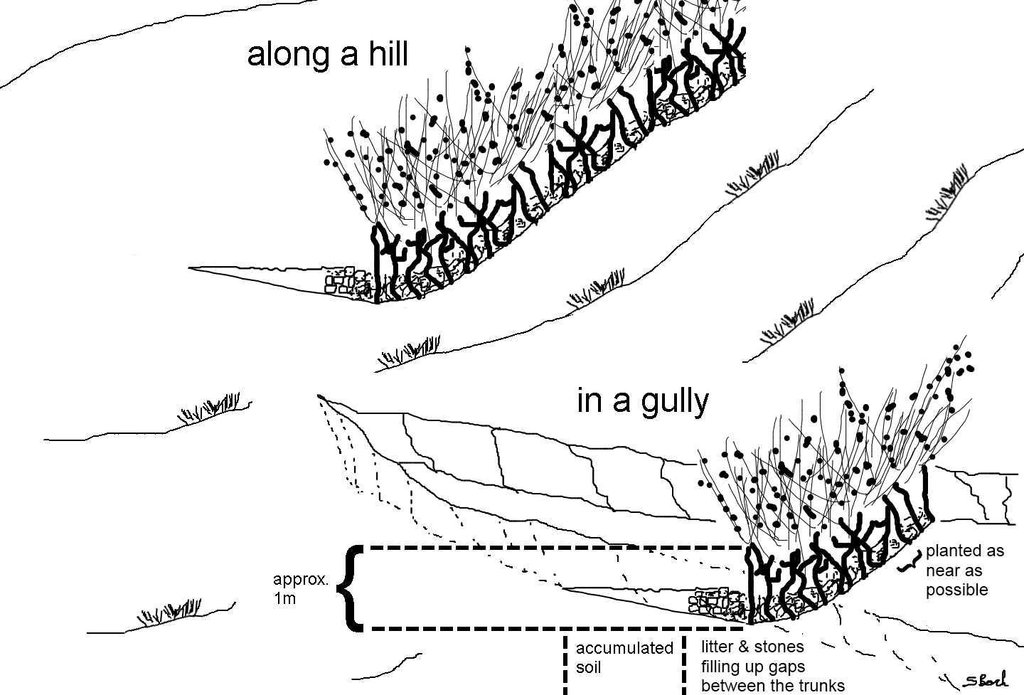
Jatropha hedges as they can be found in the region of Bati. Often the plant is used for gully rehabilitation. For that purpose it is planted (mostly by cuttings) with a minimal interval between each plant to create a barrier-like hedge. The gaps are filled up with litter or stones.
Approximately 1 m of soil can be collected by the trunk - above that height it is too thin. The Jatropha seed can create additional income besides the purpose of soil and water conservation. Often, the plant is used in combination with traditional technologies (terraces, stone walls) and planted on top or in front of these traditional structures to improve their stability.
Location: South of Bati. Bati Woreda, Amhara Region, Ethiopia
Date: 05.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Planting takes place rather randomly in places of needs.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 10 per m
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~20m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Vegetative measure: filling material
Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Jatropha curcas
Other species: Stones, shrubs, sticks - things that can be found and utilized to fill up gaps between each plant.
Auteur:
Simon Bach, CDE, Bern, Switzerland
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ethiopian Birr
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
16,82
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
1.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | One time initial sawing of Jatropha seeds (30 years ago). | Initial. Wet season. |
| 2. | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | dry season |
| 3. | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | dry season |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Seeding | person day | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools for cutting | 500m | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | kg | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 33,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1,96 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of Jatropha seeds (5 person days needed). | Off farming season(Okt.) |
| 2. | Filling up the gaps with litter (5 person days needed). | If necessary |
| 3. | Pruning of the Jatropha hedges (15 person days needed). | Yearly before wet season. |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Collection of Jatropha seeds | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Filling up the gaps with litter | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Pruning of the Jatropha | person days | 15,0 | 1,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | Person days | 15,0 | 0,333333333 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Wood | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 30,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1,78 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: saw, axe
Total costs of a hectare are calculated for a hedge of 100 m length every 20 m (500 m total hedge) in the year 2011. Tool prices were estimated and labor costs were calculated with a daily wage of 1$.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Rough topology in the area, questionable availability of construction materials if they are not found nearby.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Erratic rainfall (rainseason from June until September)
751-1000 mm ranked 1
501-750 mm ranked 2
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: tropics
LGP shorter than 90 days.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (The study site is located at 1600m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1) and valley floors (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (ranked 1), shallow (ranked 2)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Ground water table is unknown.
Availability of surface water: Only during rainy season
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, mostly groundwater)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Relative to other parts of Ethiopia.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 6%
1% of the land users are rich (Adopt the most of SWC technologies).
19% of the land users are average wealthy.
89% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm income has low importance.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (plowing by oxen, ranked 1) and manual work (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) Goat/sheep are main meat source (in household or on market).
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
gullies are transformed to fields
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
improving soil moisture
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
gully is now flat land and traversable, structure as a new obstacle
production d'énergie
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas seed oil as a biofuel
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
new fields lead to higher productivity
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
disparités économiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
additional income by selling Jatropha seeds
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
slightly labor increase, establishment and maintenance work
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
additional space for new fields
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
positive examples for other land users
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
up -downstream problems may be solved
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold). Collection of Jatropha curcas seeds - they can be sold (additional income) or processed to oil (lamp oil etc.)
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased soil moisture
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased infiltration
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
maybe due to the Jatropha curcas canopy
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow,. But additional groundwater may be logged
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas canopy
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased rooting
compaction du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased rooting
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas biomass
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
espèces bénéfiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas new habitat for worms etc
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
new habitat for rodents etc.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
flood controll by Jatropha curcas dams
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
little effect by additional plants
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas wood is a bad fire wood
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Jatropha curcas shrub as a wind breaker
Autres impacts écologiques
Increased competition
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Over water and sunlight
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
possibility of spring development
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
if a spring can develop
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased infiltration/reduced flooding
envasement en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
capacité tampon/de filtration
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increased infiltration
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
dommages sur les champs voisins
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to gully rehabilitation
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
due to gully rehabilitation
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Establishment needs a little time, although not very much. Maintenance work is very little needed and can be done if needed or in off-farming season. Establishment and mainentance costs are none or very little.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Local technology spread from farmer to farmer.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Completely based on farmer's initiative.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A lot of farmer are adopting (or already have adopted) Jatropha curcas as a SWC technology in the region.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Soil and water conservation are very important. Also the conservation of soil moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create farmer's awareness that SWC is very important for a sustainable land management. |
|
In combination, Jatropha curcas can also be used to stabilize traditional stone structuress (terraces, dams). These physical structures are not consideret very stable and need a lot of work to establish and maintain. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further research to improve physical structures, Jatropha curcas structures as well as their combination. |
|
The roots bind the soil and holding it together and help collecting additional soil that otherwise would be washed out. The root and the plant also help to slow down flowing water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Research on how tolerant is the plant on flooding etc. |
|
Jatropha curcas is also a very good life fence that animals do not browse through because the leaves are poisonous. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
|
The seeds can be sold. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Creating and improving markets, infrastructures and technologies that need Jatropca curcas oil or biofuel. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Very low labor and money input for establishment and maintenance. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep the technology as simple as it is today. |
|
Easy to atopt in a wide range of environments (Jatroha curcas is a rather tolerant plant). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Additional research to improve knowledge of Jatropha curcas. |
|
Selling of the seeds is an additional income. If the seeds are crushed to oil it can substitute for example lamp oil that has to be bought. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve market situation and find technologies suitable to use Jatropha curcas oil or biofuel. |
|
The plant can be used in a wide range of rehabilitation purposes (gully rehabilitation, hill stabilization, improvment of micro climate etc.) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create and maintain awareness of the farmers. |
|
If plantet on bare land only, the plant does not compete with food production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sensitize the farmers that food is more important than gaining an extra income so they do not give up their fields for Jatropha seed production. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| If children eat the seeds they get sick. | Rise awareness that the plant is poisonous. |
| Plant competes for soil moisture. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Plant competes for sun light. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Jatropha curcas is an alien plant although it is used for more than 30 years in the region. | Research on the long term effects of Jatropha curcas in specific areas. |
| If the plant should reach maximum yields inputs have to be increased as well and it has to be planted on fertile soil (food competition). | Make shure people only use it as fence or as a SWC plant on bare land. |
| To avoid shading the plant is often pruned every year and the yield is therefore very small (economically irrelevant). | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade to maximize yield. |
| The plant is poisonous. People have to take care and children have to be sensitized. But acording to the farmers eating the leaves or the seeds leads to stomach ache and is not too dangerous. | Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
| Farmers plant and use Jatropha curcas quite randomly and without any specific approach. | The role of science: find the best practice. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Bach S. (2012) Potentials and limitations of Jatropha curcas as a multipurpose crop for sustainable energy supply and soil and water conservation - a case study in Bati, Ethiopia, using the WOCAT approach. Unpublished master’s thesis, Centre for Development and Environment, University of Bern.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé