Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Daler Domullojonov
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
Пуркунии селрохахо
technologies_1450 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Barotov Bahrom
Welthungerhilfe
Tadjikistan
Spécialiste GDT:
Ashurov Bakhtiyor
Welthungerhilfe
Tadjikistan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe e. V. (Welthungerhilfe) - Tadjikistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Reclamation and infilling of eroded gullies using barriers of willow branches and live mulberry cuttings to trap loess soil from surface water runoff.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
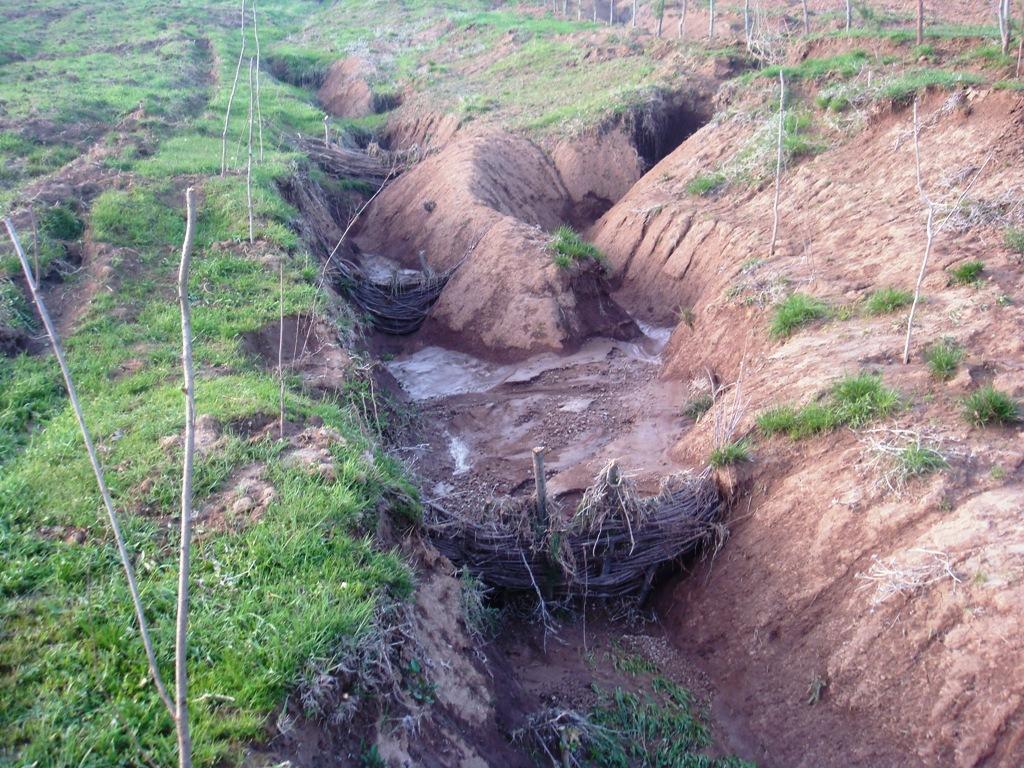
Due to many different factors and mechanisms, soil erosion is at an advanced stage in many of the hilly and mountainous parts of Tajikistan. After disrupting the soil cover in steep areas, starting the process of soil detachment and transportation water runoff gets concentrated into specific areas. As a result, rills develop on the steep areas, and eventually enlarge into gullies.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, low cost barriers are constructed from flexible living branches of a sprouting variety of tree, such as willow. These branches are placed along the gulley at intervals of 3-10 metres, so that they slow down the flow of surface water and trap the sediment, thus eventually filling in the gulley over a period of several years.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The barriers are designed to slowly help infill eroded gullies by trapping the sediment from muddy surface water runoff. This helps prevent further erosion, increases the amount of land available for pasture, and reduces the risk of mud flows or floods further down the slope.
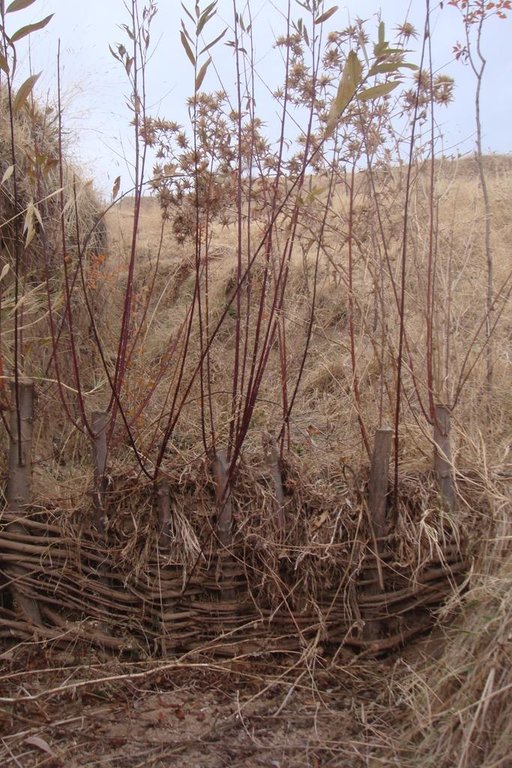
In gullies no wider than 1-2m, live cuttings from local tree varieties with a diameter of 3-5cm and 1 metre in length can be used to establish horizontal woven barriers across the gulley. The barriers are placed at 3-5m intervals along the gulley, starting at the base.
These barriers are constructed from cuttings that are woven in narrow sections with 5-6cm intervals between them. Enforcement and strengthening of these plugs can be achieved through the use of long branches of locally available mulberry. The height of the plug should not exceed 0.5m. The construction activities start in the spring and within several weeks some of the cuttings begin to sprout and grow. To avoid erosion at the sides of the structure, the cut offs are embedded into the sides of the gulley.
Natural / human environment: Gulley plugging is used in pasture land that suffers from overgrazing, deforestation and trampling, which has resulted in the degradation of the soil. Subsequently, the soil has become more vulnerable to the impact of heavy rain in the spring and autumn months, and is prone to erosion from surface water runoff.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tajikistan / Khatlon
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Khovaling / Dorobi
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.017 km2.
Approximately an 800 m long eroded gully was reclaimed.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology was developed and promoted using the framework of EC TACIS funded Welthungerhilfe project in Khatlon
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- petits fruits

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
Type d'animal:
- caprine
- bétail - laitier
- ovins
Commentaires:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing on pasture lands, that leads to reduced vegetation cover and deforestation, contributes greatly to the causes of top soil erosion and gulley formation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies are formed after intensive rainfall events. There is nothing in place to stop this erosion.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cows, goats. sheep
Grazingland comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of grazing system comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- petits fruits

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: March - June
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S6: Murs, barrières, palissades, clôtures
Commentaires:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Trees were cut from a steep slope on the side of the hillside.), overgrazing (Freely grazed area, carrying capacity less than animal numbers grazing.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More intensive rainfall.), land tenure (Lack of control of livestock grazing activities.), poverty / wealth, war and conflicts (Gullies appeared after civil war.)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
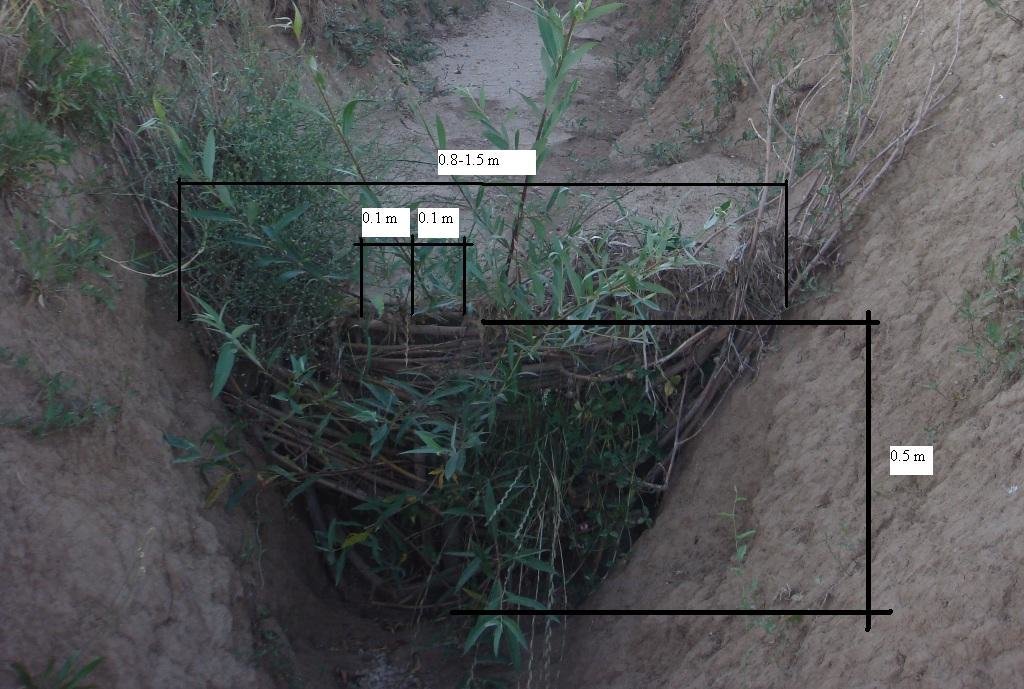
For the plugging of the gully, a low cost and simple barrier was made from locally available fast sprouting species of trees; in this case live willow cuttings were used. In the gully a narrow section was selected, and cuttings (3-5 cm diameter, 1 m length) were placed in a line with 10 cm intervals in between. One third of the cuttings were planted in the gulley, and the rest were used to create a 'wave' wall of flexible branches, which was planted with local mulberry trees (1-1.5 cm diameter). The weaved branches have to be pushed down from the top to make the barrier suitably dense. The ends of the mulberry branches have to be stuck securely to the soil inside the gulley.
Location: Dorobi village. Khovaling / Khatlon / Tajikistan
Date: 2nd July, 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: mulberry
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Construction material (wood): Willow and mulberry branches
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Auteur:
Daler Domullojonov, 14, Giprozem street, Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tajik Somoni
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
4,5
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
5.50 $
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting mulberry in willow wave structure | spring |
| 2. | establishment of barriers in gully bed | once in the beginning |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Planting mulberry | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Establishment of barriers in gully | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 90,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 20,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce structure with additional seedlings when needed | annually |
| 2. | establishment of additional barriers after filling existing barriers with sediments | once per year in beginning of rainy season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Reinforce structure | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Establishment of additional barriers | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 90,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 20,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The unit cost is for a gulley plug, 1.5 metre wide and around 1m in height.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The materials used to construct the gulley plug are locally available, and are therefore free of charge to the land user. The labour (or time in labour) is the most substantial cost, and this is directly proportional to the number of gulley plugs required to infill the entire eroded gulley. If there is a big sediment load in the surface water runoff it will back fill behind the gulley plugs rapidly and additional barriers will need to be established.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Precipitation is concentrated during the autumn and spring, averaging 1100-1200mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 1257 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Average slope 12.6%, max slope 17.2%
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil texture = loess soil
Soil fertility is low due to over use and lack of fallow time.
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: In the area around the gulley the land is compacted.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
20% of the land users are average wealthy.
80% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The trees can be harvested once the gulley is full of sediment.
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
1.5
Quantité après la GDT:
1.6
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Gully filling can help create new areas of arable land.
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Livelihood and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Sols
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Sediments are trapped
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
capacité tampon/de filtration
dommages sur les champs voisins
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
As a living barrier it needs to grow, and therefore it is sensitive to drought conditions.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
10 households in an area of 1.7 ha
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is little trend towards (growing) spontaneous adoption of the technology.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
No training and additional skills are required. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Broad promotion to other communities with similar climatic conditions and similar issues. |
| It is low cost option. |
| Easy to establish, with a low workload. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Gulley plugs are relatively easy to construct and have a low initial outlay. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be further supported by the strong involvement of local authorities, through the organisation of cross visits, and disseminating ideas between farmers. |
| It is flexible as various varieties of local sprouting trees can be used to build the gulley plug. |
| It can prevent further erosion and expansion of the gulley. It can also increase the amount of land available for pasture activities. |
| Environmentally friendly |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The gulley plug is weak in the beginning as the mulberry trees become more established. It is more susceptible to the impact of heavy rainfall events and concentrated run off down the gulley. | High levels of maintenance in the first initial few seasons. |
| The gulley plug becomes less effective as the gullies become wider and deeper. | Fencing around the gulley. |
| The gulley plug has to be protected from livestock who will eat the vegetation. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Welthungerhilfe projects in Khatlon region, Temurmalik district
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé