Multistorey agroforestry [Ethiopie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : GERBA LETA
- Rédacteurs : Julia Doldt, Noel Templer, Kidist Yilma
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mitikarsamino Ersha
technologies_6621 - Ethiopie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Gabiba Afra
A farmer
Ethiopie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Kenya1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
Agroforestry is the best technology/practice to sustainably manage the land. It has multiple economic, environmental and social benefits.
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Multistorey agroforestry is the intentional mixing of trees/shrubs with crops, pastures, and livestock. The practice creates environmental, economic, and social benefits for the end users.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
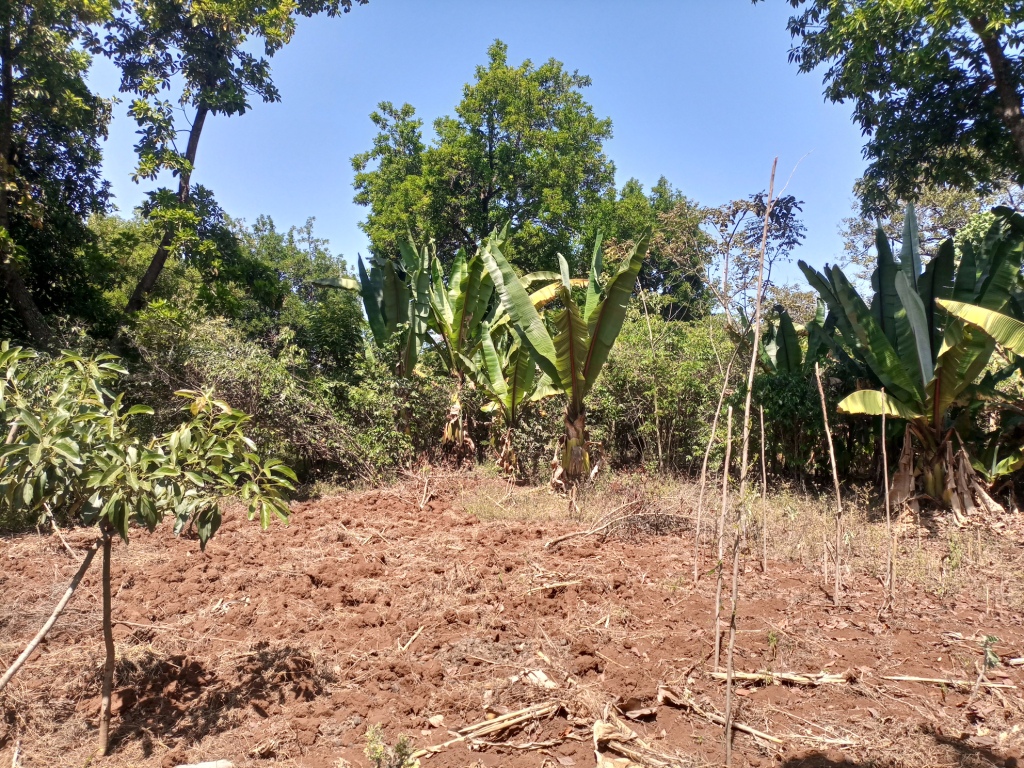
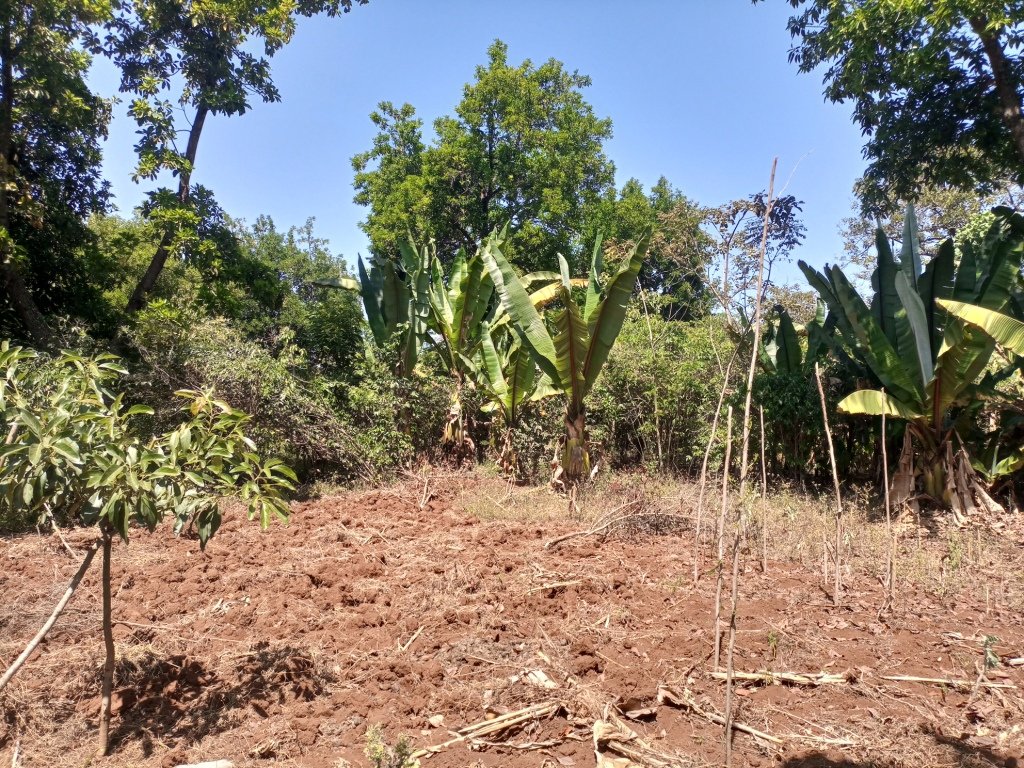
Multistorey agroforestry is the intentional mixing of trees/shrubs with crops and pasture at different levels ("storeys" or heights) and the livestock. The practice creates environmental, economic, and social benefits for the end users. Agroforestry practices provide opportunities to integrate productivity and profitability with environmental stewardship resulting in healthy and sustainable agricultural systems that can be passed on to future generations. Tree litter increases soil organic matter and reduces soil chemical and biological degradation. Tree cover can reduce soil erosion and evaporation from the soil surface. The technology is applied close to the homestead as it demands close follow-up and steady management practices, and that is where tree-crop-livestock integration can be best applied. The farmer whose practice is described here used to be very poor four decades ago. He has planted coffee gradually over the years under shade trees. As a staple perennial food crop, enset was planted also in the mixture. Livestock were also integrated. Eventually, numerous multipurpose tree species, food and fodder crops, and physical structures with productive barriers were integrated into the farming system. As a consequence, a multistorey agroforestry system has been established over years.
The purpose of the technology is to ensure ecological, economic, and social benefits. The rolling landscape of the area necessitates permanent ground cover to reduce the effect of erosive rainfall that degrades the soil. Once established, the technology needs management practices including pruning/stumping of coffee trees, managing other trees, weed control, enrichment planting with coffee and enset, and fertilization of annual and perennial crops. The livelihood of the respondent farmer has been completely changed. He has made a significant accumulation of wealth from producing and sale of tons of unprocessed coffee, avocado fruits and some indigenous bananas. This form of agroforestry creates year-round employment opportunities for proactive farmers. However, subsistence farmers with small parcels give priority entirely to the mono-cropping of cereals and other fast-maturing crops to meet their urgent demand for food. Shortage of land, capital, and a general lack of awareness about the sustainable benefits of the technology are reasons for lack of adoption of the technology.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
The farmer has integrated several crops and tree species. Over years, he noted some tree species are not the best fit for the multi-storey system. He tends to remove some of them. The high-yielding avocado fruit per se was found as an inappropriate mix for the agroforestry system as it has a complete shading effect over the undergrowth. Several other tree species such as Podocarpus species, Olea, Euphorbia, Misana (Croton macrostachyus), Doqima (Syzygium guineense), Tiqur enchet (Pygeum africanum), Pulm tree (Phonex species), Birbira (Millettia ferruginea), Wanza (Cordia africana), Sesa (Albizia species), Sesbania species, Girawa (Vernonia amygdlina) and some fodder grass species such as Napier and Guatemala grass…are all part of the system but the farmer’s choices are the latter five to seven species. Despite his views of the characteristic feature of the different trees in relation to the undergrowth such as coffee, enset, beans, pumpkins and so on, they have immense ecological benefits as well as supply food, bee forages and construction materials.
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
The video of this technology is not documented.
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ethiopie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Sidama
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Shoye kebele (Kebele - lower administrative level)
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
It is located on farm around the resident area or in homegarden.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
1980
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The farmer started to implement the technology by himself but gradually managed to access support and inputs such as coffee and tree seedling, training, and visits from the agriculture and coffee development office through the extension workers. Farm visit and mentoring services from the district experts were also commendable to inspire the farmer. The visit to the farm by researchers, local development and other actors add knowledge and motivation to the farmer.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- Legumes - Haricot beans and other climbing species, Pumpkin and root crops/tuber potato and yam.
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- bananier/plantain/abaca
- cultures fourragères - graminées
- herbs, chili, capsicum
- Enset/false banana
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- avocat
- café, cultivé à l'ombre
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Belg, short rain (March to April) and Meher, long rain (June to September).
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Haricot beans intercropped within maize and under coffee. Actually, maize grow in the buffer zone of the agroforestry farm.
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Cereal maize farm rotate to legume such as haricot beans.
Commentaires:
Adjacent small plots of land are used to grow maize to complement Enset/false banana - a staple crop for the household. Also, beans and vegetables such as local kale are integrated into the farming system.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Pâturages
- Open/free grazing
Type d'animal:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- caprine
- mules et ânes
- volailles
Est-ce que la gestion intégrée cultures-élevage est pratiquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
In an integrated crop-livestock system, crops and livestock interact to create a synergy, with recycling allowing the maximum use of available resources. Crop residues can be used for animal feed, while livestock and livestock by-product production and processing can enhance agricultural productivity by intensifying the use of nutrients that improve soil fertility and reduce the use of chemical fertilizers. Apparently, crop residues are a valuable, low-cost feed resource for animal production, and are consequently the major source of nutrients for livestock.
Produits et services:
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
Espèces:
bétail - laitier
Nombre:
10
Espèces:
caprine
Nombre:
4
Espèces:
volailles
Nombre:
3
Espèces:
mules et ânes
Nombre:
1
Commentaires:
Four decades back or before the conversion of the land into the agroforestry, it was partly wetland and the grazing land used by free roaming animals.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Agriculture is entirely rainfed that rely on bimodal rainfall intercepted twice a year.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- gestion intégrée cultures-élevage
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S2: Diguettes, digues

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
Commentaires:
Diverse SLM practices are integrated over the farmland.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wm: mouvements de masse/ glissements de terrain

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
- Ca: acidification

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pw: saturation en eau des sols
- Ps: affaissement des sols organiques, tassement des sols

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bh: perte d’habitats
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
- Bl: perte de la vie des sols
- Bp: augmentation des insectes nuisibles (ravageurs)/ maladies, baisse des prédateurs
Commentaires:
The bare land that was subjected to soil erosion is arrested and reversed. Frequent cultivation, a threat to degradation has been entirely changed. Diverse types of degradation to the farmland have been mitigated.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
Agroforestry practice helps to conserve soil and water as a barrier and via covering the ground. Tree species also serve as wind break to reduce wind velocity and wind erosion. Integrating tree species with grasses/forage not only reduces soil and water loss but also supply feed to the livestock. It also maintain soil organic matter and improve physical properties, fix nitrogen and promote efficient nutrient cycling. Furthermore, the twigs and leaves serve as mulch, green manure, etc. Integration of diverse trees/shrubs also break the impermeable layer and facilitate nutrient cycling from deep layer in certain soils, and reduce the development of soil acidity.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
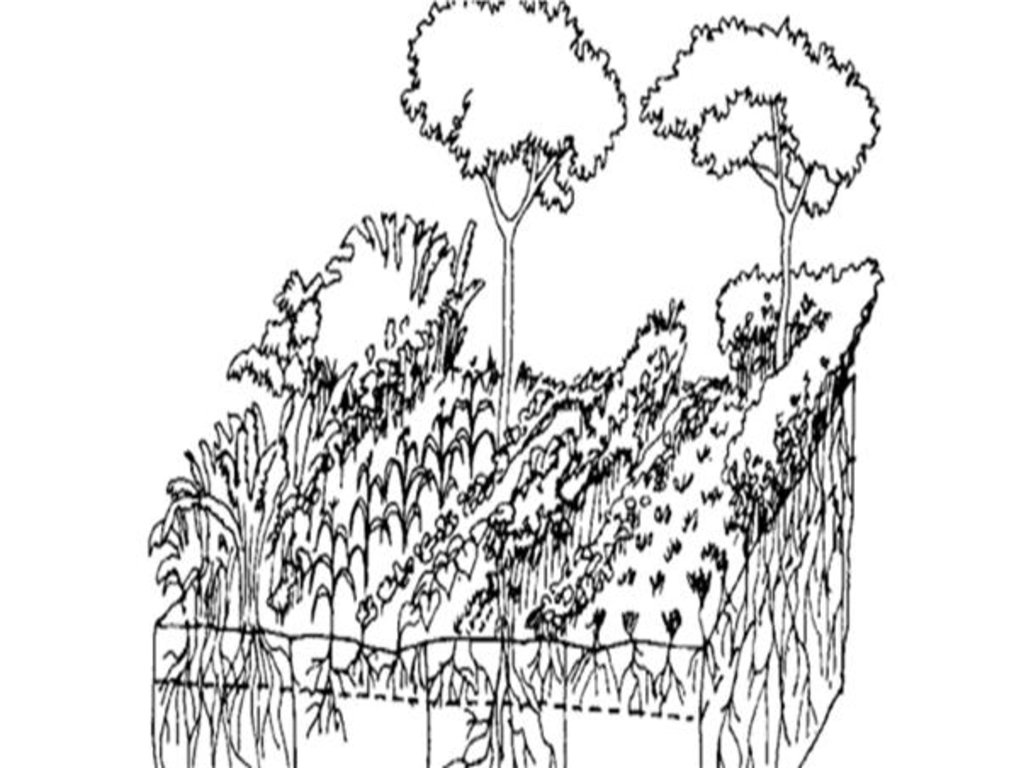
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
An adopted technical drawing/specification of the classification of tree-crop arrangement in the multistorey agroforestry system.
Auteur:
Xu J, Mercado A, He J., Dawson I (eds.) (2013); ISBN 978-92-9059-333-1
Date:
20/01/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
4Timad
Si vous utilisez une unité de superficie locale, indiquez le facteur de conversion vers un hectare (p.ex. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha = :
4 Timad = 1 ha
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ethiopian Birr
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
53,12
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
In rural area wage rate vary by type of work: coffee harvest-80 ETB/day, weeding 60 ETB/day. About 70 birr/day, on average.
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | Before and during Belg (short rain) and Meher (long rain) season. |
| 2. | Enset and Coffee planting | In Belg and Meher season, respectively. |
| 3. | Planting beans (annual crops) | In Belg season |
| 4. | Fodder and other Multipurpose trees planting | In Meher (main rainy season). |
Commentaires:
Farmer start small and keep on enriching and managing the farm with inputs and technology components. This is for a single year but two seasons with short and long rain. Actually, perennial crops such as coffee and enset are not planted every year.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Land preparation | Oxen plow | 16,0 | 200,0 | 3200,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting annual crops | Oxen plow | 4,0 | 200,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting perennial crops | PDs | 20,0 | 70,0 | 1400,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting fodder crops and trees | PDs | 5,0 | 70,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spade | Number | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hoe | Number | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Digging fork | Number | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Coffee seedling | number | 2500,0 | 10,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Enset seedling | number | 6000,0 | 5,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Tree seedling | number | 1500,0 | 2,0 | 3000,0 | 50,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Beans seed | kg | 50,0 | 42,0 | 2100,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | NSP fertilizer | kg | 100,0 | 44,0 | 4400,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Urea fertilizer | kg | 50,0 | 44,0 | 2200,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 73950,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1392,13 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
In the past, coffee seedling was freely supplied to the farmer by the Ministry of Agriculture. The trend has changed recently. Apart from some tree seedlings that are freely supplied through government nurseries, virtually all costs for the establishment of Agroforestry are covered by the farmer themselves.
Commentaires:
Commodity price in Ethiopia is frequently changing because of inflation and economic crisis. Therefore, it is impossible to confidently estimate the price of inputs, farm tools, and labor costs.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inputs | Before the onset of short/long rain. |
| 2. | Management | Throughout the year depending on the management types. |
| 3. | Farm tools | During off-season. |
Commentaires:
A farmer estimate maintenance costs of about 40,000 ETB per hectare of land. However, my calculation in the following section reduces it a bit lower by excluding the cost of plant protection, and by boosting the contribution of family labor in the household. Apart for the general calculation, as the average land holding in Sidama region is less than 0.25 ha, a farmer may not go for adopting the technology on 1 ha.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Enrichment/replacement planting | PDs | 5,0 | 70,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Fertilization | PDs | 40,0 | 70,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Weeding | PDs | 40,0 | 70,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hoes | number | 4,0 | 600,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Digging fork | number | 4,0 | 500,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spade | number | 4,0 | 400,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Coffee seedling for replacement | number | 250,0 | 10,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | NSP | kg | 100,0 | 44,0 | 4400,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Urea | kg | 50,0 | 44,0 | 2200,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 21050,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 396,27 | |||||
Commentaires:
Frequently changing prices of inputs, labor, and farm tools disable someone to give an estimate for the establishment and maintenance costs in the future. Essentially, maintenance cost demands lower investment than the establishment cost. Unlike in the past years, agroforestry doesn't start from scratch but can be built up on the existing initiative. Therefore, it would be rather an intensification of agroforestry than just establishing.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Economic crisis and the prevailing inflation in the country, and global changes in price of petroleum and other commodities such as chemical fertilizers.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The area receive adequate rainfall.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Awassa Meteorology center
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
The climate is virtually consistent except during the season of El Nino and cyclical shortage that happens once in years.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The topography feature is changing from moderate to bit slopy. However, the steepness of the farmland is not more than 15%.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Not available.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux souterraines
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Surface water is available year-round with fluctuation of the volume with the season. Besides, pollution is high during the rainy season because of soil erosion from the upstream.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The applied technology/practices comprise diverse species of tree crops. It can be characterized as a practice highly rich in agrobiodiversity.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- très riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes âgées
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
He is also engaged in fuel wood business. Of course, the business does not focus on indigenous tree species but the most commonly marketable trees for construction and fuel wood in Ethiopia i.e. eucalyptus species.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
He possesses 4.5 hectares of land. However, it is much higher than the regional average, and could be still less than a few farmers.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Non
Précisez:
Land use right is issued by the state. Of course, the land is inherited in the parent line. He also accessed more parcel during land redistribution of the Derg regime. As a rule, the land belongs to the state but the user has usufructs.
Commentaires:
Farmers are certified based on the usufructs right issued by the government via the land administration policy enshrined in the country's constitution.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Commentaires:
Tap water is accessible some distance away. The deep well the farmer has is not clean for drinking by the household but for cattle and cleaning goods and clothes.
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It is difficult to guess the increment by weight of perennial crops such as Enset. Of course, the performance is much better in the agroforestry system with intensive management and application of organic fertilizers. The integration also ameliorates the microclimate of the area and makes the situation ideal for the crops.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In the agroforestry system, a combination of livestock manure, tree litter, and a mixed cropping system contributes to soil fertility and soil health which improves crop quality.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased with improved soil fertility and soil healthy.
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Livestock access to feed during the dry spell when communal grazing land is denuded of grass. Furthermore, agroforestry promotes a cut-and-carry feeding system that strengthens reliance on one's feed reserves at disposal. This goes with the intensification of livestock production.
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The practices rather improve the resilience of the crop as it creates an ambient environment.
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The integration increase product diversity.
surface de production
gestion des terres
production d'énergie
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cattle manure is used for the production of heat and light energy through the application of biogas technology.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Agroforestry's contribution to drinking water availability and water quality was not measured and was beyond the scope of respondents to comprehend and address the questions except the merely conceptual reflection. Of course, the technology reduces runoff and recharges the ground water which directly contributes to the availability of surface water for livestock.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fertilizer supply changed more to organic than chemical fertilizer. The foliage of tree litter and in situ decomposition of organic matter added substantial value to the restoration of soil fertility.
revenus agricoles
diversité des sources de revenus
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increased management demand with gradual increase of the integration of tree crops and the overall size of the land is remarked by the farmer.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Land users generate reasonable income from the integration of different perennial and annual crops as well as livestock.
situation sanitaire
droits d'utilisation des terres/ de l'eau
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology immensely contributed to SLM by covering the farmland with perennial trees and crops and by incorporating the physical structure into the practice.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
drainage de l'excès d'eau
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The groundwater table is estimated to increase as the ground cover promotes the infiltration and vertical movement of the intercepted rain on a gradual basis.
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As some tree species such as avocados consume large amounts of water for transpiration needs, the degree of evaporation reduction of the practices is counterbalanced by the integration of the high-consumers with low-consumer species. Overall, agroforestry has a positive impact on evaporation reduction.
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
accumulation de sol
compaction du sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Nutrient cycling is highly improved because different tree species may penetrate the impervious soil layer and bring the nutrient to the surface via tree litter, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and add to the soil.
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Highly increase, though not measured for this particular farm.
acidité
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The cause of soil acidity can be diverse including the soil parent materials. However, agroforestry has positive acidity-reducing factors by improving soil fertility and soil health.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Highly increased because of the combination of trees/shrubs with food crops and fodder crops.
espèces étrangères envahissantes
diversité animale
espèces bénéfiques
diversité des habitats
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Agroforestry hosts the predators and prey and creates balanced food chains that reduce the degrees of pest development.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts de la sécheresse
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It is a climate-smart agriculture by its virtue that increase carbon sequestration as a regenerative agriculture.
vitesse du vent
microclimat
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
The practices ameliorate the prevailing adverse climatic conditions and land degradation.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Even if the impact of agroforestry plays a positive reduction role in pollution, the overall impact is compromised by the total farmland covered by a combination of tree crops.
capacité tampon/de filtration
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Agroforestry has a filtering capacity of polluted air with dust and adverse temperature such as during dry and hot days.
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Intercepted by leaves of trees and shrubs.
dommages sur les champs voisins
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
impact des gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It highly contributes to carbon absorption and storage above and below the ground.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
Agroforestry has beneficial ecological and economic functions.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | très bien | |
| températures saisonnières | saison sèche | augmente | très bien |
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | saison des pluies/ humide | décroît | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | modérément |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 11-50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
About 30% of resident farmers have adopted the technology. The prevailing farming system necessitate change in the approach, and outshined farmers motivated the others to follow suit.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- évolution des marchés
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Raising coffee prices motivated farmers to refocus on the crop which years back discouraged to shift of the coffee farm to eucalyptus plantation.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Increase production per unit of land and improve livelihoods of family farmers. |
| Reduce land/soil degradation because of permanent soil cover. |
| Ensure sustainable production, reduce risks and improve the biodiversity. Also, increase the family farmers income and their status in the society. It enables them to feel as valuable elite in the community. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Agroforestry improves total production earned from a farmland and improve the wellbeing of the adopted farmers. Implies, it has substantial economic benefits. |
| It reduces soil erosion and land degradation. Also has immense ecological benefits and improves the microclimate of the surrounding. |
| It reduces risks of crop failure owing to climate variability. Also, boost the biodiversity of trees, crops, and habitat diversity that host various living creature in the biosphere as well pedosphere. This is related to carbon sequestration, emission reduction, proper ecosystem function, and overall ecological contribution. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Demand intensive management, and there is shortage of labor. | Identify and established trees and crops that requires minimum labor for planting, maintenance & propagation. |
| Incompatible tree species to the essence of proper integration in Agroforestry. | Select and adopt trees and crops with desirable characteristics to be integrated in the technology and responsive to management practices. |
| Inconsistent product prices for the farm products such as coffee beans and avocado fruits on the local market. | Link farmers to free and fair market which is consistent and sustainable. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Failure to select tree species with desirable characteristics |
Trees/shrubs with the following desirable characteristics need to be considered: - Deep root system to draw water & nutrients. - Easy to propagate, & high biomass producers, palatable, provide more green manure, & high survival percentage. - Adaptable to close spacing like in hedgerows. - Good sprouting & positive response to pruning. - High coppicing and pollarding capacity. |
| Highly dense in some areas and slightly sparse in some part of the farm. | Try to maintain the spacing and distribution of suitable species composition. |
| Trees and shrubs less used as livestock feed except during the shortage period | Promote feeding the diverse fodder trees to the livestock to ensure their access and benefited from trees/shrubs as well than rely only on grass family. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
An intensified agroforestry system visited.
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Only one farmer interviewed.
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
Land users, regional bureau of agriculture natural resource management expert and GIZ regional advisor consulted.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
13/01/2023
Commentaires:
Extensive field visits and interviews were conducted with Land users, Regional NRM expert, and ISFM + regional advisor.
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
World Agroforestry Centre. 2008. Annual Report 2007-2008: Agroforestry for food security and healthy ecosystems. Nairobi, Kenya: World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF). ISSN 1995-6851
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
www.worldagroforestry.org
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Agroforestry System for Ecological Restoration: How to reconcile conservation and production options for Brazil's Cerrado and Caatinga Biomes. Miccolis, Peneiveirok Marques et al. 2016. ISBN: 978-85-63288-18-9
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://apps.worldagroforestry.org/downloads/Publications/PDFS/B19034.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Indigenous Agroforestry Practices and their Implications on Sustainable Land Use and Natural Resources Management: The Case of Wonago Woreda. Sustainable Land Use Forum (SURF), 2006. Research Report No 1, Addis Ababa
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
www. devinet.org/sluf
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
The Center for Subtropical Agroforestry (CSTAF)
URL:
http://www. cstaf.ifas.ufl.edu/
Titre/ description:
World Agroforestry (ICRAF)
URL:
https://www.worldagroforestry.org; https://www.cgiar.org/research/center/world-agroforestry-centre/
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
The questionnaire is comprehensive and give the opportunity to add additional techniques/approaches via the "other" options. However, it is demanding as it requires for videography and sketching skills for every technology.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé