Retention ditches for soil and water conservation [Kenya]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : William Akwanyi
- Rédacteurs : Innocent Faith, JARED AYIENA, Noel Templer, George Onyango
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mitaro ya kuhifadhi maji (Kiswahili)
technologies_6675 - Kenya
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Odongo Rosemary Ogola
Welthungerhilfe
Kenya
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Kenya1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
Farmers who have implemented the technology have been able to control surface runoff at their farms.
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
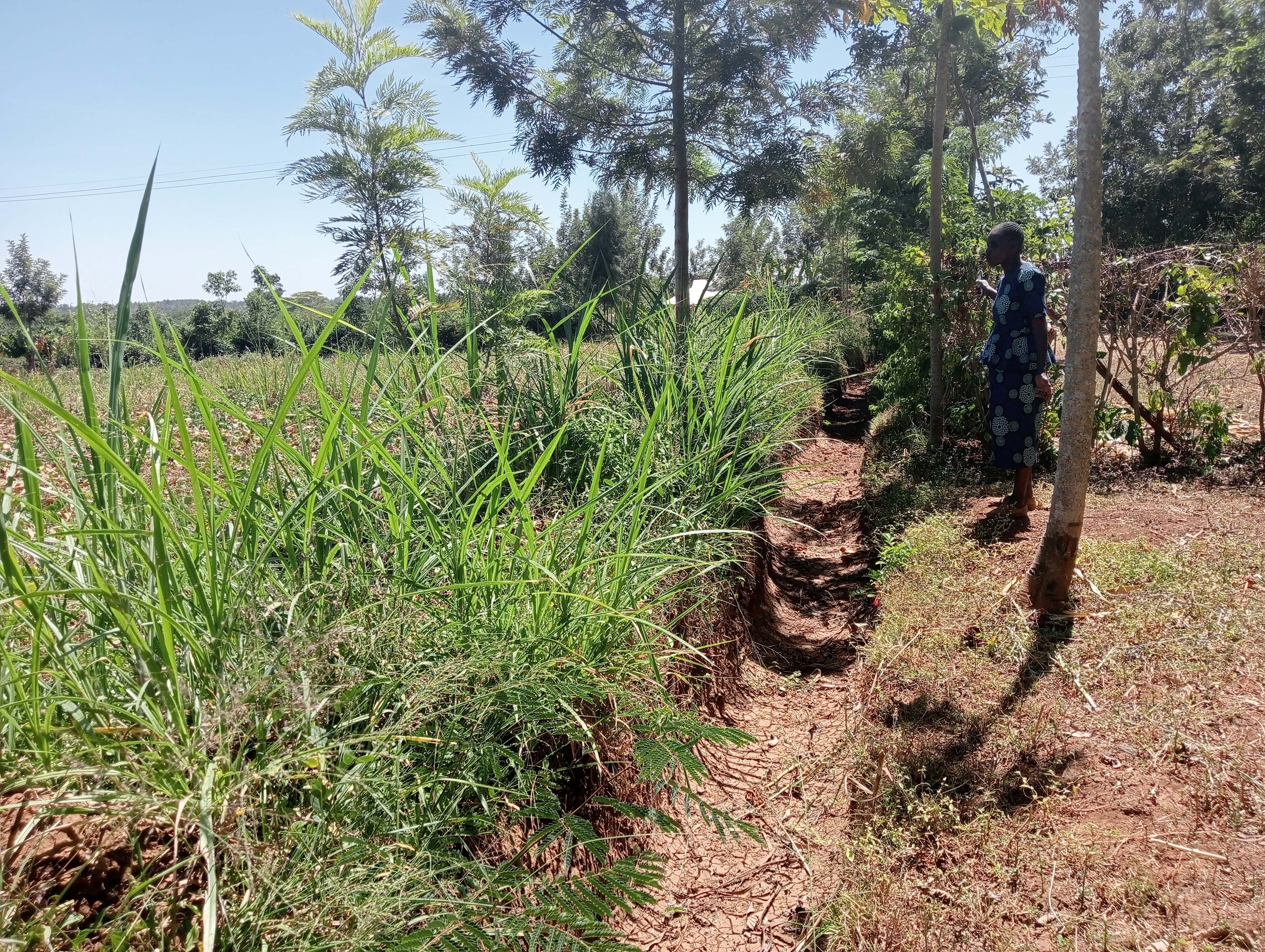
Retention ditches are channels aligned along the contour which are designed for surface runoff management. They improve water infiltration into the ground and prevent soil erosion.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Retention ditches are soil and water conservation practices. They are channels dug along contours (i.e., across the slope), especially at the uppermost part of the farm to retain stormwater/ surface runoff. They typically comprise two components: (a) vegetational-biological and (b) mechanical-structural components which are integrated to collect surface runoff, allowing for sediment carried by runoff to settle as water infiltrates into the ground. The mechanical-structural component consists of channels dug in such a way that they follow the contour and run perpendicular to the flow of water in areas where runoff naturally flows or collects. The soil excavated from the ditch forms a bund below the ditch. Retention ditches prevent surface runoff from outside the farm from flowing into or through the farm. The vegetational-biological component consists of plants grown on the bunds. The plant roots bind the soil thus increasing the slope stability, especially of the bunds; thus, preventing soil from collapsing and falling back into the channel. Retention ditches thus harvest and retain water (especially in low rainfall areas) preventing fertile soil from being washed away by surface runoff and increasing water availability for plants. In high-rainfall areas, they play the role of discharging excessive runoff into waterways.
Retention ditches are dug to about 60 cm deep and about 50 cm wide. To ensure stability, especially in areas with unstable soils, the top width is made wider than the bottom width allowing for slanting walls that are more stable than vertical walls. An understanding of the slope angle is an important factor in the designing and construction of retention ditches. A line-level (a spirit level attached to a string suspended between two poles) can be used to determine the measure slope. The slope angle determines the size of the ditch (depth and width) and the spacing between successive ditches on the same piece of land. In low-rainfall areas (such as Siaya), retention ditches are spaced at about 50 – 70 m while in high-rainfall areas the space between the ditches are closer (about 20 m). Similarly, the size of the retention ditches increases with increasing slope.
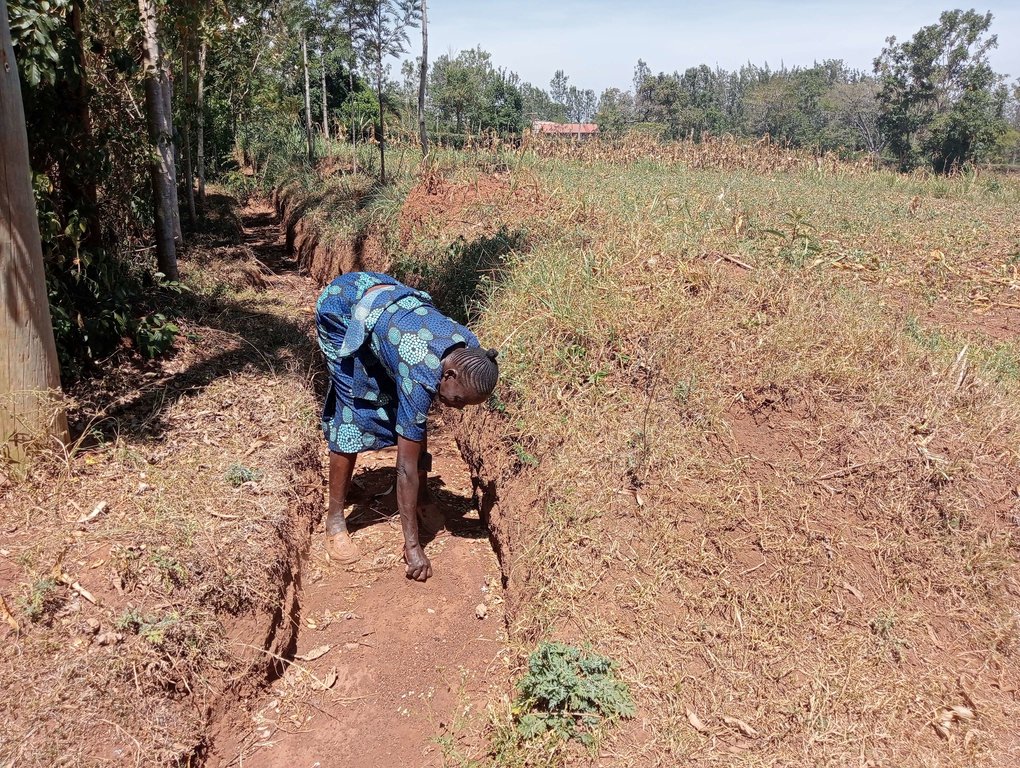
Some crops, especially bananas, arrowroot, etc. that demand a lot of water can be established in the ditches. Maintenance of retention ditches involves regular desilting, whenever the ditch is about 1/3 filled with silt. Hoes, shovels/ spades, and a panga (machete) are some of the tools used in digging and maintaining retention ditches. Farmers like retention ditches because they help in controlling soil erosion.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kenya
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Siaya County, Nyanza Region
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Uloma Village, Bondo Municipality, Bondo Sub-county
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
The farm where the technology is implemented is not in a protected area.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2018
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security (ProSoil) project
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agro-sylvo-pastoralisme

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- cultures fourragères - graminées
- cultures fourragères - autres
- légumineuses et légumes secs - fèves
- légumineuses et légumes secs - autres
- légumes - autres
Système de cultures annuelles :
Culture en jachère - maïs/sorgho/mil en culture intercalaire avec des légumineuses
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- bananier/plantain/abaca
- cultures fourragères - graminées
- fodder crops - legumes, clover
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- avocat
- arbres fourragers (Barbe jolote, Faux mimosa, Prosopis, etc.)
- fruits, autres
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
- papaye
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Long and short rain seasons
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Maize and legumes e.g., beans
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Some sections of the farm are left fallow during the short rains to allow for soil regeneration.

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
- Prairies améliorées
Type d'animal:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- volailles
Est-ce que la gestion intégrée cultures-élevage est pratiquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Fodder (nappier grass) planted on the berms is fed to the cattle. The manure from the cattle and droppings from the chicken is used as manure for the crops.
Produits et services:
- oeufs
- viande
- lait
Espèces:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Nombre:
3
Espèces:
volailles
Nombre:
100
Commentaires:
There are assorted trees on the farm, including fruit trees. Some of the trees are planted on the berm of the retention ditches.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Crops are planted only during the rainy seasons since there is no irrigation.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous
Commentaires:
Trees and grasses are planted on the berms of the retention ditches.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
The retention ditches, especially when applied at the top of a plot and the design is to heap the soil below the channel ('fanya chini') has helped control gully erosion. Gullies were common in the farm before the digging of the retention ditches.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
The retention ditches saved the land from gullies, and are still controlling soil erosion.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Ditch dimensions: length = 70m, width = 50cm, depth = 60cm
Slope of the field = 4%
Plants on the berm: nappier grass
Auteur:
William Akwanyi
Date:
01/07/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
0.4 ha
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
KES
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
122,95
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
300
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slope measurement and determination of position for the retention ditch | During the dry season |
| 2. | Digging the ditches | Before onset of rains |
Commentaires:
The ditches should be constructed during the dry season or before the rains start when the soil is light and easy to remove from the ditches.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Digging the ditches | Man days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Hoe | No. | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Panga (broad blade) | No. | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Wheelbarrow | No. | 1,0 | 800,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spade | No. | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Planting rope | No. | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spirit level | No. | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Autre | Slope measurement and determination of position for the retention ditch (professional service) | Professional service | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 6690,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 54,41 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
ProSoil project
Commentaires:
The costs of the implements are KES 400/- for a hoe, KES 4,000/- for a wheelbarrow, KES 300/- for a planting rope and broad blade, KES 3,000/- for a spirit level, and KES 450/- for a spade. It is assumed that the farmer will be able to use the hoe, planting rope, broad blade, and spade over a period of 5 years, and a wheelbarrow over a period of 10 years before these implements will have depreciated to a point where they will not be useable. The cost is thus spread over the years when the farmer will be able to use the implement.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desilting | Whenever the ditch is about 1/3 filled with silt |
Commentaires:
Maintenance activities do not happen at regular intervals but depend on volume of runoff and amount of silt carried by surface runoff for desilting the ditch, rate of growth of weeds for weeding, and factors that lead to lead of plants for plant re-establishment.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de l'entretien de la Technologie:
2000,0
Commentaires:
the above cost is based on the farmer's estimate.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Rate of man-days vary from one place to another and also depend on the kind of work.
Exchange rate for January 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Rainfall pattern is bimodal. Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Bondo Meteorological Station
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
The area is found near Lake Victoria which influences the climate.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations convexes
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Retention ditches divert the flow of surface runoff. The slope of the farmer's field is 4%.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
N/A
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depts are not more than 50 metres. Lake Victoria is a permanent surface water body in the area.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The area has high agrobiodiversity as most farms are under crops and trees.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Semi-nomade
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
- personnes âgées
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The farmer uses the land together with his other family members.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
Farmers with more than 2 ha in the area are considered to have large pieces of land since there is high level of land fragmentation in the area.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Non
Précisez:
Each landowner has full control of the way he/ she wants to use his/ her land.
Commentaires:
The farmer has a title for his piece of land.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Commentaires:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
2
Quantité après la GDT:
4
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Quantity refers to the number of 90 Kg bags of maize produced per acre. Based on estimation by the farmer.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, the crops are doing better compared to how they were before the retention ditches were dug.
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
1
Quantité après la GDT:
3
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Quantity refers to harvesting cycles for nappier grass from the same farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not easy to quantify but according to the farmer, fodder is doing better compared to how it was before the retention ditches were dug.
production animale
Quantité avant la GDT:
1
Quantité après la GDT:
3
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Quantity refers to the amount of milk in litres from one cow. Milk production is often at the peak during early lactation months. Based on estimation by the farmer.
risque d'échec de la production
Quantité avant la GDT:
80
Quantité après la GDT:
40
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Quantity refers to the percentage probability of the crop failing to do well. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Revenus et coûts
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Refers to the number of hours that the farmer can be free in any working day. During the rainy season, the farmer spends some time desilting the ditches. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
5
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Quantity refers to the number of months in a year when there is total lack of food in the house, and the farmer has to buy all the food required in the house. Based on estimation by the farmer.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Quantity refers to the estimated percentage of knowledge in SLM/ land management. This is a farmer's estimate.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Refers to the amount of water that flows through the farm. Not easy to quantify. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Sols
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not easy to quantify.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Refers to the farmer's estimated percentage vegetation cover at the farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by her.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.
envasement en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not easy to quantify. All silt is deposited in the retention ditches and scooped by the farmer for replenishing parts of the farm with low soil levels.
dommages sur les champs voisins
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Not easy to quantify. Retention ditches have reduced the amount of water that flows to the farms in the lower areas. This has reduced soil erosion in these farms.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
It was not possible for the farmer to quantify the above.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| températures saisonnières | saison sèche | augmente | modérément |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The retention ditches have generally improved crop production.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 11-50%
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Controls soil erosion. Silt collected in the ditches is used to replenish other sections of the farm with poor soils. |
| Improved crop yields. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Controls road damage due to runoff as most of the water is collected by the ditches before it destroys the road. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Establishment investment is capital and labour intensive. | The farmer has to be committed. |
| Maintenance is labour intensive. | The farmer has to be committed. Proper planning of farm work. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| If not managed properly by regular removal of silt, the ditch can easily fill up. | The farmer must be committed to remove silt regularly. |
| May overflow and collapse during high rainfall leading to high levels of soil erosion. | Proper designing in consideration of runoff volumes and slope angle. Regular maintenance. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
One visit at one farm
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
One farmer interviewed at his farm. Follow-up questions on phone.
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
ProSoil team and project implementers from Welthungerhilfe consulted.
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
Siaya County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022 and online sources reviewed.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
27/01/2023
Commentaires:
One field visit and several follow-up consultations.
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Climate Smart Extension Manual by KCEP - CRAL, 2021
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Download free at https://www.kalro.org/files/kcep/CSA-extension-manual-18-06-21.pdf
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Siaya County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022
URL:
https://repository.kippra.or.ke/bitstream/handle/123456789/1218/2018-2022%20%20Siaya%20County%20CIDP.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, UNCCD, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé