Pre-Monsoon Dry Sowing (PMDS) [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Santosh Gupta
- Rédacteurs : Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Kim Arora
- Examinateur : Udo Höggel
technologies_6697 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
GIZ India (GIZ India) - IndeNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - KenyaNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology described here is related to sustainable land and other resource management systems.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
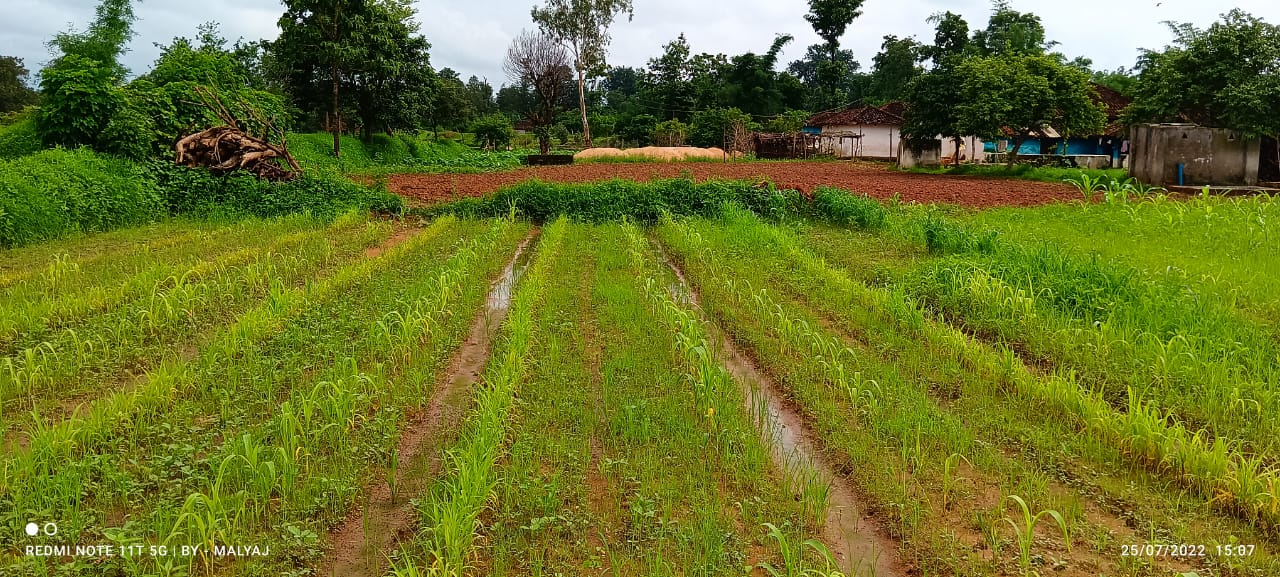
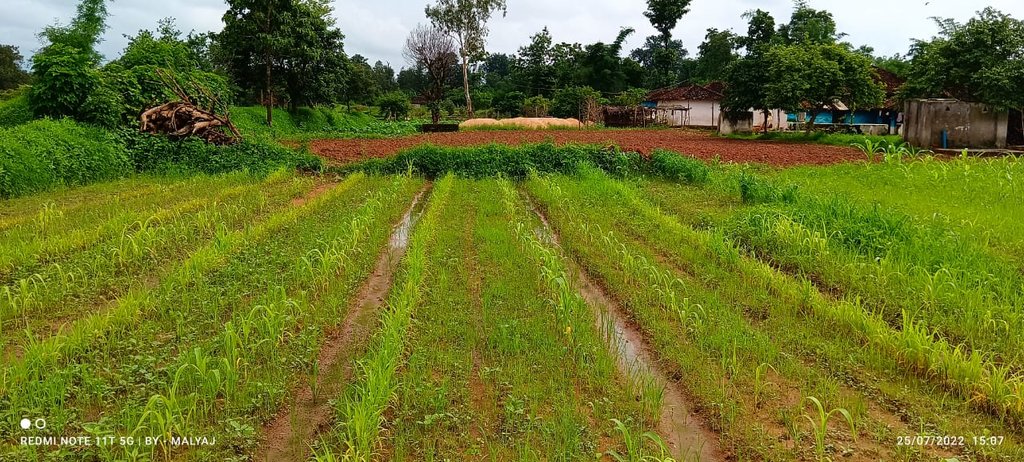
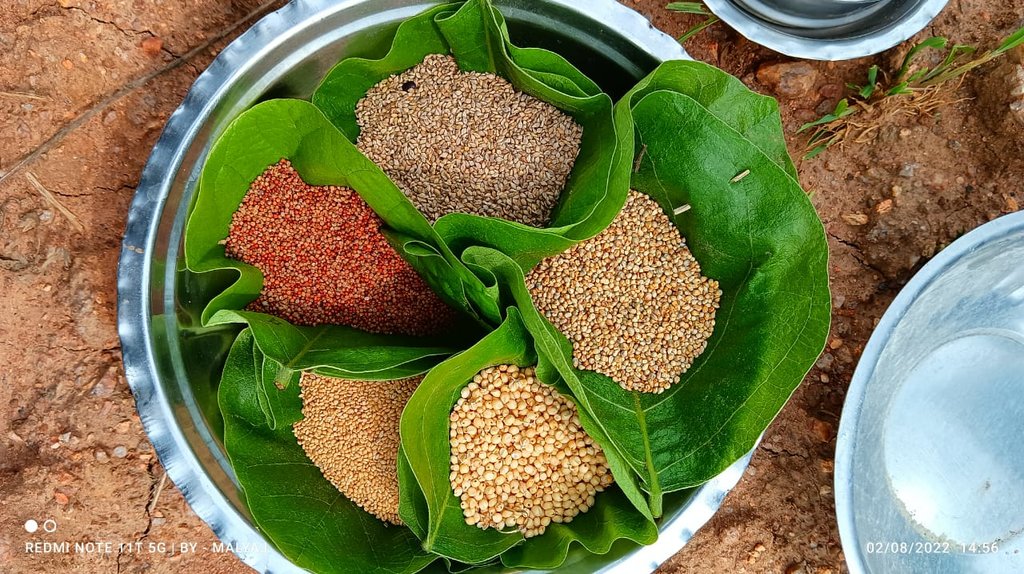
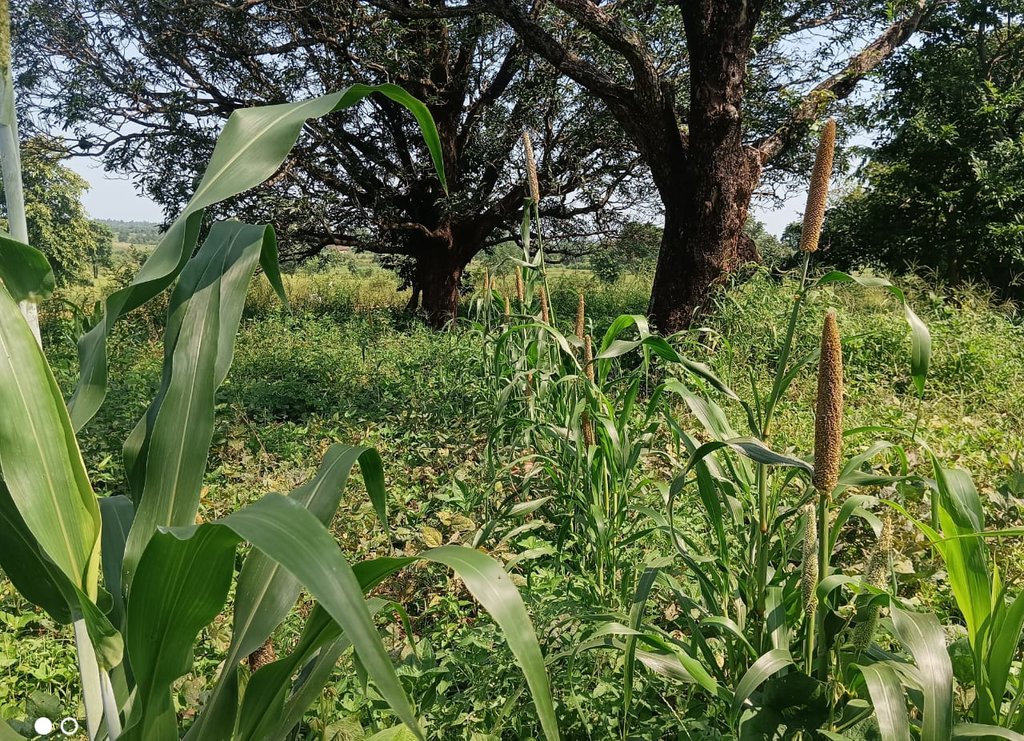
The Pre-Monsoon Dry Sowing Technology aims to sow 12 to 15 different crop varieties in April without waiting for rain. To achieve this the seeds are pelletized with a mixture of clay soils, bio-inoculants like dried Ghanjeevamruth and Dravajeevamrit, and ash. The main objective of this technology is to empower rainfed farmers by utilizing the initial rainfall in April and May for crop cultivation. By using pelettized seeds, they can maximize the effectiveness of rainfall showers before the arrival of the monsoon season. Such seeds can also survive, if there are delay in the rainfall as the pellets around the seed help it in maintaining the moisture.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Pre-monsoon dry sowing (PMDS) is a system of sowing, tilling and tending the land wherein the farmer grows crops in non-farming seasons or whenever there is no crop cover on the land. This can be practised before the advent of monsoon, during summer (April-May), after Kharif and before the beginning of the Rabi season (September and October). PMDS harnesses the water vapor from air that gets settled in the form of early morning dew. The dew supplies the required moisture to the soil. (Reference:-https://apcnf.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/IDS-2020-2021-APCNF-PMDS-Report.pdf)
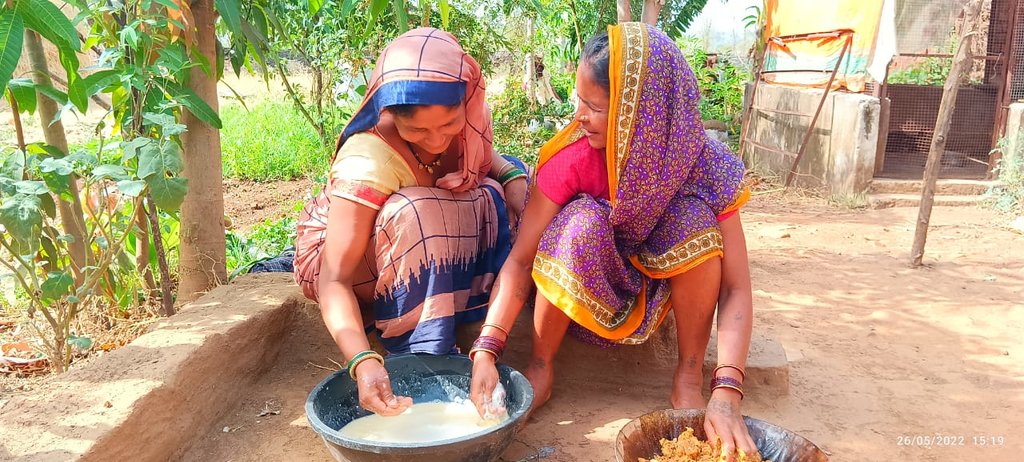
In the study where PMDS was practised before the onset of the monsoon season, typically during the dry month of April. The seeds are pelletized with a mixture of clay soils, bio-inoculants, and ash, which creates a protective coating around the seed and helps it to germinate even in the case of delayed rains or very little rainfall. The coating around the seed, helps it to maintain moisture and support its germination. As the name suggests, the technology is good for utilising the pre-monsoon season by advancing the sowing cycles, using the usually dry months of summer and utilising the pre-monsoon rains.
This technology benefits rainfed areas where farmers rely solely on rainfall for irrigation. PMDS aims to promote an extended duration of crop cover under rainfed conditions, allowing farmers to cultivate crops with a reduced risk of crop failure in the cases of delayed or lower rainfall. Since seeds are germinated before the arrival of monsoon, there are times when they can also survive the heavy rains. This technology is useful in utilising moisture to the best extent possible as seeds are covered with the outer layer of clay and other stuff. In the Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh, farmers utilized seeds from their homes, comprising 12 to 15 crops, including cereals, pulses, and spices. These collected seeds were pelletized, dried for 24 hours, and broadcasted into minimally tilled soil. The diversified crop combination was grown until July and mixed with the soil before paddy transplanting. This process improves the soil's microbial activity, resulting in increased yields in crops grown before paddy and in the paddy crop itself. Therefore, the farmers benefit from increased production and yields through this technique of PMDS.
PMDS not only improves the economics of farmers but it also improves soil health. The covering of the soil with different crops protects it from heat, pounding rain, and wind. It also improves diversity in soil microorganisms, beneficial insects and other species. Covering soil for 365 days with plant diversity is also critical to protect soil health and balance climate change. PMDS can facilitate all these functions.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Madhya Pradesh
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Bichhiya block
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology is applied by rainfed farmers in the Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2022
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The modified PMDS technology used in another program, the Andhra Pradesh Natural Farming Program, has been adopted here.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - riz (de terres humides)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Generally, Paddy is transplanted in July Month in the Mandla District and harvested around November. This region is majorly rainfed, and only 9% of the area has some irrigation source.
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Non
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- céréales - sorgho
- legumes and pulses - lentils
- Lentils include - Black gram, Cowpea, Green Gram, Red Gram and Oil seeds including sesame and Coriander.
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
The above mention crops are generally mixed together and grown on the same patches of land in April.
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Non
Commentaires:
The PMDS technology has enabled crop diversification in the Mandla District from April to July.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- perturbation minimale du sol
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A6: Gestion des résidus des cultures
A6: Précisez la gestion des résidus des cultures:
A 6.5: Résidus retenus

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
Commentaires:
The PMDS (pre-monsoon dry sowing) technique involves crop diversification and the utilization of rainfed land from April to July, typically left unused, to improve soil health. This is achieved by planting green crops that are later harvested, leaving the crop biomass in the soil to retain moisture, and subsequently growing paddy crops on the same land. This approach has the added benefit of increasing yields, improving crop quality, and reducing farmers' reliance on only one single crop.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pu: perte de la fonction de bio-production en raison d’autres activités

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Mandla district receives rainfall of around 1500mm, and soil is highly susceptible to erosion. Covering the soil with different crops reduces the erosion potential, and mixing the soil with biomass improves soil health.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Land degradation by water erosion is reduced by covering the topsoil with crops for an extended duration. The addition of crop biomass improves soil health.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
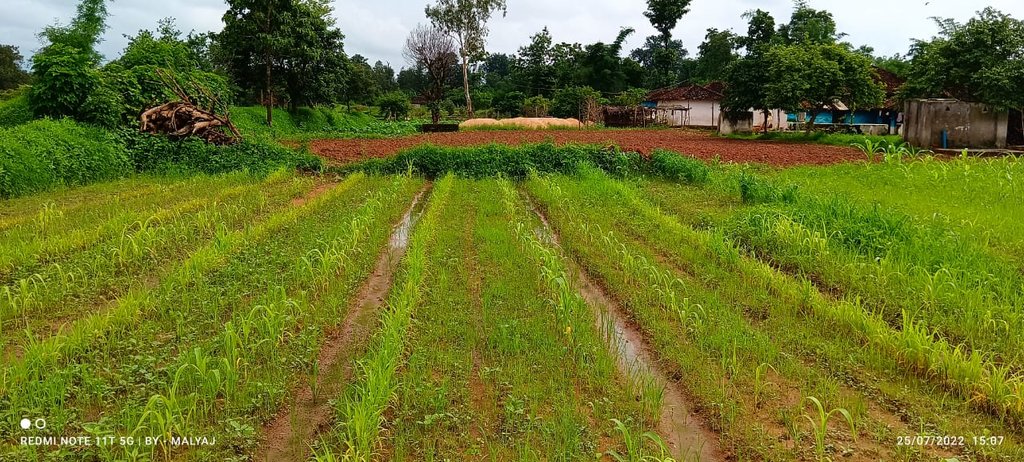
PMDS was undertaken at various sizes of plots based on the availability of land with farmers. Some farmers did at 0.10 acres of land while others did at 2 acres. Also, there was no fixed pattern that was followed for the quantity and variety of seeds. Whatever seeds were available were sown. In the image above, it can be seen that the field where PMDS was undertaken has multiple crops at different stages of their growth while the area with no PMDS has no crop and fallow red soil can be seen.
Auteur:
Santosh
Date:
22/02/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
1 acre
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
INR (March, 2023)
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
82,5
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
204 INR
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
Commentaires:
There are no establishment activities under the PMDS.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
There are no establishment costs required for PMDS as it's only a sowing activity. Farmers do hire agriculture equipments to undertake the activity.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of seeds | 1 month before the onset of Monsoon (mid May in project area) |
| 2. | Seed treatment and preparation of seed balls | End of May in project area |
| 3. | Broadcasting of the seed balls | End of May in project area |
| 4. | Soil rotation | 2-3 days after the broadcasting of seed balls |
| 5. | Harvesting of leafy vegetables, fodder and other produces | Mid of June to mid of July |
| 6. | Mixing the green manure in soils | End of July or before transplantation of rice |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Seed treatment, preparation of seed balls | Person days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Broadcasting of seeds | Person days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Harvesting of the crops | Person days | 2,0 | 150,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Agriculture equipment for soil rotation | Hour | 0,5 | 600,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Cultivator | Hour | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds of different crops | kg | 6,0 | 75,0 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Bio-inputs | LS | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 2450,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 29,7 | |||||
Commentaires:
Technical inputs were provided from the project around the seed treatment, sowing, and monitoring of the crops.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Availability of seeds, bio-inputs, and rainfall pattern. Usually, there are rains during the pre-monsoon season in the project area, however, in case of no rains at all during the entire summer, farmers may not be in a position to achieve the desired results.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1427,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Monsoon season is from June-September, which has the majority of the rainfall.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
District at glance report of Ministry of Water Resources, Central Groundwater Board, North Central Region BHOPAL, 2013
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
The National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning (NBSS&LUP) developed twenty agroecological zones based on the growing period as an integrated criterion of adequate rainfall, and soil groups. It delineated boundaries adjusted to district boundaries with a minimal number of regions. Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh lies in a Hot subhumid ecoregion with red and black soil. Precepitation - 1000–1500mm; Potential evapotranspiration -1300–1500 mm; Length of growing period-150–180days.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Bichhiya is a block in the Mandla district characterized by diverse topography. The block is located in the southern part of the District and is situated in the foothills of the Satpura range.
The topography of the Bichhiya block is hilly. The block has an average elevation of around 550 meters above sea level. The hills are covered with forests and are rich in flora and fauna.
The region has several small streams and tributaries that flow through it, which are mostly seasonal and originate in the hills.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
The region has several small streams and tributaries that flow through it, primarily seasonal and originating in the hills. The area is also known for its waterfalls, including the Patalpani waterfall, a popular tourist destination.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The area is surrounded by Kasha National Park and Phen Wildlife Sanctuary, with a good presence of forest area. Thus biodiversity is outstanding.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Bichhiya block has a significant tribal population. According to the 2011 Census of India, the block has a total population of around 47,000, of which approximately 41% are classified as Scheduled Tribes (STs). The powerful tribes inhabiting the region include the Gonds, Baigas, and Korkus.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Based on the discussion with land users and implanting agency, production of the main crop (Paddy) increased by 20-25%. (The crop combination under PMDS has some nitrogen-fixing crops and the crop biomass improves the nutrient availability for the next crop which is paddy, also the better moisture helped the improvement in productivity of paddy crop as well.). Additional production from crops sown in April month was generated. An impact assessment study to document the quantifiable results has not been conducted so far.
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Risk of of production failure reduced due to crop diversification
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop diversification by sowing multi crops of cereals, millets, pulses, and oilseeds in otherwise paddy predominant area
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The gross sown area increased as the land was brought under cultivation from April to July
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Through this technology crop biomass was added to improve soil to improve its organic content and structure
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase in farm income due to additional crop production and increase in yield of the main crop
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
12 to 15 different crops are grown in PMDS, reducing the crop failure chances and improvements in soil structure, therefore storing the soil moisture for an extended duration
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Diversity in crops will reflect in increased and more diverse food availability
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduction in evaporation loss from April to July and effective utilization of soil moisture and rainfall in this duration
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved soil structure due to the addition of crop biomass in the soil leads to the retention of soil moisture. The extended duration of crop cover also reduces evaporation losses.
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Extended duration of crop cover from April - July
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduction in soil loss due to crop cover
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop biomass increases organic carbon in the soil improving the availability of nutrient in the soil
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Extended duration of vegetation cover of the soil
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase in biomass above ground by using pre-monsoon rainfall
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
12-15 different crops are sown togehter
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
microclimat
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
All the impacts indicated here are based on the discussions with land users and implementing agency. The reported outcomes are based on eye observations and estimations. Some of the impacts are also based on the reports and secondary documents published on the PMDS.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
PMDS method is farmland-specific technology wherein effective utilization of natural resources (land and rainfall) is done. Therefore no direct off site impact of the technology is observed.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| autre changement climatique progressif | Adaptation to climate vulnerabilities by crop diversification and effective utilization of natural resources | augmente | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Autres extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
| autre (précisez) | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? |
|---|---|
| Adaptation to climate change | très bien |
Commentaires:
The technology adapts well to climate change, as crop diversification sustains rainfall variability. An increase in soil biomass improves soil health. Making the system more resilient to climate variability.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The PMDS technology does not require any higher establishment cost, as most of the material is locally available. The maintenance of technology is also limited as once the pelleted seeds are sown there is hardly any maintenance required. The returns on the use of technology are very positive as an additional source of income is available.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
Approximately 100 farmers have adopted the newly introduce PMDS technology in 2020-21.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
Approximately 100 farmers have adopted the newly introduce PMDS technology in 2020-21, supported by capacity building and training programs
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
autre (précisez):
Diversified Combination
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
The crop combination is diversified based on the seeds available and household nutrition requirements
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Increase PMDS crop productivity and yield 20-25% subsequent crops, especially paddy crops |
| Soil structure is improved |
| Crop Diversification: 12 - 15 different crops are grown on the same piece of land |
| Fodder availability to animals during the summer season |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Ensuring a crop cover for 365 days leads to reduced soil erosion and improved soil health |
| Maintaining the soil moisture for the subsequent crops, which are cultivated in the rain-fed conditions |
| Regular practice of PMDS can increase the soil's organic carbon as a lot of green manure is incorporated in the soil resulting in higher carbon content |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Open grazing of cattle during summer is a common practice. As there are no standing crops in the field, farmers tend to allow their animals for open grazing. However, the cultivation of crops using the PMDS method tends to attract cattle as other fields in the project areas do not have any green cover. | Village-level community institutions can develop a system to minimize the grazing in the fields having crops or the higher adoption of PMDS by the farmers will gradually reduce this risk as PMDS can be a good source of green fodder as well. |
| Farmers are putting in extra quantities of seeds for various crops for sowing during the PMDS. In normal cases, they will sow the seeds only after the onset of the monsoon and when the field is ready for sowing. Thus in PMDS, they may feel like losing their seeds if there is no germination due to delays in monsoon or other reasons. | Farmers can be supported by providing seeds for the first year to mitigate the risk and exchanging weather-related information in advance. So that they can make an informed decision. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Very low to no awareness of the PMDS methodology and benefits among the project farmers. | Regular handholding and demonstrations along with good audio-video documentation for dissemination. |
| Possible delay in sowing and harvesting of the Kharif and Rabi crops due to delayed monsoon or appropriate soil conditions. | Scheduling the crops based on a crop calendar is one solution; another solution is to explore the seed varieties suitable for delayed sowing. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
4
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
3
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
1
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
2
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
22/02/2023
Commentaires:
During the field visit, interviews were conducted with land users and the project implementation team to understand the process, impact, and challenges in the adoption and implementation of PMDS technology.
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Assessing the Impact of Andhra Pradesh Community Managed Natural Farming: A comprehensive Approach Using Crop Cutting Experiments Pre-Monsoon Dry Sowing Farming in Andhra Pradesh
URL:
https://apcnf.in/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/IDS-2020-2021-APCNF-PMDS-Report.pdf
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé