Rehabilitation of Fallow Land Through Agroforestry [Bhoutan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Nima Dolma Tamang
- Rédacteur : Tashi Wangdi
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Sa Tong Lar Log
technologies_6839 - Bhoutan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Zangpo Dawa
Khengrig Namsum Cooperative
Bhoutan
exploitant des terres:
Wangmo Tashi
Khenrig Namsum Cooperative
Bhoutan
exploitant des terres:
Wangmo Pema
Khenrig Namsum Cooperative
Bhoutan
exploitant des terres:
Dolkar Tshering
Khenrig Namsum Cooperative
Bhoutan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Bhoutan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
As per the responses made by the land users (cooperative representatives), the rehabilitation of fallow land through agroforestry has been a successful SLM indicator towards mitigating and adapting land degradation, securing food, and ultimate livelihood enhancement.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
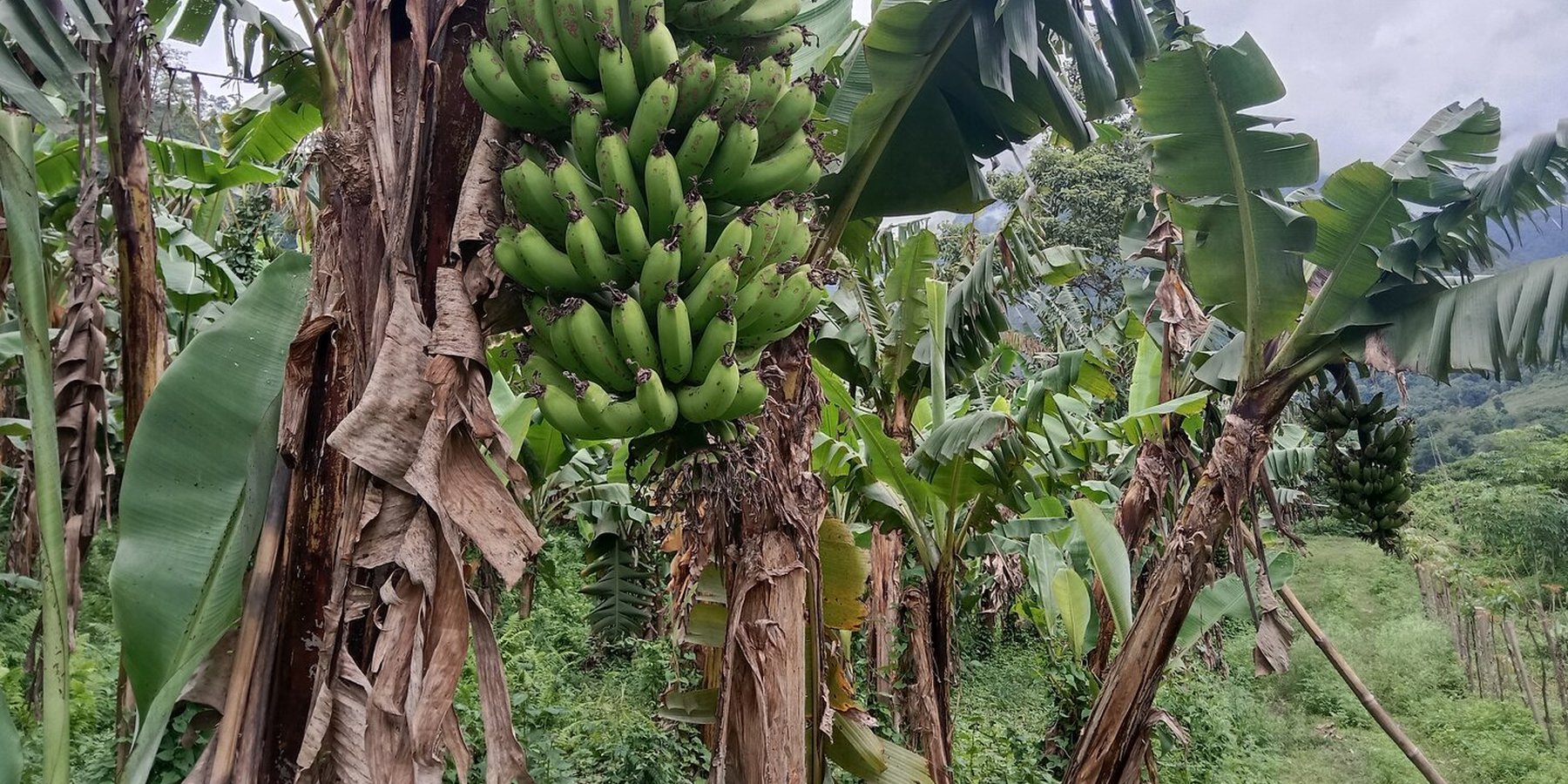
Fallow is arable land deliberately set aside due to challenges faced in cultivation. The rehabilitation of lands left fallow for decades through the adoption of agroforestry has been one success story of the Khengrig Namsum Cooperative in the central region of Bhutan. The integration of perennial trees (fruit and high-value trees) and seasonal crops creates environmental, economic, and social benefits.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Fallow land is the term for arable fields either partially or completely left unused and unproductive, owing to reasons such as labour shortages, lack of irrigation, human-wildlife conflict and/or the plots being far away from the settlements. Land rehabilitation is a promising approach towards mitigating the fallow land issue. Thus, the Khengrig Namsum Cooperative (KNC), a registered firm under the Department of Agriculture Marketing and Cooperatives, Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock (MoAL), Bhutan has ventured into rehabilitating 235 acres (94 ha) of fallow lands since 2016, through the adoption of agroforestry. The KNC was founded by Mr. Thinley Wangdi (the current chairman), with the motive of improving the livelihoods of the people of Zhemgang Dzongkhag through locally grown farm produce.
The KNC with funds from the Global Environment Facility - Small Grant Program (GEF–SGP) through the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), Bhutan, revived the fallow through agroforestry (intercropping of banana and bamboo plants). The KNC intervened in three strategic locations, benefitting 36 households. This particular agroforestry approach was not only aimed towards enhancing livelihoods but also to diversify production: through banana chips production and bamboo product development.
Upon securing the funds, implementation started with the procurement of planting and fencing materials, hands-on training, and then planting and fencing activities. Installation of electric fencing was done to reduce human-wildlife conflict. There was specific training on product development. Moreover, the KNC was able to link up with nearby schools for the school feeding programme, to supply fruits and vegetables. The cooperative demonstrates skills in processing its own products and enabling better access to renewable natural resources in the locality. On the contrary, not having proper cold storage facilities has negative impacts on processing units and has resulted in unreliable market coupling.
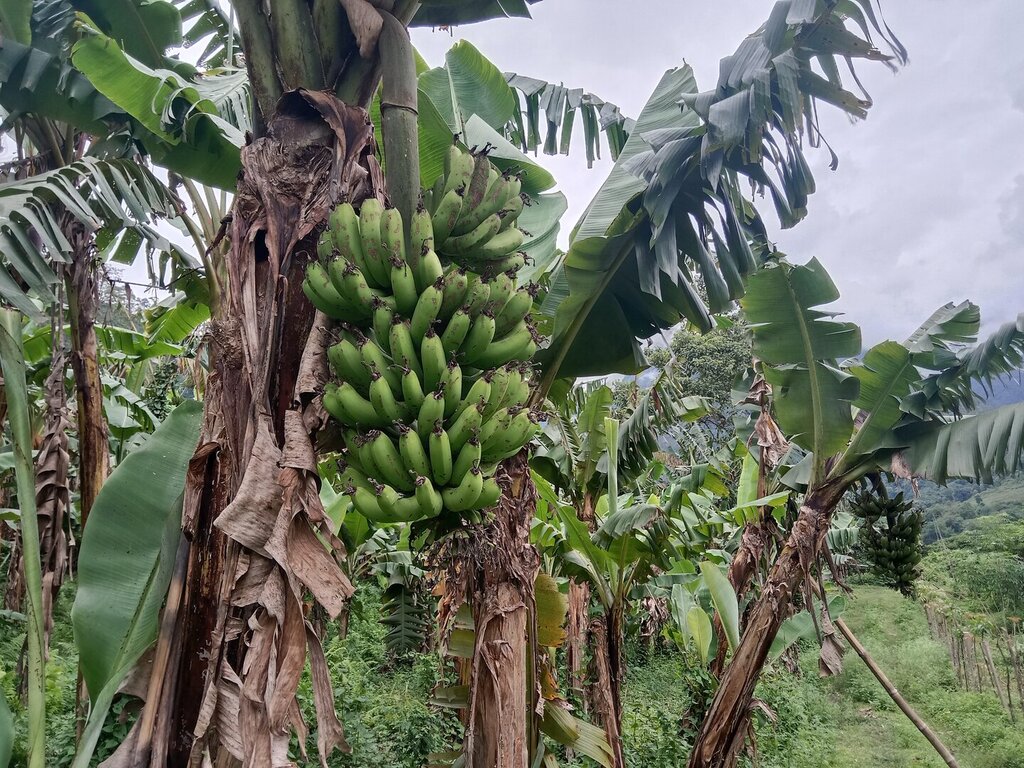
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bhoutan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Zhemgang Dzongkhag
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Rebati Chiwog under Ngangla Gewog, Brumbi and Jiwongolia Chiwog under Trong Gewog
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
0,95
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2015
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The implementation of activity in Rebati and Brumbi started in 2016, whereas for Jiwongolia, it started in the year 2019. The Global Environment Facility - Small Grant Program (GEF-SGP) under the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) has funded the program in the Rebati and Brumbi communities. Likewise, the Bhutan Foundation and the HELVETAS have funded the programme in Jiwongolia. The fallow land rehabilitation program was the initiative of Khengrig Namsum Cooperative.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - pommes de terre
- légumes - melon, citrouille, courge ou cucurbitacées
- Ginger, turmeric
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- bananier/plantain/abaca
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- avocat
- citron
- fruits à coque (noix du Brésil, pistaches, noyers de bancoule, amandes)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Bananas and bamboo are intercropped as an agroforestry measure.
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Ginger followed by trumeric

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ terres boisées: précisez le mode de gestion:
- Coupes sélectives
- Utilisation de la forêt non liée au bois
Type de forêts (semi)-naturelles:
- végétation naturelle des forêts humides subtropicales
Est-ce que les espèces d’arbres précisées ci-dessus sont des espèces d'arbre arbres à feuilles caduques ou à feuilles persistantes ?
- forêt mixte décidue/ à feuillage persistant
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Autres produits forestiers
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Pastoralisme de type semi-nomade
Type d'animal:
- bétail - laitier
Est-ce que la gestion intégrée cultures-élevage est pratiquée?
Non
Produits et services:
- lait

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ terres boisées: précisez le mode de gestion:
- Coupes sélectives
- Utilisation de la forêt non liée au bois
Type de forêts (semi)-naturelles:
- végétation naturelle des forêts humides subtropicales
Est-ce que les espèces d’arbres précisées ci-dessus sont des espèces d'arbre arbres à feuilles caduques ou à feuilles persistantes ?
- forêt mixte décidue/ à feuillage persistant
Produits et services:
- Bois d'œuvre (de construction)
- Autres produits forestiers
Commentaires:
The land use has changed in the case of Brumbi and Jiwongolia, where these places were fallow (forest) earlier. A few pockets of Jiwongolia were used as pastureland by the nearby communities. With the intervention from Khengrig Namsum Cooperative (KNC), these areas were brought under cultivation through an agroforestry approach. The land use system in Rebati however has remained the same. The KNC intervened in this community through the facilitation of banana seedlings, mainly intending to ensure the supply of bananas for their banana chip production.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bh: perte d’habitats
Commentaires:
The land users have noted that the implementation of agroforestry technology has proven highly effective in mitigating surface runoff and gully erosion, especially in the area of Jiwongolia. This issue was exacerbated by the drainage outlet from the nearby highway motor road.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Agroforestry plays a crucial role in both preventing and alleviating land degradation. Lands that are incorporated into agroforestry practices are effectively managed and optimized for various uses, resulting in increased ground coverage throughout the year and appropriate nutrient management. The stewardship of these productive lands through agroforestry not only mitigates land degradation in areas already affected by it but also serves as a preventive measure in potential sites susceptible to land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
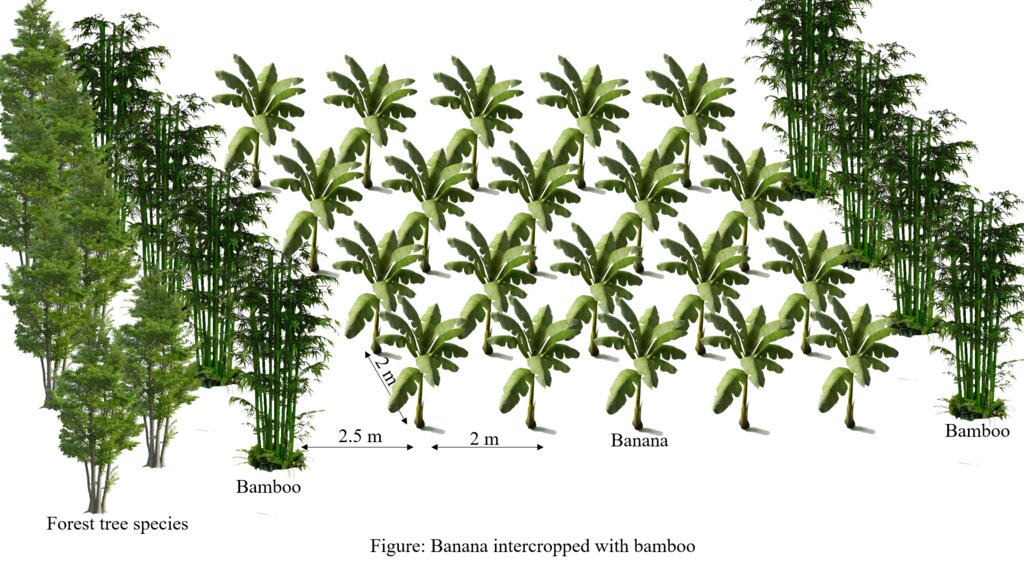
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The technical drawing shows the banana plant and bamboo intercropped.
Auteur:
Ongpo Lepcha
Date:
11/12/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
235 acres
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ngultrum (Nu.)
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
80,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
Nu. 450
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Explored funds from UNDP through development of project proposal, led by the chairman | 2016 |
| 2. | Forest clearing and development using tractor at Brumbi and Rebati | December 2016 - November 2018 |
| 3. | Electric fencing | February 2017 - May 2017 |
| 4. | Procurement of fruit seedlings (local banana and bamboo) from Bhur nursery, Sarpang Dzongkhag | May 2017 - July 2018 |
| 5. | Hands-on-training on fruit tree plantations (KNC members and other farmers) and product development from bamboo | May 2017 - November 2018 |
| 6. | Plantation of banana seedlings and bamboo | June 2018 |
Commentaires:
The plantation of bananas and bamboo in Rebati was done at the periphery of the community, not encroaching on the actual cultivated agricultural fields. Whereas, in Brumbi and Jiwongolia, mass plantation was carried out.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labor | person days | 1440,0 | 451,0 | 649440,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Land preparation | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 725432,0 | 725432,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Cost of seedlings (local banana and bamboo) | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 979170,0 | 979170,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Electric fencing | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 267410,0 | 267410,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Plantation of bamboo and banana | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 231594,0 | 231594,0 | |
| Autre | Project administration and participation | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 182042,0 | 182042,0 | |
| Autre | Project signboard and installation | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 19500,0 | 19500,0 | |
| Autre | Formulation of by-laws and agreements | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 72301,0 | 72301,0 | |
| Autre | Hands-on-training on plantations and product development | Lumpsum | 1,0 | 100781,0 | 100781,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 3227670,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 40345,88 | |||||
Commentaires:
The expenditure amounts are reflected as 'lumpsum' as the listed activity head comprises many sub-activities with different units of expression, which are not at all possible to mention completely.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replacement of electric fence poles | Every after three years (winter) |
| 2. | Replacement of solar batteries | replaced once (1 battery) |
| 3. | Replacement of fruit plants | Every season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
The replacement of poles and fruit seedlings has not incurred any cost as these activities are carried out by the land users as an when required.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most important factors affecting the costs while implementing this technology is land preparation and plantation of seedlings.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The rainfall data of 2017 was used
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Station: Bhur, Type: Class A, Station ID: 23310046
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
The area falls under the warm and humid Subtropical zone among the six Agroecological zones of Bhutan.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The slope of the area ranges from about 6 - 15%.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Moisture content 2.25%, organic matter 3.27%, Organic carbon 1.90%, pH 6.42, electrical conductivity 213.47 µs/cm, nitrogen 0.10%, phosphorus 0.66 ppm, Potassium 138.73 mg/100ml, texture sand.
The soil analysis was conducted at the Science Laboratory of College of Natural Resources, Royal University of Bhutan, Lobesa, Punakha.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The lush surroundings at the periphery, abundant vegetation cover, and the noticeable presence of agroforestry practices all point to a significant level of diversity in species and habitats
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- coopérative
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
The land area spreads over 235 acres, falling under the large-scale category referring to the local context. In general, the average household land holding in Bhutan is 3.4 acres.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- Family land ownership
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
Précisez:
The land use rights in Bhutan is traditional legal system guided by formal land act and land rules and regulations.
Commentaires:
The 230 acres land of Rebati (150) and Brumbi (80) have the the family ownership, whereas the 5 acres land of Jiwongolia is on lease (state land).
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop production increased exponentially in Rebati, where crop production prevailed before the introduction of the agroforestry system. For the reverted fallow land in Brumbi and Jiwongolia, crop production increased by 100%. The abundant availability of bananas from the rehabilitated areas has greatly facilitated the cooperative employees in procuring a sufficient quantity of bananas for banana chip production. Previously, they had to embark on time-consuming journeys to various locations to source bananas, which not only proved laborious but also led to an increase in production costs.
qualité des cultures
Quantité avant la GDT:
Local varieties
Quantité après la GDT:
Improved varieties
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The cultivation of enhanced banana varieties, including G9, Jaji, and Dosari, has resulted in a noticeable enhancement in quality
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Following the harvest of banana fruit, the stems and leaves are utilized as fodder for livestock
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The risk of production failure is minimized as the land users engage in agroforestry, diversifying their income sources. Their earnings do not rely solely on one crop; instead, they come from a variety of sources, including bamboo products, bananas, vegetables, and spices. Consequently, if one crop encounters difficulties or fails, the other crops can continue to generate income for the cooperative
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Agroforestry promotes the diverse cultivation of both forest and agricultural plants, resulting in a wide range of products. As an example, the land users are able to produce bamboo products, spices, and banana chips due to the diversity of their cultivation practices
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology is implemented in the previously uncultivated land (fallow) leading to the increased production area.
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The conversion of fallow land into cultivated land has enhanced land management and stewardship. This transformation involves the addition of manure and timely interventions, effectively reducing soil erosion and improving the overall care of the land
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
There are increased expenses on agricultural inputs. However, the increased expenses are compensated by the income generated from the farm.
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
Nu. 23,00,000/- annual income
Quantité après la GDT:
Nu. 55,00,000/- annual income
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The ready availability of bananas as a raw material has significantly boosted the production of banana chips and led to a substantial increase in the annual revenue of the cooperative. Furthermore, land users supplying bananas to the cooperatives have also experienced a rise in their annual income
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The KNC has diverse value-added products and natural products such as watermelon, bamboo products, and homemade pickles diversifying their income sources.
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced workload due to increased availability of raw materials for banana chip processing.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The staff of the KNC is food secure due to increased income generated from the cooperative. Likewise, the land users supplying raw materials are also meeting the food security from the income generated by supplying raw materials to the KNC. The land users are self-sufficient in bananas, bamboo and some spices.
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land users shared that the improved annual income is directly related to improved health and well-being of the family/community.
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Their venture into such activity has added value to the community, where the community has been recognized as one of the successful pilot sites for rehabilitating fallow lands. Moreover, external visitors are attracted to witness the success of the community.
Also, the community bond has been strengthened, through an approach like labour sharing practised during the implementation of the technology.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Before, the land users' knowledge about SLM technologies was confined to a few technologies. Now they have realized that SLM is a holistic approach involving different technologies. Therefore, the understanding and knowledge of agroforestry as one of the SLM measures has been enhanced.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Disadvantaged families constrained by poor market access benefited from this technology.
Impacts écologiques
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The plantation of banana plants and bamboo has covered a wide range of land, leading to better vegetation cover.
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The increased vegetation cover by different fruit, bamboo, and vegetables leads to increased above-ground biomass.
espèces bénéfiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Agroforestry harbours various plant species attracting diverse beneficial insects that feed on these plants.
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The destruction of natural habitats has been decreased due reduced dependency of land users on wild bamboo products.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The risk of surface erosion has been mitigated due to improved ground cover.
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cultivation of bamboo species reduces wind velocity reducing surface erosion.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
Biological diversity conservation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Biological diversity increased due to the cultivation of different plant species which also act as a habitat for different insects and birds.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | très bien | |
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | très bien |
| orage local | très bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| canicule | très bien |
| conditions hivernales extrêmes | très bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The agroforestry with banana and bamboo plantations has been advantageous with both short-term and long-term benefits. For instance, banana gives fruiting in less than a year (9 months) after plantation.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
36 households and one cooperative (KNC)
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Increased production area. The reversion of fallow land through agroforestry significantly increased the production area for the land users. |
| Increased income. The easy access to the raw materials for KNC and easy market access for the land users leads to improved income for the KNC staff and land users supplying bananas to the cooperative. |
| The technology is easy to implement as bananas and bamboo are perennial providing continuous income to the land users with little maintenance required. The land users need not be involved in agronomic practices such as land preparation and sowing every year. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Restoration of cultivable land lost to forest encroachment. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Loss of cooperative members due to better opportunities, which ultimately would affect sustainability. | Provide timely incentives and adequate facilities. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Youths do not prefer to work in agriculture as it is viewed as laborious. | Introduce fully mechanized and smart farming systems to attract youth. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
Visited all the three different locations under KNC (Rebati, Brumbi, and Jiwongolia)
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Four employees of KNC
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
UNDP documents, and archived documents of KNC
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/07/2023
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Rehabilitation of fallow land through agroforestry, UNDP, 2020
URL:
https://www.undp.org/bhutan/stories/rehabilitation-fallow-land-through-agroforestry
Titre/ description:
Background on Fallow Land Bank, NLCS, n.d.
URL:
https://flb.nlcs.gov.bt/index.php/background-on-fallow-land-bank/
Titre/ description:
Khenrig Namsum Cooperative, HELVETAS Bhutan, 2019
URL:
http://csogrant.bt/khenrig-namsum-cooperative/
Titre/ description:
WFP Bhutan Country Brief, OCHA services, 2023
URL:
https://reliefweb.int/report/bhutan/wfp-bhutan-country-brief-february-2023
Titre/ description:
KNC-Zhemgang, Bhutan, n.d.
URL:
https://www.bhutan-network.org/portfolio/knc-zhemgang-bhutan/
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé