Improved Cattle Shed Flooring for Conservation of Cow Dung and Urine for Biofertilizer Production at Farm Level [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Santosh Gupta
- Rédacteurs : Noel Templer, Stephanie Katsir, Kim Arora
- Examinateurs : Udo Höggel, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_6721 - Inde
- Résumé complet en PDF
- Résumé complet en PDF pour impression
- Résumé complet dans le navigateur
- Résumé complet (non formaté)
- Improved Cattle Shed Flooring for Conservation of Cow Dung and Urine for Biofertilizer Production at Farm Level: 25 juin 2023 (inactive)
- Improved Cattle Shed Flooring for Conservation of Cow Dung and Urine for Biofertilizer Production at Farm Level: 14 septembre 2023 (inactive)
- Revêtement de sol d'étables amélioré pour la conservation des bouses et de l'urine des vaches en vue de la production de biofertilisants au niveau de l'exploitation agricole: 11 avril 2024 (public)
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - AllemagneNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - KenyaNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ecociate Consultants (Ecociate Consultants) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
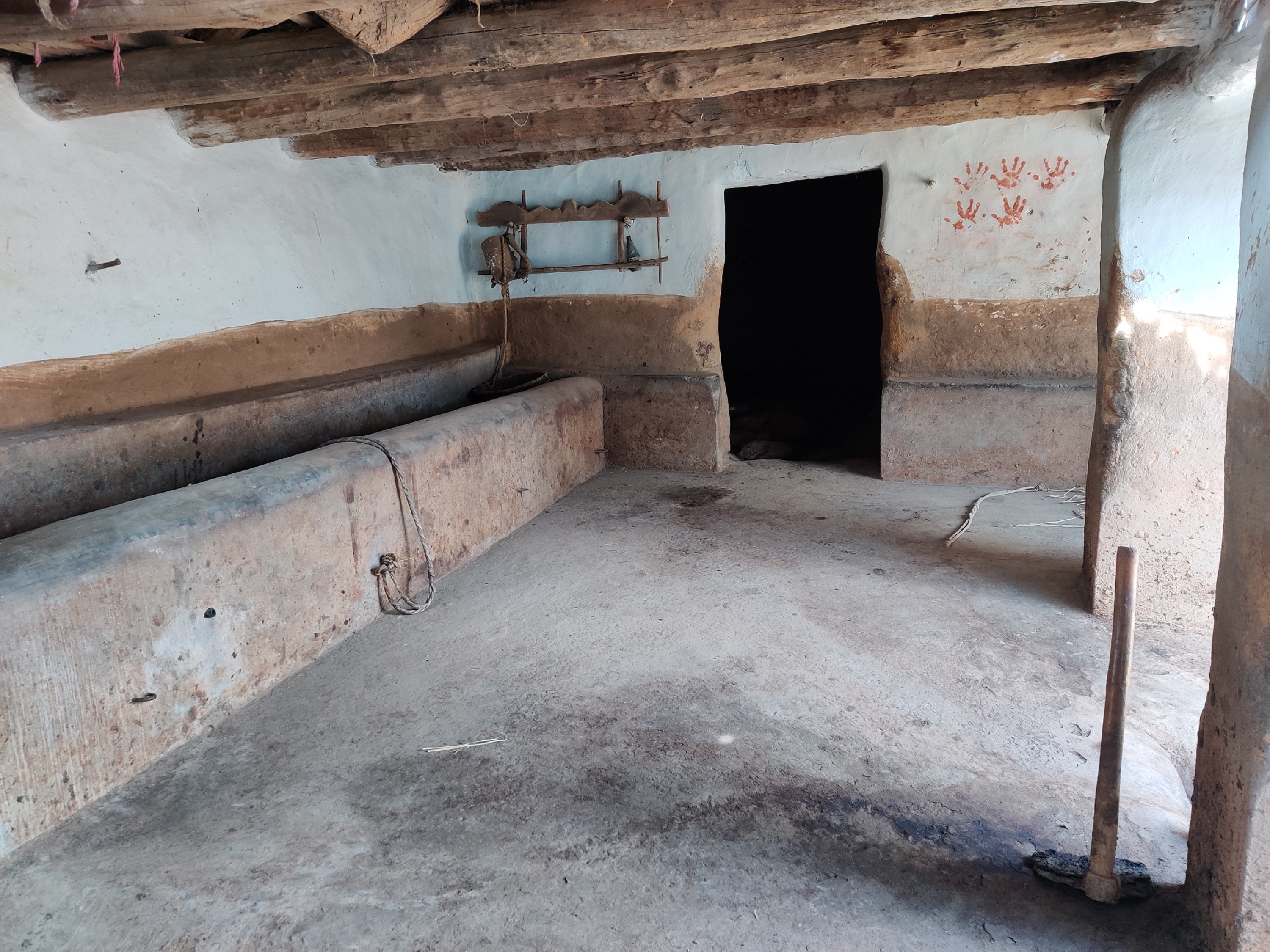
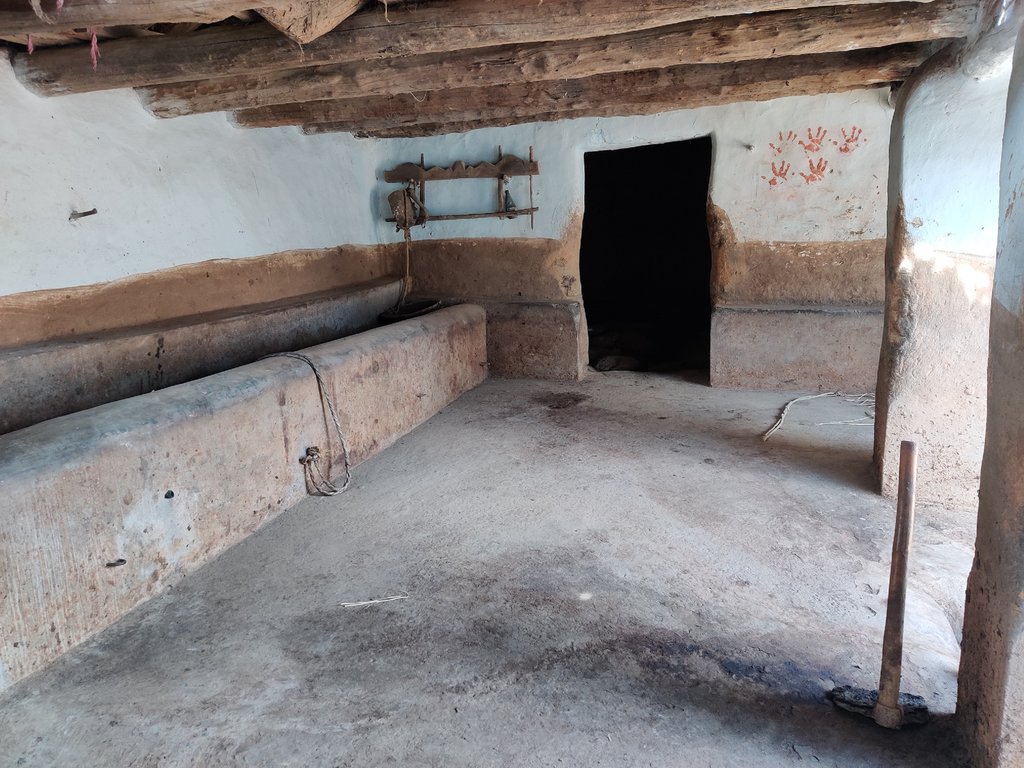
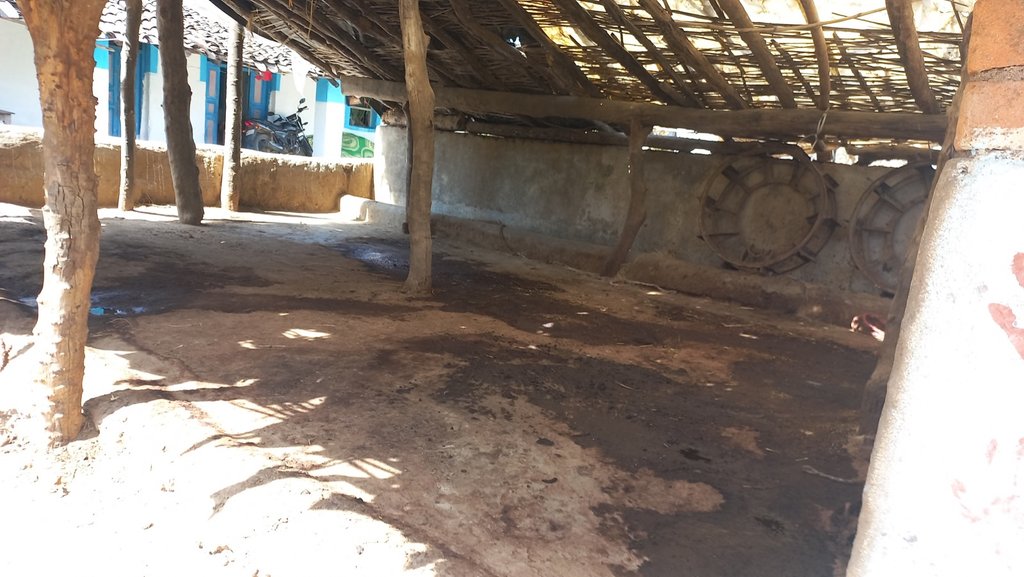
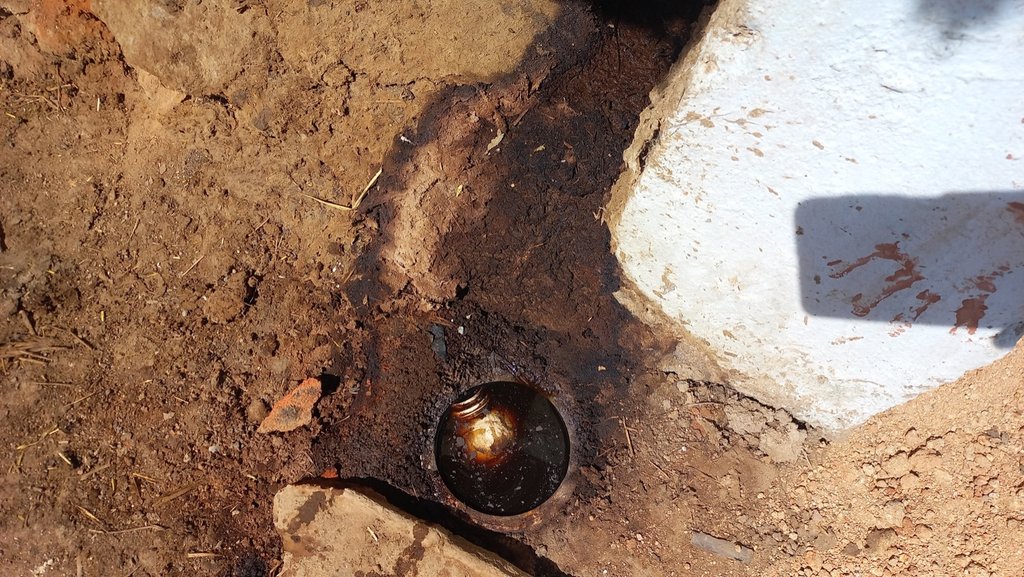
In the cattle shed management system, the cattle shed should be constructed with an elevated concrete floor that slopes slightly toward a cow urine collection point. The collection point should be equipped with a drainage system to easily remove cow dung and urine.
An elevated concrete floor for cow dung and urine collection can improve hygiene, and waste management, and reduce labour costs in cattle sheds. Collected cow urine and cow dung can be used to prepare biological inputs and compost for nutrient and pest management in agriculture.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Cattle shed management technology, including the use of a concrete elevated floor for cow dung and urine collection, is a cost-effective and efficient technology to support the natural farming system. This technology can be applied in both natural and human environments. In natural environments, such as rural or agricultural areas, cattle sheds are typically used for dairy and farmyard manure production. The use of this technology can improve the hygiene of cattle and their environment, reduce waste and pollution, and promote the sustainable use of natural resources. The cow dung and urine so collected can be used as fertilizer to improve soil quality, and the improved hygiene of the cattle can reduce the risk of diseases spreading to other animals or humans. The use of this technology can help to reduce the negative impacts of cattle farming on the surrounding environment, such as odours and pollution. It can also improve the hygiene of the cattle and their environment, which is important for both animal welfare and public health.
Traditionally farmers were constructing the floors of cattle sheds using mud and soil. These floors absorb the cow urine and the movement of animals also makes holes in it because of that cow urine and cow dung are used to get filled in these halls. Which made the entire floor unhygienic for both animals and farmers. Because of such surfaces, it was very hard to clean these sheds. The use of an elevated floor made with cement-concrete and a waste management system can help to keep the cattle shed clean and dry, which can reduce the risk of disease and infection among the animals. The collection and disposal of cow dung and urine can help preventing environmental pollution, reducing the negative impacts of cattle farming on the surrounding area, and promoting sustainable use of natural resources. The use of a concrete elevated floor can make cleaning the cattle shed faster and easier, reducing labour costs and improving the efficiency of the farming operation.
Technical specifications for the construction of cattle sheds can vary depending on factors such as the size of the herd, local environmental regulations, and available resources. However, in general, the main characteristics and elements of cattle shed management technology are designed to promote animal welfare, hygiene, waste management, and sustainability. Proper cattle shed management technology can provide a comfortable and safe environment for the animals, which can reduce stress and promote animal welfare. Proper waste management and ventilation can help to minimize unpleasant odours from the cattle shed, which thus reduces negative impacts on the surrounding community.
Establishing and maintaining cattle shed management technology requires a combination of technical expertise, labour, and resources. By investing in these inputs, farmers can promote sustainable and efficient cattle farming practices and improve the health and welfare of their animals.
The collected cow urine and cow dung are the main resources for preparing the biological inputs and different types of compost for meeting the nutritional requirement of crops while also addressing the challenges of pest and disease management in a natural or organic farming system. The improved flooring of cow shed units has been a great intervention to replace and reduce the usage of synthetic fertilisers and pesticides in the project region.
The views of land users, such as farmers or livestock keepers, about cattle shed management technology, including the use of a concrete elevated floor for cow dung and urine collection, can vary depending on their experiences and perceptions. The interviewed land user liked or appreciated, cattle shed management for improving animal health and productivity, increasing farm profitability, cleaning the cattle shed easier and faster, reducing labour costs, improving efficiency, and for environmental benefits.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
All of these phots have been taken with the consent of participants.
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Gd6u8yZ9DqY&si=EnSIkaIECMiOmarE
Date:
01/02/2021
Lieu:
Mandla, Madhya Pradesh, India
Nom du vidéaste:
Soil Matters
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Madhya Pradesh
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Mandla District
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology is being adopted by more than 100 farmers across the 10-15 villages of the Bichhiya block in Mandla District of Madhya Pradesh
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Initially, the project supported the farmers in the construction of cemented cow shed floors in a limited area. However, there has also been investment from the users either by putting extra funds to extend the area or by contributing labour.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- créer un impact économique positif
- Control cattle diseases
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- céréales - riz (de terres humides)
- céréales - blé d'hiver
- legumes and pulses - lentils
- cultures oléagineuses - tournesol, colza, autres
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
In kharif (summer) season farmers are sowing paddy in wetlands and in rabi (winter) season wheat, chickpea, mustard, maize and other vegetables
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Chickpea intercropping with beans, mixed cropping system of vegetables present
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Rice- Chickpea
Rice-Wheat
Rice- Maize
Commentaires:
The intervention is mostly focused on improved cattle shed units. However, collected cow urine and cow dung are good for restoring the degraded agricultural land.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
For irrigation, most of the farmers were dependent upon rain in the Kharif and Rabi season. Some of the farmers were using additional irrigation during critical crop stages by using water canals.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée cultures-élevage
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A6: Gestion des résidus des cultures
A6: Précisez la gestion des résidus des cultures:
A 6.5: Résidus retenus

structures physiques
- S9: Abris pour plantes et animaux

modes de gestion
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
Commentaires:
The implemented technology led to the management and use of waste for productive purposes. While it has improved the productivity of animals by reducing the occurrence of diseases, it has also enabled the preparation of organic inputs to replace the synthetic fertilisers in farming.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bp: augmentation des insectes nuisibles (ravageurs)/ maladies, baisse des prédateurs

dégradation hydrique
- Hp: baisse de la qualité des eaux de surface
- Hq: baisse de la qualité des eaux souterraines
Commentaires:
Proper collection of cow dung and cow urine minimised run-off these substance and mixing with surface water used for various purposes including drinking water.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Application of cow urine and cow dung in soil by mixing with other organic matters improves the soil health and also reduces the dependency on synthetic fertilisers and pesticides
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
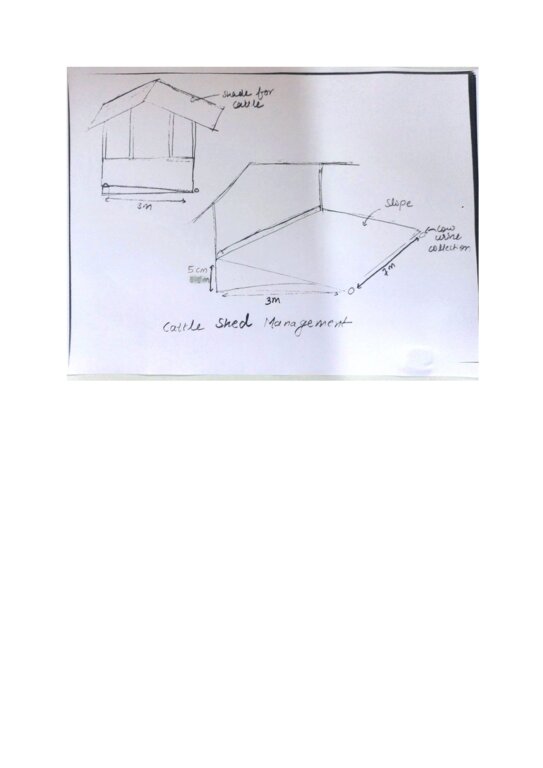
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Dimensions of the cowshed (depending on the number of cows kept):
Length: 7m
Width: 3m
Elevated: 5 cm (means in effect the slope: i.e. the front floor of the cowshed is 5 cm higher than the floor at the end, where dung and urine get collected)
Auteur:
Payal Dewangan
Date:
22/02/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
one cattle shed
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
meter
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Indian Rupee
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
82,24
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
240
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Concrete floor construction for cattle shed | March |
| 2. | Cattle shed roof development | April |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de la mise en place de la Technologie:
28000,0
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Gram Paryavaran Samiti and Prakritik Sansadhan Prabhandhan Samiti
Commentaires:
Village groups were formed for the implementation of the technology
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of concrete floor | Once in a day |
| 2. | Collection of cow dung | Once in a day |
| 3. | collection of cow urine from the pit or drum | Twice in a week |
| 4. | Fodder and drinking water provision | Twice in a day |
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Design and technical specifications: The cost of the technology can vary depending on the design and technical specifications of the cattle shed, including the size and materials used.
Construction materials and labor costs: The cost of construction materials and labor can vary depending on local market conditions and availability.
Location: The cost of transporting materials and labor to the construction site can vary depending on the location of the farm.
Maintenance and repair costs: The cost of maintaining and repairing the cattle shed can also add to the overall cost of the technology.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity building to farmers and workers on proper cattle shed management techniques can add to the overall cost of the technology.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
1427,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Highest rainfall occurs between June to September.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Mandla, Madhya Pradesh
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
The climate of the District is tropical, with moderate winters, severe summers, and well-distributed rainfall received from the southwest monsoon. However, due to higher general elevation and abundance of forests, summer temperatures do not rise as much as in other areas.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The topography of the project area consists of a hilly area and a forest area. Mandla District is hilly and forested (Satpura hill range) and highly undulating with a narrow strip of cultivated plains in the valley portion of the river. The plateau is in the northern part formed by basalt, and east-west trending hills in the southern part. The highest elevation is 934 m amsl in the northern part, and the lowest is around 400 m amsl in the northwestern part of the area. The elevation of the studied block Bichhiya is 453 m amsl.
Source: District at a Glance; Ministry of Water Resources, Government of Madhya Pradesh
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil Testing Parameter status (Average) 2017-20 for the project areas is as follows. This data is based on the soil samples tested by the FES in its soil labs from the project villages.
Sail pH:-5.906548628; EC (electrical conductivity): 0.122993577: Soil Organic Carbon: 0:83%; Nitrogen:- 293.3696598; Phosphorus:- 25.77762582; Potassium (K):- 139.6696636: Sulphur
(S)-18.93457993; Zinc (Zn):-0.955246706; Boron (Bn):-0.490850376
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
The groundwater status is within the safe limits as per the reports by the Government of Madhya Pradesh. People use water from rivers, streams, and traditional small wells for domestic purposes. In the absence of good vegetative cover, the rainwater washes off the fertile topsoil from the farmlands making the land barren and resulting in the siltation of ponds and other water bodies. Further, a heavy infestation of invasive species such as Lantana Camara compounds the degradation.
The studied block Bichhiya is in a better position in terms of stage of groundwater development with 17%, stage of groundwater development refers to the % of groundwater being used for various purposes from the available groundwater in that area e.g. net annual groundwater availability in Bichhiya block is 9087 ham (hectare meters) while the existing annual groundwater draft for all usage is 1523 ham, making it a 17% groundwater development stage, while the district average is 79%.
Source: http://cgwb.gov.in/District Profile/MP/Mandla.pdf
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The cattle shed management unit or center is present nearby the forest area of Kanha National Park. There is high biodiversity present in the technology implementation area. Ecological assessment report in Mandla (where this Technology is applied) showed improved biodiversity on common lands under village governance compared to open-access or commons under government ownership. On average, the Shannon Diversity Index of managed common lands was 1.45 compared to 0.42 for the open access of ungoverned commons. Most of the sites under open access lands are infested by Lantana Camara, which is the main reason for the lower biomass and diversity of the ungoverned lands.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- jeunes
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
- individuel
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
Précisez:
Some of the land parcels are ancestral land units while some have been transferred into private ownership by the State Government over the years
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It was observed and noted from the field site that instead of using chemicals, the application of cow urine and cow dung in the form of farm yard manure has helped in improved production as it led to the reduction of pest infestation and better nutrient uptake from the soil.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduction in the use of chemicals in the field and application of collected cow urine and other bioresource products made from cow dung helped in improving the quality of crop in terms of harder crops, good weight of grain, test etc.
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The improved cattle shed played a crucial role in maintaining the hygiene of animal sheds, which led to the lesser occurrence of disease among animals. Also, the stress level of animals due to the presence of insects and flies reduced significantly. A combination of all these factors improved the milk yield.
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Using sustainable methods for crop production by application of bio inputs not only helps in increasing soil fertility but also contributes to increasing crop resistance, pest control, and better crop development.
diversité des produits
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Reduced to some extent as now farmers can make their own bio-inputs using the cow urine and cow dung collected from the cattle shed
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
A combination of improved productivity, reduced cost towards agriculture inputs and better milk productivity has helped farmers in improving their income.
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Some of the farmers have initiated their own bio resource centres to sell cow urine and cow dung-based bio-inputs, vermicompost etc.
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The workload of women members in the household was reduced very significantly due to covering the mud-based cow floor with cement-concrete-based cow floor, earlier cleaning of the cow dung and cow urine used to take a lot of the time. However with new floor, it can be cleaned in less than 5 minutes saving almost an hour in a day.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improved hygiene is good for both animal and human health
opportunités culturelles
institutions communautaires
Impacts écologiques
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Application of cow dung, compost and other bio-inputs have improved the soil moisture
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Application of cow dung, compost and other bio-inputs will help in improving the nutrient cycling in the soil and will enhance the soil microbial activities
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Some of the farmers are using the collected cow dung as an input for their 'Bio-gas' plants. Thus, the use of biogas plants not only reduces the use of fire wood and LPG for cooking but its waste (slurry) is also used as inputs for agriculture fields. Thus reducing the overall footprint of GHG emission.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les champs voisins
impact des gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Some of the farmers have installed bio gas plants. Use of biogas plants not only reduces the use of fire wood and LPG for cooking but its waste (slurry) is also used as inputs for Some of the farmers are using the collected cow dung as an input for their 'Bio-gas' plants agriculture fields. Thus reducing the overall footprint of GHG emission.
Also the improved floor have helped in proper collection of cow dung and cow urine for the purpose of composting. Composting makes the compounds in manure more stable and therefore reduces the amount that is released into the atmosphere.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | très bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Low maintenance cost compared with benefits of higher animal productivity and hygienic living
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Reduced labour of urine and dung collection |
| Better animal management |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Reduced GHG emission because of better handling of dung and urine |
| Increased productivity because of the use of animal manure |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High establishment cost | Subsidies and grants |
| Regular maintenance cost | Technological innovation |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Possibilities of disadoption because of maintenance cost | Increase returns of the units by extending new products from Urine and dung |
| No demand | Increase communication and extension on the benefits of different products from animals |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Repairing cattle shed floor
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Foundation for Ecological Security, Mandla, MP, India
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Cattle sheds: one intervention, several benefits for farmers
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gd6u8yZ9DqY
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé