Contour Grass Hedgerows on Steep Slopes [Bhoutan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : ONGPO LEPCHA
- Rédacteur : Kuenzang Nima
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Tsayi Gaytshig (ཙྭའི་རྒད་ཚིག།)
technologies_6854 - Bhoutan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Daza Khemo
Boucholing village
Bhoutan
exploitant des terres:
Dorji Ugyen
Boucholing village
Bhoutan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Bhoutan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology described is not problematic with regard to land degradation.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
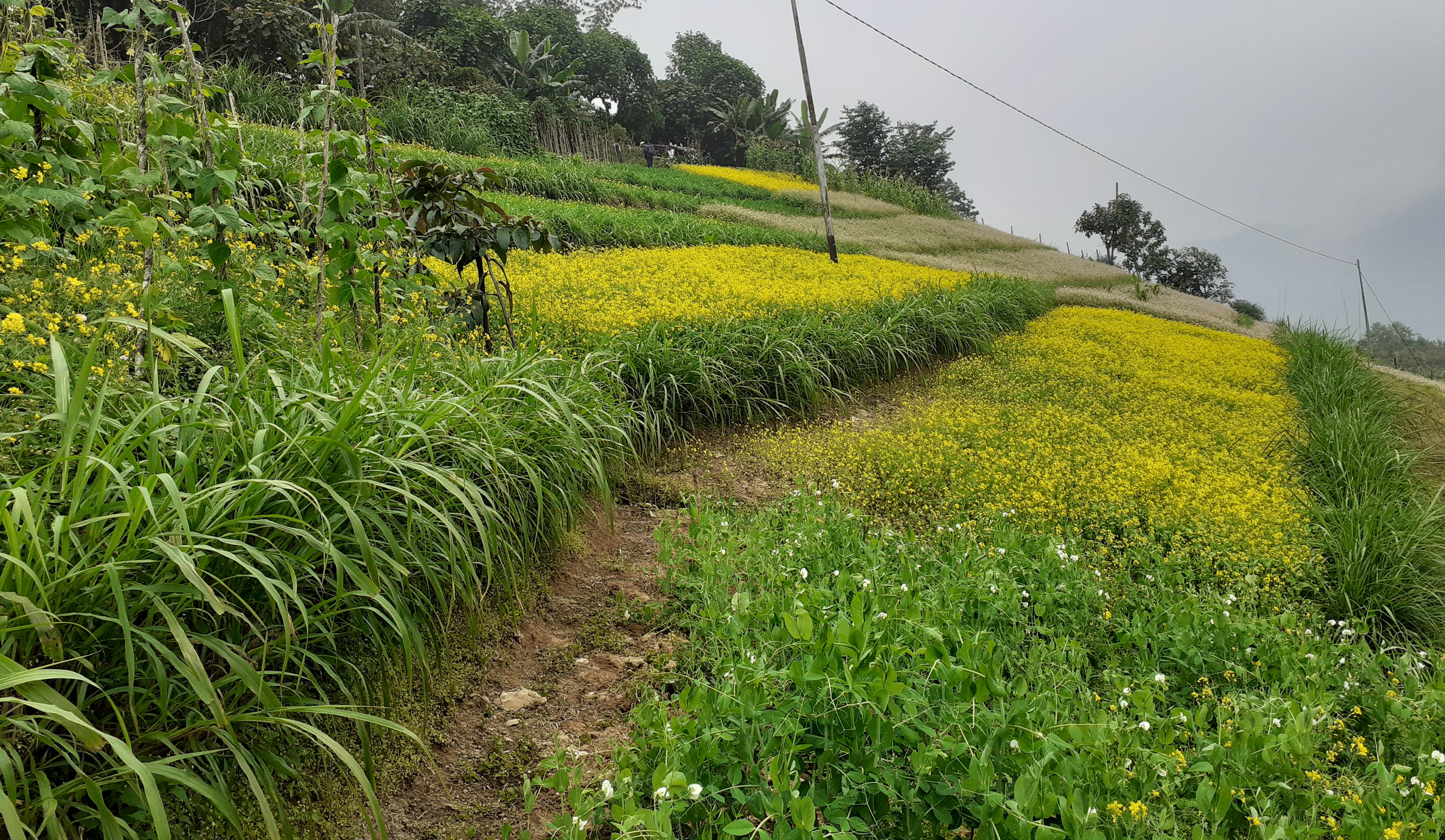
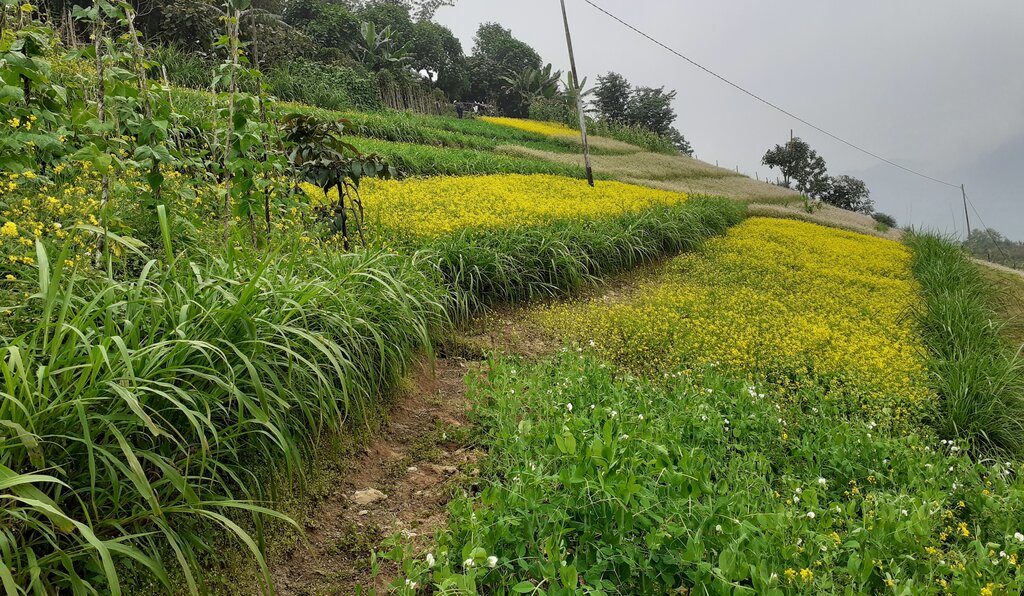
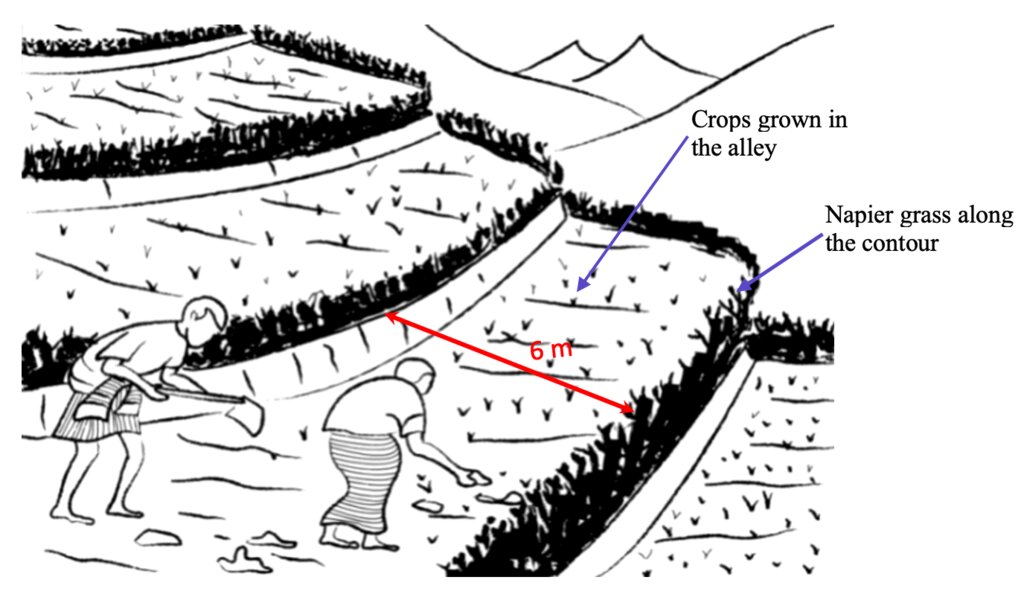
Contour hedgerows are a soil and water conservation technology that involve planting of Napier grass cuttings along contour lines on the slope at a horizontal distance of 6 m. The area between the contour hedgerows is used for crop cultivation.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Contour hedgerows are a soil and water conservation technology that involves planting Napier stem cuttings along contour lines on slopes. They are planted at a horizontal distance of 6 meters between rows and 15-20 centimeters between cuttings within lines. On average it requires 3500-4000 Napier slips to cover one acre (0.4 ha). Hedgerows form living barriers that trap sediment and reduce surface runoff. With time, as the sediment builds up behind the hedges, the area between the hedgerows develops into flat alleys or “terrace beds”. This technology is effective in reducing soil erosion and conserving water. The hedgerows also boost crop productivity. The contour hedgerow system is widely used in hilly terrain in Bhutan and elsewhere.
The main purposes of the technology are to 1) serve as a barrier to check the movement of soil and water down the slope, 2) effectively utilize sloping areas for agricultural purposes, and 3) increase crop and fodder production.
The major activities/ inputs needed to establish/ maintain contour hedgerows are: 1) surveying of the area by an SLM specialist (planning and site assessment), 2) selecting suitable hedgerow planting materials, 3) registration of interested farmers, 4) training of farmers, 5) layout of contour lines using A-frames, 6) distribution of planting materials and establishment of hedgerows in farmland, 7) monitoring and evaluation of hedgerows, and 8) maintenance of hedgerows. Maintenance includes replacement of cuttings in gaps - either damaged by cattle or natural mortality and trimming of grass back to 15 centimeters after reaching 1 meter. Inputs required include: 1) planting materials (Napier grass), 2) A-Frame for contour lines, 3) spades, pickaxes, shovels, crowbars, etc., and 4) human resource input by SLM specialists.
Contour hedgerows have many benefits/ impacts on the livelihood of the land users including 1) soil and water conservation, 2) use of the sloping areas for crop or fodder production, 3) effective conservation through using local materials with a 90% survival rate, 4) habitat for natural predators, pollinators, insect-eating birds, and rodent predators, 5) groundwater recharge, and 6) they beautify the overall agricultural landscape. Another important benefit of the hedgerows is the availability of fodder grass for livestock, which otherwise would have to be collected from the forest. The disadvantages include the need for regular maintenance and gapping up. At times, conflicts arise within the community due to grazing of hedges by neighbors’ cattle.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bhoutan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Mongar
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Boucholing village, Thangrong gewog (block), Mongar Dzongkhag (district)
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 10-100 km2
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2014
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The project was funded by UNDP and technical support was provided by the SLM Specialists from the National Soil Service Center and the agriculture extension agent of Thangrong gewog.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- réduire les risques de catastrophes
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - patates douces, igname, taro, colocase, autres
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
- chilli
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Vegetables are grown for two times in a year but the cereal crops are grown for only one time.
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
Maize and legumes
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Maize followed by vegetables
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water is a major constraint and land users mostly depend on rain for irrigation.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes
Commentaires:
Napier grass were planted on the bunds if the already constructed terrace.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
The technology addresses the issue of soil erosion through rain and prevented the degradation the top soil.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
The main goal of the technology is to combat farm land degradation and prevent soil erosion.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical drawing as per the specification given in the SLM Guidelines 2021. See steps for the establishment of hedgerows below:
a)Determine the hedgerow interval for each landform based on the gradient (but based on farmers feedback, the interval is generally set at 6 meters) and then lay out the contour lines. Along the contours, prepare a strip of land with a width of about 40-50cm wide to plant the grass slips or broadcast fodder grass seeds. Napier (Pennisetum spp.) and Pakchong grass spp. is recommended as hedgerow plants for areas that are below 1600 m. However, for areas above 1600 m, temperate grass mixture should be considered;
b)A row of fodder grass slips or seedlings should be planted with a spacing of 15-20 cm. If grass slips are used, at least two nodes should be inserted into the soil for proper establishment/rooting. On the other hand, if grass seeds are used, the seed rate should be 25g per square metre;
c)Mulching should be done right after the grass slip planting or grass seeding to reduce surface erosion, conserve soil moisture, and aid proper germination;
d)Gap filling and trimming of hedgerows should be done as and when required. The trimmed materials can either be used as fodder or mulching materials; and
e)If desired, improved fruit trees suitable at the proposed site can be planted along the hedges at 5 x 5 m spacing. Fruit trees in two adjacent hedgerows should be planted in staggered position to avoid competition for sunlight, water, and soil nutrients.
Auteur:
NSSC
Date:
10/09/2021
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
Ha
Si vous utilisez une unité de superficie locale, indiquez le facteur de conversion vers un hectare (p.ex. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha = :
0.4
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ngultrum
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
82,08
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
250
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planning | done between the stakeholders several times |
| 2. | Community meeting and member agreement | twice |
| 3. | Training and workshop | for almost a week |
| 4. | Demonstration | once |
| 5. | Implementation (Planting of napier in the field in groups) | based on the land users convenience and season of plantation |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labours | person-days | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Napier | bundle | 35,0 | 200,0 | 7000,0 | |
| Autre | Payment for resource persons | No of days | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 7500,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 15500,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 188,84 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
The funding was provided by UNDP, with technical support from the National Soil Services Center and the Dzongkhag.
Commentaires:
The cost breakdown of the technology establishment was for one acre of land.
The total grant amount was Nu. 2,834,416, however, the total budget for Boucholing specifically was not available.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvesting, cutting of napier and maintaining the height of the plant | when the napier reaches a height of one meter |
| 2. | Replacing of missing and damaged hills | whenever possible |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | person-days | 2,0 | 250,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Napier slips | Bundle | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 2500,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 30,46 | |||||
Commentaires:
Minimal cost go into the maintenance of the hedgerows.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour cost and cost of the planting materials.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The data used was from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Dry subtropical zone
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Contour hedgerows can be applied in both concave and convex situations, so not relevant
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
épisodiquement
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
The flooding of the area occurs mostly due to heavy rainfall and some surface water.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Higher diversity because Napier grass adds to diversity to already existing crops.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
There are a total of 130 acres of land with an average area of around 2.3 acres for each household.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
Précisez:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the land act and rules and regulations which dictate the land use in the country.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Crop production is higher than in the past since the contour hedgerows have helped control soil erosion and allowed for proper land utilization. The land user reported about a 25% increase compared to the past.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The crop quality is also relatively better now compared to the past when the technology was not applied. The land users reported that crops near the hedgerows were found more greener.
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
No fodder was produced
Quantité après la GDT:
After napier plantation, napier are harvested as fodder for cattle.
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Napier grass was not planted in the past. It was introduced by the National Soil Services Center as part of this technology. The Napier grass planted along the contour has helped not only with soil erosion control but also provided fodder grass for the cattle. The land user reported that there was a 100% increase in fodder because unlike in the past now they don't have to send their cow for grazing in the forest.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Compared to normal grass that the cattle would graze on, napier is nutrient-rich and of better quality than the normal grass.
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The napier plantation has helped prevent soil erosion that would normally occur in the farm lands thereby preventing crop failure due to soil fertility and moisture conservation.
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
With the help of the project, the land users were able to utilise the sloping land. This enabled land users to grow crops other than maize.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The contour hedgerows have allowed for the sloping and degraded lands to be revitalised into usable cultivable lands.
gestion des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
Hard manual land management
Quantité après la GDT:
mechanization of the agriculture in the community
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
With the help of the project, farm lands in the community were made into terraces and made land management easier compared to the past.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The expenses on agricultural inputs have stayed relatively the same, however, has made working on the farm land easier.
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
With fodder availability, land users can now focus more on agriculture instead of herding cattle for grazing. The project has also allowed for land users to diversify their products.
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Workload has decreased due to farm mechanization through use of power tillers, which was not possible prior to the SLM intervention.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Prior to hedgerow establishemt, there was serious surface erosion, which is not the case now.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
primarily maize was cultivated
Quantité après la GDT:
maize, cole crops, tubers and chilies are cultivated
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In the past, the community members would normally cultivate maize and small amounts of vegetables for self consumption, but now a diverse variety of crops are cultivated.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
Quantité avant la GDT:
More prominent in the summer season
Quantité après la GDT:
occurrence is very minimal
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The presence of a terrace and hedgerows in the bunds of the terrace has prevented the erosion of the soil in the farm lands of the farmers.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Downstream flooding is relatively less, since the hedgerows has prevented or reduced surface eorsion which would otherwise impact the downstream settlements and water bodies.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| orage local | très bien |
| averse de grêle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| glissement de terrain | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Since the project was fully funded and minimal cost went into its establishment by the land users, the benefits are higher.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
40 households
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
Since the program was supported by project, the labor were contributed by the land user while the inputs in all sites were provided by the project at every household level.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Hedgerow requires less management |
| Napier are also used as fodder for livestock |
| Prevents the land from erosion due to heavy rain |
| Helps in build up of terraces and facilitates in mechanization of farm |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Additional income opportunities through the production of marketable products from hedgerow vegetation. |
| Improved livelihoods for communities through long-term agricultural productivity. |
| Support for sustainable agricultural practices and resilient farming systems. |
| Preservation of fertile land and protection of agricultural resources. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Grazing of hedges by free cattle in absence of fences in farm land | Establish community byelaws not to let their cattle free in the fields or install fencing aroung the field. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Shading and potential competition with crops for soil nutrients by hedges | Maintaining height and width of hedges |
| The establishment and maintenance of contour hedgerows require time, effort, and financial resources | The funding for the establishment of technology has already been provided and for maintenance, the expenditure is minimal. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
1 household
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
2 individuals
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
ICIMOD. (1999). Manual on Contour Hedgerow Inter-cropping Technology. ICIMOD.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://lib.icimod.org/record/31840/files/manual_on_contour_hedgerow_inter-cropping_technology.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Pellek, R. (1992). Contour hedgerows and other soil conservation interventions for hilly terrain. Agroforestry Systems, 17, 135-152.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00053118
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Kaushal, R., Mandal, D., Panwar, P., Rajkumar, Kumar, P., Tomar, J. M. S. & Mehta, H. (2021). Chapter 20 - Soil and water conservation benefits of agroforestry.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128229316000204
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Sustainable Land Management for improved land productivity and community livelihood in Thangrong, Mongar
URL:
https://sgp.undp.org/spacial-itemid-projects-landing-page/spacial-itemid-project-search-results/spacial-itemid-project-detailpage.html?view=projectdetail&id=27647
Titre/ description:
Soil erosion control with contour planting
URL:
https://apps.worldagroforestry.org/Units/Library/Books/Book%2082/imperata%20grassland/html/4.1_soil.htm?n=20
Titre/ description:
Sustainable Land Management: Guidelines and Best Practices 2021
URL:
https://www.nssc.gov.bt
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé