Reconstitution of Soils [Italie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Chiara Cassinari
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Ricostituzione
technologies_7346 - Italie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Manfredi Paolo
mcm Ecosistemi
Italie
co-compiler:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NEW LIFE Project (NEW LIFE)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
m.c.m Ecosistemi (m.c.m Ecosistemi)1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
Reconstitution is a technology that counters land degradation and according to the theory of "Circular Economy" it's a sustainable land management technology
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [Italie]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- Compilateur : Chiara Cassinari
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Reconstitution of soils is a pedotechnique based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials to achieve benefits in areas with barren, degraded, desertified and/ or sealed soils.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
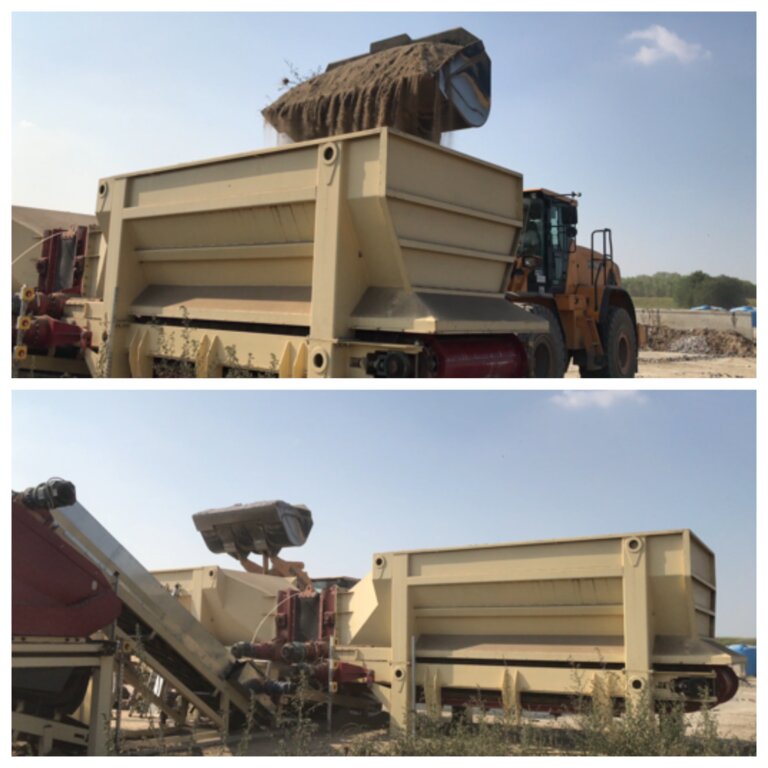
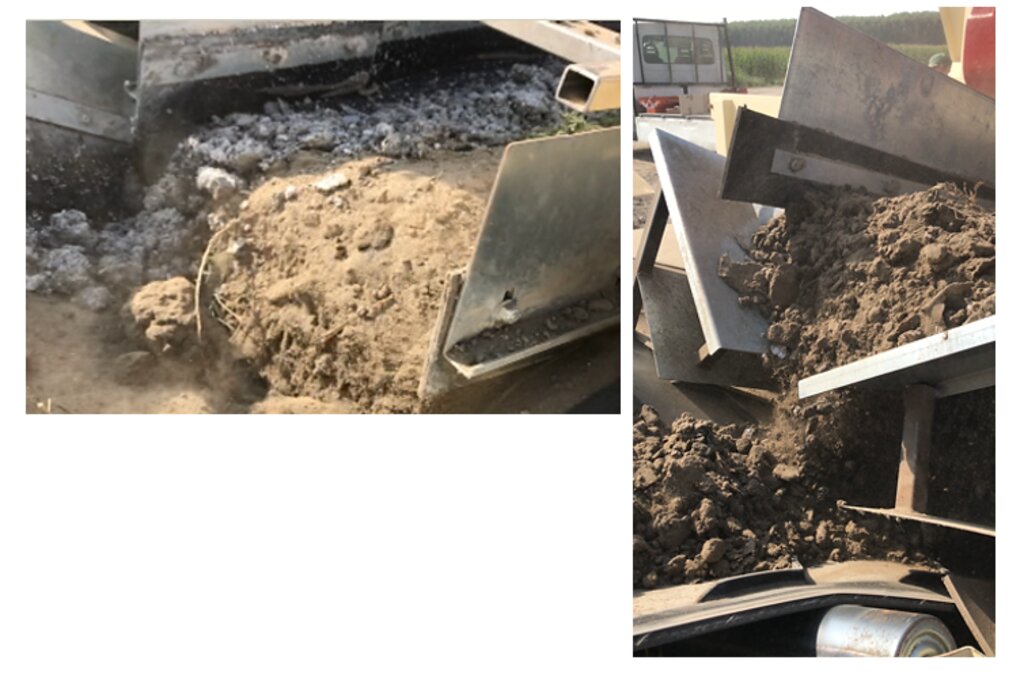
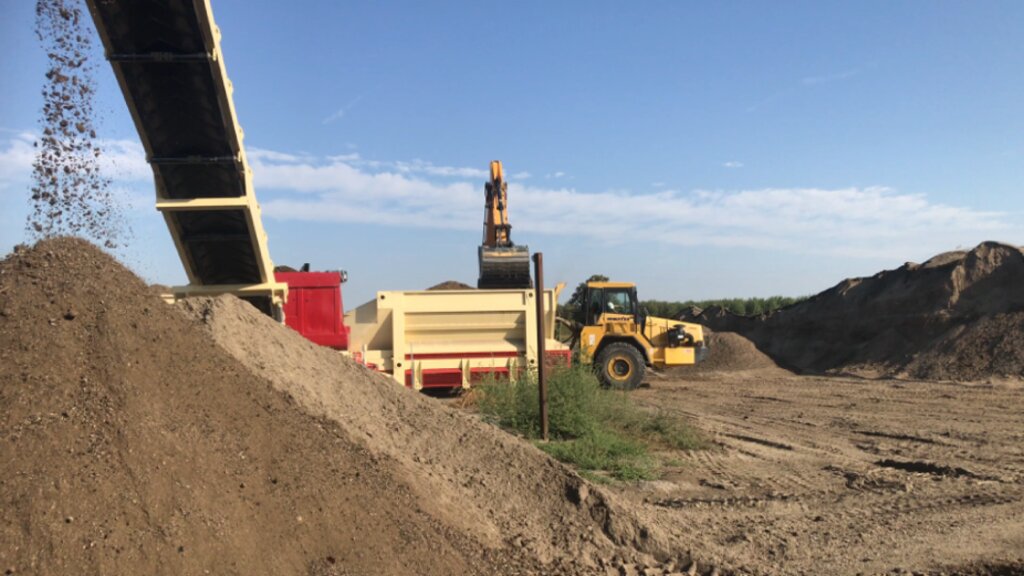
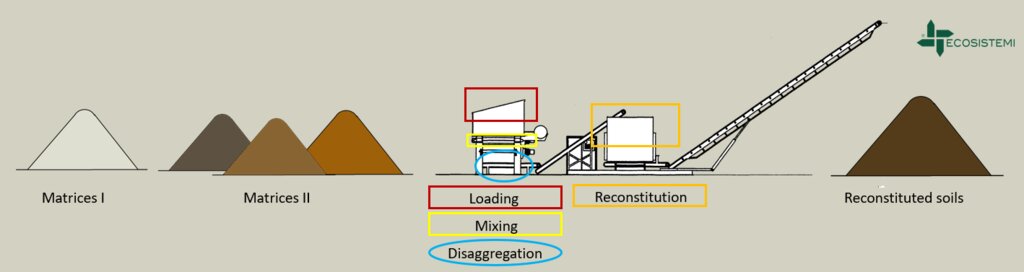
Reconstitution of soils to generate an Anthroposol is a technology based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials or “matrices” (from “matrix” in Latin: everything that is the foundation of something) to achieve ecosystem benefits, especially in areas with degraded, desertified, barren and/or sealed soils. The technology applies a conceptual model based on the production of new soil aggregates with targeted environmental and soil characters generated via a chemico-mechanical process that entails reusing residues of specific origin. The activity is consistent with the principles of a “Circular Economy”, applying restoration ecology, use of compatible waste and saving the non-renewable resource of soil. Reconstitution is covered by two patents of the mcm Ecosistemi s.r.l. company.
Reconstitution applies the process to two groups of pedomaterials. Firstly, primary matrices (matrices I), represent the main material to be converted into fertile soil. These could be degraded soil itself or inorganic mineral pedomaterials. Secondly, secondary matrices (matrices II) refer to byproducts and waste from production activities. Secondary matrices are divided into two. First, organic - from wood and cellulose processing production activities and from textile and agro-food industries. These are characterized by a high organic component with a high carbon/nitrogen ratio, and a high presence of plant fibres. Second, mineral matrices - especially from mining, the preparation of drinking and industrial water and the management of hydroelectric reservoirs and internal canals. There are four stages.
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected according to the type of soil desired and then loaded in the plant. Dosage is calculated through an application program (PEDOGÉNIA), which estimates the chemical properties of the finished product.
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity.
3) Disaggregation: Breakup and defibering through rotating movements at variable power.
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
The treatment generates an Anthroposol whose characters and properties are different from the materials of origin.
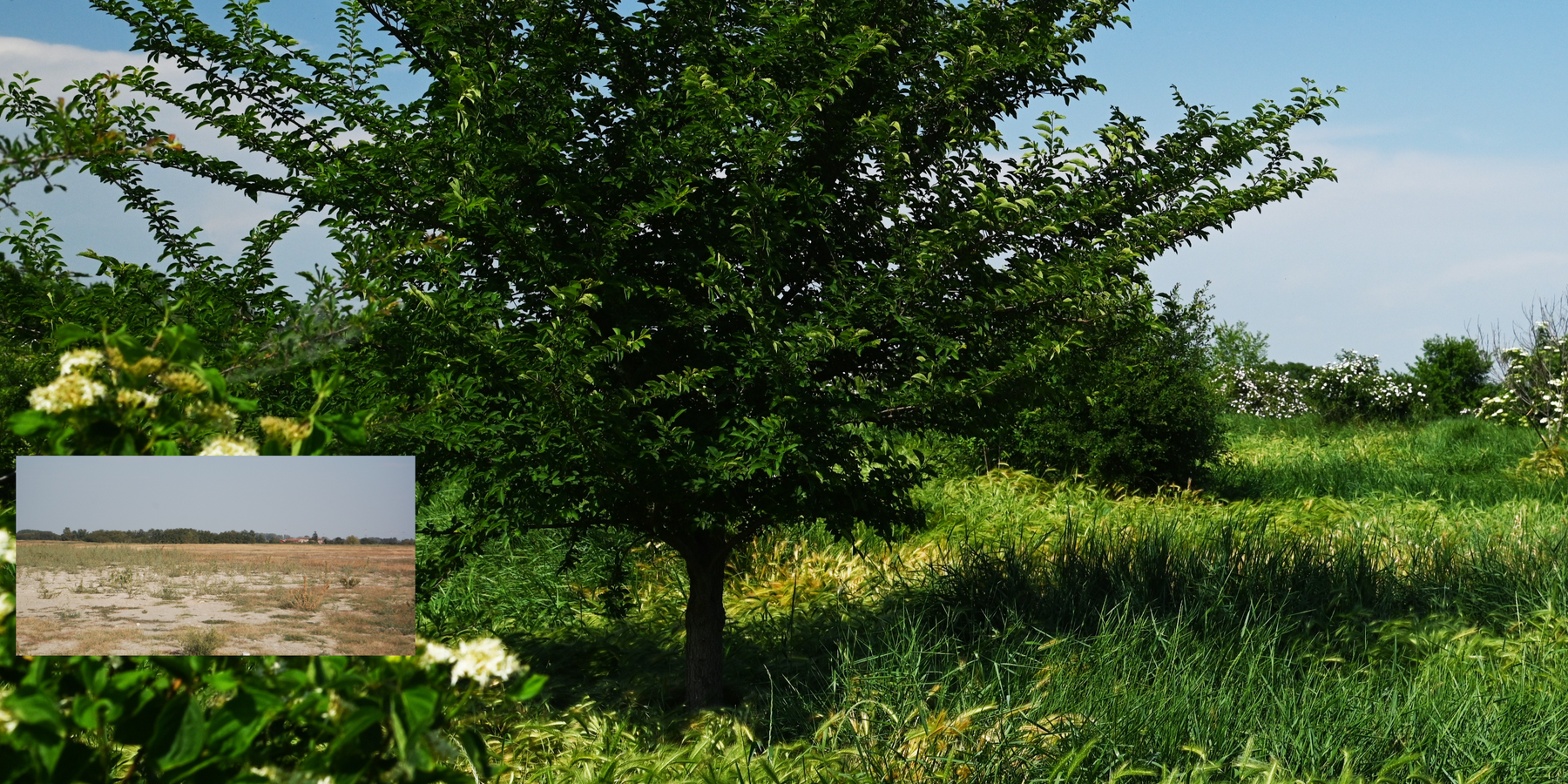
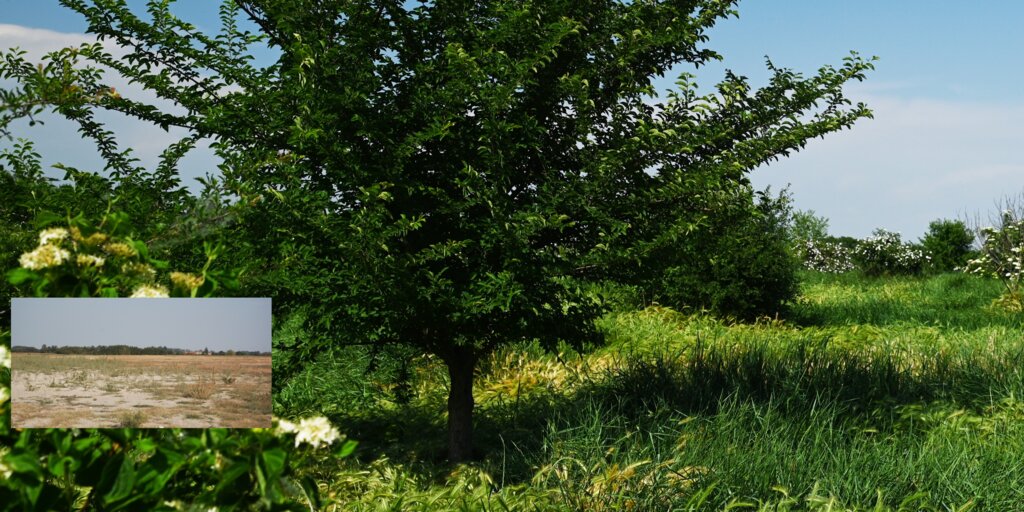
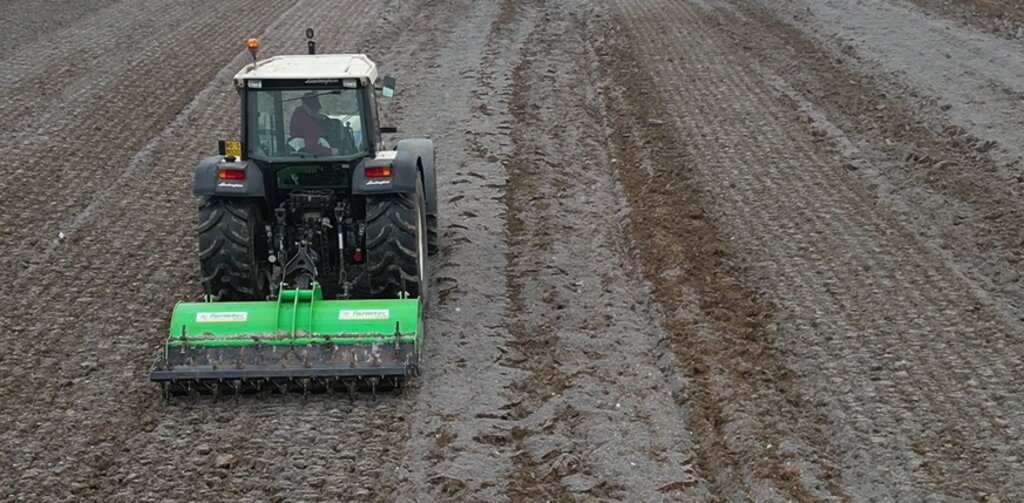
The properties of the reconstituted soils and the technical-economic sustainability of the pedotechnology have been demonstrated over the years with agronomical tests and experiments, as well as comparative analysis between degraded soils and reconstituted soils. This demonstrates the reconstituted soil’s ability to create a stable pedosystem to carry out its basic functions - storage, filtration, transformation of nutrients and biodiversity pools - for various forms of land use, and ecosystem benefits. Agroforestry restoration with reconstitution has social impact, as it is demonstrated by a EU project (“New Life”), where the Park of Trebbia river has increased utility to people after restoration. Agronomic restoration allows farmers to increase yields using less fertilizer and water. Another environmental and economic advantage is that manufacturing companies which produce waste can reduce costs through the recycling process of reconstitution. For reconstitution, a plant has to be installed near the land to be restored; an overview is presented in 4.1. In addition, earth moving vehicles are needed for the transport and placement of reconstituted soil.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nF3nl4S5X8M
Reconstitution plant
Date:
18/12/2024
Lieu:
Piacenza, Loc. Mortizza
Nom du vidéaste:
Paolo Manfredi
Commentaire, brève description:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kjy95Kz-e70
Construction site: collection of degraded soil to be reconstituted
Date:
18/12/2018
Lieu:
Piacenza, Gossolengo
Nom du vidéaste:
Paolo Manfredi
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Italie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
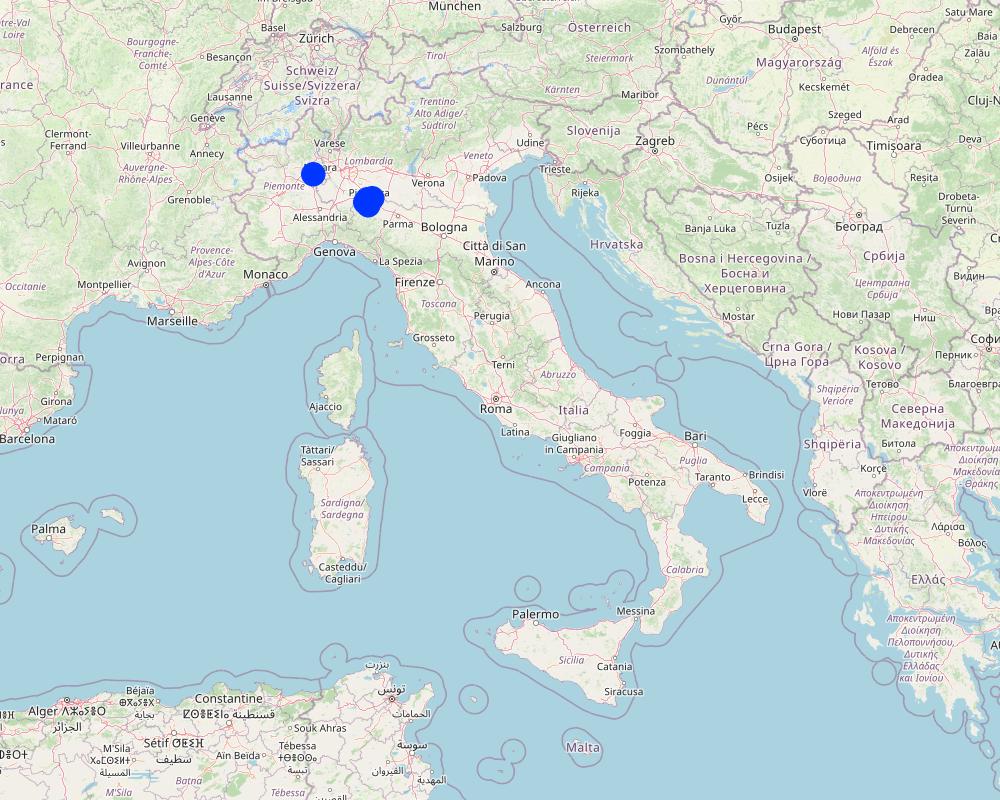
Emilia Romagna, Piacenza; Piemonte, Vicolungo
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Regional, National and International projects
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- tomato, fodder crops
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
maize - wheat - tomato

Forêts/ bois
- Forêts (semi-)naturelles/ bois
- Plantations d'arbres, boisements
Type de forêts (semi)-naturelles:
- végétation naturelle des forêts sèches subtropicales
Plantation d'arbres, afforestation: Précisez l'origine et la composition des espèces. :
- Variétés mixtes
Type de plantation d'arbres, d'afforestation:
- plantations de forêts sèches subtropicales
Type d’arbres:
- Espèces d’Acacia
- Espèces de Populus (peuplier)
- Salix species
Est-ce que les espèces d’arbres précisées ci-dessus sont des espèces d'arbre arbres à feuilles caduques ou à feuilles persistantes ?
- forêt mixte décidue/ à feuillage persistant
Produits et services:
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
- Loisirs/ tourisme
- Protection contre les aléas naturels
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie
Mines, industries extractives

Terres improductives
Précisez:
degraded, desertified and sealed soils
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion intégrée de la fertilité des sols
- gestion des déchets/ gestion des eaux usées
- ecosystem rehabilitation
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A4: Traitement de la couche profonde du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S11: Autres

modes de gestion
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
- M7: Autres

autres mesures
Précisez:
addition of organic matter, new soil aggregates, increase water holding capacity
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
- Ca: acidification
- Cs: salinisation/ alcalinisation

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pk: scellage et encroûtement
- Pi: imperméabilisation des sols

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bh: perte d’habitats
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
- Bl: perte de la vie des sols

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Reconstituted technology: phases of work:
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected and dosed
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity
3) Disaggregation through rotating movements at variable power
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
Auteur:
Paolo Manfredi
Date:
12/04/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
10 hectares
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
EUR
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
0,89
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
123.00, gross income
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | characterization of the intervention site | no timing |
| 2. | morphological planning | no timing |
| 3. | environmental planning | no timing |
| 4. | pedo-agronomic planning | no timing |
| 5. | moving-plant placement only if the area to be restored is distant from the area where the permanent plant is located | no timing |
| 6. | degraded soil removal and collect | after harvest of crops, if there are |
| 7. | reconstitution | no timing |
| 8. | replacement of reconstituted soil | no timing |
| 9. | final soil placement | no timing |
| 10. | site-specific planting to make soil ready for use | dependence of plants species |
| 11. | land use | no timing |
Commentaires:
The reconstitution plants are 2: one is fixed that is located in an area, the other is a moving-plant: that is it can be located near the area to be restored.
According to the distance between the intervention site and the fixed plant it can be more useful using the moving-plant
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | 3 Workers | person/day | 232,0 | 123,0 | 28536,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Construction area - mobile plant | number | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Earth moving vehicles | number | 2,0 | 20000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Matrices to be used | m3 | 75000,0 | 15,0 | 1125000,0 | |
| Autre | Reconstitution | m3 | 100000,0 | 2,5 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 1473536,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1655658,43 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Costs related to the matrices to be used and transport (1125000.00 EUR) are covered by company producing waste used. The costs to dispose of matrices II are much higher than taking them to the reconstitution plant.
Commentaires:
degraded land value 0 EUR
restored area value 390000 EUR
restoration using allocation of natural soil (8 EUR/m3, cost of natural soil in Piacenza) added to transport costs = 2100000.00 EUR
restoration using reconstituted soil technology = 28536 + 30000 + 40000 + 250000.00 EUR because 1125000.00 EUR are covered by company producing waste and so not spent for restoration.
Cost related to construction area and mobile plant are the costs for the set up of the area where to put the mobile plant and for it' transport to the intervention site.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ordinary plant maintenance | every 6 months or when needed |
| 2. | Reconstituted soil analysis | every 6 months |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | 1 Worker | person/day | 20,0 | 123,0 | 2460,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | 3 Laboratory staff | person/day | 100,0 | 115,0 | 11500,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 13960,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 15685,39 | |||||
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most important factor affecting costs could be the transport of degraded soil or matrices I to be used to the restoration site in the case of soil sealed
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
891,02
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
May: average monthly regionally anomaly +230% (heavy rains); October: heavy rains
February 2023 is the month with less rain 27.6 mm; in May is the rainiest 250.7 mm
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Bulletin ARPAE 2023
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
mean annual temperature 14.4 °C Bulletin ARPAE 2023
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Following the soil characterization (data are mean of 30 soil samples) of the last area of intervention with reconstitution; the data describes soil condition before reconstitution.
The soil texture is silty-loam
The aggregate stability index describes soils with poor stability
pH (1:2.5 in H2O) 6.98 ± 0.37
EC (saturated paste) 0.93 ± 0.41 dS m-1
tot CaCO3 10.33 ± 4.36 g kg-1 SS
active CaCO3 3.08 ± 1.24 g kg-1 SS
tot C 10.62 ± 3.68 g kg-1 SS
organic C 10.26 ± 3.44 g kg-1 SS
tot N 1.47 ± 0.43 g kg-1 SS
HA + FA 2.54 ± 1.26 g kg-1 SS
Olsen P 87.83 ± 44.19 mg kg-1 SS
available Fe 74.68 ± 32.97 mg kg-1 SS
available Mn 27.92 ± 15.78 mg kg-1 SS
available Zn 2.30 ± 1.72 mg kg-1 SS
available Cu 4.32 ± 1.34 mg kg-1 SS
soluble B 0.71 ± 0.25 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable K 21.61 ± 34.72 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable Mg 92.68 ± 28.13 mg kg-1 SS
CEC 26.22 ± 4.42 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Mg2+ 2.39 ± 0.50 cmol(+) kg-1
exch K+ 0.42 ± 0.33 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Na+ 0.48 ± 0.22 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Ca2+ 11.82 ± 4.75 cmol(+) kg-1
Chemical fertility is low, intrinsec fertility is poor, global fertility lower-intermidiate
In the link other data about soil analysis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Hb0PcmSYGY&list=PLXcG4R_rAdFaqGnKCa0qaL6FcrafvU0VE
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux souterraines
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- accès libre (non organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
60%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKrAG6jrqXA
qualité des cultures
Quantité avant la GDT:
70%
Quantité après la GDT:
95%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 70% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that wheat quality. in terms of proteins, increased in reconstituted soils
production fourragère
Quantité avant la GDT:
65%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
these increment are estimation
risque d'échec de la production
Quantité avant la GDT:
40%
Quantité après la GDT:
0
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 40% to 0: this decreasing is an estimation, it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D0II3SGNhKo
gestion des terres
Quantité avant la GDT:
40
Quantité après la GDT:
100
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
simplified from 40% to 100%; because of the physical properties of reconstituted soils; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ld8YzGcx6Qw
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
60%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 60% to 10%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
60%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils and so also farm income increases
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
60%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 60% to 100%; because of it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
opportunités culturelles
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in a EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJ8gFmV1Onc
possibilités de loisirs
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
40%
Quantité après la GDT:
15%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 40% to 15%, this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMazUuMaa6o
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
40%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; some laboratory tests demonstrated that reconstitution improves soils permeability
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/oDhW-YlBjHA
Sols
humidité du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
40%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 40% to 100%; analyzing the water retention curves in many experimentation sites and comparing them with degraded soils, reconstituted soils has demonstrated to have better water holding capacity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yqtl4-xYMeo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qy_B3oCyIAM
couverture du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
20%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species were sprouted naturally
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
50%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils as soil stability index
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g1GhoyIy4sk
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
50%
Quantité après la GDT:
0%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 50% to 0%; we tested a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aPQRoaYmrIQ
compaction du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
50%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 50% to 100%; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil compaction in reconstituted soils
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Quantité avant la GDT:
60%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 60% to 100%; the high chemical fertility of reconstituted soils has been demonstrated in a lot of field tests
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 10% to 80%; reconstituted soils has high organic carbon with a high C/N ratio; the SOC/clay is optimal
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
20%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 20% to 100% in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFnUsjYLwfw
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Quantité avant la GDT:
20%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
diversité végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
20%
Quantité après la GDT:
100%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
espèces bénéfiques
Quantité avant la GDT:
20%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Q8tqJNai3o
diversité des habitats
Quantité avant la GDT:
10%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Quantité avant la GDT:
40%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, physical reconstituted soil properties
impacts de la sécheresse
Quantité avant la GDT:
40%
Quantité après la GDT:
0%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 40% to 0%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, phisical reconstituted soil properties
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Quantité avant la GDT:
40
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; this is an estimation considering reconstituted soils microbial activity (tests about biological fertility), soil water content (humidity), soil temperature, nutrient availability and pH-value
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag5wzRVFg9s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Anetp8gKaQg
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
capacité tampon/de filtration
Quantité avant la GDT:
20%
Quantité après la GDT:
50%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
increasing from 20% to 50%; because of the CaCO3 content of some matrices II
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Quantité avant la GDT:
50%
Quantité après la GDT:
10%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| précipitations saisonnières | saison des pluies/ humide | décroît | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| conditions hivernales extrêmes | modérément |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
The recycle of suitable waste materials used defrays the reconstitution technology in short and long term
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
autre (précisez):
the Technology is partly modified to face every restoration project
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
design, matrices to be used
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Strengths: to change soil class in Land Capability Classification, to improve soil workability, to create new soil aggregates (the organic matter is covered by fine soil mineral fractions) |
| Advantages: to increase soil fertility, to implement Circular Economy |
| Opportunities: to create a non-renewable resource (soil) and/or to restore it, to implement Circular Economy |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Strengths: to produce the suitable soil for the environment where it will be placed |
| Advantages: to reduce the use of fertilizers |
| Opportunities: to restore soil using suitable waste, Circular Economy |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: demand exceed supply, concerning current number of workers employed in the reconstituted plant | formation of new workers |
| Risks: crisis of industries producing suitable waste | non-stop search for suitable waste to use |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: contamined soils | studies about possibility of using reconstitution to clean soils |
|
Risks: the pedotechniques include all the anthropic activities that determine a growing influence of man on pedogenesis and pedolandscapes; they have to satisfy man needs while avoiding any undesirable environmental consequences (Dazzi et al., 2010). This is the main core of reconstitution of soils, but sometimes, the use of waste material, even if, environmental suitable, isn't understood because of waste are considered materials only for disposal. |
Dissemination concerning the laboratory analysis before the waste use, studies and research projects with University to test environmental suitability of reconstituted soils |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
2 visits/survey a year
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
each land user where technology was adopted
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/03/2023
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
The reconstitution pedotechnique: Applications, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., 10.1016/j.eti.2021.102246
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
The reconstitution: environmental restoration assessment by means of LCC and FCC, 10.6092/issn.2281-4485/8500
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Trees and shrubs monitoring using an ecological approach: the conclusion of the restoration project of Borgotrebbia landfill (Northern Italy), Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Meloni F., Stragliati L., Trevisan M., Giupponi L., 10.31031/EAES.2019.06.000635
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
A new technology to restore soil fertility: Reconstitution, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Francaviglia R., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201933
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Growth and yield response of tomato (Solarium lycopersicum L.) to soil reconstitution technology, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Gatti M., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201916
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Test on the effects of reconstituted soil on emergency speed and root growth in maize, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Salvi R., Battaglia R., Marocco A., Trevisan M., 10.1515/contagri-2018-0035
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Osservazione di Lycogala terrestre Fr. e Stemonitis axifera (Bull.) T. Macr. su suoli ricostituiti sabbiosi, Manfredi P., Salvi R., Bersan M., Cassinari C., Marocco A., Trevisan M.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Relationship between hydraulic properties and plant coverage of the closed-landfill soils in Piacenza (Po Valley, Italy), Cassinari C., Manfredi P., Giupponi L., Trevisan M., Piccini C., 10.5194/se-6-929-2015
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Soil temperature fluctuations in a degraded and in a reconstituted soil, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., ISBN 20385625
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Confronto tra dati produttivi di mais coltivato su terre ricostituite e terre naturali, Manfredi P., Tassi D., Cassinari C.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Scientific Journal
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Ecosistemi web site
URL:
https://www.mcmecosistemi.com/
Titre/ description:
Paolo Manfredi ResearchGate
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paolo-Manfredi-2
Titre/ description:
Chiara Cassinari ResearchGate
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chiara-Cassinari
Titre/ description:
All the publications with DOI mentioned above
Titre/ description:
Ecosistemi YouTube channel
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCOloFv-BLgvIVt9kBZuZyZg
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
Very useful questionnaire
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [Italie]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- Compilateur : Chiara Cassinari
Modules
Aucun module trouvé