Terracing on the hill slope areas [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Rustam Nugmanov
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Planting of fruit trees on terraced slope in rain fed areas with a perimeter fence
technologies_1033 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Agency for Technical Cooperation and Development Tajikistan (ACTED Tajikistan) - Tadjikistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Planting of trees and bushes in the rain fed slope areas by using mulching, rain water harvesting and organic fertilizers
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
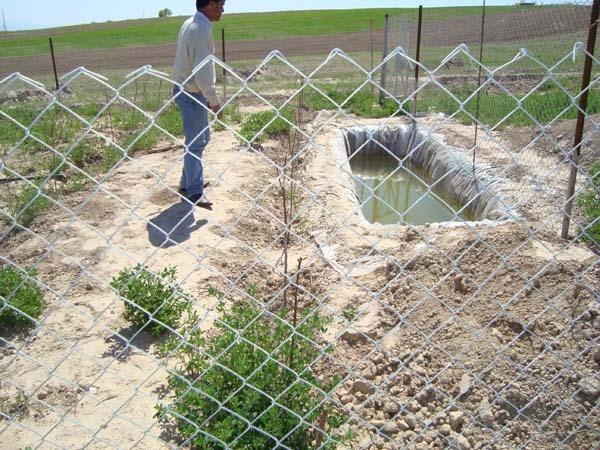
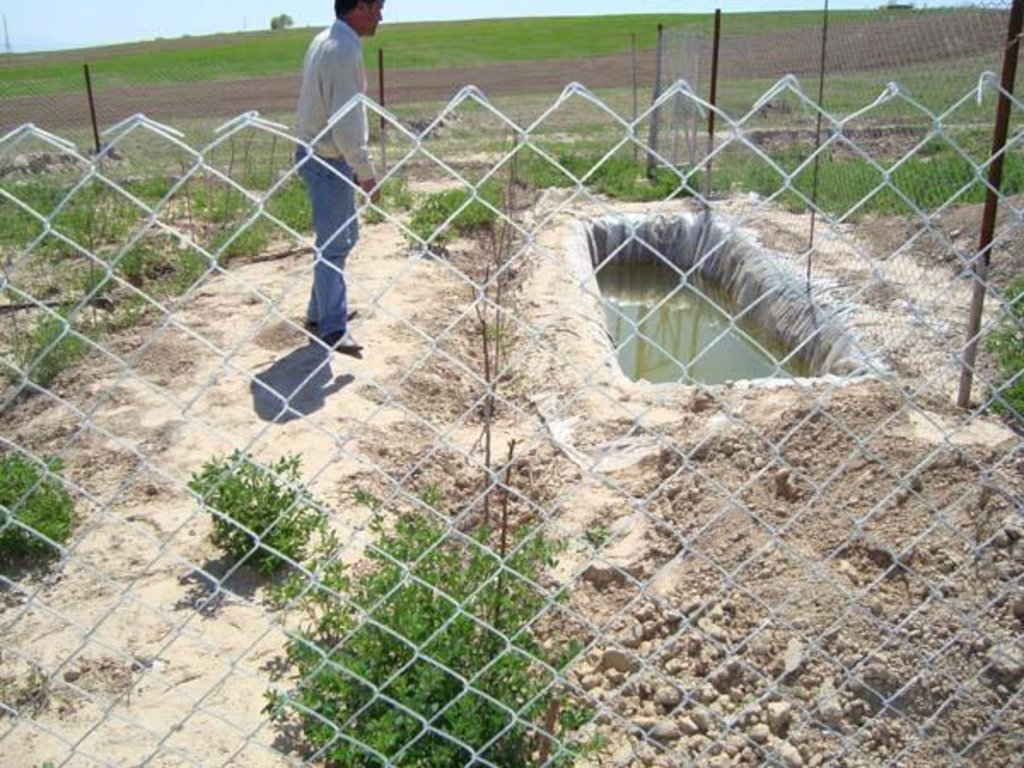
6 vulnerable households are selected to carry out this pilot activity. They maintain terraced plots of 0.01 ha (10m x 10m) each. Households fence the entire area to protect it against animals. The plots are constructed on the slope of a hill by digging terraces/steps with intervals of 1m. 10 fruit seedlings are planted along one row and 10 rows are planted in total. In some areas where there is a probem with watering of new seedlings simple basin covered with plastic sheet could be installed in order to harvest rain water for the purpose of irrigation of seedling in ht summer periods or when there is a lack of water
Purpose of the Technology: The terracing will help to mitigate wind erosion by preventing top soil losses. The terraces will also provide protection against water erosion by catching water and improving natural infiltration of water. The terraced plot also provides an economic benefit to land users by functioning as an orchard.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The criteria for the establishment of the plots are the local conditions: this takes into account the sensitivity of the land to erosion, that the land is rainfed, and the vulnerability of households in or near the potential target areas/slopes. If the criteria are met, households then establish a fenced area of 0.01 ha in the target slope/area. They receive the task of planting and maintaining the orchard plots by watering (if necessary), pruning, mulching, and using organic fertilizers.
Natural / human environment: The issue with the target area/slopes is that they suffer from water or wind erosion. Therefore, they require terraced plots to mitigate the effects of erosion. In terms of human influence, the lands have either been overgrazed and were unproductive for vulnerable households in the area.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Khatlon province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Farkhor district
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0006 km2.
6 demoplots established in 6 different jamoats of Farkhor district, each demonstration plot area is 0.01 ha.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
This technology has been in use since the 1940ies / 50ies. It is mainly used by the local population in rural areas.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- fruits à pépins (pommes, poires, coings, etc.)
- fruits à noyaux (pêche, abricot, cerise, prune)
- fruits à coque (noix du Brésil, pistaches, noyers de bancoule, amandes)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: February-May

Pâturages

Forêts/ bois
Type d’arbres:
- Acacia albida (Faidherbia albida)
- shrubs
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): water insufficiency for irrigation purposes
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): water insufficiency, especially in summer period
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?

Pâturages
Commentaires:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S1: Terrasses
Commentaires:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting of trees by people), other human induced causes (specify) (Cutting of forests for wood), change of seasonal rainfall (Insufficient rainfalls), population pressure (overgrazing of animals on the same area)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The plots are constructed on the slope of a hill by digging terraces/steps with intervals of 1m. 10 fruit seedlings are planted along one row and 10 rows are planted in total. In some areas where there is a probem with watering of new seedlings simple basin covered with plastic sheet could be installed in order to harvest rain water for the purpose of irrigation of seedling in ht summer periods or when there is a lack of water. Beside this all plots are surrounded with metalic fence in order to avoid animals from damaging the new palnted seedlings
Farkhor district
Date: 20.12.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 7500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Trees/ shrubs species: acacia, shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apple, almond trees, apricot trees, cherry trees, quince trees
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 45%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 40%
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 1
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Construction material (other): metal lath and pipes for the poles (stand)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 45%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 45%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0,06
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Garden
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
500 trees
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
somoni
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
2,46
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
25
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging of the holes | in the early spring |
| 2. | planting of trees | in the early spring |
| 3. | Terracing of slope areas | in the early spring |
| 4. | Fencing of the area | during planting of the trees |
| 5. | Digging of water harvesting basin | while esteblishing of terraces |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Digging of the holes | persons/day/unit | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | |
| Main d'œuvre | Planting of trees | persons/day/unit | 5,0 | 25,0 | 125,0 | 73,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Terracing of slope areas | persons/day | 2,0 | 25,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Digging of water harvesting basin | person/basin | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Fencing of area | unit | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 830,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 337,4 | |||||
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | watering the plants | 2 times per week |
| 2. | Mulching the new plants | when it is necessary |
| 3. | using of organic fertilizers for trees | During the planting and after couple of months |
| 4. | rain water harvesting near the kitchen gardens for watering of new trees | when available |
| 5. | Supervision and observing | on constant base |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Watering the plants | persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Mulching the new plants | persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Using of organic fertilizers for trees | persons/day | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Rain water harvesting near the kitchen gardens for watering of new trees | persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Fertilizer | kg/unit | 1000,0 | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1085,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 441,06 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: spade, pail, chopper
area used for the technology: fenced plot of 0.01 ha
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Soil structure, slope
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Mostly in winter and spring period. Dry periods starts from the end of spring till September, October
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor and one of the main reasons of gully forming
Soil water storage capacity is low during dry seasonal periods
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
faiblement potable (traitement nécessaire)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Water quality (untreated): Mostly hand water pumps
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production de bois
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Impacts socioculturels
opportunités culturelles
livelihood and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Behavioral change, people got information on the advantages of applying organic fertilizers and water harvesting to develop their plots on rainfed lands
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
salinité
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
vitesse du vent
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
Commentaires:
main damage may be caused by droughts, thus plants will feel water insufficiency
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Establishment of plots with terracing on slope areas does not demand lots of funding and planting of fruit trees will become a source of alternative income in the near future
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| The technology is user-friendly and does not require complicated tools or agro-inputs. Land users can replicate this technology with minimal cost. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| It does rely on climactic conditions. If there is an extended period of dry weather this can have a detrimental effect on the tree seedlings. | By ensuring that land users maintain these plots by regularly watering them and using mulching. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
03/05/2011
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé