Road runoff management - Nyeri [Kenya]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : James Gatero Njuki
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
MRP - soil conservation pilot project
technologies_1094 - Kenya
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development of Kenya (MoA) - Kenya1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
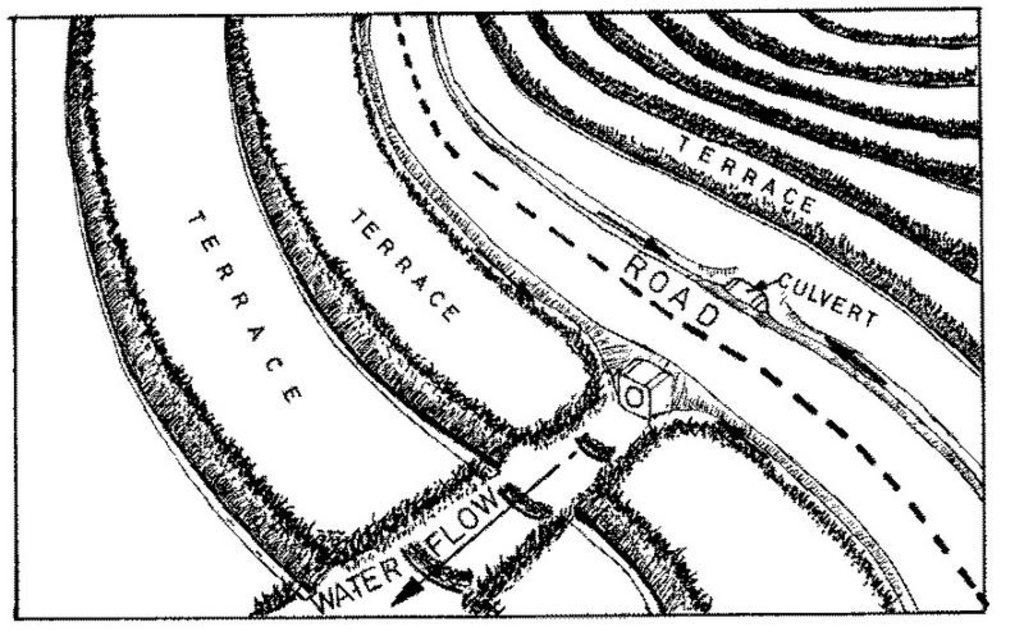
management of runoff water on the road and its environment to reduce land degradation
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
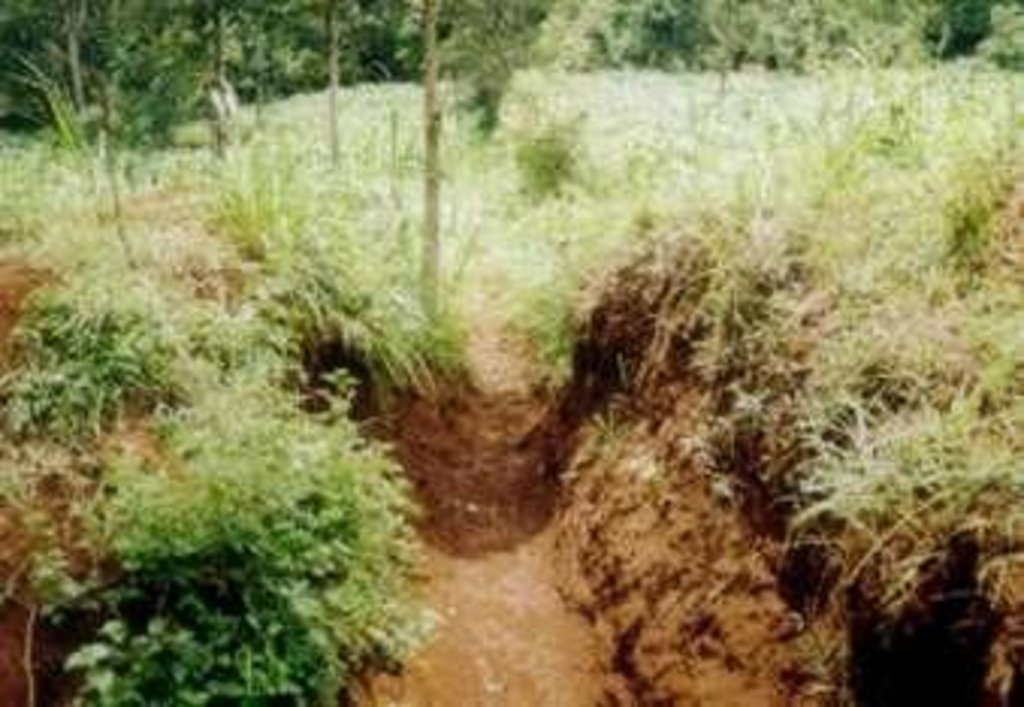
It encompasses agronomic, vegetative, structural and management aspects to minimise land degradation within the road catchment and its environment using participatory methods. The purpose of the technology was to improve on the managent of water from the road so that it does not cause degradation. Establishment and maintenance of the technology was done by the local community bordering the roads.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Kenya
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Central
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
the area covered depend on the area of the road. In total the technology was duplicated in roads totalling about 33 kilometres
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
SWC specialists and land users
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - MaySecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec

Implantations, infrastructures
- Trafic: routes, réseaux ferroviaires
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Declining soil fertility and soil erosion, land subdivision leading to small parcels of land
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Marketing/pricing of farm produce, high costs of inputs and lack of credit
Grazingland comments: stall feeding is the most common grazing system as there are no delienated portions for grazing , due to the small holdings
Type of grazing system comments: stall feeding is the most common grazing system as there are no delienated portions for grazing , due to the small holdings
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S4: Fossés isohypses, trous
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour ridging
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (road surface & Agricultural causes), roads
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
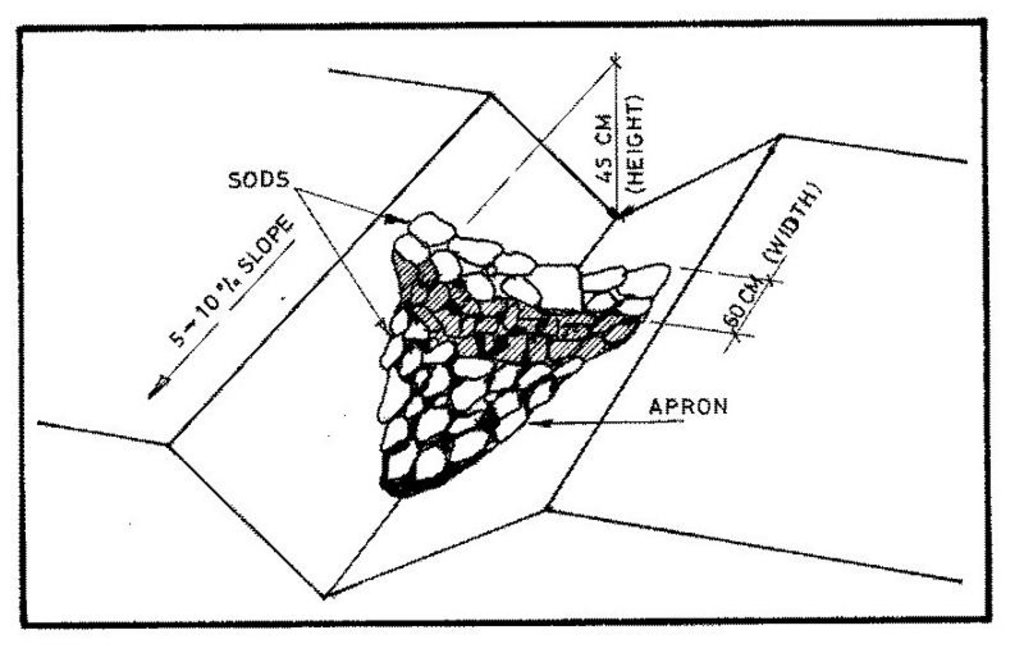
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
Grass species: napier grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0.00%
Construction material (stone): for scour checks in the waterway
Construction material (wood): small posts for scour checks
Construction material (other): grass, brush wood, live vegetative material
Lateral gradient along the structure: 8%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: exclusion of land under waterway
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Kenyan Shilling
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
33,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.96
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting napier grass cuttings | after first rains |
| 2. | establish scour checks | on set of rains |
| 3. | excavation | dry spell |
| 4. | planting grass for stabilisation | on set of rains |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | contour ridging | dry season / beginning of season |
| 2. | weeding | dry spell /once per season |
| 3. | desilting channel | dry season/each cropping season |
| 4. | gapping the grass | wet season/each cropping season |
| 5. | slashing grass in channel | wet season/each cropping season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
For the length of the waterway in metres. The length of the structure was kept constant
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The general ground slope determines the cost of the structures and the distance of the safe discharge point from the road
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Landforms: Also valley floors
Slopes on average: Also moderate
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is medium-high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium-high
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
5% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: mainly from employment in the nearby urban areas
Level of mechanization: With hand tools
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
50
Quantité après la GDT:
20
Sols
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
25
Quantité après la GDT:
15
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
neutre / équilibrée
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
210 households in an area of 10 ha
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: technology adoption not spontaneous because of dependency on material support from donor
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
farm management handbook of Kenya. 1983.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
SWC branch, MoA, Nairobi
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
minor roads soil conservation project. Final report. 1992.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Ministry of Public Works. Nairobi.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé