Crop rotation including annual crops and Esparcet cultivation [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Malgorzata Conder
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1150 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Crop rotation with current Esparcet production
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
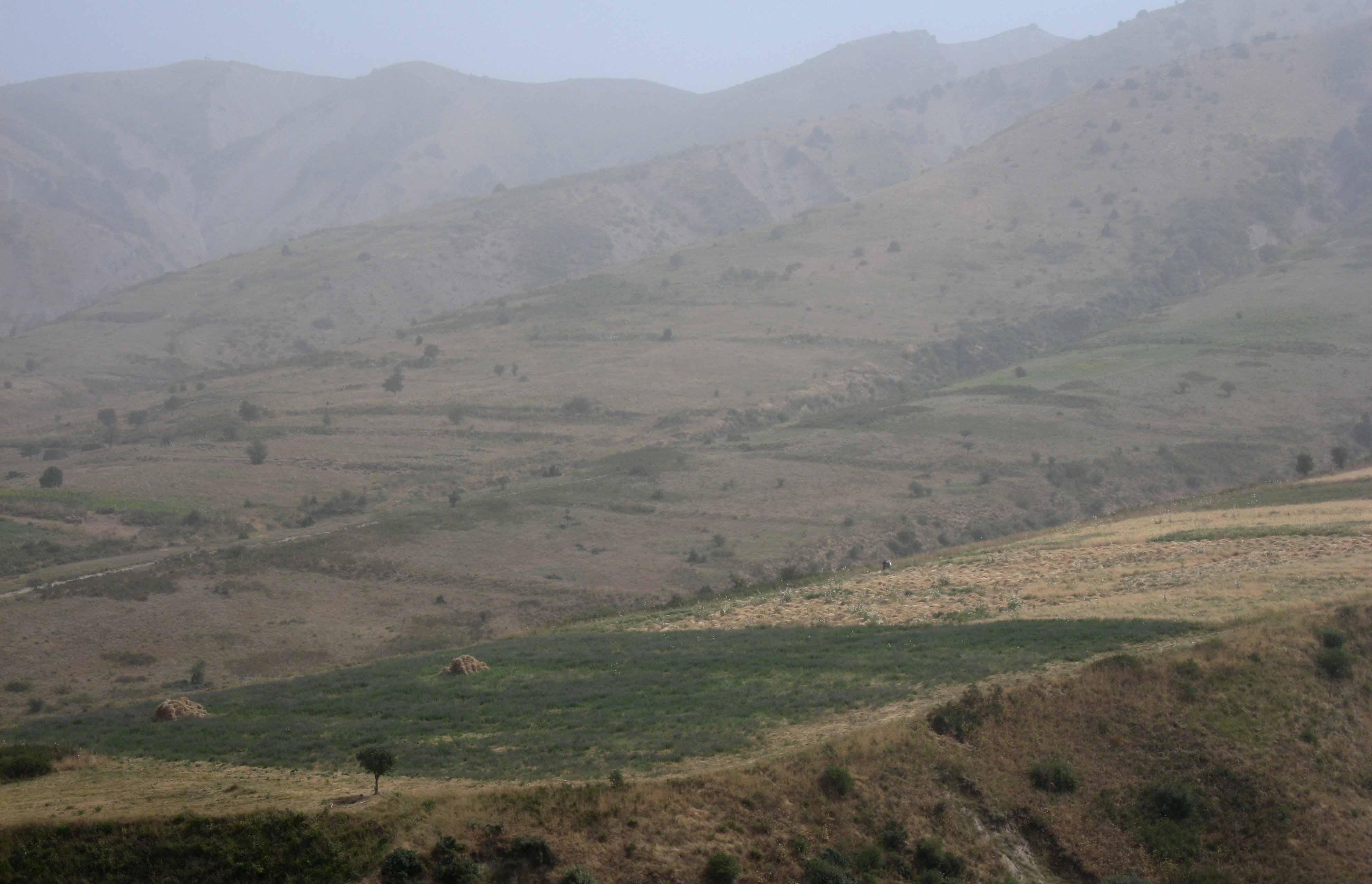
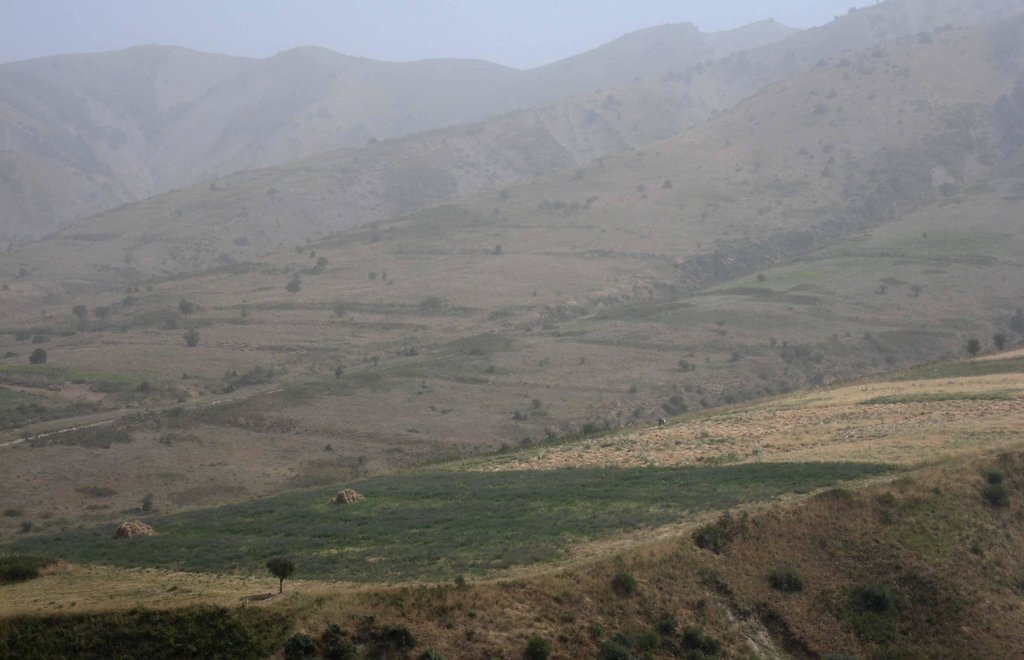
An Esparcet plot of one hectare is located on a hillslope in the Chukurak watershed. The owner lives in the valley far away from the plot. During the harvest, he is staying in the hills a whole week, because a daily journey to his house would take too much time. For the last three years, the farmer is cultivating Esparcet with the main aim to feed his cows. In two years, he will switch to a wheat or chickpea plot. In total, the farmer owns19 hectares of cropland, out of which the Esparcet plot accounts for 20% of his income. Next to the Esparcet plot, other farmers cultivate wheat and chickpea. In contrast to Esparcet, those plots must be protected from boars. Even though irrigation is impossible and the water point is situated far away, Esparcet grows very well because of the straight and spread-out roots. Esparcet is beneficial for the state of soil fertility and soil stabilization. Their seeds are more expensive than wheat seeds, but also result in a higher harvest. Esparcet can be harvested up to three times a year depending on water availability.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of Esparcet cultivation is fodder production for the cows. The farmer owns other plots where he cultivates wheat. Moreover, it’s a good location for an Esparcet plot: Even though water is not available Esparcet maintains the soil moisture and nutrients while reducing soil erosion. Thanks to the crop rotation, the soil is in a healthy state. Yield quantity and quality are very satisfying for the farmer.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The farmer stresses that good knowledge is needed to know where, what and how to cultivate. He learned from other farmers. Before establishing the perennial crop, he first planted a nurse crop of fodder grain in spring. Nurse crops strengthen soil stability while minimizing weed and overly sunlight. Plowing, sowing and cutting are initial as well as recurrent activities. No fertilizer and no plot guarding are needed. Initial costs when growing Esparcet are higher than for wheat, because Esparcet seeds are more expensive. Additionally, seeds of the nurse crop are needed.
Not to neglect is the long way from the farmers’ house to the plot which takes time and fuel, but the farmers of that hillslope often give a lift to each other. Also during harvest the neighboring farmers are helping out.
Natural / human environment: The plot on the hillslope is located far away from the farmer’s’ village Sarmaydon 2. It’s situated at around 2000m asl below the hill peaks, where boars are entering. On three sides, the plot is delimited naturally by incised riverbeds which make accessibility more difficult. Due to the high altitude, there are low temperatures and high moisture. Above the Esparcet cultivation, wheat and chickpea plots are cultivated leading to off-site effects on the Esparcet plot. In the Esparcet plot, a deep rill developed originating from the wheat plot situated upslope.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Muminabad
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - blé de printemps
- céréales - blé d'hiver
- Lucerne, Esparcet, Chickpea
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept

Pâturages
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The Esparcet plot is quite beneficial for soil and water properties. It is hence a good initial cultivation for future crop types. Soil stability is crucial as the plot is delimited by a riverbed on both sides. A wheat plot is located just above the Esparcet production. A rill developed in the upper plot, so that off-site effects like rill formation and sediment deposition are affecting the Esparcet plot.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Esparcet is maintaining soil stability and moisture which prevents major degradation. Several km2 got affected by washed soil form the upper part. No irrigation is possible.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
Commentaires:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: rotations / fallows
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Bad accessibility to settlement, market etc. Water point is far away)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
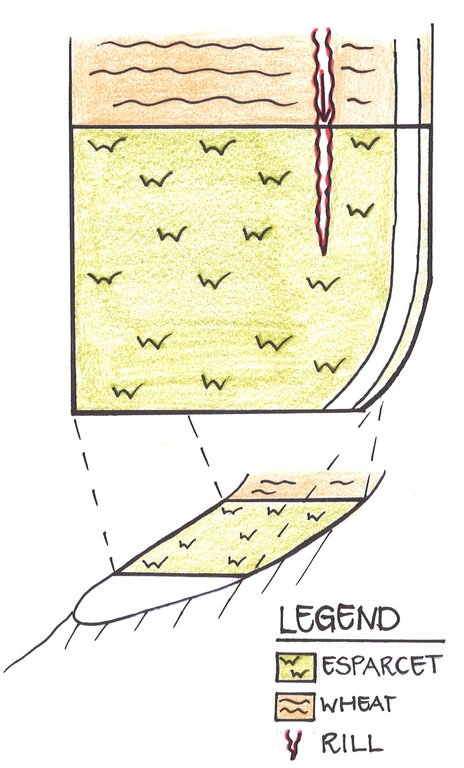
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The Esparcet plot is located on a hillslope and is laterally delimited by embankments. The density of the vegetation cover varies within the plot. A rill building was observed in the upper part of the plot, originating in the wheat cultivation with very low vegetation cover located upslope.
Location: Chukurak watershed. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Date: 14.02.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Basic agricultural knowledge is required. If technical knowledge about cultivation is available Esparcet cropping is not especially challenging. Nurse crop may be possibly applied.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: Esparcet
Quantity/ density: 3.75t/ha
Remarks: with fodder grain as nurse crop
Auteur:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
12.40
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing- lab. light: 1.5 hours, 1 person | |
| 2. | Plowing - tractor rent | |
| 3. | Plowing - petrol | |
| 4. | Fodder grain seeds | |
| 5. | Esparcet seeds | |
| 6. | Sowing Grain and Esparcet - lab.light: 1.5 hours, 1 person |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Plowing | Person/day | 0,2 | 15,5 | 3,1 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Sowing | Esparcet seeds | 0,2 | 15,5 | 3,1 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tractor rent | hours | 3,0 | 6,9 | 20,7 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Petrol for plowing | litres | 40,0 | 1,14 | 45,6 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Fodder Grain seeds | kg | 70,0 | 0,414285 | 29,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Esparcet seeds | kg | 20,0 | 6,21 | 124,2 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 225,7 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 225,7 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.033 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting Esparcet | 2 times a year (1. cut and 2. cut) |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Cutting Esparcet | Person/day | 94,5 | 12,43 | 1174,63 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | machine use to cut | hours | 2,0 | 31,1 | 62,2 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Petrol | litres | 40,0 | 1,14 | 45,6 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1282,43 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1282,43 | |||||
Commentaires:
Second labor input for harvesting Esparcet was calculated proportionally to the yield: 100% first harvest and 50% for second harvest.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most determinate factor is theoretically the cost to harvest the Esparcet. Labour input is not based on money, but on mutual support among the farmers. So the farmer will have to work on plots of other farmers to compensate the support he gets. Besides, seeds and tractor renting are the most expensive aspects of Esparcet cultivation.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Totally 800mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200m asl, weather Station Muminabad). Precipitation increases with the altitude: in average 60mm per 100m (in here approx.1300mm)
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate
LPG from April until September
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone is just around 2000m a.s.l. and might belong already to upper part of Watershed system
Slopes on average are 17-25%
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
< 5 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water (medium): Autumn - spring
Availability of surface water (poor/none): July - September
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: 20% of income of the lucerne plot, rest from other cropland of totally 19 ha and 5 ha of pasture
Level of mechanization: Mechanized/motorized mostly for plowing and harvesting, whereby sowing is manual work.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
2.06 ha, if 7.7 pers/household
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
First year only one cut possible but after that yield increases to a positive extent
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
production animale
risque d'échec de la production
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Esparcet seeds are relatively expensive compared to other seed types
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No guarding needed
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
apaisement des conflits
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
évaporation
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
encroûtement/ battance du sol
compaction du sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Autres impacts écologiques
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
envasement en aval
capacité tampon/de filtration
dommages sur les champs voisins
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
High vegetation cover, improvement through more uniform sowing. Sowing manually causes an irregular soil cover and might be less tolerant to heavy rainfalls and drought.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
très positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Yield is lower in the first year of the establishment but more cuts are possible in the next years. In the longer term, it is more beneficial for soil properties: Good soil nutrient and soil moisture availability, soil stabilization and reduced soil erosion and off-site effects.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1 Household
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There is no other perennial crop in the Chukurak watershed, but neighbors of the farmer with the Esparcet plot may change in future into Esparcet production for rotation.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: No adoption is done, but farmers might think about it.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Good yield, if you sell it you can buy comparatively a good quantity of wheat |
| Guaranteed fodder availability for livestock |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Several harvests per year (up to three harvests) possible especially in the hills where precipitation is high |
|
Esparcet has many beneficial on- and off-site effects concerning soil quality, reduced soil erosion etc. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge transfer to other farmers |
|
Moderate work load (no guarding of the plot from boar) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote perennial crops among local farmers |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| First year only one cut is possible, and thus the farmer has to accept a lower yield compared to the cultivation of wheat |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Farmers need to cultivate food crops. A small scale farmer would only produce Esparcet if he already has a wheat crop somewhere, even if the latter is less profitable | Knowledge transfer |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé