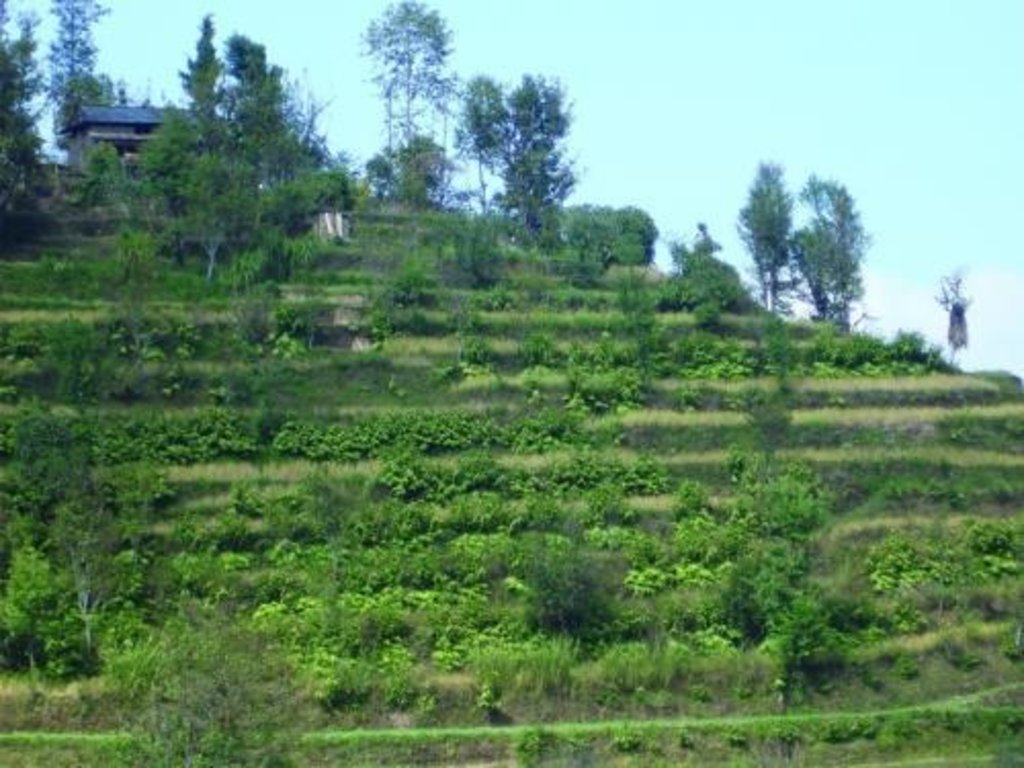
Fodder cultivation [Népal]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Sabita Aryal
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Daale ghans utpadan
technologies_1231 - Népal
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Adhikari Shova
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Shrestha Sumesh
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Manandhar Loonibha
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Ghimire Somnath
Népal
Spécialiste GDT:
Singtang Ganga Raj
Népal
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Kathmandu University (KU) - Népal1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
It is a technology where slope, waste land, remains of crop land, marginal lands, rising terraces are protected by fodder cultivation.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
This technology involves the cultivation of various trees, grasses, legumes and shrubs that can be used as livestock feed. The slopes in the hills, rising terraces, waste and barren land and other land types with many limitations that cannot be used for agriculture are used for fodder cultivation. In this way, the land is protected from landslide, erosion by wind and water and the loss of soil fertility due to over-compaction of soil and overgrazing is reduced. In addition, the feed quality and quantity of the livestock is improved and their productivity consequently is also increased.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is practiced:
-mainly for protection of land from erosion or landslide,to protect from over-compaction and overgrazing leading to soil fertility loss i.e. for land management
-for the purpose of providing food for livestock even during the winter months.
-for increasing the quality of feed for livestock and thus, improve their productivity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: This technology involves the plantation of trees, legumes, shrubs and grasses in the wastelands and lands deemed unfit for agriculture. The suitable plant seedlings are planted at a particular season i.e during spring mainly in the month of Baisakh. Depending upon the amount of nourishment and the nutritional content requirement and availability of seedlings,the nutrient contents of feeds and fodders on the basis of soil composition, use of manures and fertilizers on the land, irrigation facilities, stage and speed of growth frequency of cutting the variety and strain of feed resources are determined. It needs watering and removal of unwanted weeds for some months and the plant needs no further caring. They grow by themselves. These plants are mostly rain-fed and have no other economical or aesthetic values as such and hence, these can be used only exclusively for fodder cultivation. The tree branches, leaves, twigs, shrubs, legume plant bodies used for feed can either be cut and harvest either from time to time when required or they may also be cut and stored in fodder storages for the winter months when other sources of feed are scarce or during the planting season (Asar) when labor is scarce.
Natural / human environment: We need not to create any human or artificial environment for cultivation. The trees grow naturally and create a pleasant environment in nature. Sometimes, for crop fodder cultivation, agricultural lands may come in use. For example, in maize crop used as fodder supplement, the main plots were sown with maize varieties, and the subplots were cutting of added rows of maize after different days after sowing. Thus, young maize plants were cut before drying out in the sun and may be used as fodder. Tropical grass species and improved grasses and legumes are also introduced in barren terrace landscape during the off season after harvesting.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Népal
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Chyamrang besi
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kavre
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
2,0
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2 km2.
This technology has been applied in the hole state which covers around 2 sq.km in about 146 houses. A number of fodder trees, ground legumes, shrub legumes, fodder crops and cultivated grasses have been used on the basis of the traditional and experience-based choice of fodders species by farmers which reflects their knowledge on nutritional values, cultivation easiness and seasonal variability of growth in warm temperate environment.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
It is a traditional method. The analysis corresponds to farmers’ preference of fodder tree species to their nutritional values. The traditional and experience-based choice of fodders species by farmers reflects their knowledge on nutritional values, cultivation easiness and seasonal variability of growth in local environments has been the basis of fodder cultivation in Nepal.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- cultures fourragères - graminées
- cultures fourragères - autres
- rice
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- arbres fourragers (Barbe jolote, Faux mimosa, Prosopis, etc.)
- coffee
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Kartik to chaitra; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Ahsad to ashwin
Commentaires:
major cash crop: Coffee
major food crop: Paddy and fodder
other: Maize
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, landslide, decreased fertility, over compaction of soil
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Flooding during heavy rainfall, landslides
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Terres improductives
Précisez:
wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
Also rainfed and full irrigation
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- use of wasteland for agriculture
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M3: Disposition/plan en fonction de l'environnement naturel et humain
- M5: Contrôle/ changement de la composition des espèces
Commentaires:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -along boundary
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wm: mouvements de masse/ glissements de terrain

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Before fodder cultivation), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Landslide)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (People left land unfit for cultivation completely barren and without any vegetation at all causing top soil erosion), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Before this technology people depend upon forest), overgrazing (Result in desertification, irreversible loss of to soil, increase in turbidity of surface water and increase in flooding intensity and frequency), change of seasonal rainfall (Many areas that were set aside for rain fed agriculture become waste land due to drastic change in rainfall pattern.), floods (Mass movement landslide), droughts (Affects cultivation), poverty / wealth (The resource poor have to depend upon the natural environment for the fodder requirements and need to take their livestock for grazing in whatever grassland areas available causing soil degradation), education, access to knowledge and support services (most people do not know about conservation measures), governance / institutional (No govermental supports)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (They can decide which plants may be best on the basis of organic matter content, crude protein, tannin, fiber, lignin, fat, minerals and dry matter.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (The land users mostly cultivate plants based on their indigenous knowledge and whatever seedlings are available which give fast and a more quantitative rather than qualitative yeild.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Trees/ shrubs species: Brassiopsis hainla(Chuletro), Alnus nepalensis (Uttis), Garuga pinnata (Dabdabe), Crateva unilocularis (Siplikan), Terminalia bellirica (Barro) planted trees;Desmodium introtum, Desmodium ovalifolium, Tephrosia candida(Mendola) all are planted shrubs
Grass species: Cynodon dactylon(Dubo), Desmostychia bipinnata(Kush), Imperata cylindrica(Siru), Melinis minutifolia (Bandhar Dhapaune Ghash)
Other species: cultivated legumes for fodder Lablab purpureus (Bean), Macroptilium atropurpurum (Atro/Siratro), Trifolium alexandrium, Trifolium pretense (Red Clover), Trifolium repens (White Clover), Vigna anguiculata( Bodi)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15%
Change of land use type: Previously the land was unused
Change of land use practices / intensity level: In order to minimise exposure to degradation processes, unused land was changed to controlled acces from barren land to fodder plants cultivated land
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Increased landscape diversity
Control / change of species composition: Previously barren land planted with grasses, legumes, fodder trees and grasses increasing the biomass and productivity of the area so encouragement of desired and introduction of new species was done
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Rupees
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
97,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
500
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plantation of the fodder plants in barren wastelands | Spring(Chaitra-Baisakh) |
| 2. | Cutting of the twigs, branches, legumes, crops and grasses | Throughout the year |
| 3. | Enrichment planting of tree seedling | |
| 4. | Introduction of higher quality feed species |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Plantation of the fodder plants in barren wastelands | persons/day/ha | 51,0 | 500,0 | 25500,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Cutting of the twigs, branches, legumes, crops and grasses | persons/day | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Enrichment planting of tree seedling | persons/day/ha | 51,0 | 500,0 | 25500,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Introduction of higher quality feed species | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 98,03 | 980,3 | |
| Equipements | Spade | pieces | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | pieces | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | pieces/ha | 200,0 | 600,0 | 120000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | pieces/ha | 200,0 | 25,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | pieces/ha | 200,0 | 25,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost / manure | kg/ha | 5,0 | 750,0 | 3750,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | new Compost/manure | kg/ha | 100,0 | 300,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 217430,3 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 2241,55 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering the seedlings | Till 2 to 3 month after plantation |
| 2. | Manuring | Till 2 to 3 month |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Watering the seedlings | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Pipes and buckets | pieces/ha | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Manuring | kg/2m | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1100,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 11,34 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: axe, spade, plough
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Tthe labour and the cost for seeding. The manure requried is prepared naturally
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
- subhumide
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
- fin/ lourd (argile)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: The local people find the soil moderately deep
Soil fertility is medium, since people use compost manure for croping
Topsoil organic matter: Compost manure are used to increase organic matter
Soil drainage / infiltration is good because of sandy soils
Soil water storage capacity is medium - low, since sandy soils can not store water well. Also no ground water is found.
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Availability of surface water: Flooding occors during monsoon. Normally people depend on surface water for irrigation.
Water quality (untreated): People directly drink
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
- traction animale
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 6%
5% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land (Living standred more than average).
90% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land (Average life standred).
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (Below average).
Market orientation of production system: There is a market for coffee.
Level of mechanization: Oxes are used for ploughing
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Good composting
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Everyone is using the slope land
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
People are getting more knowledge
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increasse in food resources
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Wood are available from fodder
diversité des produits
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No more time waste by searching for fodder
Revenus et coûts
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
No more time waste by searching for fodder
Impacts socioculturels
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
People are getting experiance
apaisement des conflits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cultivation in own land and land management
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Roots of tree absorb
qualité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Different varieties of plant purify the water
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Absorption increased
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to absorption increased
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Absorption increased
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Absorption increased
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Leaves and plant provide
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Roots of plant saves loss
compaction du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Plantation reduces
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Tree leaves acts as organic matter
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Plantation increase
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Various plants are planted
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Availability and increase of food
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Trees blocks the path of flooding
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase in photosynthesis
risques d'incendies
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Tree block high velocity
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
The plant species to be planted should be chosen according to the environmental condition in different seasons
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
Fodder plants do not need further maintainence and up keeping after they have been allowed to gow. Most are annual and some grasses are perennial. In the long term, the initial costs are duly covered and yield major economic benifits.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- 1-10%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
9 percent of stated area
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: every one uses their own land and do on their own
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: as the village lies in hilly region there are many sloppy lands applicable for plantation of fodders.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: every villagers find it effective as the waste land is also utilized and in addition productivity is also increased.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| decrease in waste as animals fees almost all |
| increase in number of animal husbandary |
| Stall-feeding has been encouraged |
| Availabitlity of fodder even during harsh winter when there is scarcity of forage plants and during harvest season when there is lack of labour |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| This technology has been able to manage and utilize the waste land |
| the livestock production has increased by which they develop economic status |
| barren lands and to soil erosion along with increase in turbulence of surface water leading to flooding has decreased which occurred due to over grazing |
| The biomass and productivity of the ecosystem has improved due to introduction of new species in barren land |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The trees do not grow fast enough to reap benefits faster | Trees and other legumes and grasses which have high growth rates should be planted |
| The fodder species are planted on communal wastelands so there are arguments if somebody takes more forage then others | Communal properties should be equally distributed and a managing body must be present |
| The production from the fodder plantation is never enough for the whole year | Along with wastelands and marginal uncultivable lands, crop fodder production can be done (like maize) even during the plantation of cash and food crops to ensure a year round supply |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| people may find difficulties in cutting tall trees | use shrubs, and herbs for plantation |
| Since it a common property, the use and negligence in management of common properties may eventually lead its failure | fodder plants do not need looking after very much but proper management of the forage resource by everyone involved must be done |
| Traditionally used crops have been used till now which may not have the highest nutrient content and qualitative feed | Proper research needs to be done to identify the plants best suited for that climate and topography and which have the highest nutritional content to improve production of livestock |
| Barren lands are often used for recreational purposes like for games by kids and hence protection of young plants may be difficult | For the few months of plantation care should be insured for their survival |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
17/01/2014
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé