Runoff water harvesting for bananas [Ouganda]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Alex Lwakuba
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1390 - Ouganda
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Imoko-otim Charles, P.
MMAIF, DEPT of Agriculture
Ouganda
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry, and Fisheries of Uganda (MAAIF) - Ouganda1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Run off water from a hill is harnessed and concentrated in a banana plantation using diversion and retention ditches respectively.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
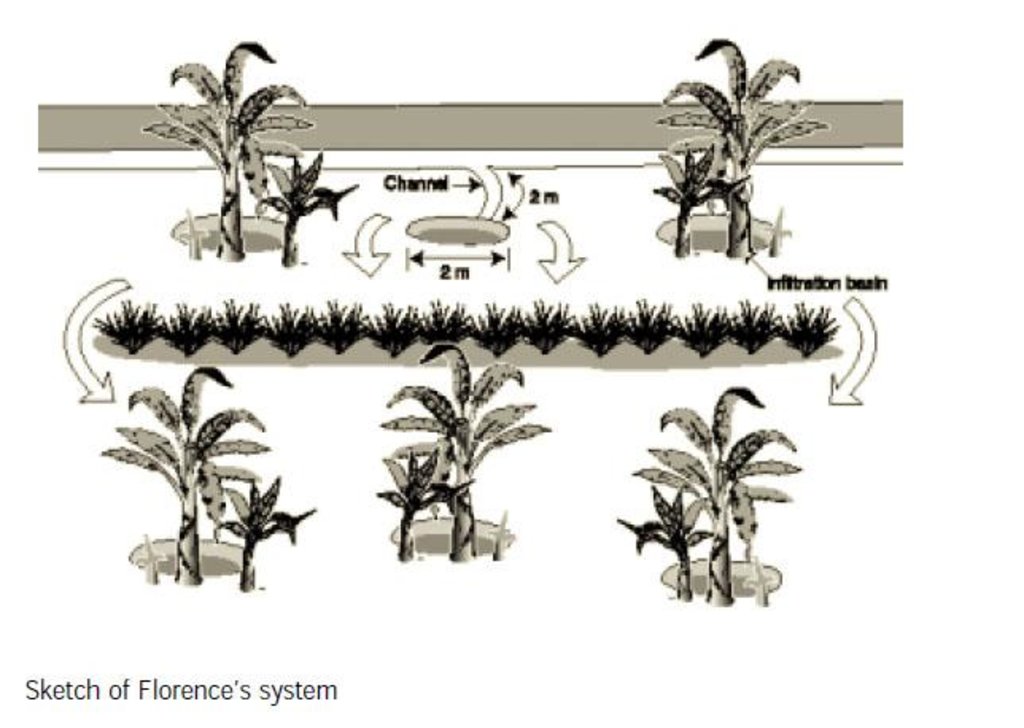
Runoff water is diverted from the road running by the farm, using diversion ditches, 0.3 m deep and 0.3 m wide. Water is led first into semi-circular infiltration ditches that are 0.3 m deep, and 2 m in diameter. From these ditches, water flows through the banana plantation and is held by infiltration basins around which are groups of banana stools. Setaria grass is planted to stabilize the edges of the basins and is also used to stabilize a bund which runs through the plantation. Mulching is practised throughout the plantation,
primarily to reduce the loss of valuable moisture.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology is used to control soil erosion by runnig water from the hill top and also to harvest water and retain soil moisture for the banana palms which need adequate soil moisture for proper production. Dry vegetation and stover are used as mulch to reinforce moisture conservation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The ditches are maintained by removing silt regularly. The grass is cut to avoid over growing.
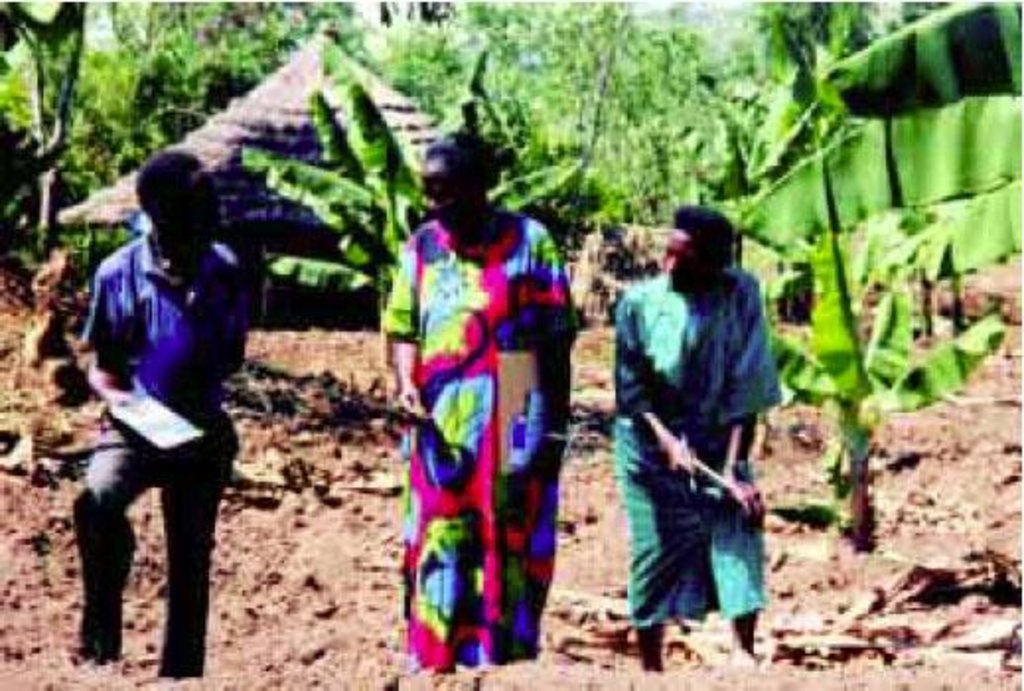
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on perennial crop land located in a semi arid area. The soil is predominantly sandy loam and shallow. Florence is a farmer and a married housewife. She is 40 years old and has a family of 12 to support
despite the fact the family is poorer than average. They own less than one hectare of land, but borrow an extra area to cultivate. Her main technical initiative is water harvesting, together with soil fertility improvement, in a matooke (cooking banana) plantation. She started in 1990. She practices harvesting of water from the road into her plantation, and has a system of trenches through which water circulates and is then held by basins around which are banana stools. She also mulches and plants grass barriers within
the plantation. There is some doubt whether the water harvesting can really be claimed as her own innovation, as there are variations of this practice in several nearby farms. Nevertheless her holistic management system is probably unique to the area.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Ouganda
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Kumi
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kumi
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 10 km2.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
it is a farmer own intiative
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Setaria grass
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- bananier/plantain/abaca
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 90Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - JunSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Nov
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): adequate soil moisture, soil erosion by wind and running water, and declining soil fertility
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): unreliable rainfall, soil erosion, pest and diseases and inadequate capital
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
water harvesting
irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
water diversion and drainage
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
- dérivation et drainage de l'eau
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation hydrique
- Ha: aridification
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Ha: aridification
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Water harvesting for banana cultivation
Location: Kumi. Uganda
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of soil structure, water harvesting
Vegetative measure: on top of earth workd
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: mango
Perennial crops species: bananas
Grass species: setaria
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): R
Spacing between structures (m): R
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): R
Structural measure: diversion ditch/cut-off drain
Vertical interval between structures (m): r
Spacing between structures (m): r
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): R
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): R
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | formation of bunds | dry season |
| 2. | planting grass | beginning of rains |
| 3. | digging ditches, making bunds | dry season |
| 4. | planting grass | beginning of rains |
| 5. | mulching | end of rain |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 120,0 | 120,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 370,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 370,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cuttin back | /each cropping season |
| 2. | mulching banana | /twice a season |
| 3. | desilting | rainy/each cropping season |
| 4. | cutting back the grass | when overgrown/each cropping season |
| 5. | mulching | each cropping season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 1440,0 | 1440,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1490,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1490,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
labour, length of structure
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
labour, soil depth, tools
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
10% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
25% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: most of the income is derived from the farm, however some members are employed outside.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (only family labour)
Market orientation: Mixed and subsistence (bananas produced for home consumption and surplus for sell)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
- customary
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From sales of bananas
charge de travail
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Intercropping
Impacts socioculturels
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Through farm visits and trainings
institutions nationales
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Autres impacts écologiques
Exposure
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
To other skills
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Grass strips and retention ditches
envasement en aval
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
50% of area covered
Commentaires:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Water harvesting in bananas is becoming an increasingly common practice in Kumi District. It is not possible to say currently how many families have taken up this technology – or indeed how many of these can be directly attributed to Florence’s example.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
big bunch of banana How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintain ditches |
| healthy banana plantation |
| increased food production |
| reduced weeding |
| increased income |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
soil erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? continue desilting |
| harvesting of runoff |
|
improved soil conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? continue mulching |
| improved yields and size of the bunches |
| increased income |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| labour is very expensive | need labour and money |
| time consuming |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| labour intensive | need of tools and money to pay the casuals |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Atlas of Uganda (1967) Dept of land and survey
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Entebbe Ministry of Agriculture, animal industry and fisheries, progress report on promoting farmers innovatio project (1997-2000) (Draft)
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Entebbe FAO - UNESCO (1990) Soil map of the world food and Agriculture org.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
ROMR The soil of Eastern Region of Uganda(1964) Dept of land and survey Entebbe
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé