Farm pond [Inde]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Channabasappa Metri
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
krushi honda (Kannada)
technologies_1474 - Inde
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Benson Roland
Danida KWDP Bijapur
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Mujibur Rahman Syed
Danida KWDP Bijapur
Inde
Spécialiste GDT:
Thippeswamaiah
KWDP Daida Bijapur
Inde
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Danida assisted Karnataka Watershed Development Project, Bijapur (Danida assisted Karnataka Watershed Development Project, Bijapur) - Inde1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
Stakeholders participation in the project activities [Inde]
SWC approach is a participatory methodology to empower the community to plan, implement, monitor, evaluate and manage the SWC technology to bring about sustainability
- Compilateur : Pranesh Jahagirdar
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
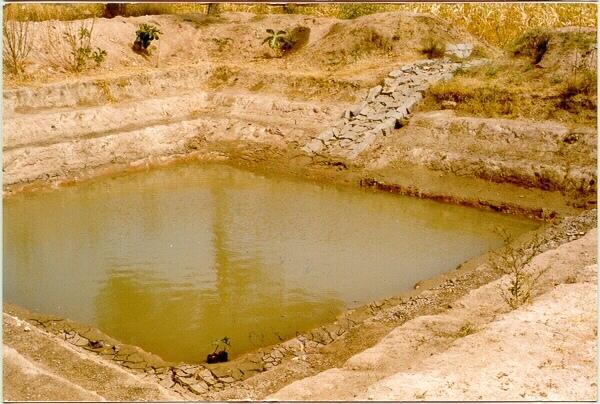
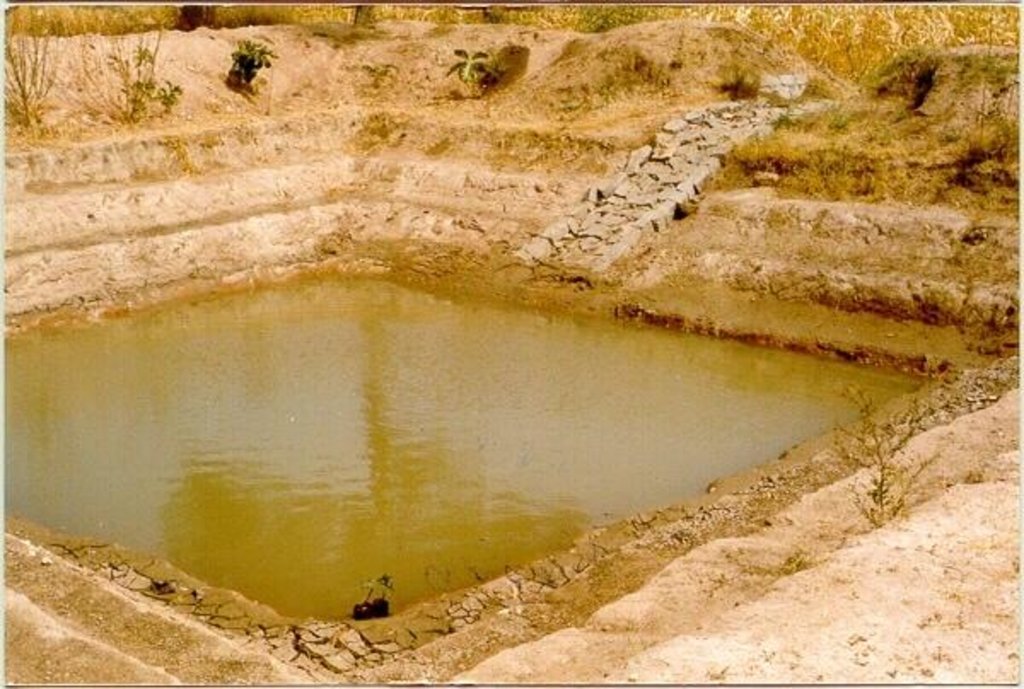
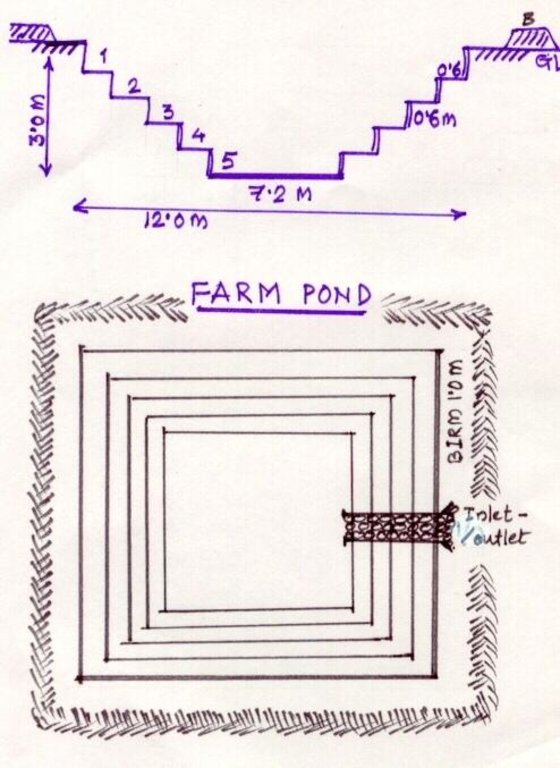
A sunken structure (12 x 12 x 3 m, more suiable), constructed by escavation in arable land with a view of temporary runoff storage tapped for protective irrigation, and to increase percolation for recharge of ground water (to convert surface to subsurface flow)
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
A farm pond comprises of excavated portions of 12 x 12 x 3 m with the steps at 0.6m depth each. The excavated earth is deposited all around the structure as a bund, with a burm space of 1m. An inlet cum outlet provided in the course of flow of rain water to collect and dispose the excess runoff.
Purpose of the Technology: (1). For storage of exess runoff. (2) to increase percolation for ground water recharge, (3). To use for protective irrigation during dry period, (4). To stop further deepening of watercourse in arable lands
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Selection of beneficiary is by the community and site selection, Design/ layout and excavation by the project staff with participation of the beneficiary. Desilting of the structure is by the beneficiary
Natural / human environment: surrounding lands are more slopy and with exposed rocks, most of the surrounding area is left for grazing
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Inde
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Karnataka
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Bijapur district, Hadalsang village
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
0,028
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.028 km2.
The technology area comprising of 2.8 ha within the overall watershed area of 2458 ha. The technology is useful in harvesting the excess rainwater in the arable land and re-use the for protective irigation after the rainy period.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Department of Agriculture, Govet. Of Karnataka
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- préserver l'écosystème
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - sorgho
- légumineuses et légumes secs - autres
- cultures oléagineuses - ricin
- Chili, brinjal (eggplants), lady's finger (okra, kind of peas)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Sep
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The lands are very undulating (Class-V as per the Land Capability Classification), with very shallow soils, feasible for only one rainfed crops.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Poor yields due to shallow soils that too only one crop in one season, undulating lands leading to more runoff.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: minor pulses - cereals (green gram-jowar)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: Highly eroded, unsuitable for any production purposes.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated (ranked 2)
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- récupération/ collecte de l'eau
- gestion de l'irrigation (incl. l'approvisionnement en eau, le drainage)
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
- Wo: effets hors-site de la dégradation
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (other (migration)), labour availability (lack of labour, cost of labour), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
The drawing showing the details of the farm pond. 12 x 12 x 3 m dimension. Five steps cutting on each side with 1:1 side slope. 1m birm (space) between the earthen bund. 1m wide spilway inlet cum outlet at suitable place of the site.
Location: Kallahalla nala watershed, Indi Taluk. Bijapur district of Karnataka state
Date: 20.4.2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Structural measure: sediment sand / trap
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 15
Construction material (earth): soil excavated from the pond is used to for bunds all around the structure with 1 m birm space.
Construction material (stone): The spillway Inlet cum Outlet is constructed using stones
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:7
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Auteur:
C.G Metri, JPO, KWDP Danida Bi
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ruppes
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
46,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
0.73
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | selection of site and survey, preparation of estimates | summer |
| 2. | submission for sanction of approval | summer |
| 3. | Excavation of the farmpond | summer |
| 4. | construction of inlet/ outlet | before monsoon starts |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 360,0 | 360,0 | 10,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 109,43 | 109,43 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 469,43 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 10,21 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meeting with the farmer | monsoon/annual |
| 2. | Desilting of farmpond | summer season/once in 2 years |
| 3. | Repair of Inlet/Outlet | summer season/Every year |
| 4. | Trimming of Bund | summer season/Every year |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 7,3 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 0,16 | |||||
Commentaires:
12 m x 12 m x 3 m size with all side slope of 1:1 (five steps of 0.6 m deep), Inlet cum outlet spilway constructed with stones. This indicates only the actual cost of construction. (excavation / earth wotk and stone work for inlet/outlet)
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
If the implementation site is having the hard strata, then the cost will be more.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
550,00
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Located on the latitude 16-49'N and longitude 75-43'E .Characterised by hot dry summer (42 °C) and cold dry winters monsoon (July-September) is characterised by high intensity showers followed by pro
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (594 m a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Gentle (ridge and valley portion)
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (30 cm)
Soil texture: Medium (medium in valley portion)
Soil fertility: Low (along the slope of the ridge, ranked 1) and medium (valley portion, ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (in valley portion)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (hill portion, ranked 1) and medium (valley portion, ranked 2)
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
15% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
25% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Through sheep and goat rearing
Level of mechanization: Animal traction, (ranked 1, for ploughing, seed sowing harrowing), manual work (ranked 2, clod crushing, harvesting, threashing) and mechanised (ranked 3, Deep ploughing, levelling)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Commentaires:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
1-2 ha (ranked 1, marginal farmers [since the land holding decreases because of the fractionation the production and productivity also reduces])
2-5 ha (ranked 2, small farmers)
5-15 ha (ranked 3, big famers)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Second crop also taken
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From trees
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From trees
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Difference in the crop like on bunds and in the patches of crops.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
15m x 15m land loss average land holding is very less, thus small & marginal farmers face reduction in the production area with this SWC
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
After implementing SWC less area is left for very small and marginal land holding.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau pour l'élevage
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Subsistance agriculture
Autres impacts socio-économiques
Input constraints
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
To bring new area into cultivation
Impacts socioculturels
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
perte en sol
Autres impacts écologiques
Soil fertility
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
inondations en aval
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Water storage in farm pond
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The community is motivated with the benefits from this SWC structure. Some of them have already deepened the farmponds to increase its storage capacity.However, since most of the farmers are having very small land holdings and there was continous dry season from last three years, even if the farmers are motivated and aware of the technology of farmpond, they could not take up on their own (without financial assistance from the project.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Increased storage of water How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting by the farmer |
| Reduce gully formation |
|
Bring more area under irrigation How can they be sustained / enhanced? By giving life saving irrigation |
|
Economic benefits How can they be sustained / enhanced? By yields (monocropping to multiple cropping) --> more income |
|
Recycle the silt is beneficial How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other the silt would been lost every year and it is good to retain the soil fertility. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Storage of water How can they be sustained / enhanced? By deepening |
|
Reduced runoff velocity How can they be sustained / enhanced? By mentainance |
|
Breaching of bunds down stream How can they be sustained / enhanced? By reducing the run-off |
|
Replicability How can they be sustained / enhanced? if a famer has his own labour/ man power then he can go for its construction. |
|
Water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? recycle for protective irrigation during peak season. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Inability to contribute 100% towards cost of construction. | By giving schemes / financial assistance |
| Loosing of portion of cultivable land | By utilizing bunds, change in cropping system/ cropping pattern etc. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Difficult to excavate in hard strata | can be done in shallow soils |
| Silt accumulation, if upper catchment is not treated | Treatment of upper catchment |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Department Guidelines,Project Implementation plan, UAS Dharwad
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
In the office, personal contact
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
PIP
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
in the office
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
University of Agril. Sciences Dharwad
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
personal contact
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Stakeholders participation in the project activities [Inde]
SWC approach is a participatory methodology to empower the community to plan, implement, monitor, evaluate and manage the SWC technology to bring about sustainability
- Compilateur : Pranesh Jahagirdar
Modules
Aucun module trouvé